38 arterial blood gas diagram
An arterial blood gases (ABG) test is a blood test that measures the acidity, or pH, and the levels of oxygen (O2) and carbon dioxide (CO2) from an artery. The test is used to check the function of the patient's lungs and how well they are able to move oxygen into the blood and remove carbon dioxide.
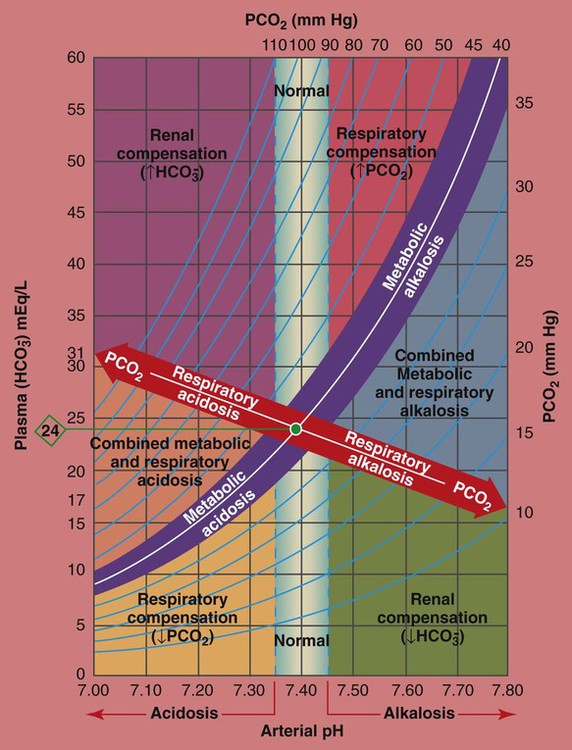
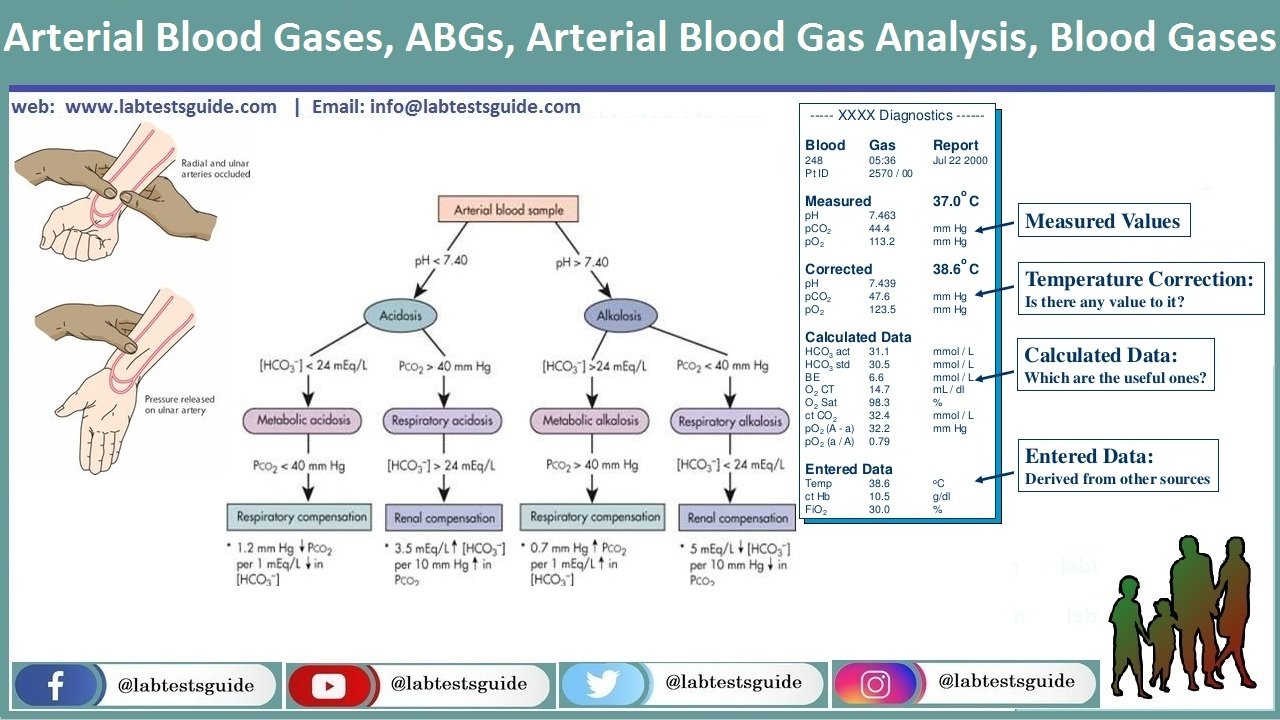
A simple diagram for arterial blood gas tensions was constructed from values obtained from normal volunteers at rest, during voluntary breath-holding and during maximal voluntary hyperventilation.
A simple diagram for arterial blood gas tensions was constructed from values obtained from normal volunteers at rest, during voluntary breath-holding and during maximal voluntary hyperventilation.

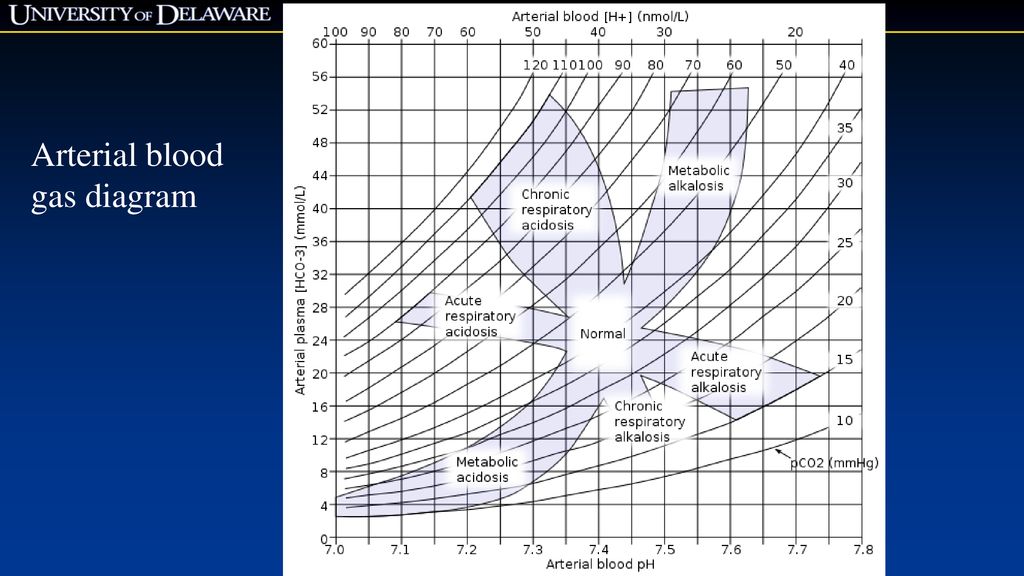
Arterial blood gas diagram
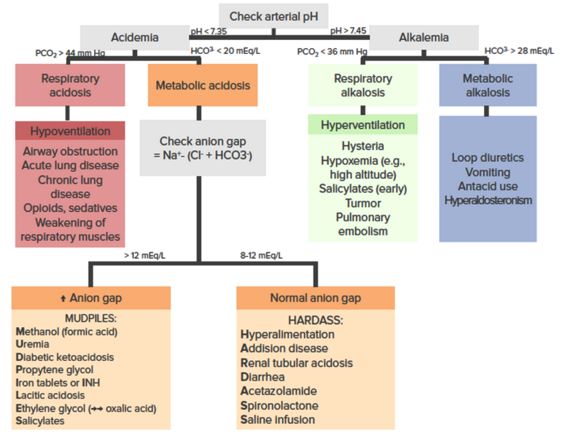
Arterial blood gas (ABG) analysis plays a vital role in the management of critically ill patients but the interpretation is sometimes an arduous task if the acid-base disturbances are complex.
Download scientific diagram | Chart and associated table showing the results of arterial blood gas values of a subadult female rhinoceros control that did not receive O2 supplementation. Note ...
Arterial blood gas (ABG) analysis is an essential part of diagnosing and managing a patient's oxygenation status and acid-base balance. The usefulness of this diagnostic tool is dependent on being able to correctly interpret the results.
Arterial blood gas diagram.
An arterial blood gas (ABG) tests explicitly blood taken from an artery. ABG analysis assesses a patient's partial pressure of oxygen (PaO2) and carbon dioxide (PaCO2). PaO2 provides information on the oxygenation status, and PaCO2 offers information on the ventilation status (chronic or acute respiratory failure).
ABG. Synonyms: Arterial blood gas. CPT Codes: 82803 – Gases, blood, any combination of pH, pCO2, pO2, CO2, HCO3. (including calculated O2 saturation).
Master arterial blood gas analysis based on an understanding of relevant physiologic principles. You'll cover crucial factors that determine oxygenation of blood in the lungs, and oxygen transport and delivery to peripheral tissues. Learn about the interplay between blood gas and acid-base analysis and how carbon dioxide affects arterial pH.
Specimen Collection - Arterial Blood Gas The primary responsibility of a phlebotomist is to collect blood for laboratory analysis, which is necessary for diagnosis and care of the patient. Collection of a quality specimen is the first step in providing an accurate test result.
Doctors use an arterial blood gas (ABG) test to determine a patient's ability to take in oxygen and expel carbon dioxide 1. The ABG test results indicate the pH, partial pressure of carbon dioxide and the bicarbonate content of the blood sample. Rather than write a long sentence describing the calculated measurements of each component or ...
b. QT is total pulmonary blood flow, or cardiac output c. O2 content of non-shunted blood is calculated based on equilibration of that blood with alveolar gas, i.e., PO2 = 100 mm Hg d. Arterial O2 content is calculated based on the measured arterial PO2 e. Venous O2 content is calculated based on the measured venous PO2
Arterial Blood Gas Analysis: Example Set 1. Case A. A patient is brought back to the floor from the operating room on a patient controlled analgesia (PCA) pump with hydromorphone. The patient hits his PCA button several times in the first hour. Shortly thereafter, the nurse walks in the room and finds him somnolent and difficult to arouse.
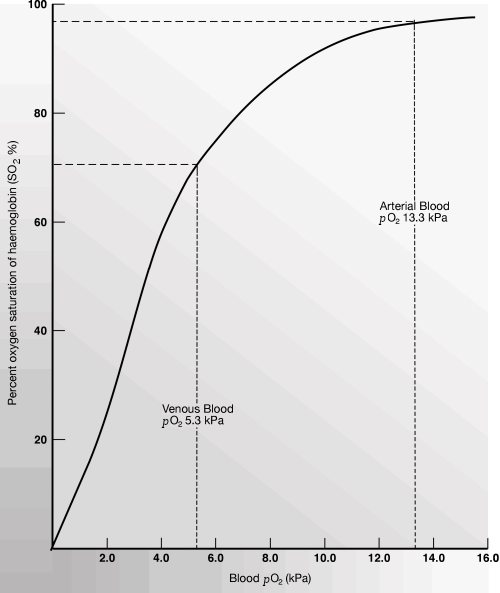
The blood cell diffuses through the membrane carbon dioxide and receives oxygen. The oxygen-rich blood (arterial blood) then travels to the pulmonary veins and into the left chambers of the heart to pump blood to the rest of the body (Brashers, Pulmonary and Bronchial Circulation section). Figure 2. Gas exchange GIF
An Arterial Blood Gas Diagram for Clinical Use* Edward E. Mays, Lt Col, USA, MC, F.C.C.P. o o A simple diagram for arterial blood gas tensions was constructed from values obtained from normal volunteers at rest, during voluntary breath-holding and during maximal voluntary hyperventilation. Thus, an appropriate arterial oxygen
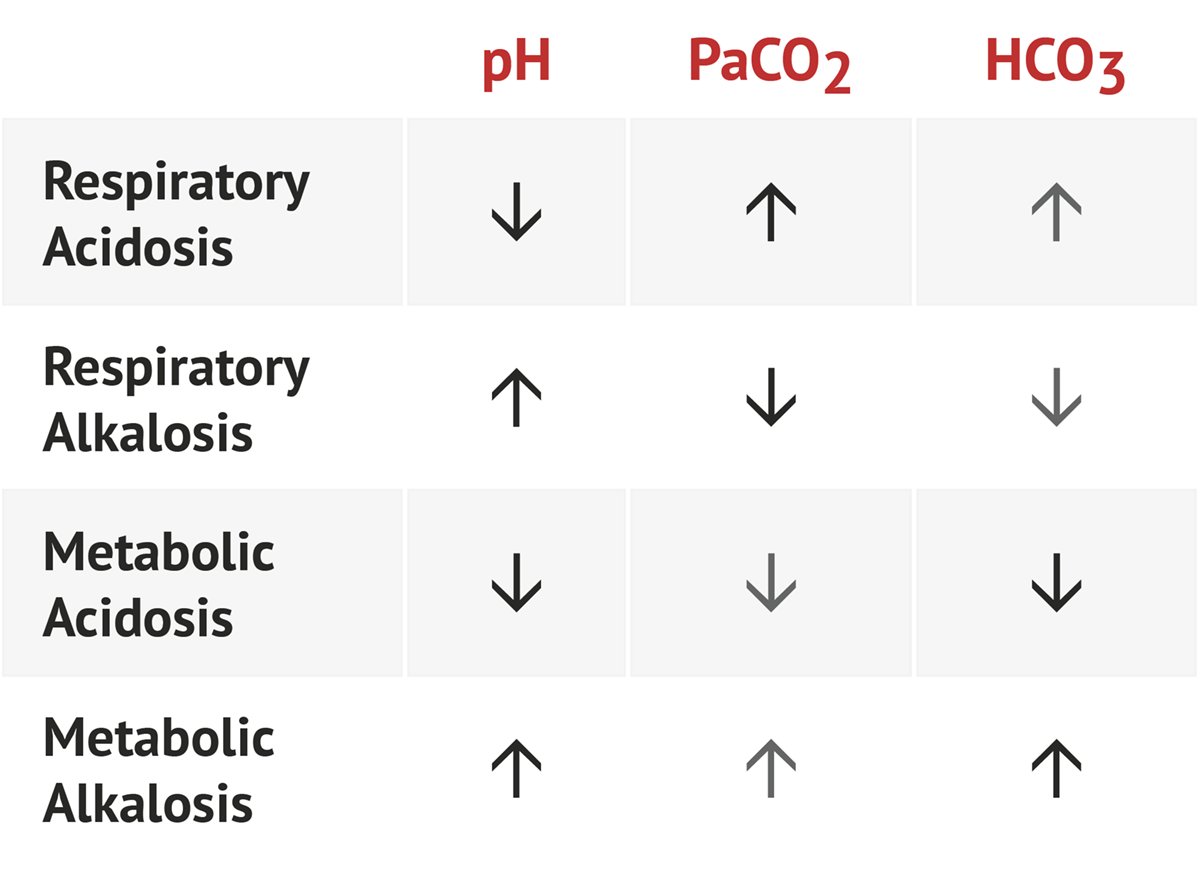
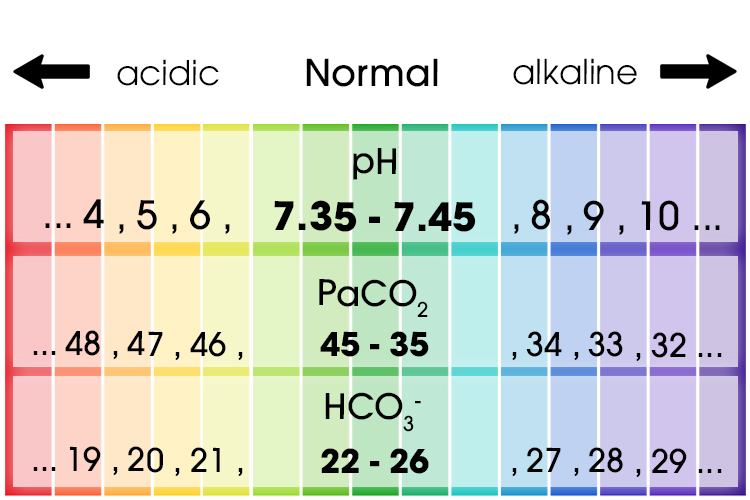
There are six components of arterial blood gas (ABGs): pH The pH is the concentration of hydrogen ions and determines the acidity or alkalinity of body fluids. A pH of 7.35 indicates acidosis and a pH greater than 7.45 indicates alkalosis. The normal ABG level for pH is 7.35 to 7.45. PaCO 2 (Partial Pressure of Carbon Dioxide)
Lactate is produced via pyruvate metabolism under anaerobic or aerobic glycolytic conditions. In the presence of adequate oxygen and mitochondrial capacity, pyruvate is normally converted to acetyl CoA which then enters the Krebs cycle. In the absence of oxygen or in the presence of excessive glycolysis, pyruvate is shunted into lactate ...
Typical reference ranges in blood gas analysis-1 Parameter Normal range p H 7.35 -7.45 H⁺ ions ( 35-45mmol/ lt ) Arterial pO₂ 95- 100 mm of Hg Arterial pCO₂ 4.7 -6.0 Kpa ( 1.02 -1.35 mmol/ lt or 35-45 mm Hg ) Total CO₂ 25-39 mmol /lt Carbon dioxide combining power 53-75 ml per 100ml of plasma HCO₃⁻ 21- 28 mmol /lt ( mequ/lt ) Base ...
5 Terms. willjenkins2003. Blood Gases. PaO₂ (partial pressures of oxygen) PCO₂ (partial pressures of carbon dioxi…. HCO³⁻ (bicarbonate) pH (a measure of hydrogen ion concentra…. 80 - 100 mmHg. 35 - 45 mmHg.
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia An arterial blood gas ( ABG) test measures the amounts of arterial gases, such as oxygen and carbon dioxide. An ABG test requires that a small volume of blood be drawn from the radial artery with a syringe and a thin needle, but sometimes the femoral artery in the groin or another site is used.
venous blood from the patient to a gas exchange device (oxygenator) where blood becomes enriched with oxygen and has carbon dioxide removed. This blood then re-enters the patient's circulation. Circuit flow is achieved using a pump either centrifugal or a roller pump. ECMO evolved from cardiopulmonary by-pass.
Components of the Arterial Blood Gas The arterial blood gas provides the following values: pH Measurement of acidity or alkalinity, based on the hydrogen (H+) ions present. The normal range is 7.35 to 7.45 Remember: pH > 7.45 = alkalosis pH< 7.35 = acidosis PO2 The partial pressure of oxygen that is dissolved in arterial blood.
The pH, base excess and pCO 2 (acid-base status) of arterial blood flowing through the umbilical cord provides valuable objective evidence of the metabolic condition of neonates at the moment of birth; a notion that has assured a role for the blood gas analyzer in hospital delivery suites in cases of suspected fetal distress/asphyxia.. The intended purpose of this review article is to detail ...
by EE Mays · 1973 · Cited by 26 — An arterial blood gas diagram for clinical use. ... Oxygen / blood; Pulmonary Alveoli; Pulmonary Fibrosis / diagnosis; Respiratory Insufficiency / diagnosis ...
The Davenport diagram shows that shifts in pH at various levels of arterial carbon dioxide tension (PaCO2) with, A, normal bicarbonate concentrations, B, increased carbonic acid levels, C, decreased carbonic acid levels in the blood. The line connecting the points is the buffer line for arterial blood. Changes in arterial carbon dioxide tension
Nanduri R. Prabhakar, in Chemosensory Transduction, 2016 Blood Flow and O 2 Consumption. Arterial blood supply to the carotid body is derived from branches of internal and external carotid, the occipital, and the pharyngeal arteries. The carotid body has high blood flow for its volume, which ranges between 1000 and 2000 ml/min/100 g of tissue weight, which 25-28 in terms of weight of the ...
Arterial blood gases (ABG's) is a blood test which is used to give an indication of ventilation, gas exchange and acid-base status and is taken from an ...
Interpreting an arterial blood gas (ABG) is a crucial skill for physicians, nurses, respiratory therapists, and other health care personnel.
أفكار مشابهة رائجة الآن · Nurse Accessories, Supplies & Equipment · Arterial Blood Gases · Metabolic alkalosis and respiratory alkalosis diagram · 3D Printing ...
How To Draw An Arterial Blood Gas 9 Steps With Pictures. 1 2c Transferring Methods Inert Atmospheric Methods. Glass Syringes. Gas Syringe Technosklo Ltd. How To Draw An Arterial Blood Gas 9 Steps With Pictures. Specimen Collection Procedure Performing A Venipuncture. New Page 2.
The Importance of Arterial Blood Gas Analysis. 1. Oxygen. 3. Carbon Dioxide and Respiratory Failure. 4. Bicarbonate and Metabolic Imbalance. 5. Respiratory and Metabolic Compensation.
Taking an arterial blood gas (ABG) involves using a needle and syringe to directly sample blood from an artery (typically the radial artery). Below is a step-by-step guide to taking an arterial blood gas sample in an OSCE setting, with an included video demonstration.
An Arterial Blood Gas (ABG) is a blood test that measures the acidity, or pH, and the levels of oxygen (O2) and carbon dioxide (CO2) from an artery. The test is used to check the function of the patient's lungs and how well they are able to move oxygen and remove carbon dioxide Must be taken from an artery Measurement of.. PH Pao2 PaCO2 HCO3-
Arterial Blood Flow Chart Artery Lateral Femoral Circumflex. Author: Tim Plagge Created Date: 4/24/2012 6:44:50 AM ...









![PDF] Arterial blood gas analysis. | Semantic Scholar](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/1a0a3209910a5b74141239a24ee0c9fad8459240/5-Figure1-1.png)

















0 Response to "38 arterial blood gas diagram"
Post a Comment