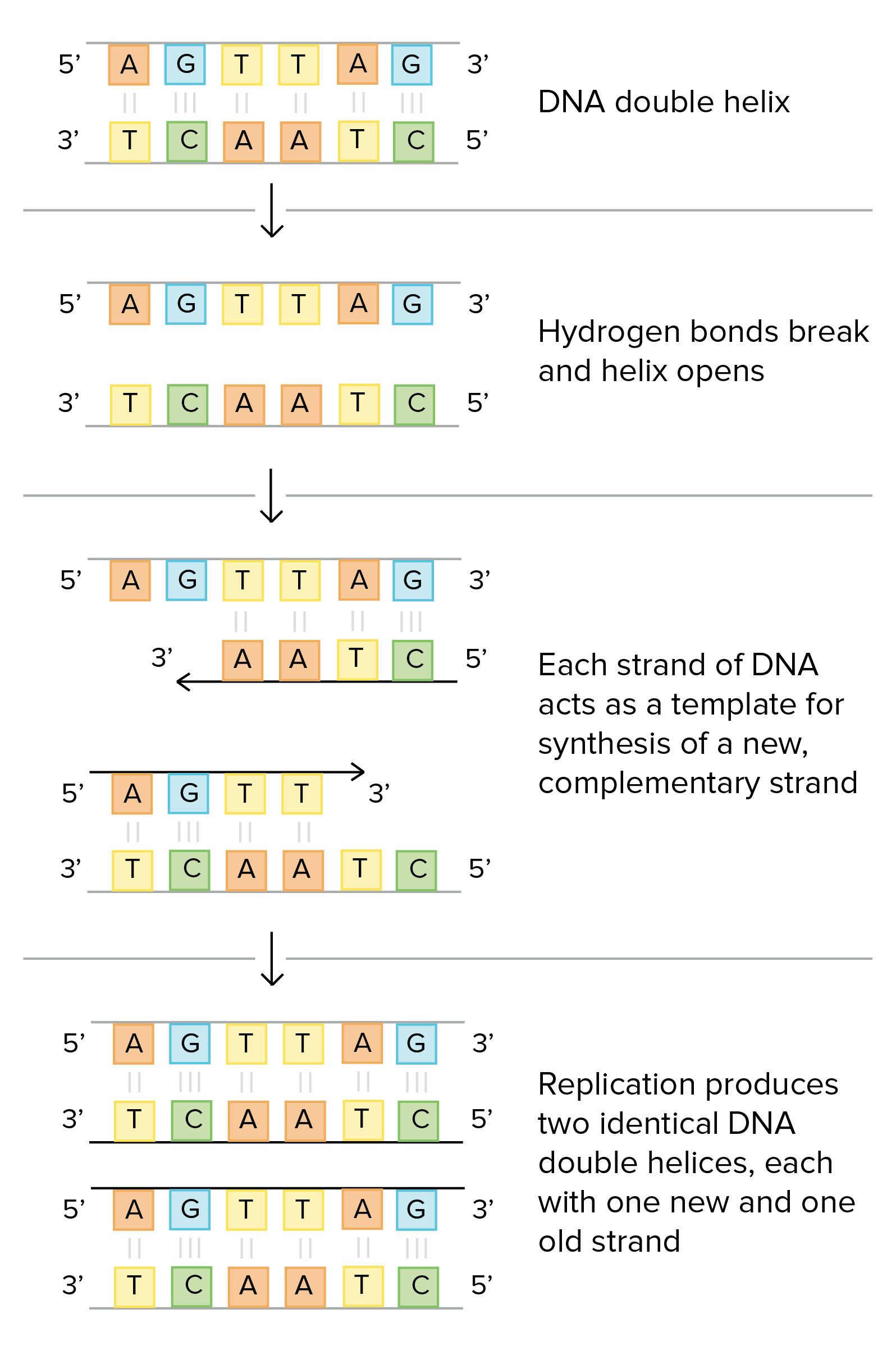
37 The Diagram Below Shows A Double-stranded Dna Molecule (parental Dna).
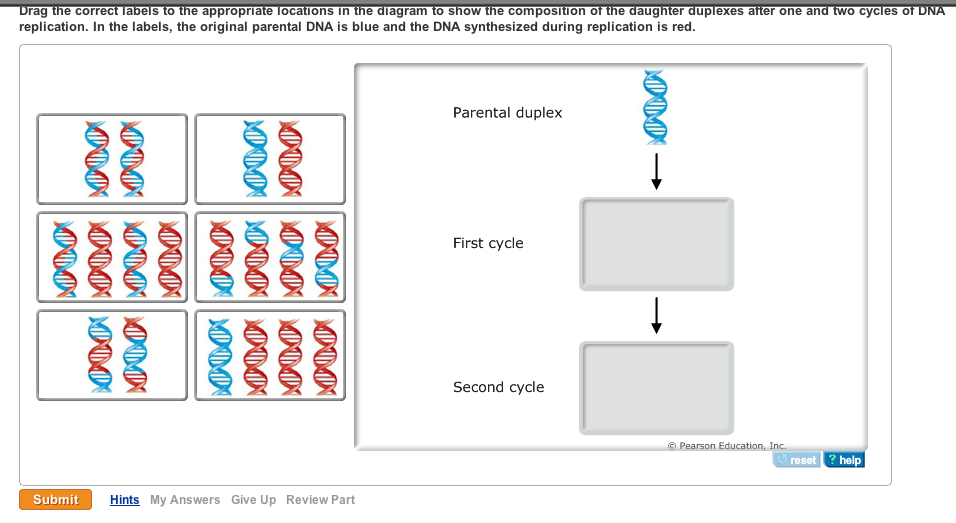
Mastering Biology Chapter 13 Flashcards - Quizlet The diagram below shows a double-stranded DNA molecule (parental DNA). Drag the correct labels to the appropriate locations in the diagram to show the composition of the daughter DNA molecules after one and two cycles of DNA replication. In the labels, the original parental DNA is blue and the DNA synthesized during replication is red. Solved I am new with this. Please help DNA replication is ... The diagram below shows a double-stranded DNA molecule (parental duplex). Drag the correct labels to the appropriate locations in the diagram to show the composition of the daughter duplexes after one and two cycles of DNA replication. In the labels, the original parental DNA is blue and the DNA synthesized during replication is red. Best Answer
Chapter 11 Flashcards | Quizlet The diagram below shows a double-stranded DNA molecule (parental duplex). Drag the correct labels to the appropriate locations in the diagram to show the composition of the daughter duplexes after one and two cycles of DNA replication. In the labels, the original parental DNA is blue and the DNA synthesized during replication is red.

The diagram below shows a double-stranded dna molecule (parental dna).
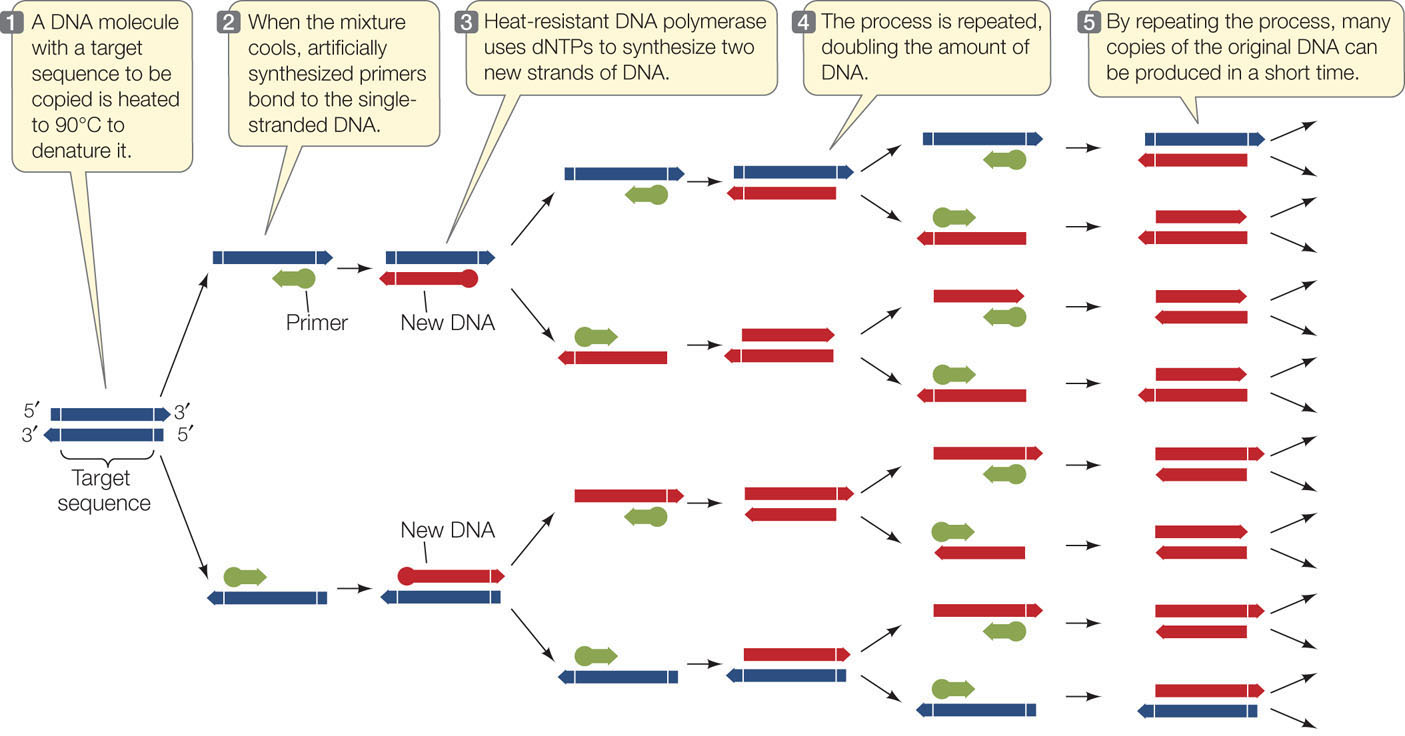
the mechanism of dna replication mastering biology the mechanism of dna replication mastering biology June 14, 2017 Gaurab Karki Genetics, Microbiology, Molecular Biology 0. Structure and ion-release mechanism of PIB-4-type ATPases ... DNA: Structure, Forms and Functions (With Diagram) The DNA of E. coli appears to consist of a single, enormous double-stranded DNA molecule with a molecular weight of about 2.8 x 10 9, a thickness of about 2.0 nm and a contour length of about 1,360µm. E. coli DNA contains 4 million deoxyribonucleotide pairs. DNA Replication Mechanisms - Molecular Biology of the Cell ... Initially, the simplest mechanism of DNA replication seemed to be the continuous growth of both new strands, nucleotide by nucleotide, at the replication fork as it moves from one end of a DNA molecule to the other. But because of the antiparallel orientation of the two DNA strands in the DNA double helix (see Figure 5-2), this mechanism would require one daughter strand to polymerize in the 5 ...
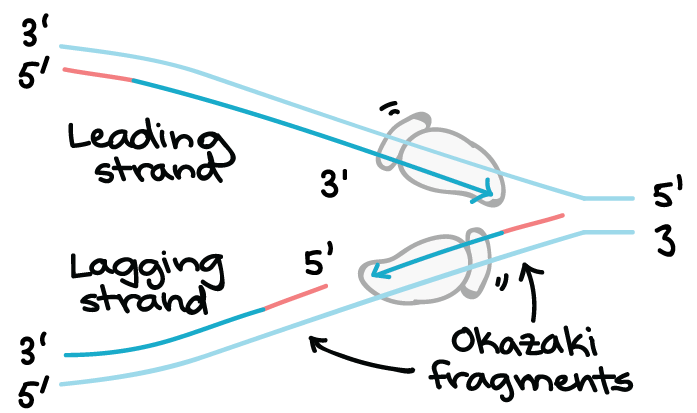
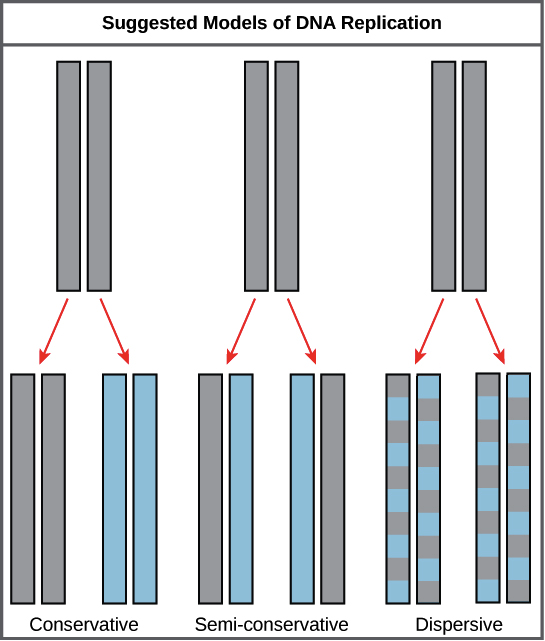
The diagram below shows a double-stranded dna molecule (parental dna).. The Diagram Below Shows A Bacterial Replication Fork And ... Part A The mechanism of DNA replication The diagram below shows a doublestranded DNA molecule (parental DNA)%(11). Mar 19, · The diagram below shows a bacterial replication fork and its principal proteins. Drag the labels to their appropriate locations in the diagram to describe the name or function of each structure. yokoben.fabbro.fvg.it The first diagram shows the parent DNA molecule; label the nucleotides in the right-hand strand. On the diagram to the right: x Circle and label a nucleotide. Label the sugar and phosphate molecules. Designed for SNAB Biology Topic 2 (Genes & Health) but also suitable for other exam boards. The diagram below shows a replication fork with the ... Chapter 9: DNA Replication - Chemistry In the dispersive model, all resulting DNA strands have regions of double-stranded parental DNA and regions of double-stranded daughter DNA. Figure by Parker, N., et.al. (2019) Openstax Matthew Meselson and Franklin Stahl devised an experiment in 1958 to test which of these models correctly represents DNA replication (Figure 9.2). Answered: Shown below is a double stranded DNA… | bartleby Shown below is a double stranded DNA molecule.Replicate this DNA and show the products formed from this replication. In your answer, indicate which strands are the new daughter strands (mark with D and in a different color) and which strands are the already existing parent strands (mark with P as shown below). Label the 5' and 3' ends of all DNA.
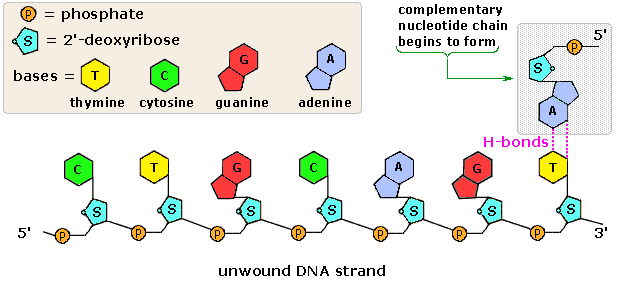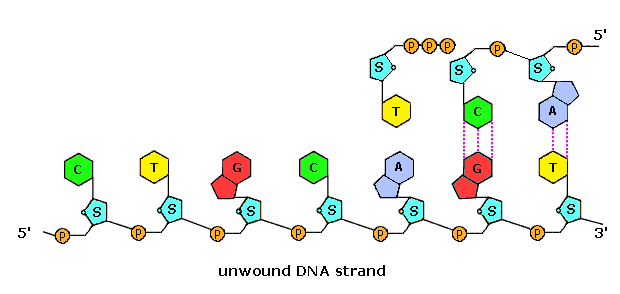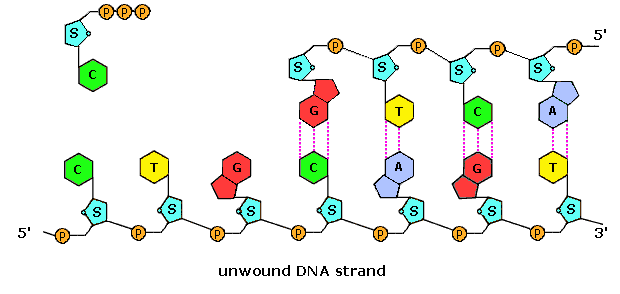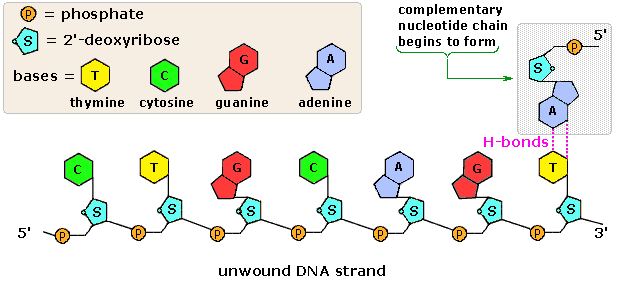
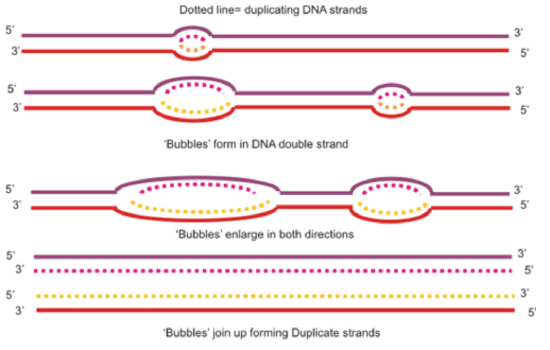
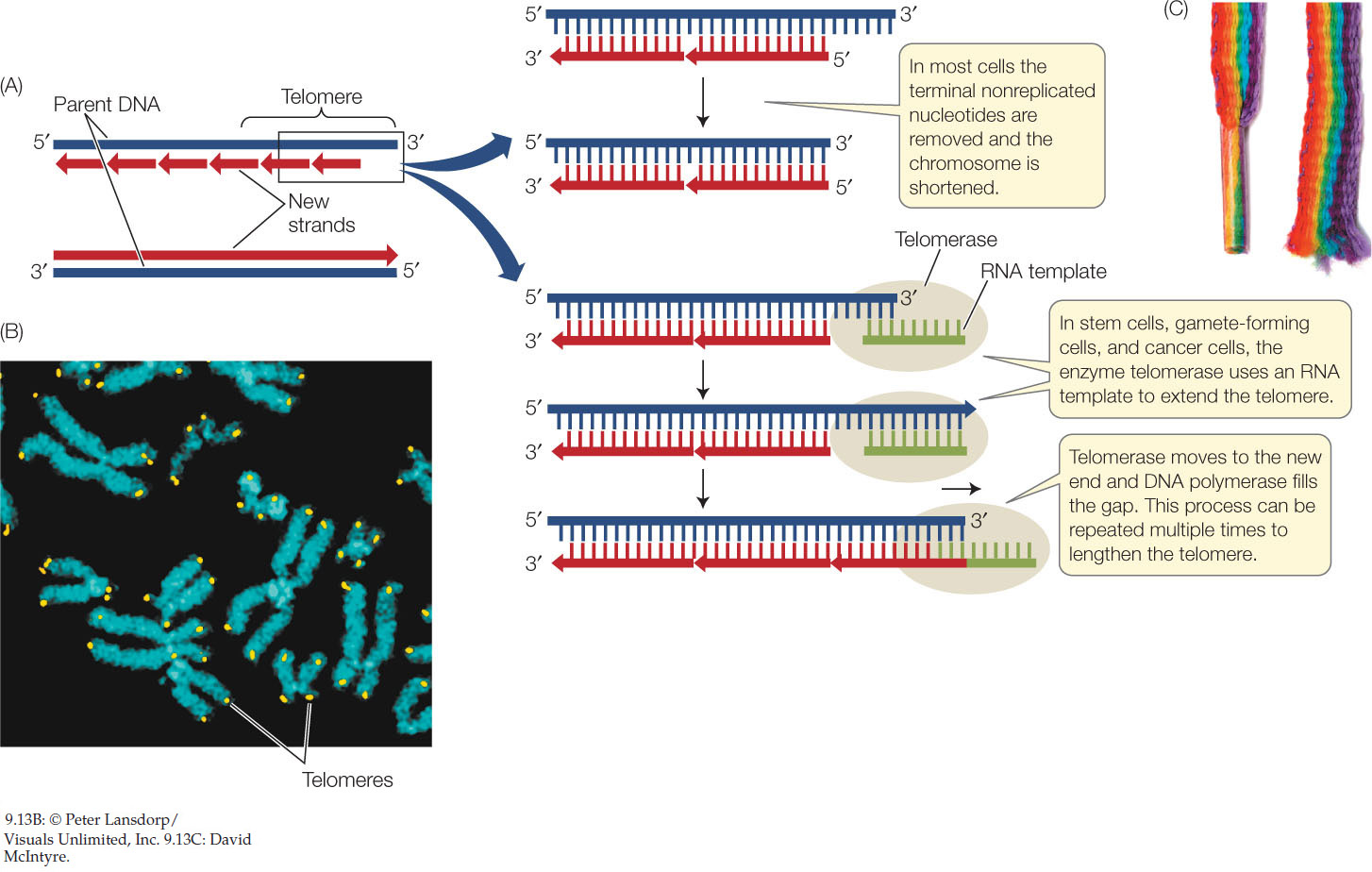
The Structure and Function of DNA - Molecular Biology of ... A DNA Molecule Consists of Two Complementary Chains of Nucleotides. A DNA molecule consists of two long polynucleotide chains composed of four types of nucleotide subunits. Each of these chains is known as a DNA chain, or a DNA strand.Hydrogen bonds between the base portions of the nucleotides hold the two chains together ().As we saw in Chapter 2 (Panel 2-6, pp. 120-121), nucleotides are ... This figure shows a section of a double-stranded DNA ... This figure shows a section of a double-stranded DNA molecule. What aspects of the structure of DNA are explained by this model? A Paired nucleotides are held together by covalent bonds. B. Adenine is paired with thymine, and guanine is paired with cytosine. C. Paired nucleotides are held together by hydrogen bonds.-D. online - RHS Homework The diagram below shows a replication bubble with synthesis of the leading and lagging strands on both sides of the bubble. The parental DNA is shown in dark blue, the newly synthesized DNA is light blue, and the RNA primers associated with each strand are red. The origin of replication is indicated by the black dots on the parental strands. Mastering Biology Chapter 16 - RHS Homework The diagram below shows a replication bubble with synthesis of the leading and lagging strands on both sides of the bubble. The parental DNA is shown in dark blue, the newly synthesized DNA is light blue, and the RNA primers associated with each strand are red. The origin of replication is indicated by the black dots on the parental strands.
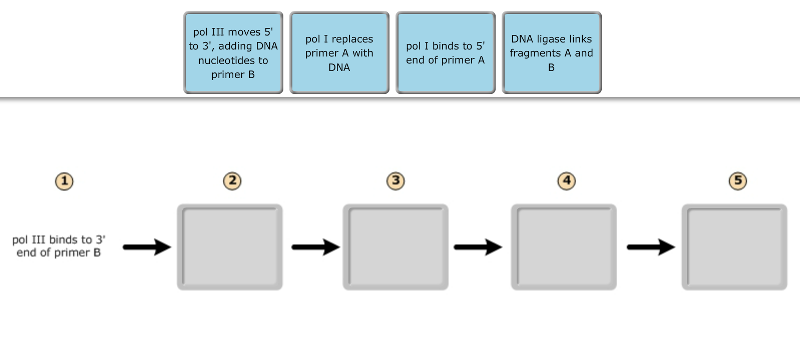
Replication Label Diagram Dna [M26BRE] During replication, enzymes called _____ untwist the double helix, separating the two parental strands. DNA: The Molecule of Heredity Worksheet DNA Structure 1. Termination of DNA replication in E. (2) Label the leading and lagging strands. (each circle needs to be labeled as either 3' or 5') J. Dna Replication Diagram Labeled. PDF Bio 102 Practice Problems Chromosomes and DNA Replication 6. The diagram below shows a DNA molecule in the process of replication. Arrows show the direction of new DNA synthesis. a. Some of the enzymes and features are labeled, but some labels are incomplete or have been omitted. Fill in the boxes with the appropriate labels. b. Mastering Bio DNA.png - Part A The mechanism of DNA ... View Mastering Bio DNA.png from BIOLOGY 171L at University of Hawaii, Manoa. Part A - The mechanism of DNA replication The diagram below shows a double-stranded DNA molecule (parental DNA). Drag the 9.2 DNA Replication - Concepts of Biology - 1st Canadian ... During DNA replication, each of the two strands that make up the double helix serves as a template from which new strands are copied. The new strand will be complementary to the parental or "old" strand. Each new double strand consists of one parental strand and one new daughter strand. This is known as semiconservative replication.
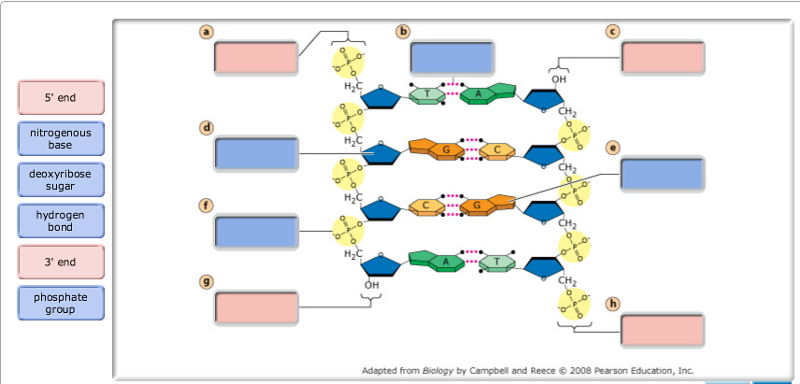
HELP PLS ASAPDirections: Drag the nitrogenous bases to the ... HELP PLS ASAP Directions: Drag the nitrogenous bases to the correct locations on the image. Each base can be used more than once, but not all bases must be used. A section of a DNA molecule is shown in the diagram below, but only one strand is complete.
PDF Chapter 22. Nucleic Acids - latech.edu Watson and Wilkins for the discovery of the molecular structure of DNA - the double helix. Chemical Structure of the DNA double strands DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is a double-stranded molecule that is twisted into a helix like a spiral staircase. Each strand is comprised of a sugar-phosphate backbone and numerous base chemicals attached in ...

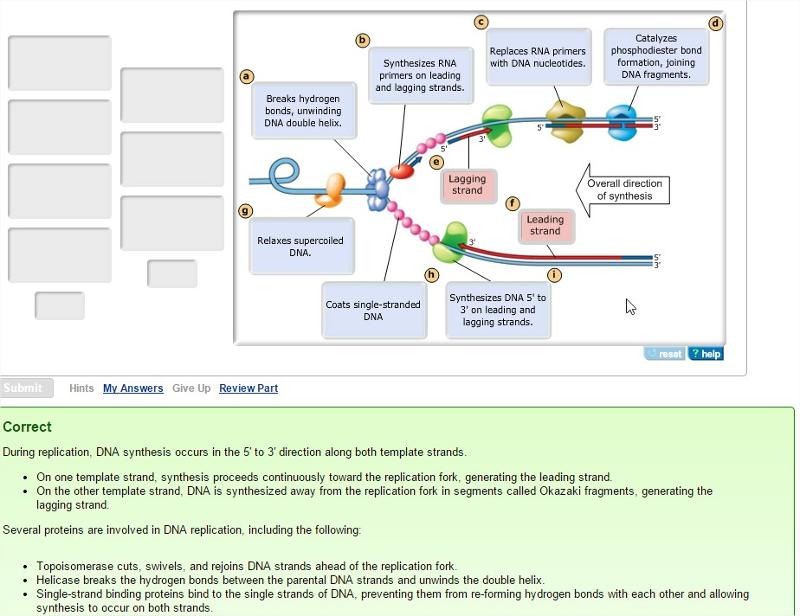
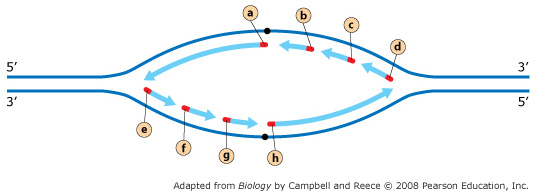
The diagram below shows a bacterial replication fork and its principal proteins. Drag the labels to their appropriate locations in the diagram to describe the name or function of each structure. Use
Mastering biololgy-Chapter 16 - BIO 210 - Biology I - StuDocu Because A is always paired with T and G with C, the order of bases on one strand determines the order on the other strand. Thus, if a DNA molecule were unwound, each strand could be copied into a complementary strand, producing an exact replica of the original molecule. Chapter 16 Question 56
DNA - Wikipedia DNA is a long polymer made from repeating units called nucleotides, each of which is usually symbolized by a single letter: either A, T, C, or G. The structure of DNA is dynamic along its length, being capable of coiling into tight loops and other shapes. In all species it is composed of two helical chains, bound to each other by hydrogen bonds.Both chains are coiled around the same axis, and ...
What is DNA? - BYJU'S Online learning Programs For K3, K10 ... DNA was first recognized and identified by the Swiss biologist, Johannes Friedrich Miescher in 1869 during his research on white blood cells. The double helix structure of a DNA molecule was later discovered through the experimental data by James Watson and Francis Crick.
DNA Replication Steps and Process - ThoughtCo DNA Structure . DNA or deoxyribonucleic acid is a type of molecule known as a nucleic acid. It consists of a 5-carbon deoxyribose sugar, a phosphate, and a nitrogenous base. Double-stranded DNA consists of two spiral nucleic acid chains that are twisted into a double helix shape. This twisting allows DNA to be more compact.
Mastering Biology Chp. 13 HW - Subjecto.com The diagram below shows a double-stranded DNA molecule (parental DNA). Drag the correct labels to the appropriate locations in the diagram to show the composition of the daughter DNA molecules after one and two cycles of DNA replication. In the labels, the original parental DNA is blue and the DNA synthesized during replication is red.
Chapter 16 Homework - In the accompanying ... - Course Hero Part A - The mechanism of DNA replication The diagram below shows a double-stranded DNA molecule (parental DNA). Drag the correct labels to the appropriate locations in the diagram to show the composition of the daughter DNA molecules after one and two cycles of DNA replication. In the labels, the original parental DNA is blue and the DNA ...
Modes of DNA Replication Semi-Conservative, Conservative, & Dispersive models of DNA replication. In the semi-conservative model, the two parental strands separate and each makes a copy of itself. After one round of replication, the two daughter molecules each comprises one old and one new strand.
DNA Replication Mechanisms - Molecular Biology of the Cell ... Initially, the simplest mechanism of DNA replication seemed to be the continuous growth of both new strands, nucleotide by nucleotide, at the replication fork as it moves from one end of a DNA molecule to the other. But because of the antiparallel orientation of the two DNA strands in the DNA double helix (see Figure 5-2), this mechanism would require one daughter strand to polymerize in the 5 ...
DNA: Structure, Forms and Functions (With Diagram) The DNA of E. coli appears to consist of a single, enormous double-stranded DNA molecule with a molecular weight of about 2.8 x 10 9, a thickness of about 2.0 nm and a contour length of about 1,360µm. E. coli DNA contains 4 million deoxyribonucleotide pairs.
the mechanism of dna replication mastering biology the mechanism of dna replication mastering biology June 14, 2017 Gaurab Karki Genetics, Microbiology, Molecular Biology 0. Structure and ion-release mechanism of PIB-4-type ATPases ...












0 Response to "37 The Diagram Below Shows A Double-stranded Dna Molecule (parental Dna)."
Post a Comment