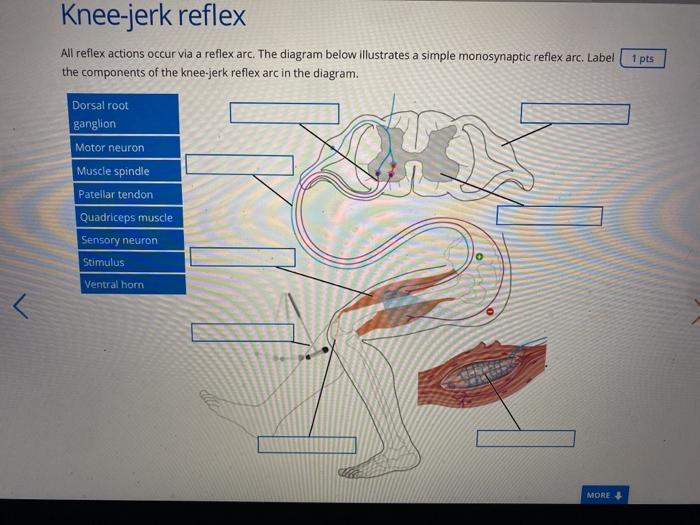
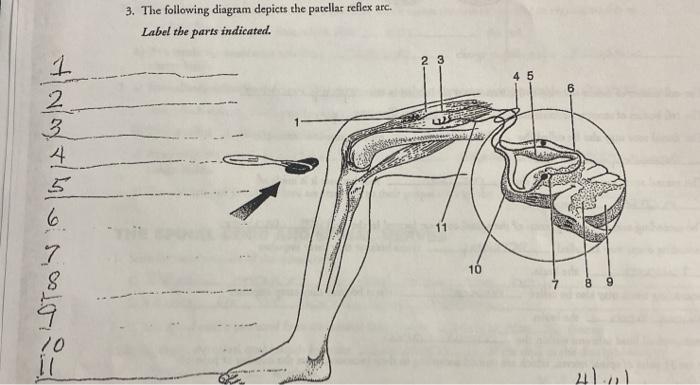
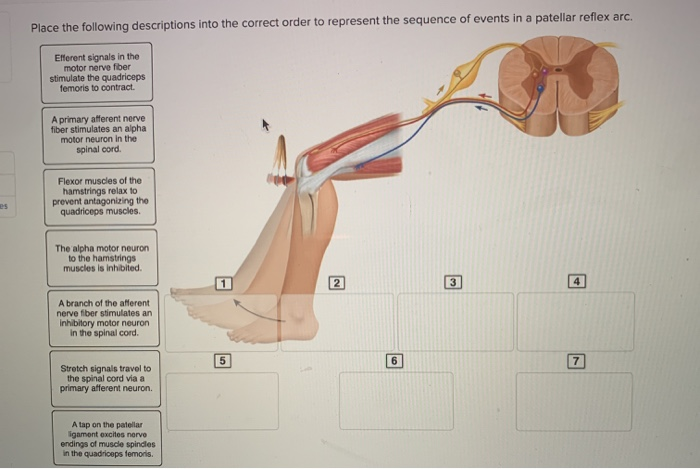
38 drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the parts of a knee-jerk reflex.
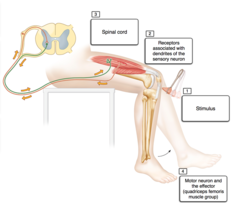
Solved part a drag the labels onto diagram to identif. Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the parts of a knee jerk reflex. What is the role of reciprocal inhibition. Start studying physiology chapter 13 assignment ml. Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the parts of a knee jerk reflex. Label the parts of a monosynaptic reflex arc. Part A Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the parts of a monosynaptic reflex arc. Previous Answers Help Reset Submit Sensory receptor (muscle spindle) Sensory (afferent) neuron Motor (efferent) neuron Effector (quadriceps femoris muscle)
Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the various synapse structures. Part a structure of a chemical synapse part complete drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the various synapse structures. Mastering biology chapter 13 hw. ... Solved Label The Components Of A Knee Jerk Reflex Part A
Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the parts of a knee-jerk reflex.
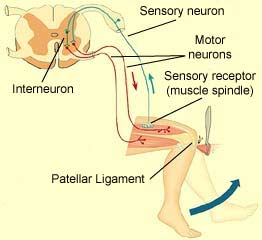
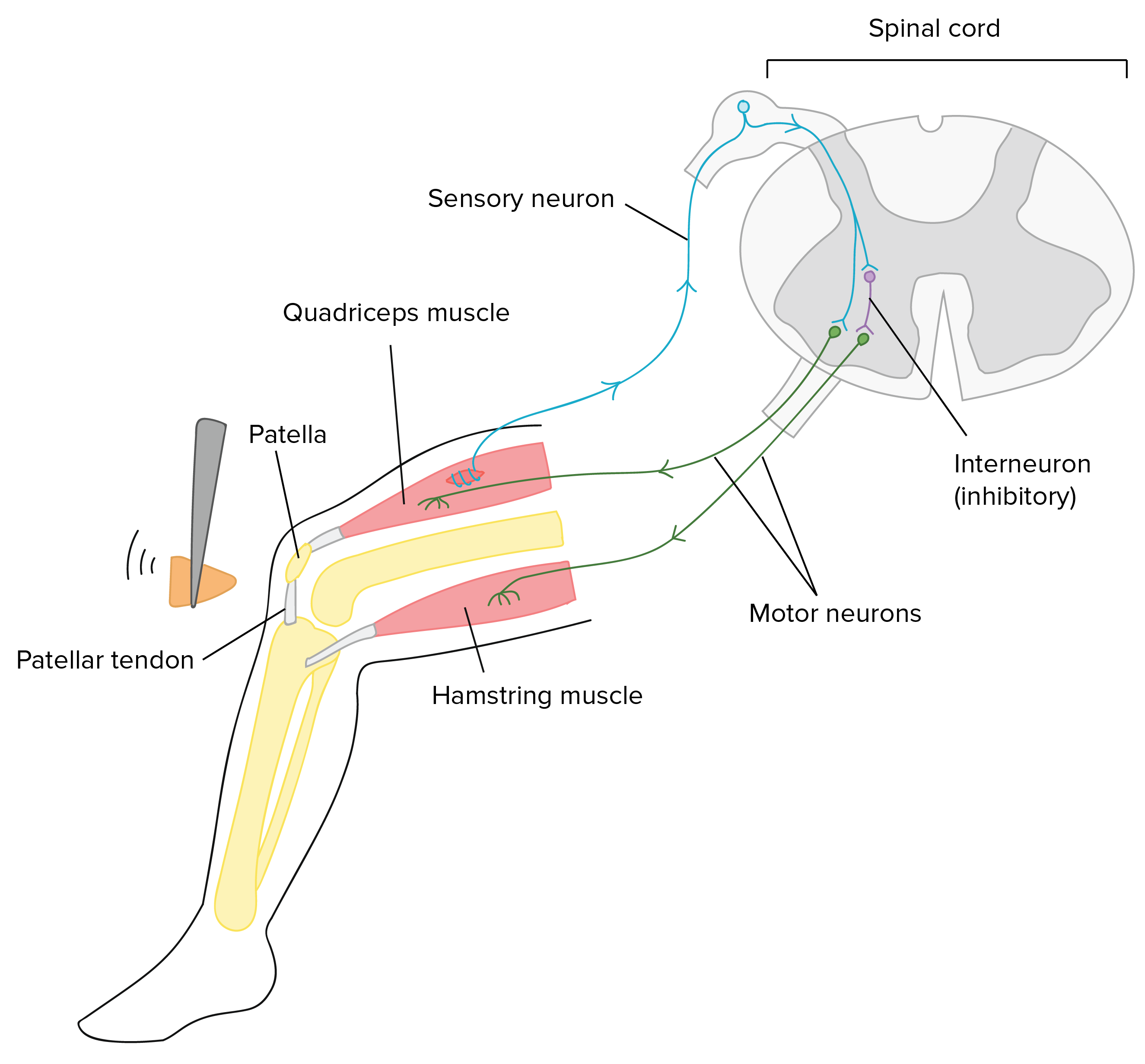
For example, if they are tired, have a lot of energy, had coffee recently, etc. Why do you think these do or don't affect the reflex? Don't hurt yourself or anyone else investigating this, but does the speed or amplitude depend at all with the force you strike the knee with? Why might this ... Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the different types of gated ion channels. ... Clenching the fists often enhances the knee jerk reflex. This is an example of _____. positive feedback ... Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the parts of the hypothalamus and surrounding structures. 3) Motor neurons send activating impulses to the quadriceps, causing them to contract, and extending the knee 4) at the same time as 3 The interneurons make inhibitory synapses with the ventral horn neurons that prevent the antagonist muscles (hamstrings) from resisting the contraction of the quadriceps.
Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the parts of a knee-jerk reflex.. Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. back 3. ... Which ligament would one tap to generate the knee-jerk reflex? back 53. patellar ligament. front 54. Which of the following is CORRECTLY paired? ... Identify the saddle joint of the skeleton. back 57. Carpometacarpal joint of the thumb. A reflex action, also known as a reflex, is an involuntary and nearly instantaneous movement in response to a stimulus. When a person accidentally touches a hot object, they automatically jerk their hand away without thinking. A reflex does not require any thought input. The path taken by the nerve impulses in a reflex is called a reflex arc. The knee-jerk reflex is what's known as a mono-synaptic response, because there is only one synapse in the circuit needed to complete the reflex. Main Digest The reflex test is simple yet informative and can give important insights into the integrity of the nervous system at many different levels. Hypothalamus Limbic system Thalamus Correct Art-labeling Activity Figure 13.6 Label the components of a knee-jerk reflex. Part A Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the parts of a knee-jerk reflex.
March 1, 2016 - In this video, I discuss the knee-jerk reflex. The knee-jerk reflex, also known as the patellar reflex, is a simple reflex that causes the contraction of the quadriceps muscle when the patellar tendon is stretched. I describe the course of the reflex arc from muscle spindles in the quadriceps musc A reflex is defined as an involuntary, unlearned, repeatable, automatic reaction to a specific stimulus which does not require input from the brain. The muscle stretch reflex is the most basic reflex pathway in the body and as such, understanding this allows understanding of more complex reflexes. This article shall discuss the components of a reflex arc, the monosynaptic reflex and relevant ... Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the structural features, ligaments, and associated tendons of the shoulder joint. Anteriorly, on the costal surface, . The humerus fits relatively loosely into the shoulder joint. Black and white diagram of the ear showing labels on the different parts . Label the components of a knee jerk reflex part a drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the parts of a knee jerk reflex. What is the physiological function of this reflex. Label the components of a knee jerk reflex part drag labels onto reflex arc of the knee reflexes are quick involuntary reaction to a stimulus here we see jerk first somatic receptors in figure 21 3 the patellar knee ...
Please note that this is just a preview of a school assignment posted on our website by one of our clients. If you need assistance with this question too, scroll to the bottom of this post or CLICK HERE to Order Now Question: Part A Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the […] In the last part of this coaching activity you will turn your attention to the crossed extensor reflex. You will first order the events that take place during this reflex. Then you will identify the type (s) of synapses found in this reflex arc. Finally, you will test your knowledge by applying what you have learned to a different/new reflex. Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the parts of a knee jerk reflex. Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the various synapse structures. Golgi tendon organ myotatic unit basal ganglion muscle spindle correct artlabeling activity figure 136 label the components of a kneejerk reflex. Bio 201 central nervous system flashcards easy notecards knee jerk reflex patellar monosynaptic ... knee-jerk reflex, also called patellar reflex, sudden kicking movement of the lower leg in response to a sharp tap on the patellar tendon, which lies just below the kneecap. One of the several positions that a subject may take for the test is to sit with knees bent and with one leg crossed over the other so that the upper foot hangs clear of the floor.
Question. : Part A Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify factors that affect mean arterial pressure Reset Help Mean Arterial Pressure Blood distribution between venous and arterial vessels Stroke volume Arterioles Left ventricle Elastic arteries Mean arterial pressure Mean arterial pressure α cardiac output resistance (b) Factors that ...
The diagram below shows how this reflex works. Knee-jerk reflex, also called patellar reflex, sudden kicking movement of the lower leg in response to a sharp tap on the patellar tendon, which lies just below the. Identify the patellar tendon, a thick, broad band of tissue extending down from the To see a video of the normal patellar reflex exam ...
Wilhelm Heinrich Erb (1840–1921) and Carl Friedrich Westphal (1833–1890) simultaneously reported the patellar tendon or knee reflex in 1875. The term knee-jerk was recorded by Sir Michael Foster in his Textbook of physiology in 1877: "Striking the tendon below the patella gives rise to ...
draw a globe and label the parts. draw a globe and label the parts draw a globe and label the parts. November 18, 2021 | In point-of-care creatinine
Transcribed image text: Label the components of a knee-jerk reflex Part A Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the parts of a knee-jerk reflex.
In a knee-jerk reflex arc the sensory neuron ______ connects to the motor neuron in the spinal cord. directly.
Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the parts of a knee jerk reflex. Epimysium covers whole muscle allows muscles to contract with respect to each other without friction between them perimysium covers the fascicles endomysium covers each muscle fiber tendons formed by the fusion of these 3 connective tissues. Label the components of a knee jerk reflex part a drag the labels onto the ...
Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the parts of a knee jerk reflex. Label the parts of a monosynaptic reflex arc. Carpometacarpal joint of the thumb. The patellar tendon inhibited motor neuron does not activate antagonistic muscle response extension of the leg muscle spindle stretched and nosyn tic activation of somatic motor stretch sensitive neurons are neuron activated. The ...
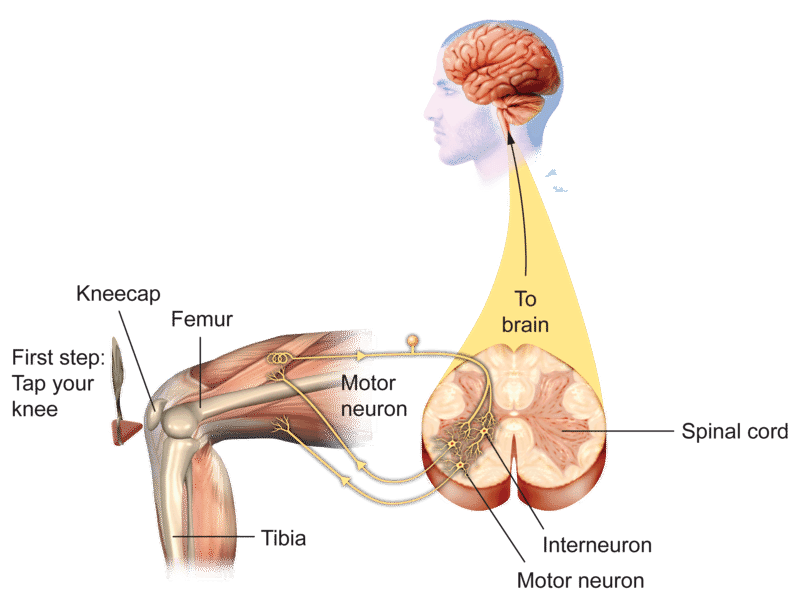
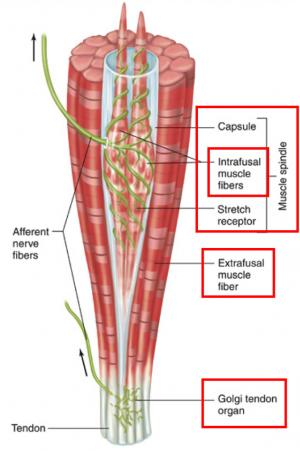
Reflex Arc Components. Most reflex arcs have five main components: receptors, sensory neurons, interneurons, motor neurons and muscles. However, not all reflexes use interneurons.
Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the parts of a knee-jerk reflex. _____ are stretch receptors inside skeletal muscles. muscle spindles. In a stretch reflex, what causes the response to stop? After the response, the stretch receptors are no longer stretched.
Transcribed image text: Part A Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the parts of a knee-jerk reflex. THE PATELLAR TENDON (K Monosynaptic activation of somatic motor neuron Sensory neuron an action potential Muscle spindle stretched and Effector contracts stretch-sensitive neurons are activated Inhibited motor neuron does not activate antagonistic muscle Response extension of the leg ...
FlexBook® Platform + CK-12 Overview
Drag and drop the descriptive labels of events into the correct sequence at the chemical synapse. Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the stages in which the lagging strand is synthesized. Drag the labels to their appropriate targets to correctly identify the various chromosome structures.
Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the parts of a knee jerk reflex. Solved part a drag the labels onto diagram to identif. 68 diagram and label the knee jerk reflex. The patellar tendon inhibited motor neuron does not activate antagonistic muscle response extension of the leg muscle spindle stretched and nosyn tic activation of somatic motor stretch sensitive neurons are neuron ...
Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the parts of a knee jerk reflex. Muscle reflexes click on the link or the image below for an interactive concept map activity then answer the questions to the right. Part a drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the parts of a kneejerk reflex. Label the parts of a monosynaptic reflex arc.
For example, triggering the knee-jerk reflex occurs as a result of the activation of a motor neuron. The motor neuron is activated in response to the stimulation of a mechanoreceptor in the knee. Proprioceptors, also called position sensors, communicate information about the location of our body parts in relation to other body parts.
There are five steps in a knee-jerk reflex arc as follows: A tap on the patellar tendon (tendon attached to the kneecap) is sensed by stretch receptors in the muscle (muscle spindles). The muscle spindle produces a pattern of nerve impulses that are conveyed along a sensory (afferent) nerve fiber, past its cell body in the dorsal root ganglion ...
A major part of the spinal cord function is regulated by the brain.Many functions of the spinal cord are also executed independently from the brain, such as a spinal reflex.. The definition of a spinal reflex as well as their components, functions, pathways, and physiology will be described in this article and is a must-know for every student that is passionate about neurosciences.
Label the components of a knee-jerk reflex Part A Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the parts of a knee-jerk reflex.
Explain, using illustrations, the function of a motor neuron and a sensory neuron in a reflex arc using the example of a knee jerk (patellar) reflex. Question 4 (2.1) Describe and explain the transmission of an action potential in a myelinated neurone. Question 5 (2.2) Describe the all-or-nothing nature of nerve impulses. Question 6 (2.3)
Label the components of a knee jerk reflex part a drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the parts of a knee jerk reflex. Muscle spindles are sensory receptors that are located in muscle. Part a the mechanism of dna replication. This is a process that inhibits the stretch reflex in antagonistic pairs of muscles.
1. activate glands. 2. activate smooth muscles. 3. activate cardiac muscles. Stretch reflexes are important for maintaining and adjusting muscle tone for posture, balance, and locomotion. Recall from the video that the patellar reflex is a specific example of a stretch reflex test.
The H reflex is a monosynaptic reflex response that can be obtained from the soleus muscle after stimulation of the tibial nerve. Stimulation of afferent fibers in the tibial nerve triggers a reflex response in the motor nerves to the soleus via the spinal cord (Fig. 1-57). The F Wave. The F wave requires a more potent stimulus than the H reflex.
Stretch reflexes can be used for clinical testing, such as tapping the patellar tendon to stimulate the knee-jerk reflex, which slightly stretches the quadriceps muscle. Testing many stretch reflexes helps determine integrity of peripheral nerves and predictable spinal cord areas (Table 1.4).
3) Motor neurons send activating impulses to the quadriceps, causing them to contract, and extending the knee 4) at the same time as 3 The interneurons make inhibitory synapses with the ventral horn neurons that prevent the antagonist muscles (hamstrings) from resisting the contraction of the quadriceps.
Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the different types of gated ion channels. ... Clenching the fists often enhances the knee jerk reflex. This is an example of _____. positive feedback ... Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the parts of the hypothalamus and surrounding structures.
For example, if they are tired, have a lot of energy, had coffee recently, etc. Why do you think these do or don't affect the reflex? Don't hurt yourself or anyone else investigating this, but does the speed or amplitude depend at all with the force you strike the knee with? Why might this ...
















0 Response to "38 drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the parts of a knee-jerk reflex."
Post a Comment