40 the axes on a hertzsprung russell hr diagram represent
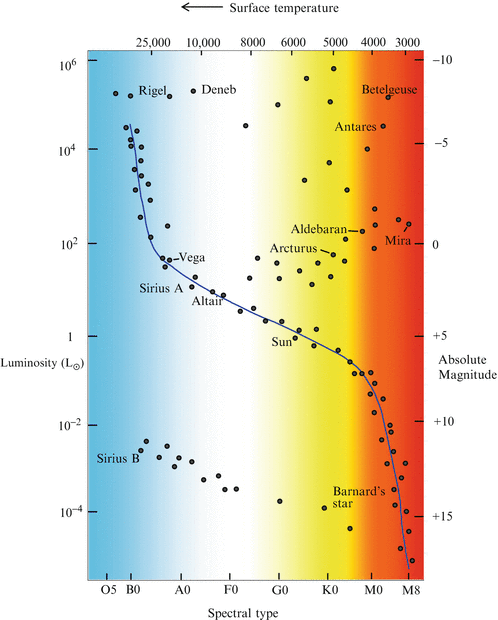
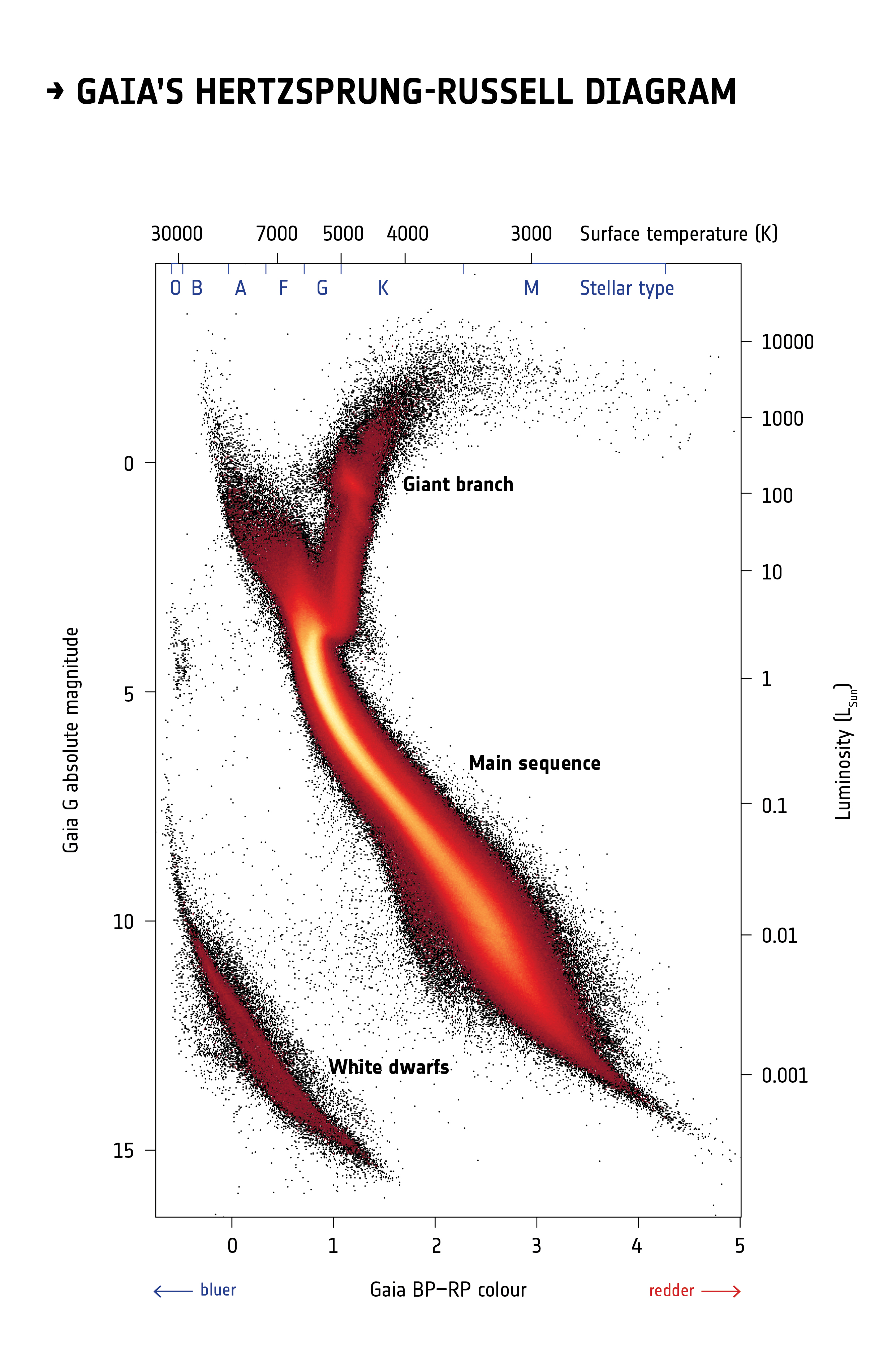
The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram. A view through a telescope will quickly convince you that there is a wide variety of stars in the sky. The most immediate impression is one of a range of colors, from blue-white through white, yellow, orange, and into deep reds. A comparison of stars at the same distance (as in double and multiple stars and star ... The axes on a Hertzsprung- Russell (H- R)diagram represent _ . A)mass and luminosity B)mass and radius C)luminosity and surface temperature D)luminosity and apparent brightness Correct Answer: Explore answers and other related questions
The key point to remember when considering the Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) diagram of a star cluster in determining the evolution of stars is that all of the stars in the star cluster have the same: asked Jun 6, 2017 in Physics & Space Science by Nathalia. introductory-astronomy.

The axes on a hertzsprung russell hr diagram represent
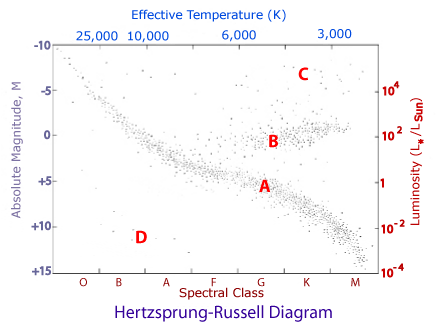
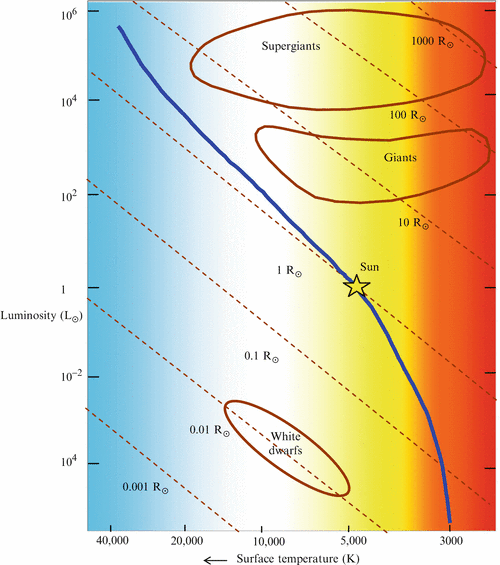
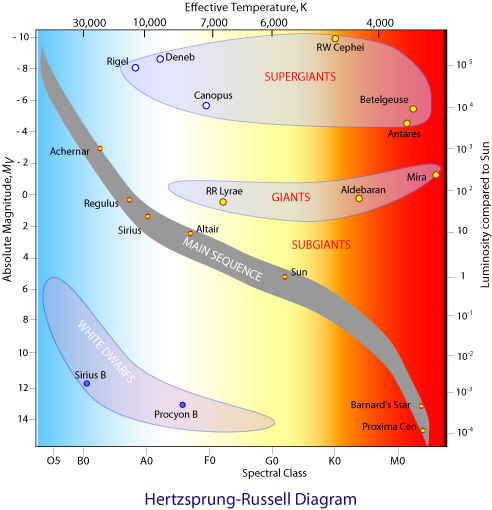
In an H-R diagram the luminosity or energy output of a star is plotted on the vertical axis. This can be expressed as a ratio of the star's luminosity to that of the Sun; L* / Lsun. Astronomers also use the historical concept of magnitude as a measure of a star's luminosity. The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram is a graph that plots the temperature of a star against its absolute magnitude or luminosity. It was created by astronomers Ejnar Hertzsprung and Henry Norris Russell about 1910, and can be used to chart the life cycle or evolution of a star. The axes on a Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) diagram represent _____. luminosity and surface temperature. On an H-R diagram, stellar radii _____. increase diagonally from the lower left to the upper right. On an H-R diagram, stellar masses _____.
The axes on a hertzsprung russell hr diagram represent. letters, that would best represent the evolution of the Sun starting from its present position. _____ (1) (Total 10 marks) Q7. (a) The graph shows the axes of a Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) diagram. (i) Label the spectral class axis with a suitable scale. (1) (ii) Complete the H-R diagram by marking the positions of the main sequence, The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram ( HR diagram) is one of the most important tools in the study of stellar evolution. Developed independently in the early 1900s by Ejnar Hertzsprung and Henry Norris Russell, it plots the temperature of stars against their luminosity (the theoretical HR diagram), or the colour of stars (or spectral type) against their absolute magnitude (the observational HR diagram, also known as a colour-magnitude diagram). Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram The importance of this diagram to astronomers cannot be overstated! In order that you understand it you will make one yourself. Follow the directions below and turn in the resulting graph and responses to questions 3, 6, and 8 - 12 for a 30 point grade. 1. Begin by labeling each axis. The x-axis is 49 Hertzsprung- Russell Diagram Hertzsprung- Russell Diagram. The Hertzsprung- Russell diagram , or the H-R diagram , is a graph which plots a star's brightness versus its color.This very-useful graphic was developed around 1910 by Danish astronomer Ejnar Hertzsprung and American astronomer Henry Norris Russell .The H-R diagram groups stars into four major classes, and shows stellar ...
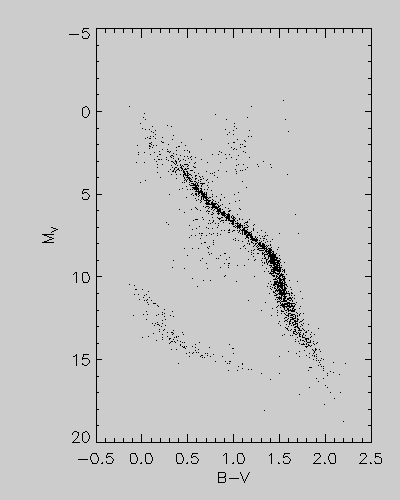
Apr 28, 2020 · In the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram, the y-axis represents the luminosity that increases with the increasing y. Luminosity is the total energy output of the star. We discussed this in the eighth article ( The Concept of Magnitude ). Alternatively, luminosity can also be defined roughly as the brightness of the object. In order to represent this wide range of values in one diagram, the Y-axis of a CMD or HR diagram is usually plotted on a logarithmic scale. What this means is that instead of each tick mark on the y-axis increasing by 1 unit (1,2,3,4,5…), the y-axis tick marks increase by a factor of 10 (0.001, 0.01, 0.1, 1, 10, 100, 1000…). The axes on a Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) diagram represent _____. luminosity and surface temperature. What can we infer, at least roughly, from a star's luminosity class? its size (radius) On an H-R diagram, stellar radii _____. increase diagonally from the lower left to the upper right. The HR Diagram for a Specific Case. figure 3 HR Diagram for Globular Cluster M5. In figure 3 above, we see an HR plot of the stars in globular cluster M5 (I shamelessly confess that I took this diagram from that page). The X-axis plots "B-V", which is the color index, and "B-V" means "B minus V", where B and V are the relative brightness of the B and V colors, in the system of magnitudes ...
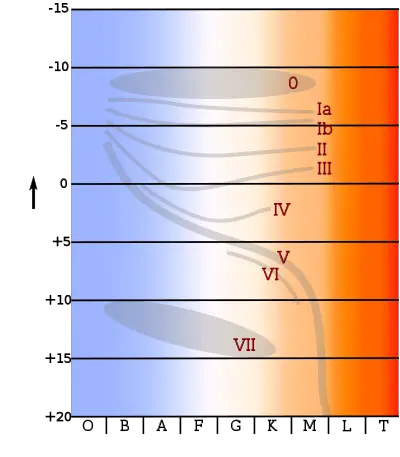
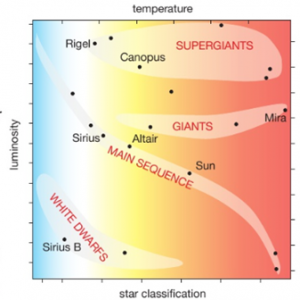
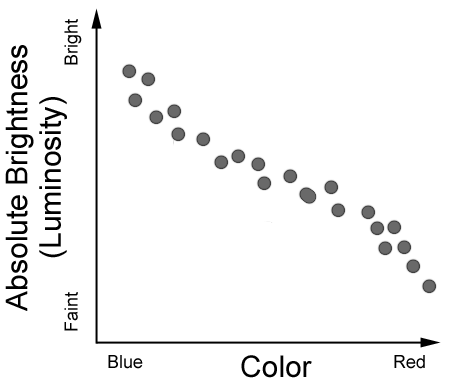
Henry Norris Russell. One of the most useful and powerful plots in astrophysics is the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram (hereafter called the H-R diagram). It originated in 1911 when the Danish astronomer, Ejnar Hertzsprung, plotted the absolute magnitude of stars against their colour (hence effective temperature). Independently in 1913 the American ... In the Hertzsprung-Russell (HR) Diagram, each star is represented by a dot. There are lots of stars out there, so there are lots of dots. The position of each dot on the diagram tells us two things about each star: its luminosity (or absolute magnitude) and its temperature. In a Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) diagram, points near the top of the diagram represent very low luminosity stars and points near the bottom represent very luminous stars The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram can be labeled many different ways. Which coordinates CANNOT be used on an H-R diagram? Example of a Hertzsprung-Russell diagram. The horizontal axis represents stellar surface temperature, which corresponds to the spectral type. The stellar spectral types are classified using letters...
What are the x and y axis on the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram? The x-axis (horizontal) is the surface temperature of the star, in degrees K, with the hottest ones at the left. The y-axis is the ...
Airey and Eriksson: Unpacking the Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram 101 1. The variables represented by the axes. 2. The major relationships that can be seen when the variables are plotted against one another. 3. The disciplinary meaning that has been assigned to these relationships. In the H-R diagram, the y-axis denotes the brightness of
May 02, 2019 · What are the on the axes of a Hertzsprung-Russell diagram? In an H-R diagram the luminosity or energy output of a star is plotted on the vertical axis. This can be expressed as a ratio of the star’s luminosity to that of the Sun; L*/Lsun. Astronomers also use the historical concept of magnitude as a measure of a star’s luminosity.
In order to represent this wide range of values in one diagram, the Y-axis of a CMD or HR diagram is usually plotted on a logarithmic scale. What this means is that instead of each tick mark on the y-axis increasing by 1 unit (1,2,3,4,5…), the y-axis tick marks increase by a factor of 10 (0.001, 0.01, 0.1, 1, 10, 100, 1000…).
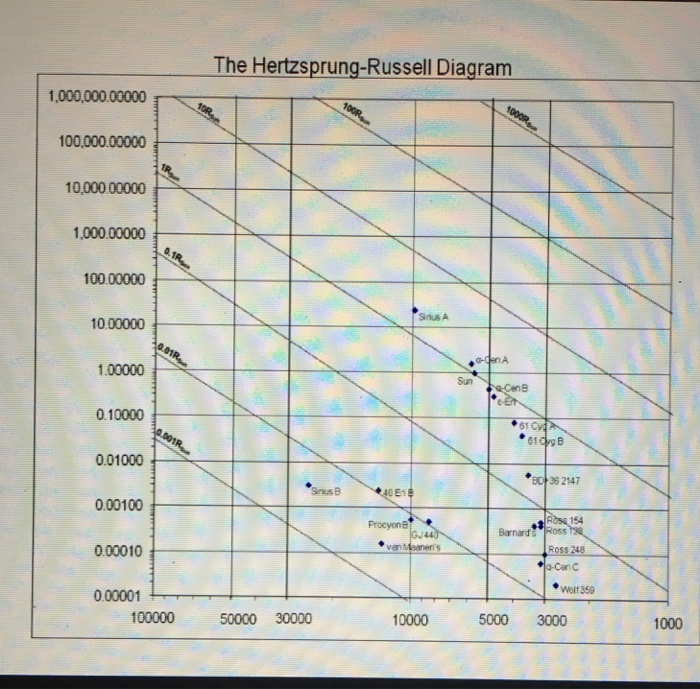
This figure appears in Russell, Nature, 93, 252 (1914) Long after Russell's graph first appeared, another astronomer pointed out that the same relationship had appeared previously in Hertzsprung's work. We now recognize the achievements of both astronomers by referring to it as the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram , or "HR diagram" for short.
Which postulate of the kinetic-molecular theory best describes the event in the diagram? Refer to the diagram to the right. the firm represented in the diagram makes; Another name for a workflow diagram is a(n) _____ diagram. Review the moth diagram. what can be correctly inferred from the information in the diagram?
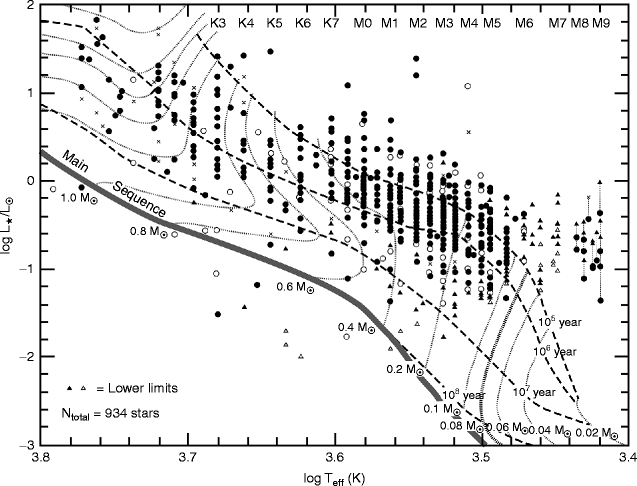
The original Hertzsprung-Russell diagrams constructed by Henry Russell and Eijnar Hertzsprung consisted of absolute magnitude on the y-axis and a spectral type or an indicator of spectral type on the x-axis. Below you can see an original HR diagram produced by Russell in 1913.
The axes on a Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) diagram represent Luminosity and surface temperature What can we infer, at least roughly, from a star's luminosity class?
This curious fact was first noticed back in the early 1900s by two astronomers, American Henry Norris Russell and Dane Ejnar Hertzsprung. As a result, this sort of graph is called a Hertzsprung-Russell diagram , or "HR diagram" for short. Norris and Russell called the diagonal strip along which most stars fall the main sequence .
The axes on a Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) diagram represent _____. luminosity and surface temperature. On an H-R diagram, stellar radii _____. increase diagonally from the lower left to the upper right. On an H-R diagram, stellar masses _____.
The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram is a graph that plots the temperature of a star against its absolute magnitude or luminosity. It was created by astronomers Ejnar Hertzsprung and Henry Norris Russell about 1910, and can be used to chart the life cycle or evolution of a star.
In an H-R diagram the luminosity or energy output of a star is plotted on the vertical axis. This can be expressed as a ratio of the star's luminosity to that of the Sun; L* / Lsun. Astronomers also use the historical concept of magnitude as a measure of a star's luminosity.









/GettyImages-112717446-1409d93b3ac7473d996de0ad3d3358ae.jpg)





0 Response to "40 the axes on a hertzsprung russell hr diagram represent"
Post a Comment