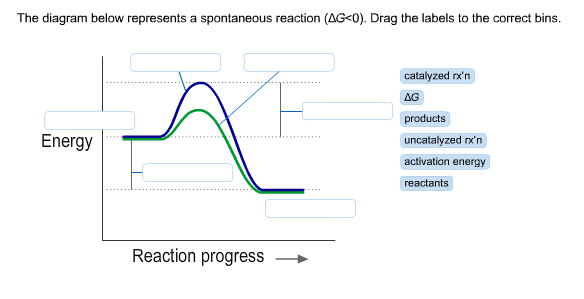
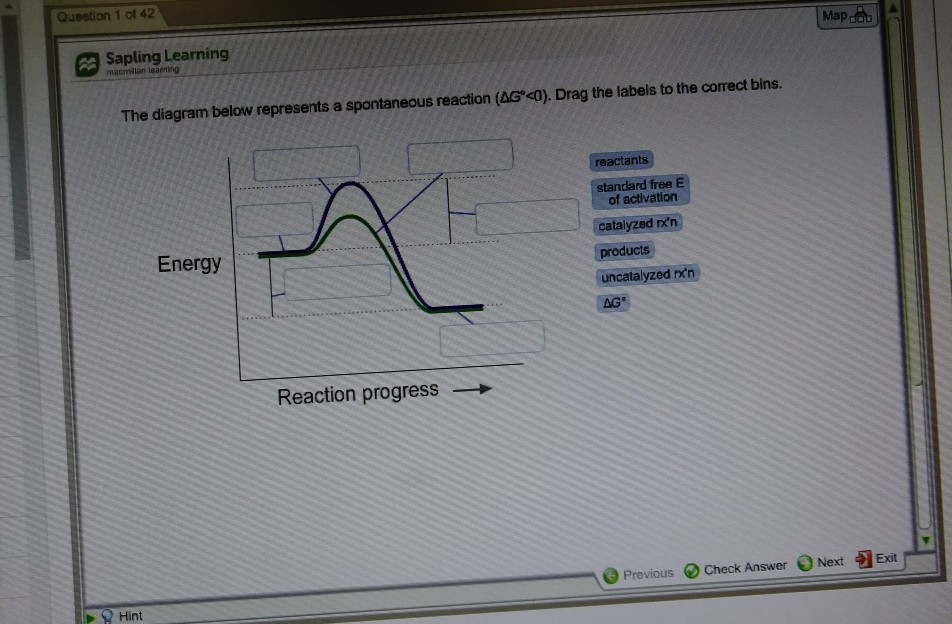
40 the diagram below represents a spontaneous reaction (δg°
G proteins: A) consist of three subunits, Gα, Gβ, and Gγ. B) hydrolyze GTP to GMP + Pi + Pi. C) completely span the cell membrane. D) A and B. E) A and C. A) consist of three subunits, Gα, Gβ, and Gγ. If an enzyme-catalyzed reaction has a low rate at low pH and high rate at higher pH, this implies that a. Which of the following is NOT true for ΔGrxn? A.) If ΔG°rxn > 0, the reaction is spontaneous in the forward direction. B.) If Q = 1, then ΔGrxn = ΔG°rxn.If ΔG°rxn = 0, the reaction is spontaneous in the reverse direction. chemistry. Answer the questions by looking at the following reaction between nitrogen oxides.
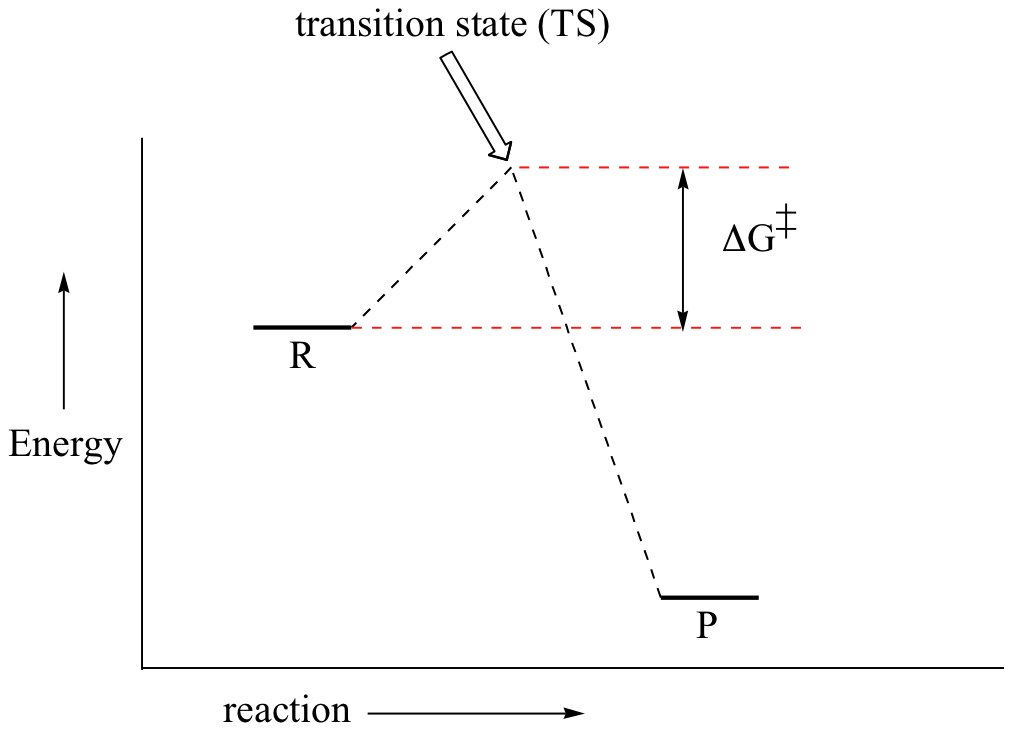
Base your answers on the information and diagram below, which represent the changes in potential energy that occur during the given reaction. Given the reaction: A + B --> C. a) Does the diagram illustrate an exothermic or an endothermic reaction? State one reason, in terms of energy, to support your answer.
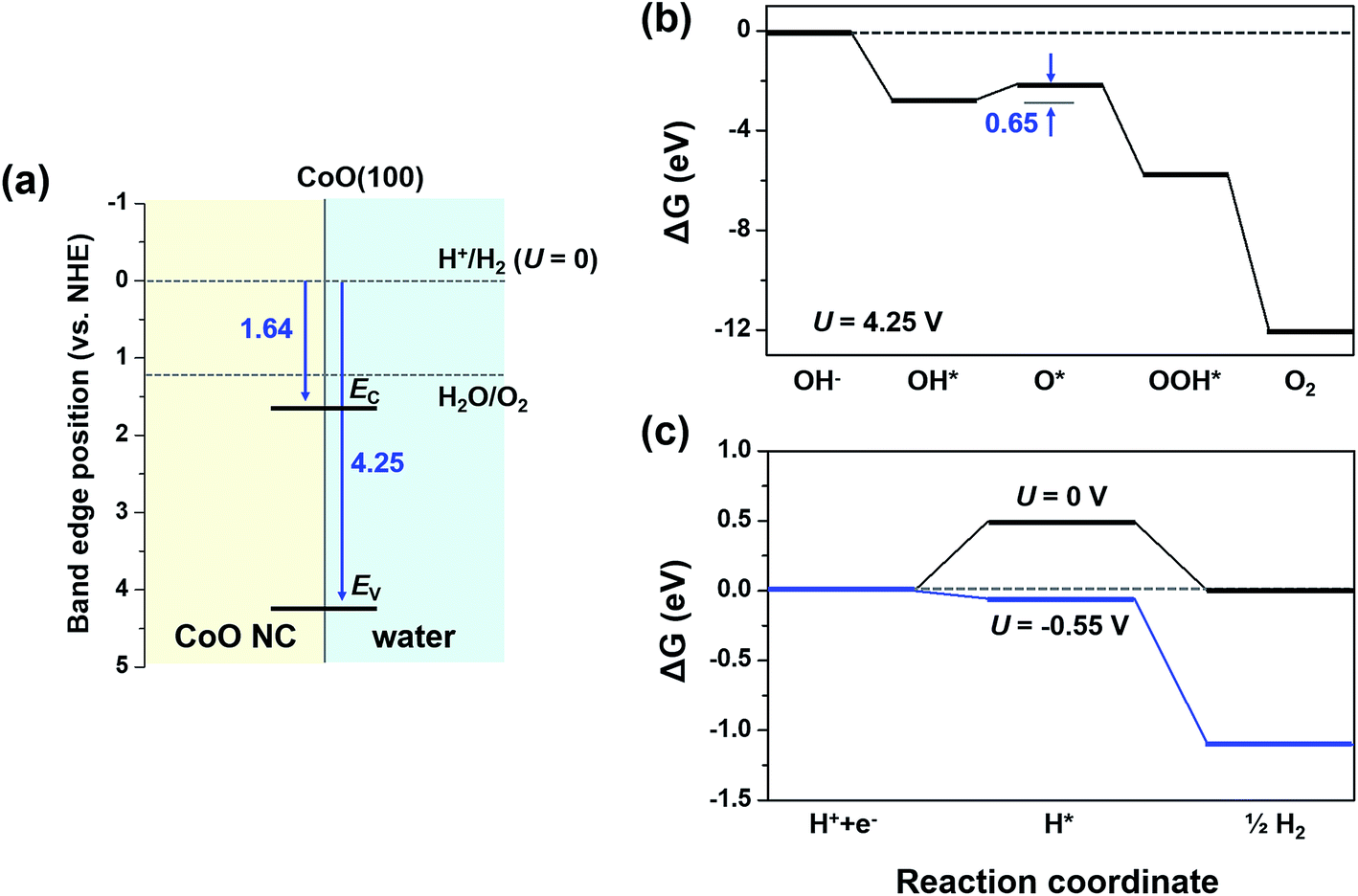
The diagram below represents a spontaneous reaction (δg°
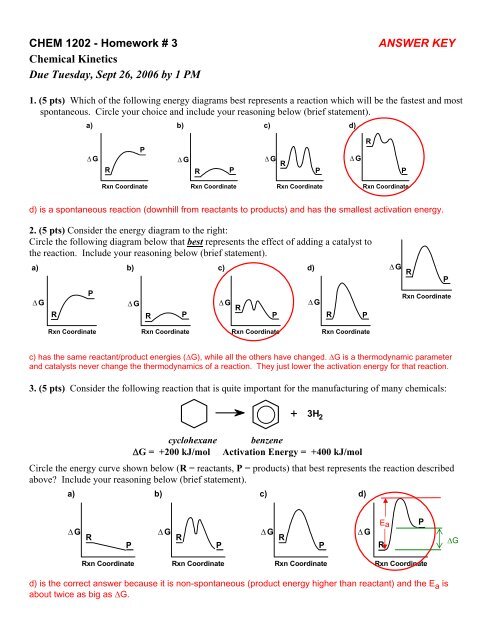
43) Consider the following reaction: CuS(s) + O 2 (g) Cu(s) + SO 2 (g) A reaction mixture initially contains 2.9 M O 2. Determine the equilibrium concentration of O 2 if Kc for the reaction at this temperature is 1.5. A) 1.9 M B) 1.7 M C) 2.2 M D) 1.2 M E) 0.59 M 44) Calculate the ΔG°rxn using the following information. l Diagram 2, because it represents a reaction with a high activation energy barrier for molecules to overcome and a very slow reaction rate, even if it is thermodynamically favorable with ΔG < 0 Diagram 2, because it represents a reaction that is thermodynamically favorable with ΔH < 0 the products formed are unstable and quickly revert to form ... The diagram below represents a spontaneous reaction (deltaG degree < 0). Drag the labels to the correct bins. uncatalyzed rx'n Delta G degree standard free E of activation products reactants catalyzed rx?n. Question: The diagram below represents a spontaneous reaction (deltaG degree < 0).
The diagram below represents a spontaneous reaction (δg°. e. Under the conditions specified in part (d), is the reaction in the cell spontaneous? Justify your answer. 2001 # 7. Answer the following questions that refer to the galvanic cell shown in the diagram below. (A table of standard reduction potentials is printed on the green insert and on page 4 of the booklet with the pink cover.) a. The diagram below represents a spontaneous reaction (ΔG°<0). Fill in tthe blanks below Learn this topic by watching Gibbs Free Energy Concept Videos The reaction is spontaneous at all temperatures The normal freezing point of ammonia is -78°C. Predict the signs of ΔH, ΔS, and ΔG for ammonia when it freezes at -80°C and 1 atm: NH3(l) → NH3(s). The K b for methylamine, CH 3 NH 2, at 25°C is 4.4 x 10 -4. a. Write the chemical equation for the equilibrium that corresponds to K b. b. By using the value of K b, calculate ΔG° for the equilibrium in part a. c.
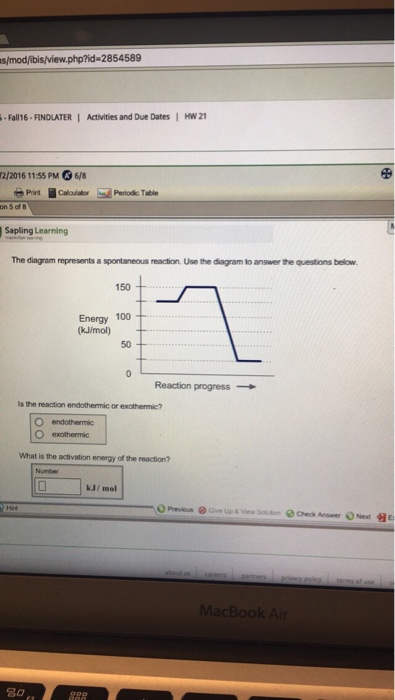
For the reaction below ΔG° = + 33.0 kJ, ΔH° = + 92.2 kJ, and ΔS° = + 198.7 J/K. Estimate ... The figure below represents the spontaneous reaction of H2 (shaded spheres) with O2 (unshaded spheres) to produce gaseous H2O. ... According to the diagram above, ΔG° is positive and the equilibrium composition is rich in reactants. Problem: The diagram represents a spontaneous reaction. Use the diagram to answer the questions below. Is the reaction endothermic or exothermic? What is the activation energy of the reaction? FREE Expert Solution. Recall that an energy diagram is usually read from left to right. A.The particle diagrams best represent that ΔH°<0 because the ions from both compounds are solvated by water molecules. B. The particle diagrams best represent that ΔH°<0 because both compounds produce about the same amount of CO 3 2− ions from the dissolution. C. The particle diagrams best represent that ΔS°>0 because both j. Based on your answers from c, g and h, determine if the following reaction is spontaneous. Explain. 2Ag(s) + Cu2+(aq) → Cu(s) + 2Ag+(aq) No, the reaction a written above is not spontaneous. Based on the spontaneous reaction written in part c, Cu(s) is more likely to give up electrons and Ag+(aq) is more likely to accept electrons.
18. Determine the minimum temperature for a reaction with ΔH = 271 kJ and ΔS = 195 J/K to be spontaneous. When ΔG = 0 the reaction is at equilibrium, so solve for T under these conditions. ΔG = ΔH - TΔS = 0 T = ΔH/ΔS = 271 kJ / (0.195 kJ/K) = 1389.74 K 19. Consider the reaction: CO(g) + Cl2(g) → COCl2(g) Calculate ΔGrxn at 25 °C c) When ΔG for a reaction is zero, the system is at equilibrium. d) When ΔH for a reaction is negative, the reaction is never spontaneous. e) When ΔH for a reaction is very positive, the reaction is not expected to be spontaneous. 22. For the reaction given below, ΔH° = -1516 kJ at 25°C and ΔS° = - 432.8 J/K at 25°C. The spontaneous redox reaction in a voltaic cell has _____ A) a negative value of Ecell and a negative value of ΔG. B) a positive value of Ecell and a positive value of ΔG. C) a negative value of Ecell and a positive value of ΔG. D) a positive value of Ecell and a negative value of ΔG. E) a positive value of Ecell and a value of zero for ΔG. ΔG = ΔH - TΔS. Remember that for a reaction to be feasible, ΔG has to be negative. ΔH could be negative (an exothermic reaction) or positive (an endothermic reaction). Similarly ΔS could be either positive or negative. There are four possible combinations of the signs of ΔH and ΔS. I want to look at those in turn.
The diagram represents a spontaneous reaction. Use the diagram to answer the questions below. a. Is the reaction endothermic or exothermic? b. What is the activation energy of the reaction?
Gibbs Free Energy, Spontaneity and Entropy. According to the 2 nd Law of Thermodynamics, the entropy of the universe always increases for a spontaneous process. This is illustrated by the equation: Second Law of Thermodynamics. Gibbs Free Energy is a thermodynamic property that can be used in determining the direction of a spontaneous process at either constant temperature (isothermal) or ...
The reaction SO2(g)+2H2S(g)⇌3S(s)+2H2O(g)SO2(g)+2H2S(g)⇌3S(s)+2H2O(g) is the basis of a suggested method for removal of SO2SO2 from power-plant stack gases. The values below may be helpful when answering questions about the process. Calculate the equilibrium constant KpKpK_p for the reaction at a temperature of 298 KK.
chem1101 2014 j 12 june 2014 the diagram below represents this reaction involves an increase in the number of moles of gas so Δs will be positive as Δh = Δg tΔs this means that Δh Δg for the other reactions there is a decrease in the number of moles of has so Δs is negative Δh = Δg tΔs this means that Δh Δg
The reaction is associated with a decrease in the number of particles in the same phase (3 mol→2 mol), so overall, a decrease in entropy: ΔS ⦵ for the reaction is negative. However, if T is sufficiently high, the negative product TΔS ⦵ may exceed Δ H ⦵ , resulting in ΔG ⦵ >0 and the reaction no longer begin spontaneous (not feasible).
Entropy is a mathematically defined property in thermodynamics. It can often help to understand it as a measure of the possible arrangements of the atoms, ions, or molecules in a substance. The symbol for entropy is S, and a change in entropy is shown as "delta" S or ΔS. If the entropy of a system increases, ΔS is positive.
5. Consider the reaction below and without reference to any data tables, draw the proper conclusion on which condition A-D best represents the reaction being spontaneous as written. CO 2 (g) + H 2O (g) --> HCOOH (l) ΔH = -150 kJ A. The reaction would be spontaneous at all temperatures. B.
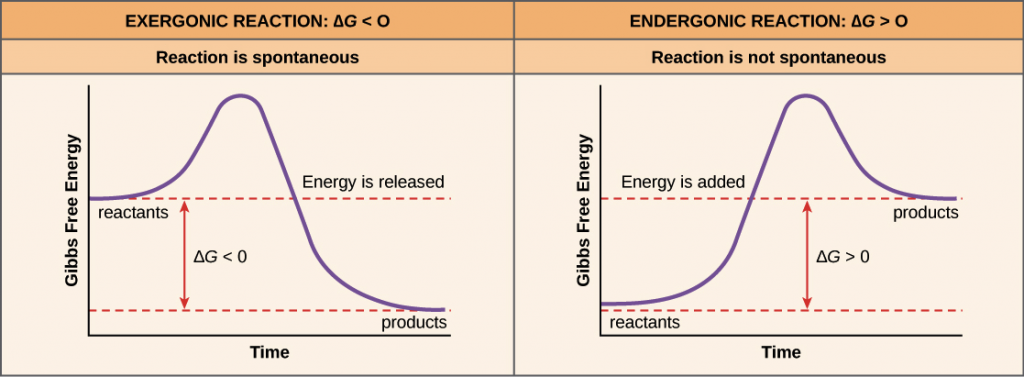
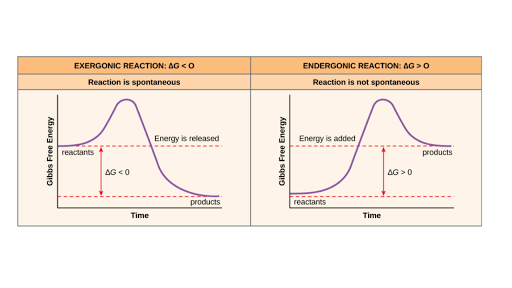
Exergonic reactions are also called spontaneous reactions, because they can occur without the addition of energy. Reactions with a positive ∆ G (∆ G > 0), on the other hand, require an input of energy and are called endergonic reactions. In this case, the products, or final state, have more free energy than the reactants, or initial state.
ΔG represents the change in Gibbs free energy for a chemical system at constant temperature and pressure ΔG = ΔH -TΔS ... We can write an equation to represent this entropy change in the surroundings at constant temperature as shown below: ... For a spontaneous reaction, ΔG for the reaction is negative (ΔG < 0).
ΔG > 0; the reaction is non-spontaneous and endergonic. ΔG < 0; the reaction is spontaneous and exergonic. ΔG = 0; reaction is at equilibrium. Note: According to the second law of thermodynamics entropy of the universe always increases for a spontaneous process. ΔG determines the direction and extent of chemical change.
When delta G is equal to zero, neither the forward nor the reverse reaction is spontaneous. The correct option is A. A system at equilibrium has its delta G equals to zero, at this point, the free energy change is neither positive nor negative; the reaction is at equilibrium and both the forward and the reverse reactions are not spontaneous.
The diagram below represents a spontaneous reaction (deltaG degree < 0). Drag the labels to the correct bins. uncatalyzed rx'n Delta G degree standard free E of activation products reactants catalyzed rx?n. Question: The diagram below represents a spontaneous reaction (deltaG degree < 0).
Diagram 2, because it represents a reaction with a high activation energy barrier for molecules to overcome and a very slow reaction rate, even if it is thermodynamically favorable with ΔG < 0 Diagram 2, because it represents a reaction that is thermodynamically favorable with ΔH < 0 the products formed are unstable and quickly revert to form ...
43) Consider the following reaction: CuS(s) + O 2 (g) Cu(s) + SO 2 (g) A reaction mixture initially contains 2.9 M O 2. Determine the equilibrium concentration of O 2 if Kc for the reaction at this temperature is 1.5. A) 1.9 M B) 1.7 M C) 2.2 M D) 1.2 M E) 0.59 M 44) Calculate the ΔG°rxn using the following information. l






















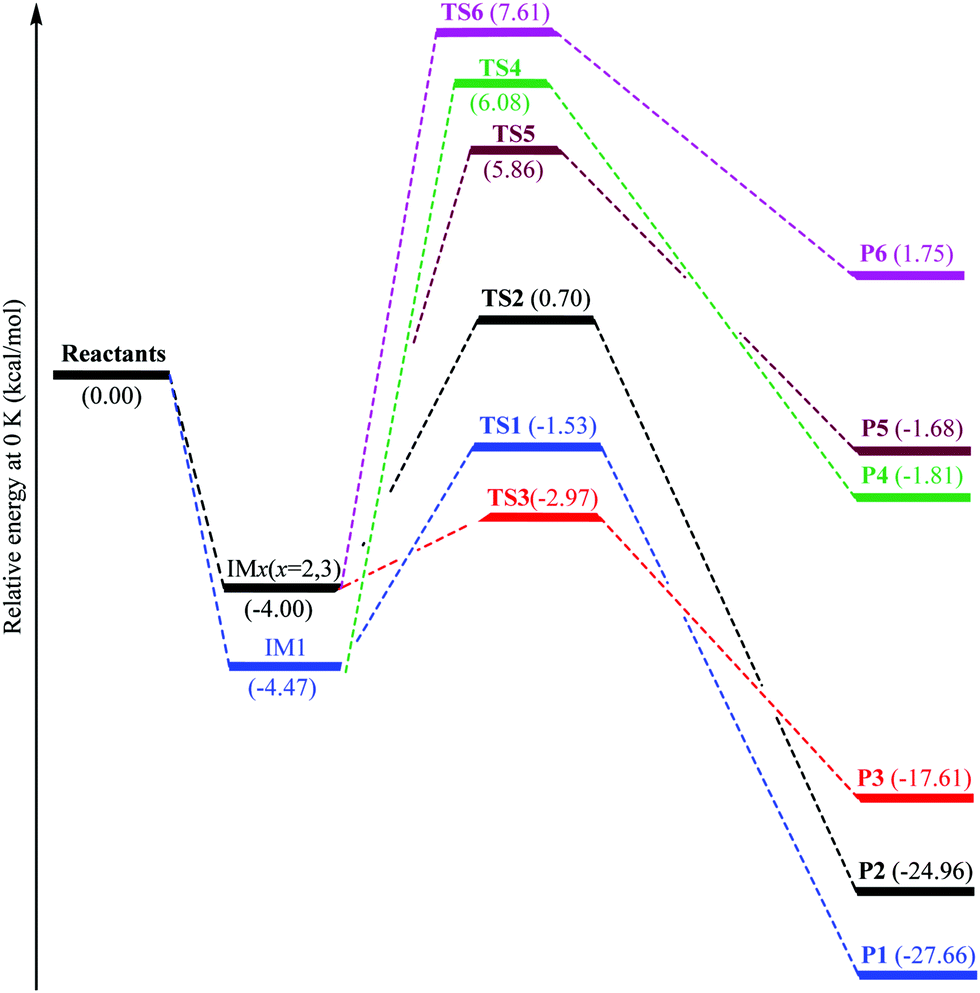
0 Response to "40 the diagram below represents a spontaneous reaction (δg°"
Post a Comment