38 hcn molecular orbital diagram
May 3, 2004 - SIGN IN · Sign in/Register · Enter words / phrases / DOI / ISBN / authors / keywords / etc. SEARCH CITATION SEARCH · Publishers · Books · Scilight · Conference Proceedings · Author Resources · Librarian Resources · Contact Us This is an online repository for Organic Chemistry active learning resources
by DC Pan · 1967 · Cited by 50 — A linear molecule with bond distances correct to 1% of the microwave spectroscopy values is obtained. Walsh's orbital-energy diagrams are found to be almost ...

Hcn molecular orbital diagram
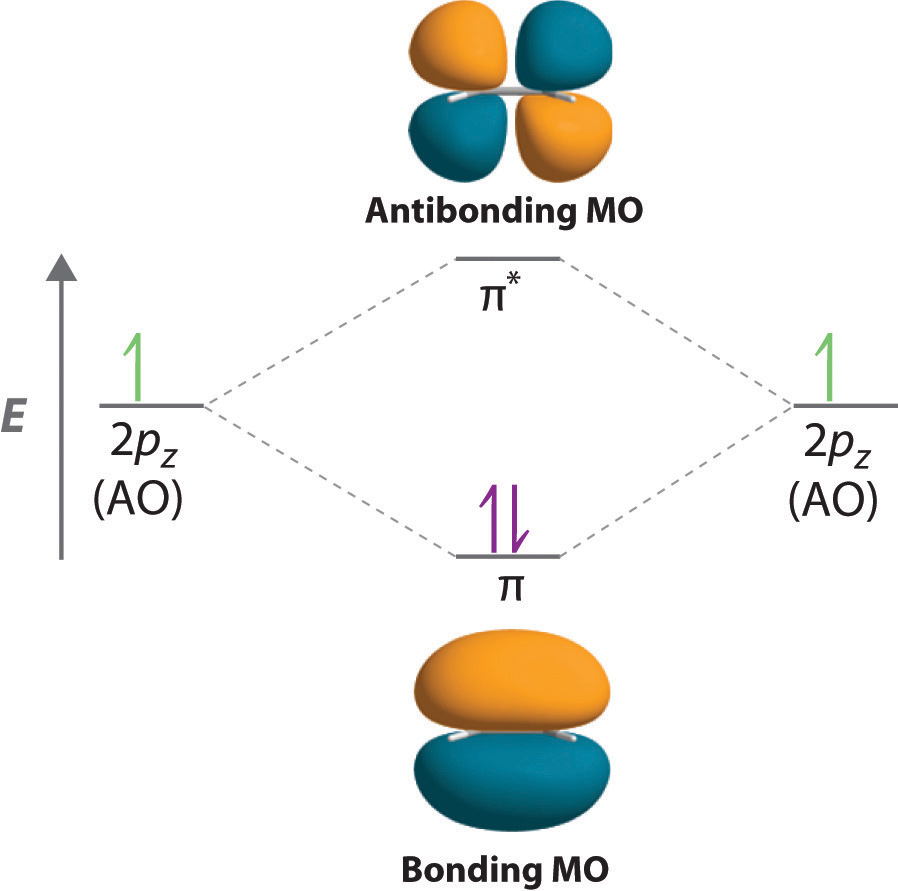
Hydrogen cyanide is a one-carbon compound consisting of a methine group triple bonded to a nitrogen atom It has a role as a human metabolite, an Escherichia coli metabolite and a poison.It is a hydracid and a one-carbon compound.It is a conjugate acid of a cyanide.It is a tautomer of a hydrogen isocyanide. December 6, 2018 - Answer (1 of 7): Summing up the number of σ -bond formed by the desired atom (here N) and the number of lone pair on it we can easily know the hybridization of it. If the sum is 2 →hybridization−sp If the sum is 3 →hybridization−sp2 If the sum is 4 →hybridization−sp3 If the sum ... Figure 9.7. 3: Molecular Orbital Energy-Level Diagrams for Diatomic Molecules with Only 1 s Atomic Orbitals. (a) The H 2+ ion, (b) the He 2+ ion, and (c) the He 2 molecule are shown here. Figure 9.7. 3 a shows the energy-level diagram for the H 2+ ion, which contains two protons and only one electron.
Hcn molecular orbital diagram. Answer (1 of 7): Summing up the number of σ -bond formed by the desired atom (here N) and the number of lone pair on it we can easily know the hybridization of it. If the sum is 2 →hybridization−sp If the sum is 3 →hybridization−sp2 If the sum is 4 →hybridization−sp3 If the sum is 5 →hybrid... an infamous small molecule known as hydrogen cyanide is shown draw a molecular orbital diagram. then draw MOs of the HCN molecule in the middle. indicate which MO is LUMO AND HOMO The molecular orbital diagram of NO shown in Figure 10.47 also applies to OF . Also, using the Molecular orbital diagram of CN-we can also find its bond order which helps us to predict its bond length and stability as well. Procedure to draw the molecular orbital diagram of CN. 1. Find the valence electron of each atom in the CN molecule. Clearly, carbon has 4 valence electrons and nitrogen has 5. Simple Molecular Orbitals - Sigma and Pi Bonds in Molecules An atomic orbital is located on a single atom. When two (or more) atomic orbitals overlap to make a bond we can change our perspective to include all of the bonded atoms and their overlapping orbitals. Since more than one atom is involved, we refer to these orbitals as molecular orbitals.
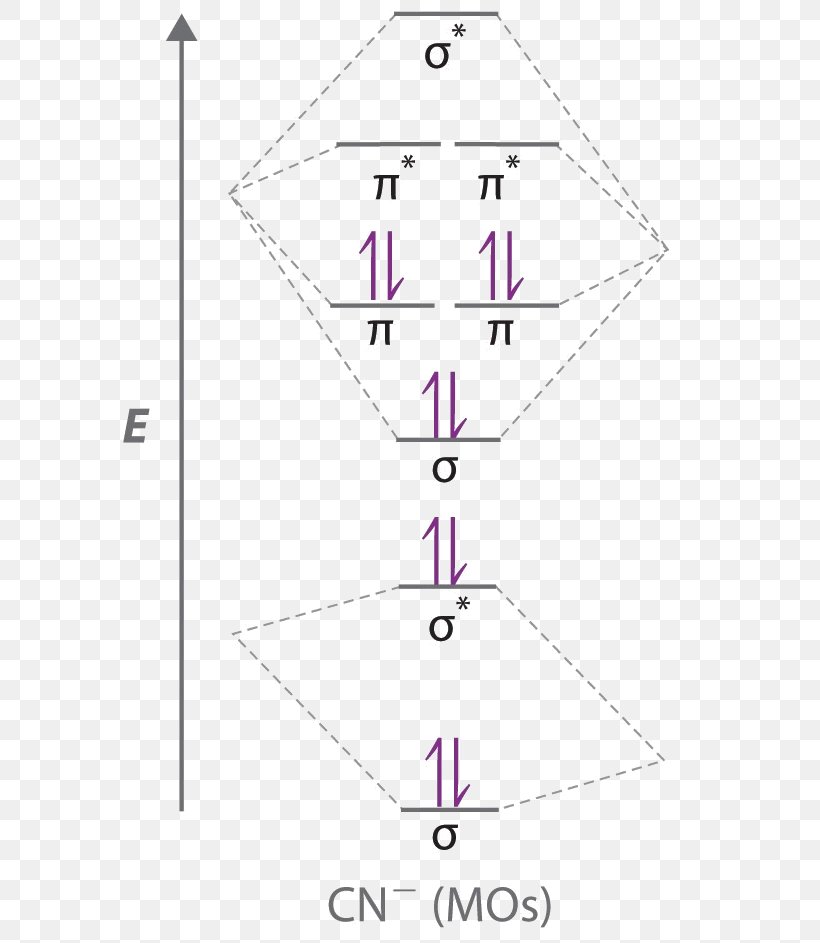
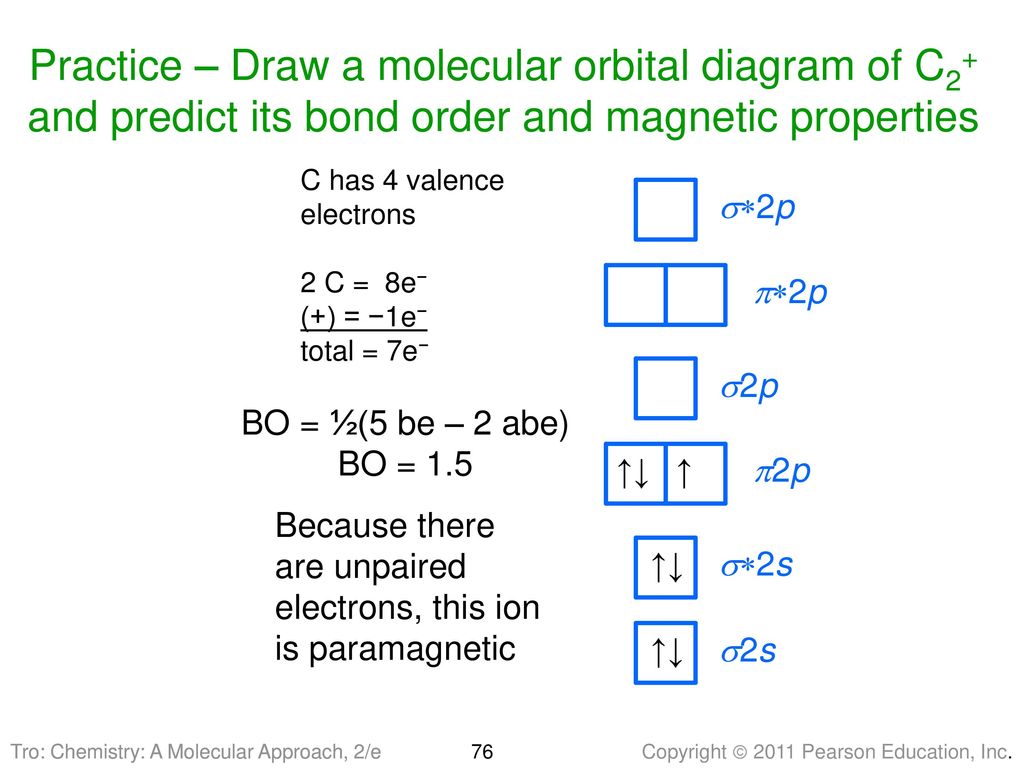
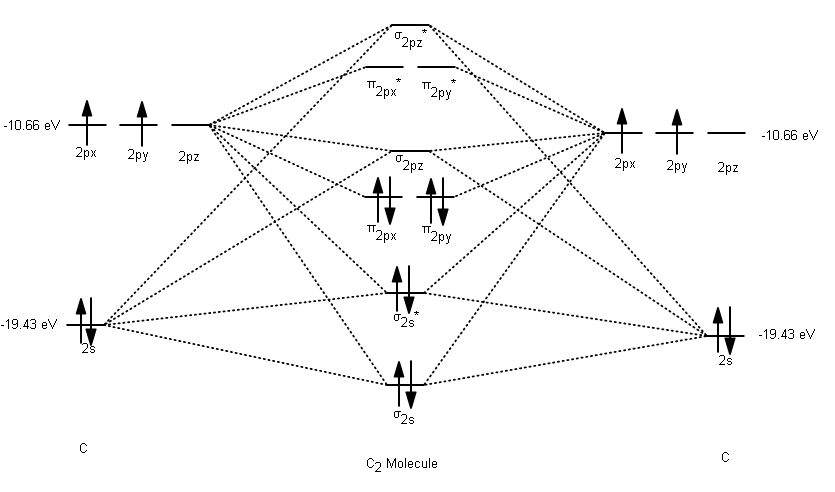
In the case of HCN, let us look at how the atomic orbitals fuse to make molecular orbitals. Electronic configuration of C is 2s2 2p2, electronic configuration of H is 1s1, and electronic configuration of N is 2s2 2p3. Here, one sp orbital of C fuses with 1s orbital of H. And the other sp orbital of C fuses with one of the p orbitals of Nitrogen. An index, called Lewis bond order, defined as the weight of bonding type bond orbitals, can be used to account for the bonding nature of the canonical molecular orbitals and thus also account for the vibrational structures of photoelectron spectroscopy. Each canonical molecular orbital of the molecules HCN and C 2 H 2 may have several Lewis ... Exercise 3.3.4. 3. Construct a qualitative molecular orbital diagram for chlorine, Cl 2. Compare the bond order to that seen in the Lewis structure (remember that an electron in an antibonding orbital cancels the stabilization due to bonding of an electron in a bonding orbital). Answer. Problem 66QP: Draw the molecular orbital diagram for the cyanide ion (CN−). (Assume the ordering of moleculer orbitals to be like that in N2.) Write the electron configuration of the cyanide ion (CN−). Oct 10, · We see the existence of the paired HOMO's and LUMO's in the molecular orbital energy diagram for HCN, shown below: Next, we move ...
Click on Chemistry 1A, Chemistry 2, or Chemistry 10 to get information about the courses that I teach · Selecting General Sites will show you a list of chemistry-related web sites Photoelectron spectroscopy. THEO CHEM ELSEVIER Journal of Molecular Structure (Theochem) 429 (1998) 153-159 Orbital interaction and the photoelectron spectroscopy of N2, CO, HCN and C2H2 Erh-hao Chen, Tse-Chiang Chang* Department of Chemistry, National Cheng Kung University: Tainan, Taiwan 700, Republic of China Received 12 June 1997; accepted ... In complex molecules, hybrid orbitals and valence bond theory can be used to describe \(\sigma\) bonding, and unhybridized \(\pi\) orbitals and molecular orbital theory can be used to describe \(\pi\) bonding. ... Describe the bonding in HCN using a combination of hybrid atomic orbitals and ... In the HCN molecule, C atom includes sp - hybridized orbital, since it will combine with only two other atoms to form HCN. One of the sp - hybrid orbitals of Carbon atom overlaps with 1 s orbital of H atom, while other sp - hybrid orabital mixes with one of Nitrogen's atom's three atomic p orbitals which were unhybridized.
uh, molecular orbital represents. So they have, like, behavior off electron. They're formed into the linear combination for atomic orbital spawned in there at them. So fair manicure. Um, the the electronic configuration off carbon and nitrogen is carbon is one is to toe to toe pay two and a ...
HCN Molecular Geometry The molecular Geometry of any given molecule helps understand its three-dimensional structure and the arrangement of atoms in a molecule, and its shape. Hydrogen Cyanide has geometry like AX2 molecule , where A is the central atom and X is the number of atoms bonded with the central atom.
June 13, 2016 - Within H-C-=N? Two sigma and 2 pi bonds. H-C-=N formally possesses 1xxC-H and 1xxC-N sigma bonds. And 2xxC-N pi bonds.
Science. HCN Lewis Structure & Molecular Geometry. Hydrogen Cyanide (HCN) is a colorless, flammable, and poisonous liquid. HCN Lewis structure comprises three different atoms: Hydrogen, carbon, and nitrogen. It is a polar molecule with bond angles of 180 degrees. HCN is used in electroplating, mining, and as a precursor for several compounds.
For the molecule hydrogen cyanide (HCN):a) Draw the filled atomic orbitals of the nitrogen atom.b) Which atomic orbitals are used for hybridization and event...
Our videos prepare you to succeed in your college classes. Let us help you simplify your studying. If you are having trouble with Chemistry, Organic, Physics, Calculus, or Statistics, we got your back! Our videos will help you understand concepts, solve your homework, and do great on your exams.
the bonding between the carban and the nitrogen in hydrogen cyanide or hydrocyanic acid is a triple bond, hence the hybrid orbital is sp, due to the linear geometry of the molecule
Free practice questions for College Chemistry - Orbital Hybridization. Includes full solutions and score reporting.
F HCN 1 + 4 + 5 =10 ... HCN. 44. 2. F F (MO Theory). F F F (Molecular Orbital Theory) ... (Molecular Orbital Diagram). MO AO. 1sA + 1sB. Bonding.
HCN has a hydrogen atom single-bonded to a carbon atom, and that carbon atom is triple-bonded to a nitrogen atom.. These are all non-metals, so the bonds are covalent and HCN is therefore a covalent (aka Molecular) structure.. Carbon brings four valence electrons with it; it needs four more to complete its valence shell.
In the case of HCN, let us look at how the atomic orbitals fuse to make molecular orbitals.
The overlap of two s orbitals (as in H 2), the overlap of an s orbital and a p orbital (as in HCl), and the end-to-end overlap of two p orbitals (as in Cl 2) all produce sigma bonds ([latex]\sigma[/latex] bonds), as illustrated in Figure 7.4.3. A [latex]\sigma[/latex] bond is a covalent bond in which the electron density is concentrated in the ...
May 9, 2021 - In complex molecules, hybrid orbitals and valence bond theory can be used to describe \(\sigma\) bonding, and unhybridized \(\pi\) orbitals and molecular orbital theory can be used to describe \(\pi\) bonding. ... Describe the bonding in HCN using a combination of hybrid atomic orbitals and ...
There are two sigma bonds in HCN: C-H and C-N. The number of sigma bonds created equals the number of hybrid orbitals. As a result, the hybridization for the HCN molecule is sp hybridization. Molecular Geometry. The liner molecular geometry of hydrogen cyanide has bond angles of 180 degrees.
CN Lewis Structure, Molecular Geometry, Hybridization, Polarity, and MO Diagram. CN is known as cyanide which exists as a pseudohalide anion. It belongs to the cyano group and consists of carbon and a nitrogen atom having a triple bond. It carries a charge of -1 and is a conjugate base of hydrogen cyanide (HCN).
Tell me about the atomic charges, dipole moment, bond lengths, angles, bond orders, molecular orbital energies, or total energy. Tell me about the best Lewis structure.
January 31, 2017 - Answer (1 of 2): Here is a useful MO diagram of HCL found on the internet: The Cl electrons residing up to 3s orbital (1s, 2s, 2px,2py,2pz,3s) are largely stabilized than H electron in 1s orbital and therefore they cannot mix and form bond. The 3p electrons of Cl have comparable energy with the ...
LCAO-MO = linear combination of atomic orbitals. In physics, this is called this the tight binding approximation. Nov 08, · RE: a thank you to entice the C-N molecular orbital diagram for the sigma bond in HCN? Label each and every molecular orbital with its call (sigma, pi) and place the obtainable electrons interior the proper atomic ...
Access 130+ million publications and connect with 20+ million researchers. Join for free and gain visibility by uploading your research.
How to make molecular Orbital diagramhttps://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UYC-ndQ6Lww&t=6s
In HCN, there are two sigma bonds, C-H and C-N. The number of sigma bonds is equal to the number of hybrid orbitals formed. So the hybridization for HCN molecule is sp hybridization. Concluding Remarks. We can say that HCN, Hydrogen Cyanide, is a linear molecule with sp hybridization to conclude this blog post.
1 Answer1. Show activity on this post. Low-lying, empty antibonding orbitals will suffice. The reaction of carbon dioxide and water to form carbonic acid serves as a parallel example. Water donates one of the lone pairs on oxygen towards bond formation, water is the Lewis base in this case. Carbon dioxide has empty, low-lying π * orbitals that ...
This formation of new hybrid orbital is possible by combining several types of orbitals (s,p,d and etc). Describe HCN molecular bond by using Valence Bond Theory
Describe HCN molecular bond by using Valence Bond Theory. Because px orbital of C and N will form sigma bond, this leaves with two N atom p-orbitals which form two mutually perpendicular pi bonds to the two atomic p orbitals on the C atom. HCN thus has one single and one triple bond. Click to see full answer.
Nov 08, · RE: a thank you to entice the C-N molecular orbital diagram for the sigma bond in HCN? Label each and every molecular orbital with its call (sigma, pi) and place the obtainable electrons interior the proper atomic orbitals and molecular wiringall.com: Resolved. Steps in predicting the hybrid orbitals used by an atom in bonding: 1.
This is the general MO diagram you need to fill with the valence electrons of BN Boron has 3 valence electrons, and nitrogen has 5 valence electrons, this makes 8 electrons. You have to start filling the orbitals from those with lowest energy to those with higher energy. So, 2 electrons on σ2s , two electrons on σ∗2s, two electrons on σ2p . You have now 2 electrons left, and two orbitals ...
Hydrogen cyanide, sometimes called prussic acid, is a chemical compound with the chemical formula HCN. It is a colorless, extremely poisonous, and flammable liquid that boils slightly above room temperature, at 25.6 °C (78.1 °F).HCN is produced on an industrial scale and is a highly valued precursor to many chemical compounds ranging from polymers to pharmaceuticals.
The bond length and bond energy have been measured to be 97.06 and 424.7 respectively. Assume that the OH molecule is analogous to the HF molecule discussed in the chapter and that the MOs result from the overlap of a orbital from oxygen and the 1 orbital of hydrogen (the O-H bond lies along the z axis). a.
Figure 9.7. 3: Molecular Orbital Energy-Level Diagrams for Diatomic Molecules with Only 1 s Atomic Orbitals. (a) The H 2+ ion, (b) the He 2+ ion, and (c) the He 2 molecule are shown here. Figure 9.7. 3 a shows the energy-level diagram for the H 2+ ion, which contains two protons and only one electron.
December 6, 2018 - Answer (1 of 7): Summing up the number of σ -bond formed by the desired atom (here N) and the number of lone pair on it we can easily know the hybridization of it. If the sum is 2 →hybridization−sp If the sum is 3 →hybridization−sp2 If the sum is 4 →hybridization−sp3 If the sum ...
Hydrogen cyanide is a one-carbon compound consisting of a methine group triple bonded to a nitrogen atom It has a role as a human metabolite, an Escherichia coli metabolite and a poison.It is a hydracid and a one-carbon compound.It is a conjugate acid of a cyanide.It is a tautomer of a hydrogen isocyanide.






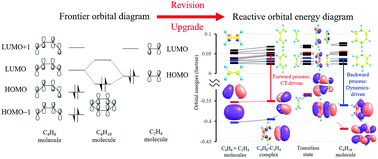


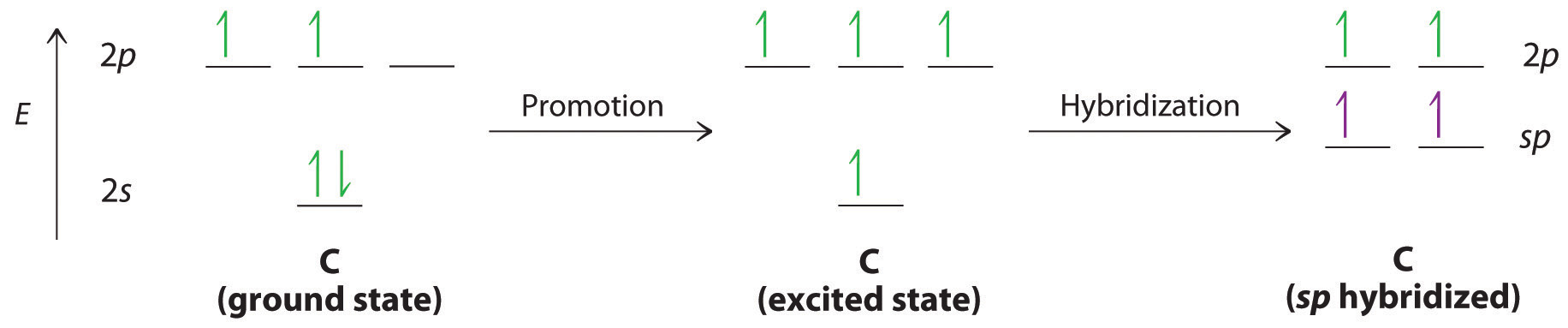
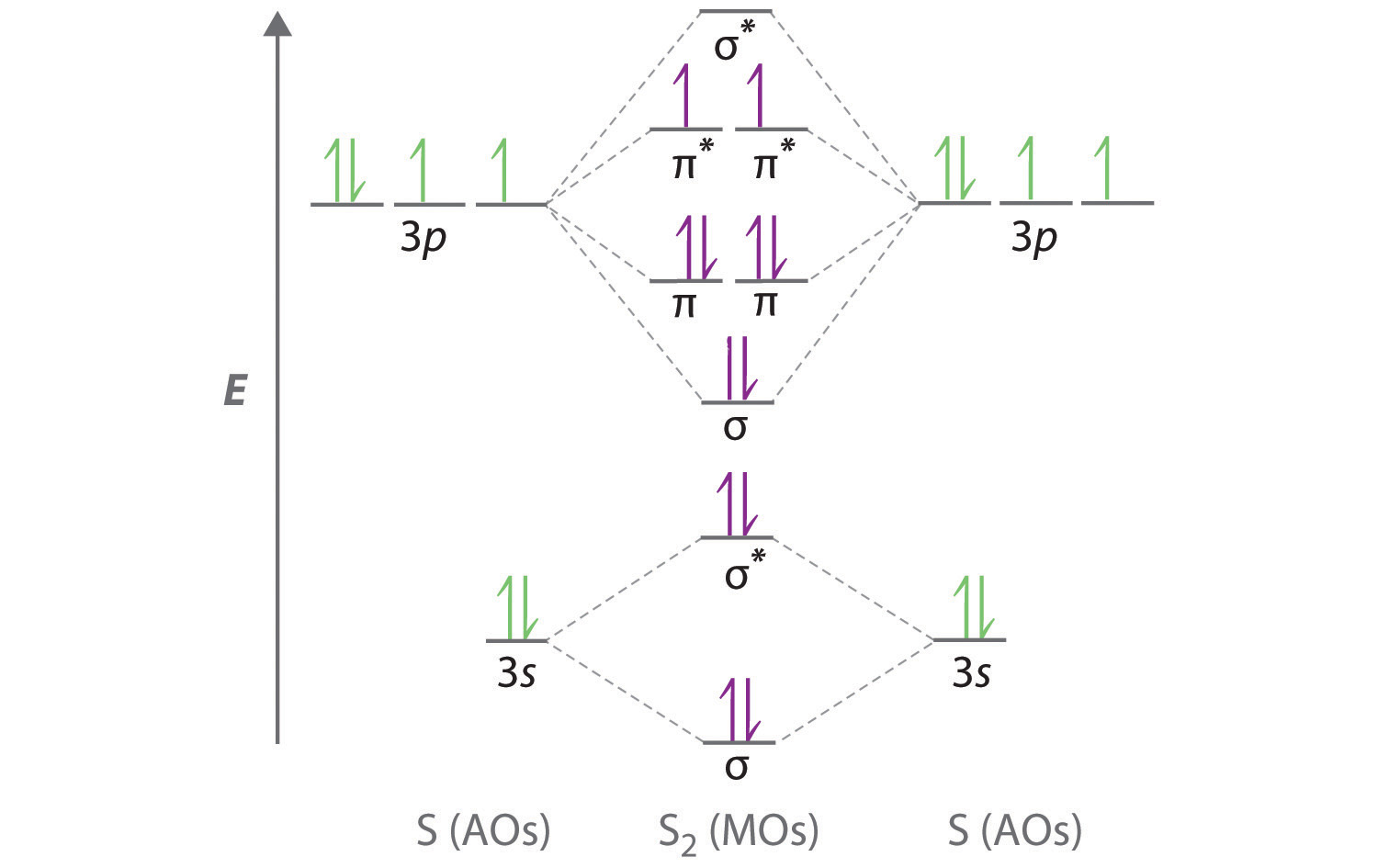

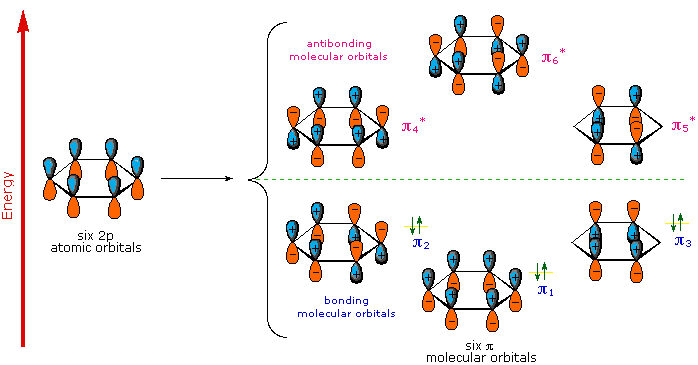









0 Response to "38 hcn molecular orbital diagram"
Post a Comment