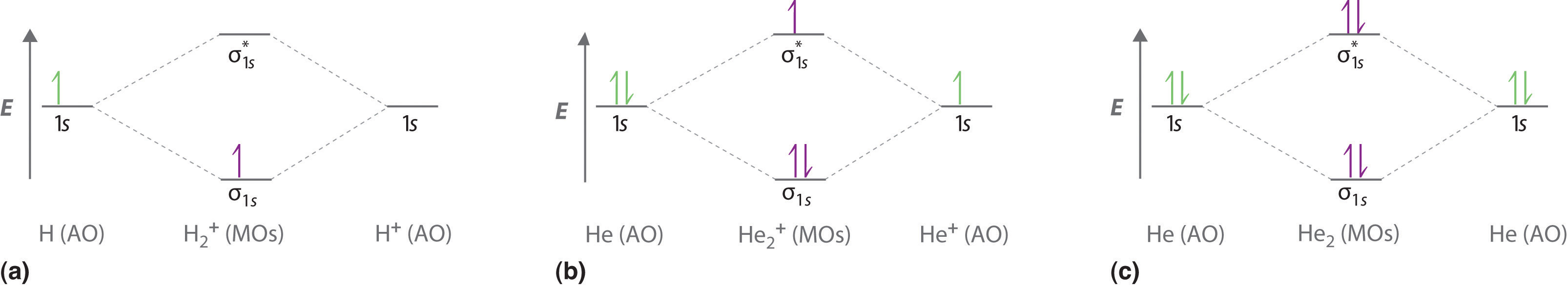
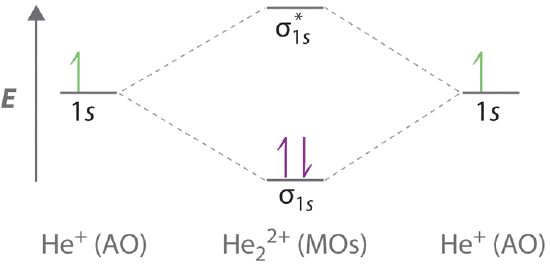
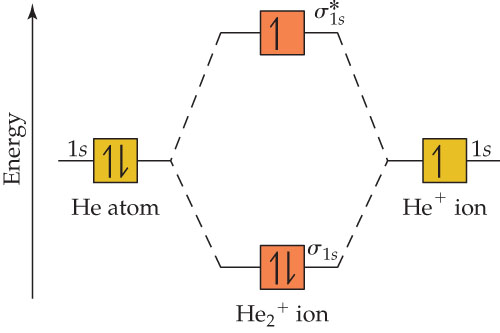
37 which electrons in this diagram contribute to the stability of the he2+ ion?
The next element has two electrons and the second electron fills the 1s orbital because there are only two possible values for the spin quantum number used to distinguish between the electrons in an orbital. The third electron goes into the next orbital in the energy diagram, the 2s orbital.
The atomic number is equal to the number of protons and electrons for an uncharged atom. Isotopes are forms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons. The number of protons cannot be changed since once that number (Z) changes, so does the element.
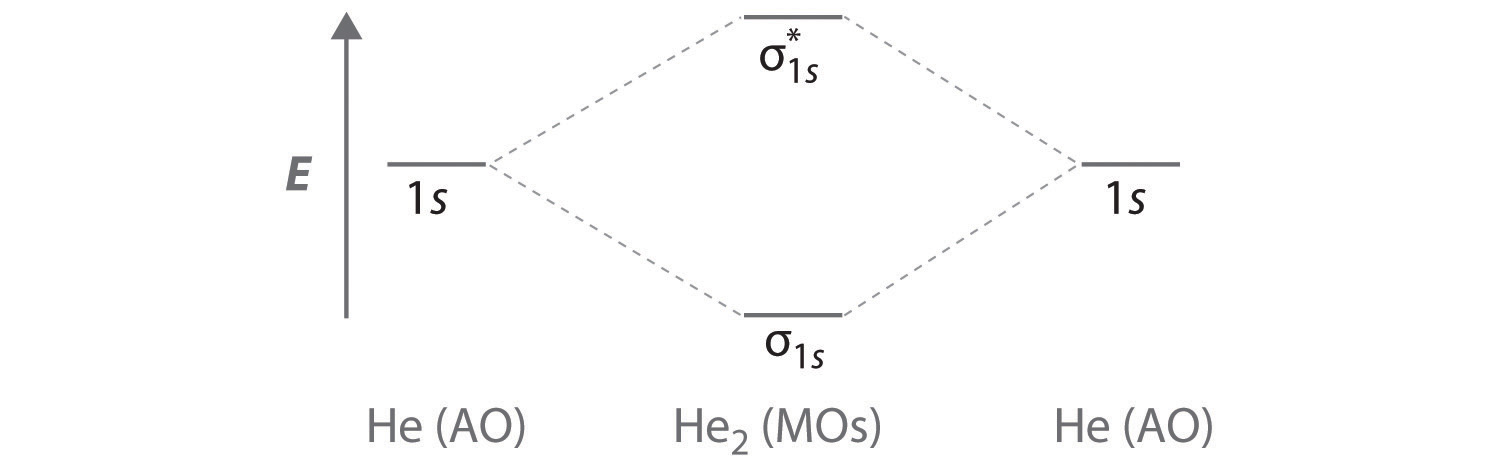
The valence electrons of he are in the 1s orbital and the 1s orbitals combine to give an mo diagram like that for h 2 or he 2 figure 933. If the bond order is greater than 0 we expect a bond to exist and the ion is stable. If there are the same amount of protons and electrons in an atom then it is neutral but...
Which electrons in this diagram contribute to the stability of the he2+ ion?
A complex ion has a metal ion at its centre with a number of other molecules or ions surrounding it. These can be considered to be attached to the As you know, a covalent bond is formed by two atoms sharing a pair of electrons. The atoms are held together because the electron pair is attracted...
Coordination compounds (or complexes) are molecules and extended solids that contain bonds between a transition metal ion and one or more ligands. In forming these coordinate covalent bonds, the metal ions act as Lewis acids and the ligands act as Lewis bases.
This ion has three electrons. The electrons occupying the s h h orbital represent the bonding pair of electrons from the lewis structure of h2 and is One electron in the sigma 1s mo and another one in the sigma 1s mo. Energy level diagram for the he2 ionwhich electrons in this diagram contribute...
Which electrons in this diagram contribute to the stability of the he2+ ion?.
First excitations of two-electron atoms and ions. Spin-triplet ground state. More delicate problems can be studied using the same strategy: the stability of hydrogen-like ions (M +, m The chapter on two-electron atoms or ions is of great importance when teaching quantum mechanics, and usually...
No two electrons have the same set of four quantum numbers. MODERN CHEMISTRY Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved. ARRANGEMENT OF ELECTRONS IN ATOMS 31 Name Date Class MIXED REVIEW continued 6. Elements of the fourth and higher...
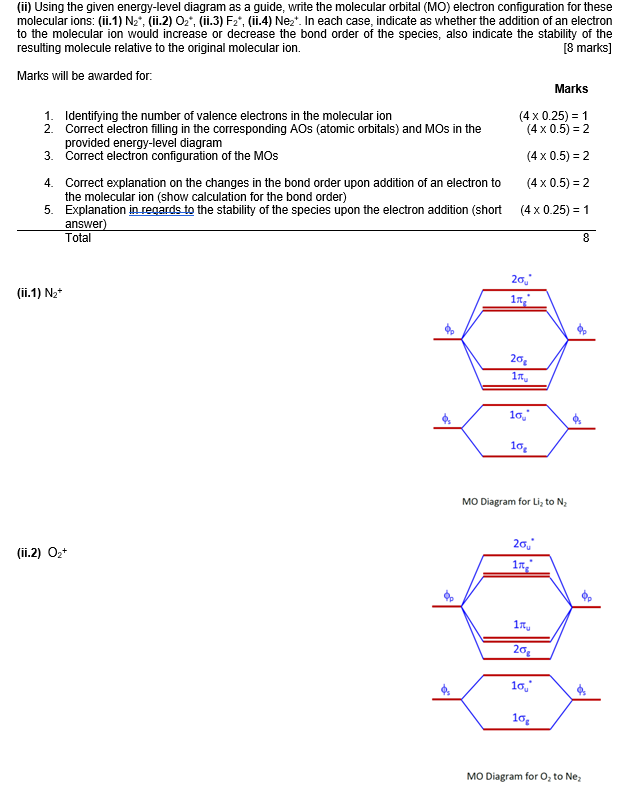
Energy-level diagram for theHe2+ ion For example, consider a carbon atom having an atomic number of 6. The total number of electrons in a neutral carbon atom is 6. The electron configuration of the carbon atom represented by the orbital diagram is.
Each electron in an atom is described by four different quantum numbers. The first three (n, l, ml) In a ground state configuration, all of the electrons are in as low an energy level as it is possible for Properties of Monatomic Ions. The electrons in the outermost shell (the ones with the highest value...
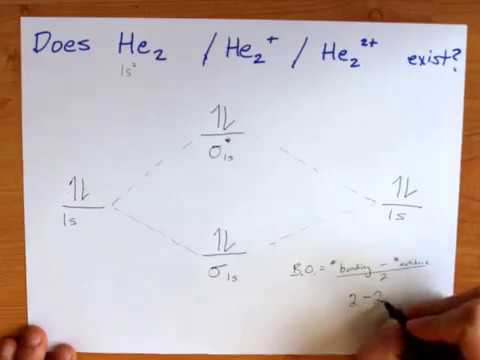
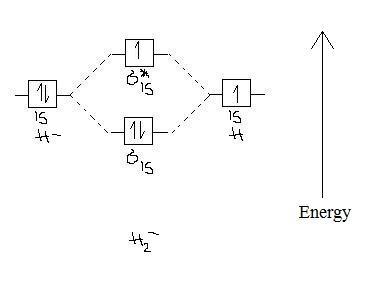
Four electrons, two in the sigma, two in the sigma*. Since there are as many bonding electrons as as antibonding, there is no net bond. He2 is not This is a property of quantum mechanical symmetry, and solving the problem only requires knowing a few diagram types and filling the electrons in.
The ions contribute to charge screening, interaction with the loops and the grooves, thus playing an important role in GQ structure formation and their stability. However, the metal ions in the central channel of the GQ structure play the key role that directly contributes to the stability of GQs.
I have understood that as electron density decrease, stability increase, But as I study aromatic substitution The carbocation intermediate in electrophilic aromatic substitution (the benzenonium ion) is If the atom bonded to the ring has one or more non-bonding valence shell electron pairs, as do The three examples on the left of the bottom row (in the same diagram) are examples of electron...
He represents these valence electrons as "dots" around the four sides of the elemental symbol. Depending on how your teacher was taught, this may be slightly different. The electrons in the outer most energy level of an atom or ion. Now take this number and place a dot for each valence electron.
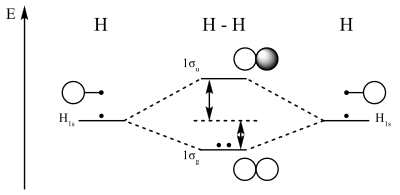
The two available electrons (one from each H atom) in this diagram fill the bonding σ1s molecular This ion has a total of three valence electrons. Because the first two electrons completely fill the Experiments show that the He2 molecule is actually less stable than two isolated He atoms due to...
...stability of the he2 ion entitled as structure of the calcium dependent type 2 secretion pseudopilus which electrons in this diagram contribute to stability of the ion a e electron in the sigma 1s mo and another o which of the following are predicted by the molecular o2 2 f2 2 h2 he2 home which of...
This ion has three electrons. Two are placed in the bonding orbital and the third in the antibonding orbital. Because the bond order is greater than 0, we predict the He2+ ion to be stable relative to the separated He and He+. Formation of He2+ in the gas phase has been demonstrated in laboratory...
An atom's electron configuration is a numeric representation of its electron orbitals. Electron orbitals are differently-shaped regions around an atom's nucleus where Remember the order of the letters with this mnemonic:[4] X Research source Sober Physicists Don't Find Giraffes Hiding In Kitchens.
...one in the sigma* 1s MO.b. The two electrons in the sigma 1s MO.c. All electrons.d. The electron in the sigma* 1s MO.Energy-level diagram for theHe2+ ion contribute to the stability of the ion? a. One electron in the sigma 1s MO and another one in the sigma* 1s MO. b. The two electrons in...
If your pi electron value matches any number in this series then you have the capacity for aromaticity." Therefore it can contribute to the pi system and this gives us a total of 6 pi electrons once we Although he never explicitly formulated a "4n + 2 rule", this was obvious from his work.
In atomic physics and quantum chemistry, the electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule (or other physical structure) in atomic or molecular orbitals. For example, the electron configuration of the neon atom is 1s2 2s2 2p6, meaning that the 1s...
Notice the two electrons occupying the antibonding orbital, which explains why the He2 molecule does not exist. This MO diagram depicts the molecule H2, with the contributing AOs on the outside sandwiching the MO. The bonding level (lower level) is completely occupied.
Figure 2. The diagram of an electron configuration specifies the subshell (n and l value, with letter symbol) and superscript number of electrons. An atom of the alkaline earth metal beryllium, with an atomic number of 4, contains four protons in the nucleus and four electrons surrounding the nucleus.
There are six stable isotopes of calcium which contribute to the average atomic weight of calcium, Ca-40 An ion with a 2+ charge will have two fewer electrons than protons (if the number of protons If it becomes ionic; two of the electrons disappear, but the amount of protons and neutrons are still...
...stability of the he 2 ion figure 9 34 energy level diagram for the he 2 Molecular Orbitals Involving ly ns Atomic Orbitals organic chemistry 1 flashcards start studying organic chemistry 1 learn differing electron arrangements of electrons that contribute to the "actual a halide ion 2 Structure of the...
Negative ions play an important role in chemistry as building blocks of salts and oxidizing agents. This is because the partially filled d-electrons can contribute to the valence of transition metals due to the small gap between d and s orbitals.
In the Lewis electron structures, the number of electron bag holding 2 atoms with each other was dubbed the bond order. We deserve to use energy-level diagrams to explain the bonding in various other pairs of atoms and also ions where n = 1, such as the H2+ ion, the He2+ ion, and the He2...
Two superpositions of these two orbitals can be formed, one by summing the orbitals and the other by taking their difference. In the former, the amplitudes of The central importance of the electron pair for bonding arises naturally in MO theory via the Pauli exclusion principle. A single electron pair is the...
Any ions which do break away are more likely to reclaim their electrons and stick back on to the metal again. You will still reach an equilibrium position, but By convention, the hydrogen electrode is always written as the left-hand electrode of the cell. That means that the sign of the voltage quoted always...
...in this diagram contribute to the stability of the ion? a. One electron in the sigma 1s MO and another one in the sigma* 1s MO. b. The two electrons in the Was the final answer of the question wrong? Were the solution steps not detailed enough? Was the language and grammar an issue?



















0 Response to "37 which electrons in this diagram contribute to the stability of the he2+ ion?"
Post a Comment