41 convex lense ray diagram
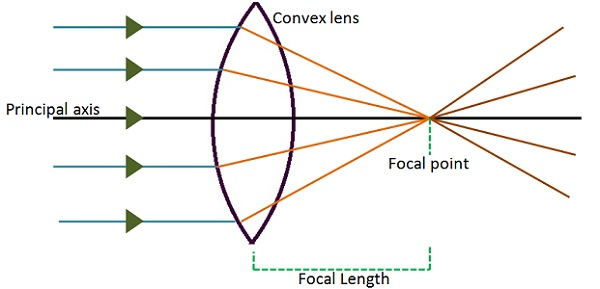
The convex lens is a lens that converges rays of light that convey parallel to its principal axis (i.e. converges the incident rays towards the principal axis) which is relatively thick across the middle and thin at the lower and upper edges. convex lens can converge a beam of parallel rays to a point on the other side of the lens. The ray nature of light is used to explain how light refracts at planar and curved surfaces; Snell's law and refraction principles are used to explain a variety of real-world phenomena; refraction principles are combined with ray diagrams to explain why lenses produce images of objects.
Find information about the College’s response to the evolving situation with COVID-19. Learn about the guidelines for coming to campus and more · Since 1821, Amherst has prepared critical and creative thinkers for lives of purpose and discovery. That tradition continues.

Convex lense ray diagram
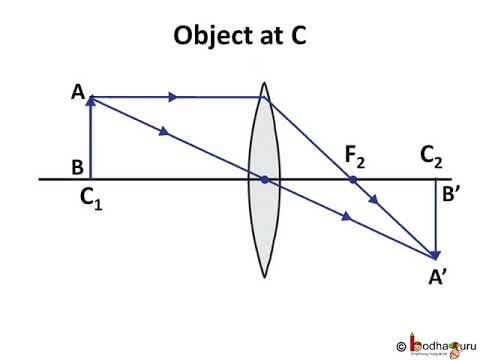
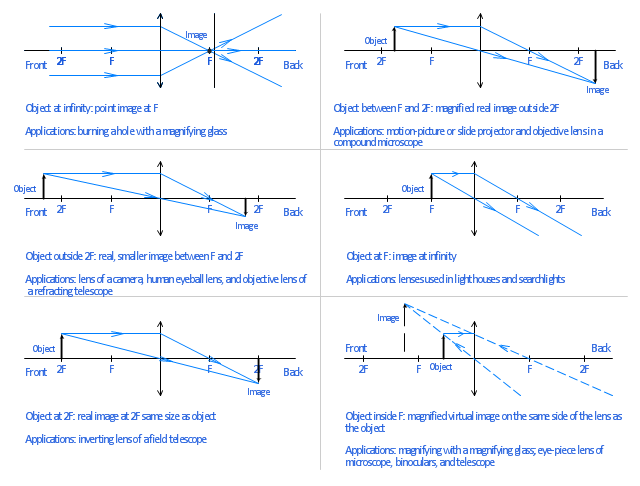
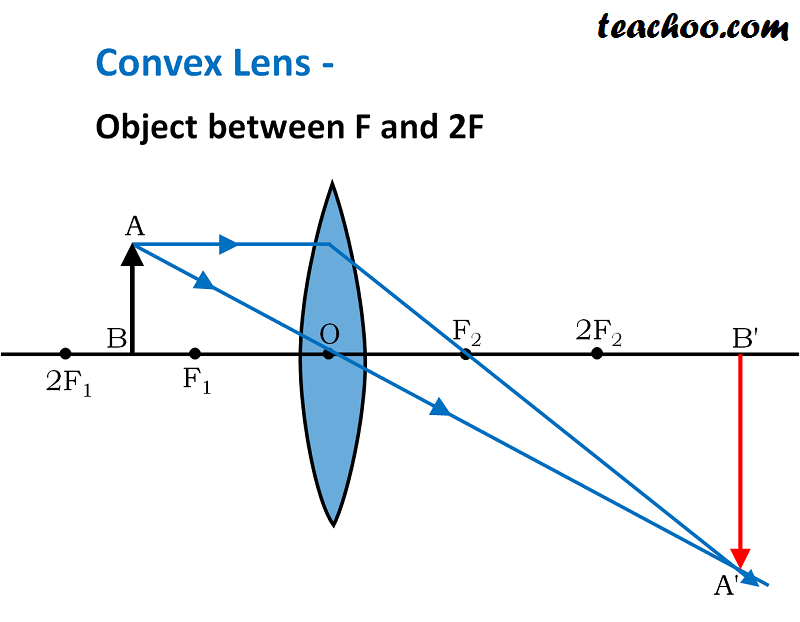
Convex lens - object between `2F` and `F`, What does the ray diagram and image on a screen for an object between one and two principal focal lengths look like? Ray Diagram. We can draw a ray diagram for a plano convex lens as follows. A ray from the top of the object passing through the optical center without a change in direction. A parallel ray from the top of the object till the optical axis. It then refracts to pass through the focal point on the other side of the lens. Tutorial: Ray Diagram for Convex Lenses Here we describe the method of drawing a ray diagram for a convex lens, for which the object is located beyond the 2F point of the lens. 1. Pick a point o the top of the object and draw three incident rays traveling towards the lens. a. Draw one ray so that it passes through the focal point on its way to ...
Convex lense ray diagram. So we're just gonna call it 2 focal lengths So with that said, let's actually try to figure out what the image of this thing would look like as the light from it gets refracted through this lens So like always, it's useful to draw one ray Every point of this object is emitting rays in every ... Physics is now simple when learning with BYJU'S - Get all important topics of physics with detailed explanation, Study newton's law, physics formulas and more here at BYJU'S. Here in this post, you will get Ray Diagrams for Images formed by convex & concave lenses as a Quick Reference. Image formation by lenses is an interesting topic of the Light chapter. Here along with the ray diagram, you will get the related details like Object position, image position, and nature of the image. http://www.physicshelp.caFree simple easy to follow videos all organized on our website
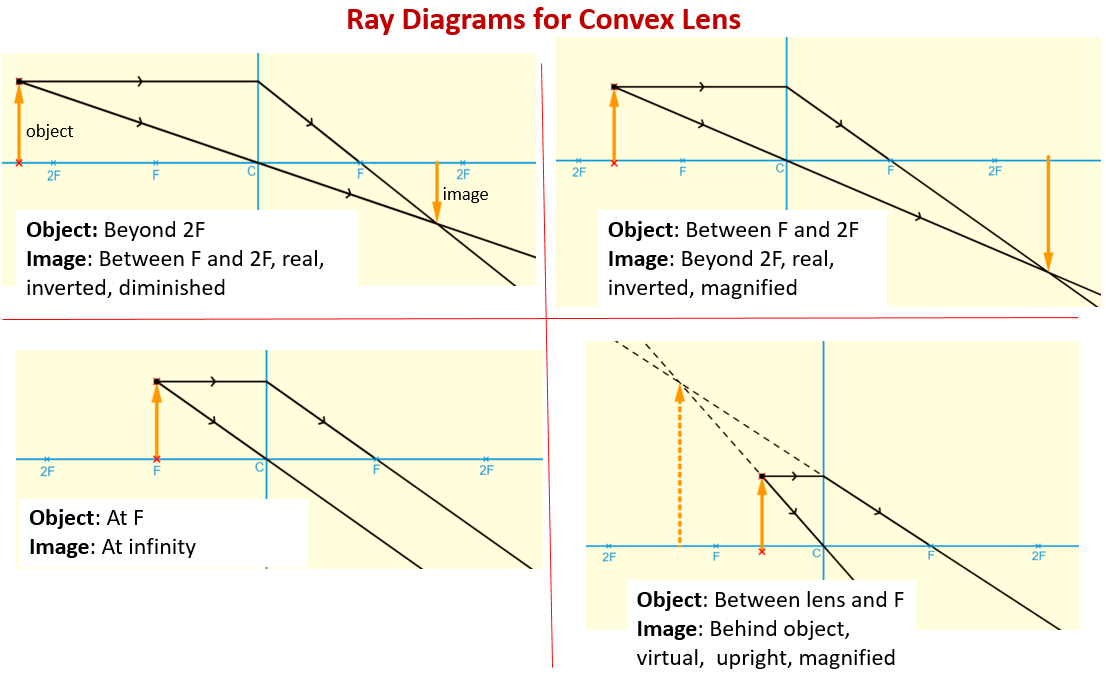
The following diagrams show the ray diagrams for convex lens. Then describe the location of the image orientation upright or inverted of the image the relative size of the image larger or smaller than object and the type of image real or virtual. The ray parallel to the principal axis passes through the focal point after refraction by the lens. Convex Lens - Ray diagram Concave Lens - Ray diagram Uses of Concave and Convex Lens Sign convention for Convex and Concave Lens Lens Formula Power of a lens NCERT Questions → Class 10. Chapter 10 Class 10 - Light - Reflection and Refraction (Term 1) Concepts ... The lens in which light rays that enter it parallel to its axis cross one another at a single point on the opposite side with a converging effect is called ... Optics The convex lens ray diagram shown in the image has been shaped so that all light rays that enter it parallel to its axis cross one another at a single point on the opposite side of the lens. Such a lens is called a converging lens for the converging effect it has on light rays.
A ray diagram is a tool used to determine the location size orientation and type of image formed by a lens. Convex lenses A convex lens is thicker in the middle than it is at the edges. Pass a parallel line through the principal focal point on the same side as the object. It is a lens that converges light rays passing parallel to its main axis. Ray tracing diagram for convex lens. "A lens is an optical device which transmits and refracts light, converging or diverging the beam. A simple lens consists of a single optical element. A compound lens is an array of simple lenses (elements) with a common axis; the use of multiple elements allows more optical aberrations to be corrected than ... Free Online CBSE Class Notes, NCERT Solutions, Self Study material for Class 6, Class 7, Class 8, Class 9, Class 10, Class 11 and Class 12 17.04.2016 · They are called convex and concave.[5] Aperture of Lense In optics, an aperture is a hole or an opening through which light is ... General layout of a TEM describing the path of electron beam in a TEM Fig 2 - A ray diagram for the diffraction mechanism in TEM 2.2.1Imaging The beam of electrons from the electron gun is focused ...
Uses of convex lens. These are used for a variety of purposes in our day-to-day lives. For example, The lens in the human eyes is the prime example. So the most common use of the lens is that it helps us to see. Another common example of the use of this type of lens is a magnifying glass. When an object is placed in front of it at a distance ...
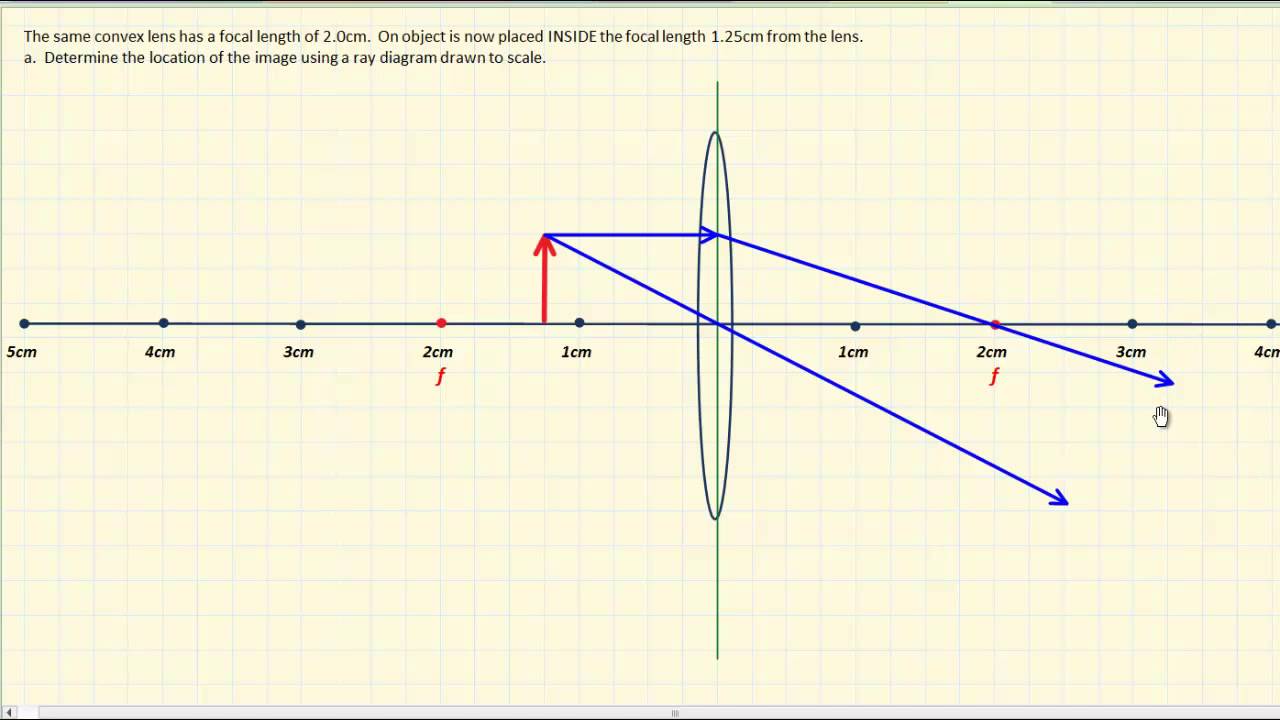
In a ray diagram, a convex lens is drawn as a vertical line with outward facing arrows to indicate the shape of the lens. The distance from the lens to the principal focus is called the focal...
Ray tracing diagram for convex lens. "A lens is an optical device which transmits and refracts light, converging or diverging the beam. A simple lens consists of a single optical element. A compound lens is an array of simple lenses (elements) with a common axis; the use of multiple elements allows more optical aberrations to be corrected than is possible with a single element.
Ray diagram | Image formation by Convex Lens when Object is beyond 2F,Ray diagram of convex lens, when object is beyond the centre of curvature,#RayDiagramOf...
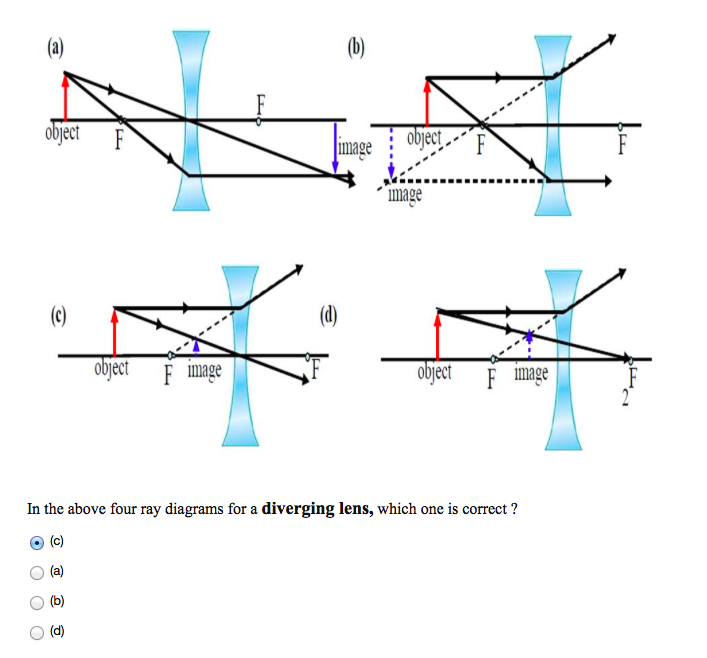
23.01.2020 · a. i. Convex lense ii. Concave lense b. Convex lense. Object will be at 2F. Question 3. a. MN represents a lens. What type of lens is this? b. What are the characteristics of the image? c. Copy the ray diagrams in the science diary and complete it Answer: a. Convex b. Magnified, real, inverted. Question 4. What do you mean by power of a lens?
The Convex Lens Ray Diagram Lens are made of glasses or plastic with the property to refract light. The lens is used in multiple devices, including cameras, telescopes, microscopes. Based on the refraction direction, lenses are of two types, concave and convex lens. Convex lenses have a thicker middle part when compared to their edges.
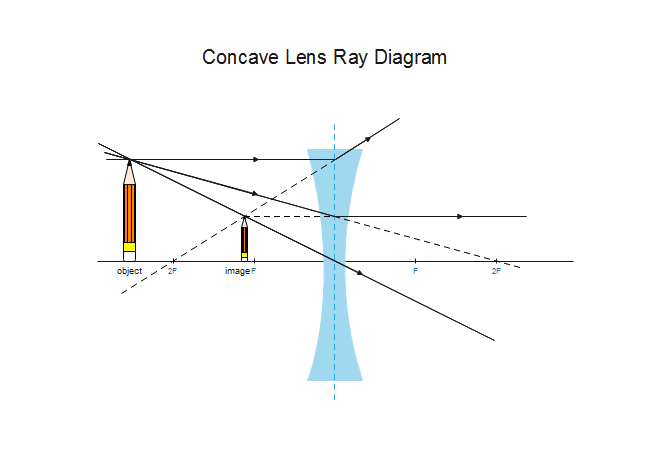
Rule 2 - Ray passing through focus will become parallel to principal axis. For a convex lens, we see that ray passing through focus on left becomes parallel to principal axis after refraction. For a concave lens , since focus is on the right side, it appears that ray passes through focus, and then it becomes parallel to principal axis.
July 27, 1999 - The table shows what happens to the image as an object is brought from infinity toward a convex lens. ... As long as the image as real the ray diagram is reversible. An object at point A creates an image at point B, while an object at point B creates an image at point A.
Shows how to draw ray diagrams to locate the image formed by a convex lens. You can see a listing of all my videos at my website, http://www.stepbystepscienc...
06.09.2021 · [234] The deviation of light ray when refracted by a parallel glass slab is – A: 90 o B: 0o C: 45o D: 180 235] An object is placed at a distance u from a convex lens, and its image is formed at a distance v.
The method of drawing ray diagrams for double convex lens is described below. The description is applied to the task of drawing a ray diagram for an object located beyond the 2F point of a double convex lens. 1. Pick a point on the top of the object and draw three incident rays traveling towards the lens.
An arrow is drawn on a piece of paper and is placed 20 cm away from a convex lens which has a focal length of 30 cm. Draw the ray diagram for the image of the arrow. Step 1: Identify the focal...
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators ...
In this explainer, we will learn how to draw diagrams of light rays interacting with convex lenses. A convex lens focuses parallel light rays at a focal ...
Refraction Questions and Answers. Get help with your Refraction homework. Access the answers to hundreds of Refraction questions that are …
Ray diagram for an object placed between 2F and F from a convex lens In a film or data projector, this image is formed on a screen. Film must be loaded into the projector upside down so the ...
convex lens concave lens how to determine focal length ray diagrams image properties real virtual inverted size correction of eye defects causes of long-sight short-sight igcse/gcse 9-1 Physics revision notes
Riemannian geometry is the branch of differential geometry that studies Riemannian manifolds, smooth manifolds with a Riemannian metric, i.e. with an inner product on the tangent space at each point that varies smoothly from point to point. This gives, in particular, local notions of angle, length of curves, surface area and volume.From those, some other global quantities can be …
Created with MicroStation http://www.Bentley.com This clip explains the rules to construct a ray diagram for a Convex Lens. A ray diagram is constructed ste...
oPhysics: Interactive Physics Simulations. Simulation of image formation in concave and convex lenses. Move the tip of the "Object" arrow to move the object. Move the point named " Focus' " to change the focal length. Move the point named " Focus' " to the right side of the lens to change to a concave lens.
BYJU’S makes an effort to bring in the important list of physics articles which when clicked upon direct to the detailed information on it.Physics articles for students are created keeping in mind to chart down important topics of physics in one sheet so that all information is available readily.Considering the syllabus, board examination and competitive examinations, the list of …
Concave Mirror Ray Diagram Concave Mirror Ray Diagram lets us understand that, when an object is placed at infinity, a real image is formed at the focus. The size of the image is much smaller compared to that of the object. When an object is placed behind the center of curvature, a real image is formed between the center of curvature and focus.
Ray diagram for an object placed between 2F and F from a convex lens In a film or data projector, this image is formed on a screen. Film must be loaded into the projector upside down so the...
November 9, 2009 - Welcome to the University of Plymouth, advancing knowledge, transforming lives.
Lens Optics Questions and Answers. Get help with your Lens (optics) homework. Access the answers to hundreds of Lens (optics) questions that are …
37965893 Bansal CLasses Physics Study Material for IIT JEE - Free ebook download as Text File (.txt), PDF File (.pdf) or read book online for free.
The example "Ray tracing diagram for convex lens" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Physics solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park. Ray tracing diagram. Used Solutions.
A convex lens is thicker in the middle than it is at the edges. Parallel light rays that enter the lens converge · . They come together at a point called the principal focus ... In a ray diagram, a convex lens is drawn as a vertical line with outward facing arrows to indicate the shape of the lens.
March 20, 2019 - Question 1 Where should an object be placed in front of a convex lens so as to obtain image on same side of lens? Question 2 The image formed by convex lens is seen to be real,inverted and diminished.What is the position of the object? Question 3 The image formed by convex lens is seen to be ...
A convex lens ray diagram is a simple way of visualising the path that light rays take when passing through a convex lens. To draw a ray diagram and find ...
November 18, 2021 - For a Convex Lens, object can be kept at different positionsHence, we take different casesCase 1 - Object is Placed at infinityIn this Case, Object is kept far away from lens (almost at infinite distance)So, we draw rays parallel to principal axisSince ray parallel to principal axis passes through t
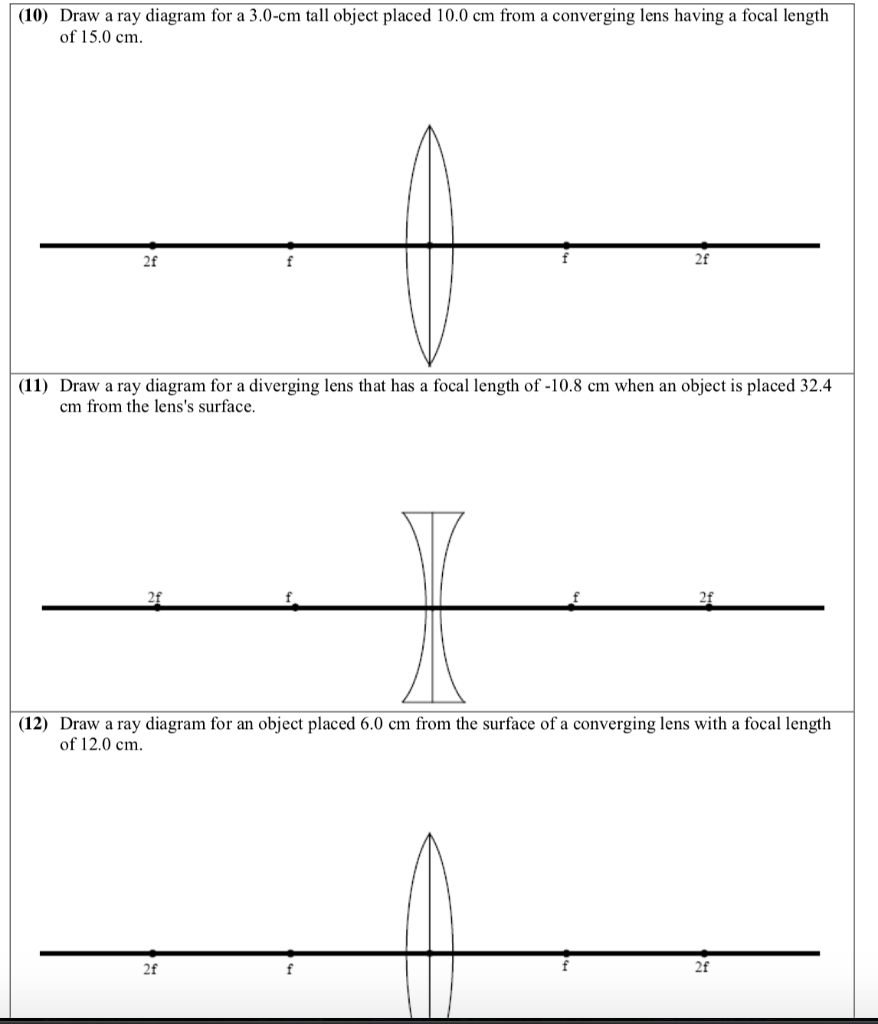
Here you have the ray diagrams used to find the image position for a converging lens. You can also illustrate the magnification of a lens and the difference between real and virtual images. Ray diagrams are constructed by taking the path of two distinct rays from a single point on the object. A light ray that enters the lens is an incident ray.
When a ray, passing through focus strikes concave or convex lenses, the reflected ray will pass parallel to the principal axis. Image Formation by Concave and Convex Lenses: Convex Lenses. When an object is placed at infinity, the real image is formed at the focus. The size of the image is much smaller than that of the object.
Now we consider a ray diagram for ... another diagram for a concave lens. ... Figure 16.29 Open the Geometric Optics simulation. This animation shows you how the image formed by a convex lens changes as you change object distance, curvature radius, refractive index, and diameter of the lens. To begin, choose Principal Rays in the upper ...
Ray tracing diagram for convex lens "A lens is an optical device which transmits and refracts light, converging or diverging the beam. A simple lens consists of a single optical element.
Ray Diagrams for Lenses. The image formed by a single lens can be located and sized with three principal rays. Examples are given for converging and diverging lenses and for the cases where the object is inside and outside the principal focal length. The "three principal rays" which are used for visualizing the image location and size are:
And the light ray would do something like that. Now there is a point out here someplace that whenever I take any ray that is parallel to the principal axis of the lens, it will be refracted through the lens to that same point. So here, we're going to be refracted a little bit like that.
Tutorial: Ray Diagram for Convex Lenses Here we describe the method of drawing a ray diagram for a convex lens, for which the object is located beyond the 2F point of the lens. 1. Pick a point o the top of the object and draw three incident rays traveling towards the lens. a. Draw one ray so that it passes through the focal point on its way to ...
Ray Diagram. We can draw a ray diagram for a plano convex lens as follows. A ray from the top of the object passing through the optical center without a change in direction. A parallel ray from the top of the object till the optical axis. It then refracts to pass through the focal point on the other side of the lens.
Convex lens - object between `2F` and `F`, What does the ray diagram and image on a screen for an object between one and two principal focal lengths look like?




















0 Response to "41 convex lense ray diagram"
Post a Comment