41 relationship between insulin and glucose diagram
Glucose Homeostasis and Starvation. Glucose Homeostasis: the balance of insulin and glucagon to maintain blood glucose.. Insulin: secreted by the pancreas in response to elevated blood glucose following a meal.. Insulin lowers blood glucose by increasing glucose uptake in muscle and adipose tissue and by promoting glycolysis and glycogenesis in liver and muscle. Dec 26, 2017 · The insulin works to shuttle glucose into the cells of the body; here, organelles called *mitochondria use the glucose to make energy (ATP). Excess glucose not used by cells is converted to glycogen, which is stored in the liver. Figure 1 demonstrates the interplay between glucose and insulin levels.
Insulin is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells within the pancreas. It is responsible for regulating movement of glucose from the blood into cells. This article will consider the structure of insulin, how it is synthesised and secreted, its actions on the body and clinical conditions that are associated with faults in its production.
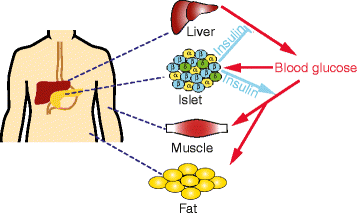
Relationship between insulin and glucose diagram
Insulin and glucagon work in what’s called a negative feedback loop. During this process, one event triggers another, which triggers another, and so on, to keep your blood sugar levels balanced. Diagram the feedback relationship of blood glucose and the hormones insulin and glucagon. INSULIN: - blood glucose levels rise - pancreas releases insulin ( beta cells) - in response to the insulin, target cells take up glucose and the liver converts glucose to glycogen GLUCAGON: Mar 30, 2021 · Insulin is a natural hormone produced by the beta cells in the pancreas that helps to regulate blood sugar levels. The insulin producing beta cells monitors the blood sugar to ensure it is constant. If your blood glucose increases after taking carbohydrate foods, your body will stimulate the beta cells to produce insulin.
Relationship between insulin and glucose diagram. The process of renal glucose reabsorption is mediated by active (sodium-coupled glucose cotransporters) and passive (glucose transporters) transporters. In hyperglycemia, the kidneys may play an exacerbating role by reabsorbing excess glucose, ultimately contributing to chronic hyperglycemia, which in turn contributes to chronic glycemic burden ... Carbohydrates and Blood Sugar. When people eat a food containing carbohydrates, the digestive system breaks down the digestible ones into sugar, which enters the blood. As blood sugar levels rise, the pancreas produces insulin, a hormone that prompts cells to absorb blood sugar for energy or storage. As cells absorb blood sugar, levels in the ... C. Insulin resistance and PCOS. The original description of enlarged, smooth polycystic ovaries (PCO) is credited to Chereau in 1844 ().In the 19th century, ovarian wedge resection became a recommended therapy (), although Stein and Leventhal first reported that the clinical features of menstrual regularity and infertility could be improved by removal of portions of both ovaries. Since insulin levels are always elevated, carbohydrates consumed are instantly taken up by cells. Elevated insulin levels also inhibit glucagon, therefore even though the body becomes hypoglycemic often, glucagon is never releases and glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis never happen. Upgrade to remove ads. Only $2.99/month.
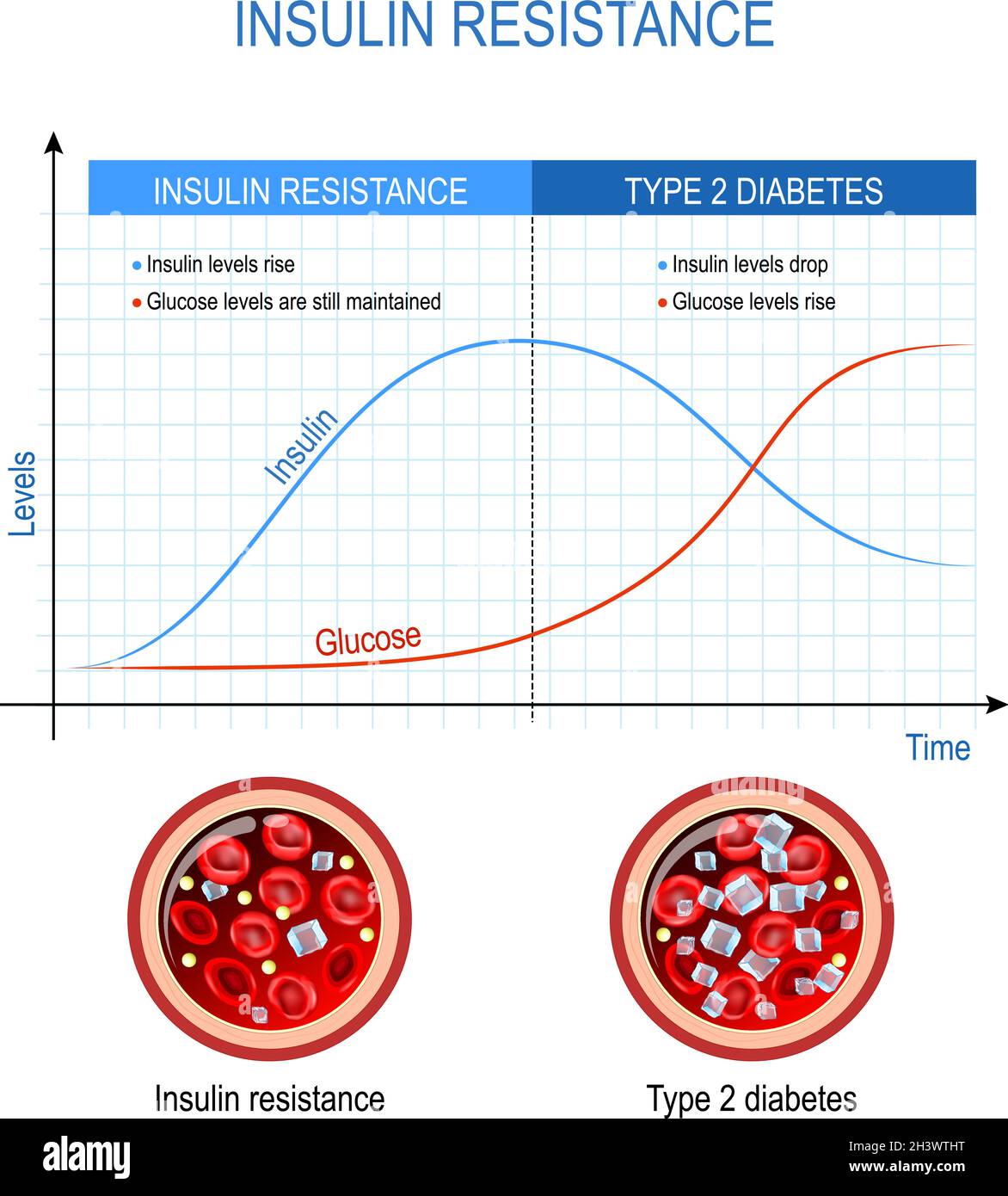
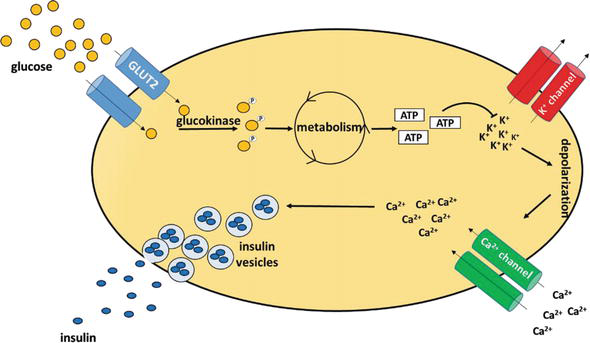
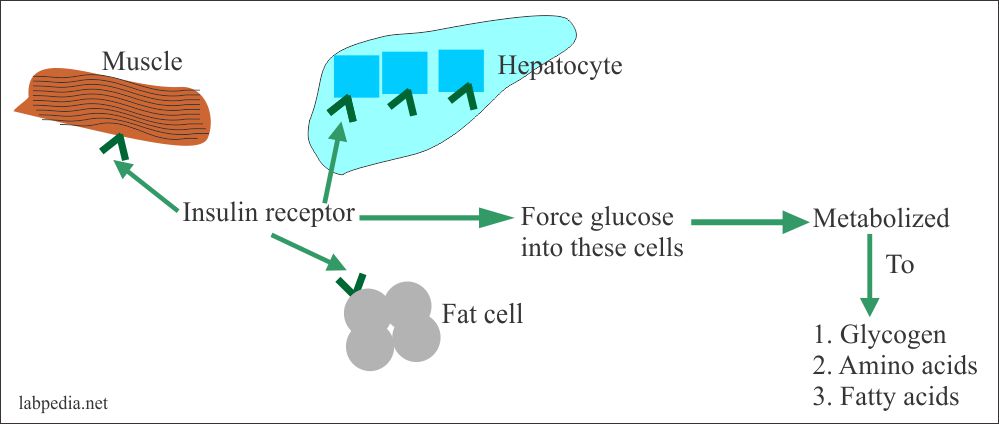
How Insulin Works. Insulin is the energy-storage hormone. After a meal, it helps the cells use carbs, fats, and protein as needed, and store what's left (mainly as fat) for the future. The body breaks these nutrients down into sugar molecules, amino acid molecules, and lipid molecules, respectively. insulin, hormone that regulates the level of sugar in the blood and that is produced by the beta cells of the islets of Langerhans in the pancreas.Insulin is secreted when the level of blood glucose rises—as after a meal. When the level of blood glucose falls, secretion of insulin stops, and the liver releases glucose into the blood. Insulin was first reported in pancreatic extracts in 1921 ... Understanding how sugar (glucose) and insulin work in your body is the foundation for knowing how diabetes works. By knowing what can affect your blood sugar levels, you can better manage it. The basics of high blood sugar. Diabetes is a problem with your body that causes blood sugar (also called blood glucose) levels to rise higher than normal. Download scientific diagram | Natural history of type 2 diabetes. The relationship between beta-cell function and increasing plasma glucose levels before and after diabetes diagnosis. Key points ...
The pancreas continually monitors the level of glucose in the blood. How insulin works. The following steps show the different changes in the body before, during and after a meal is eaten: Download scientific diagram | Relationship between WAT lipolysis and de novo lipogenesis. (A) Up-regulation of glucose transporter 4 and de novo lipogenesis-related pathways. Induction of gene ... Our results demonstrate a significant correlation between oxidative stress and insulin resistance at early stages of glucose intolerance. Both chronic hyperglycemia and GV seem to be related to insulin levels and insulin resistance, and just postload glycaemia to oxidative stress in prediabetes. 5.1.1 What is the glucose level at 3 hours after the start of the investigation? (2) 5.1.2 Explain the relationship between insulin and blood glucose by referring to the graphs. (3) 5.1.3 Name the organ in the body which produces insulin. 5.1.4. Explain the homeostatic mechanism that controls the glucose levels in the body.
Oct 18, 2012 · The Relationship Between Glucose and Insulin Glucose meet insulin, insulin meet glucose. Citations: Sources Jagoda, R. (March 7, 2011). How Does Insulin Signal a Cell to Take in Glucose from the Blood. In Livestrong. Retrieved October 15, 2012, from
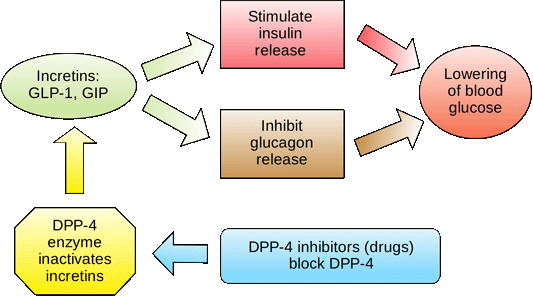
Postprandial glucose flux is a balance between glucose appearance in the circulation and glucose disappearance or uptake. Glucose appearance is a function of hepatic (endogenous) glucose production and meal-derived sources and is regulated by pancreatic and gut hormones. Glucose disappearance is insulin mediated.
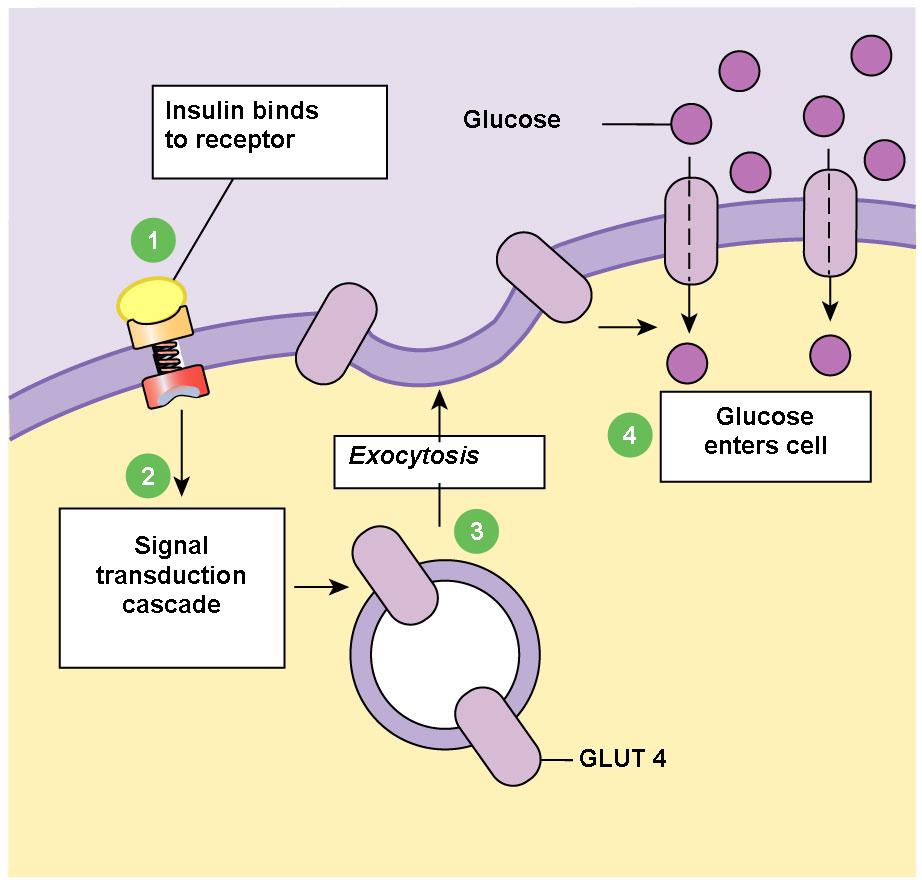
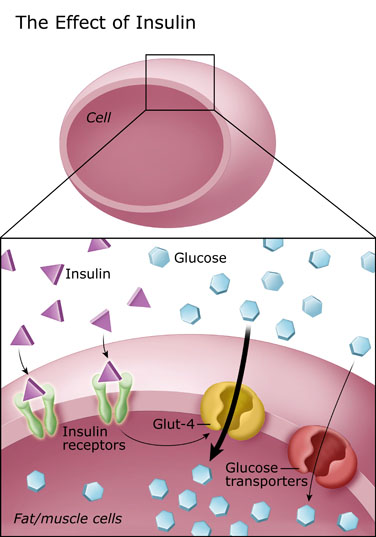
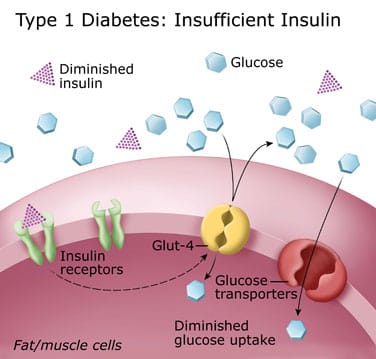
translocation of the insulin-sensitive glucose trans- porter (GLUT-4) from intracellular storage vesicles to the cell surface (71, 214). This complex process is also under intense experimental scrutiny, but the biochemi- cal connection between receptor and glucose transporter remains undescribed.
Concept Integration Q. What is the relationship between diabetes, glucose in food, saliva, microvilli, blood transport of glucose, beta cells of pancreas, diabetes- elevated blood glucose, glomerulus, glucose in urine? Amylase enzymes found in the saliva are secreted when food, specifically carbohydrates, enters the mouth.
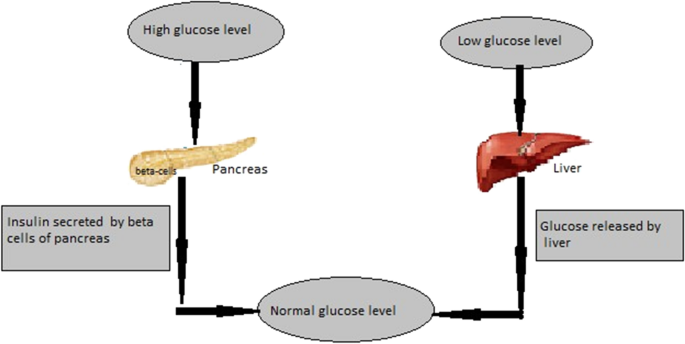
Bifurcation And Stability Analysis Of Glucose Insulin Regulatory System In The Presence Of B Cells Springerlink
Definitions and Concepts. Insulin is a peptide hormone secreted by the β cells of the pancreatic islets of Langerhans and maintains normal blood glucose levels by facilitating cellular glucose uptake, regulating carbohydrate, lipid and protein metabolism and promoting cell division and growth through its mitogenic effects.. Insulin resistance is defined where a normal or elevated insulin ...
Patients with hypertension have been shown to be resistant to insulin-stimulated glucose uptake and to be both hyperinsulinemic and hypertriglyceridemic compared with matched normotensive control groups. These abnormalities are present before the institution of antihypertensive therapy and do not necessarily improve when blood pressure is effectively lowered.
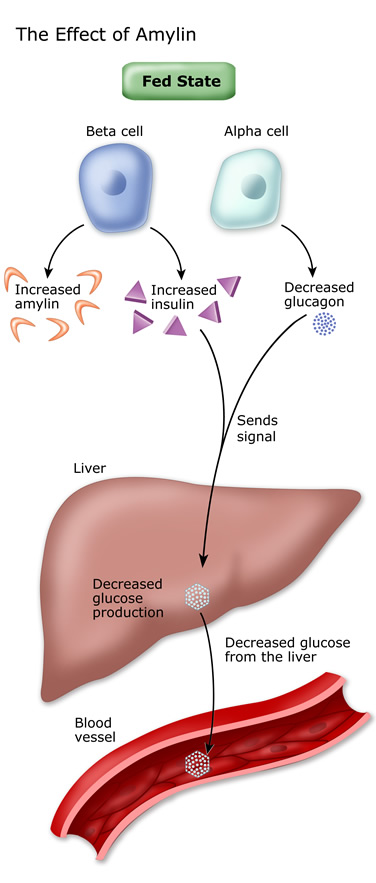
The human body wants blood glucose (blood sugar) maintained in a very narrow range. Insulin and glucagon are the hormones which make this happen. Both insulin and glucagon are secreted from the pancreas, and thus are referred to as pancreatic endocrine hormones. The picture on the left shows the intimate relationship both insulin and glucagon have to each other. Note that the pancreas serves as the central player in this scheme. It is the production of insulin and glucagon by the pancreas which ultimately determines if a patient has diabetes, hypoglycemia, or some other sugar problem. Insulin and glucagon are hormones secreted by islet cells within the pancreas. They are both secreted in response to blood sugar levels, but in opposite fashion! Glucagon is secreted by the alpha cells of the pancreatic islets in much the same manner as insulin...except in the opposite direction. If blood glucose is high, then no glucagon is secreted.
Insulin works on multiple processes, essentially providing an integrated set of signals that allows the correct balance between nutrient supply and demand [].In insulin resistance, the target cells fail to respond to ordinary levels of circulating insulin thus higher concentrations of insulin are required for a normal response [].In this vein, an insulin resistant state is defined as the ...
Background. Diabetes mellitus is a group of metabolic diseases with increased blood glucose concentration as the main symptom. This can be caused by a relative or a total lack of insulin which is produced by the β‐cells in the pancreatic islets of Langerhans.Recent experimental results indicate the relevance of the β‐cell cycle for the development of diabetes mellitus.
So insulin comes and moves glucose into the cells where it belongs. And potassium, like we said before, potassium is a really big homebody, it doesn’t like to shake things up too much or cause a ruckus, it just came out of it’s cell to see what was going on when glucose was having that big party.
Following baseline assessments of co-primary outcome measures: insulin sensitivity (by insulin suppression test, IST) and insulin secretion (by graded glucose infusion test, GGIT), participants will be placed on a weight maintenance diet and treated with 40 mg/day of atorvastatin.
2e.State the correlation between lack of FoxO1 and pancreatic hormones in mice. [1 mark] Markscheme lack of FoxO1 (correlates) with low/decreased insulin and high/increased glucagon levels. 2f. Referring to the functions of insulin and glucagon, suggest how the differences in hormone levels help to explain the blood glucose[3 marks] levels.
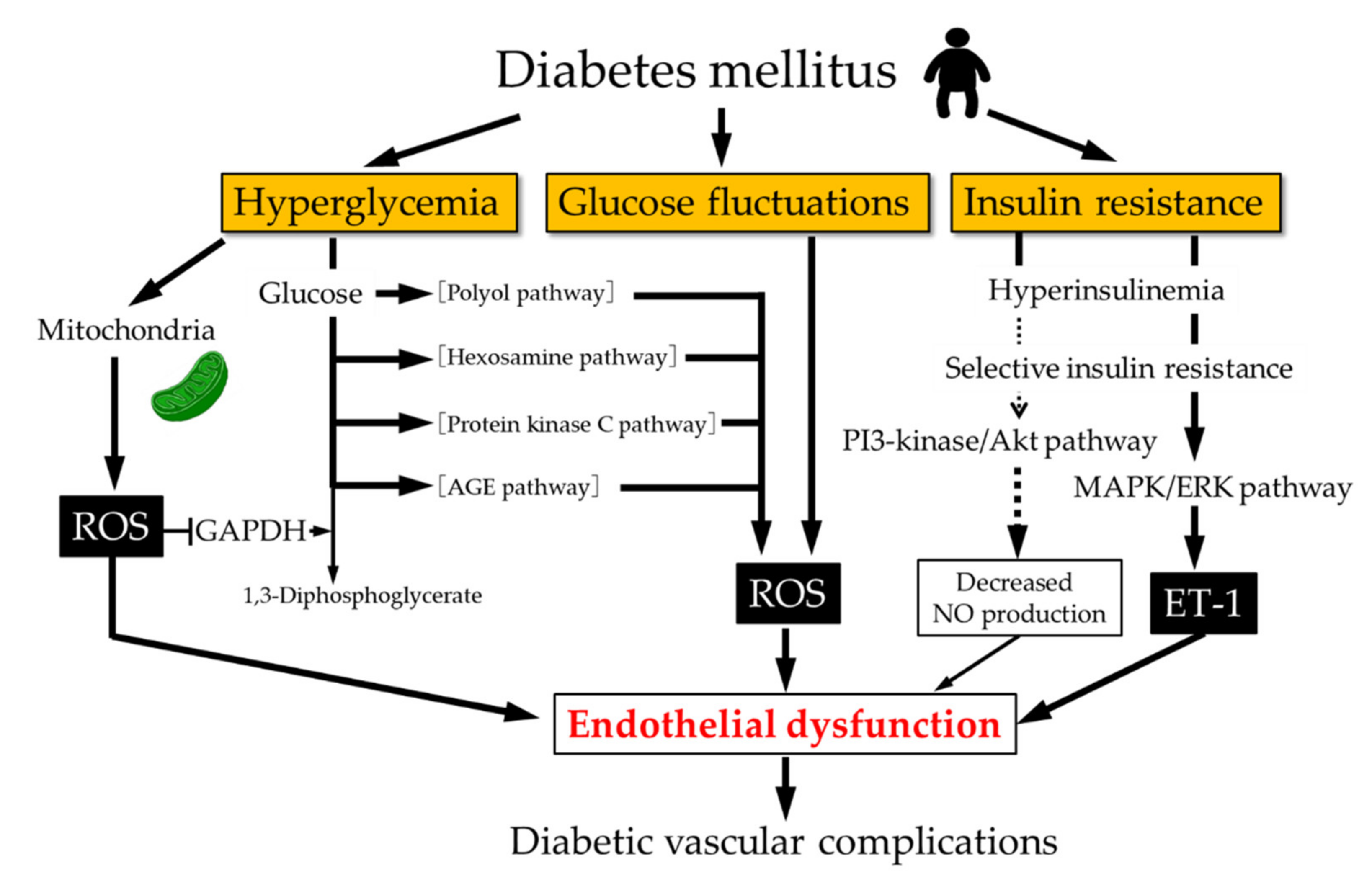
Antioxidants Free Full Text Pathophysiological Association Between Diabetes Mellitus And Endothelial Dysfunction Html
Dec 27, 2017 · The insulin producing beta cells monitors the blood sugar to ensure it is constant. If your blood glucose increases after taking carbohydrate foods, your body will stimulate the beta cells to produce insulin. Insulin controls blood glucose by signaling the fat and muscle cells to absorb glucose from the bloodstream.
Insulin and glucagon are hormones that help to regulate blood sugar levels. In imbalance of either of these important chemical messengers can play a huge role in diabetes. What is the link between ...
Our findings raised the question of whether there was ethnic variation in the relationship between insulin sensitivity and insulin response across three glucose tolerance subgroups. To address this question, we plotted the mean and 95% CI values of S I against AIR g in subjects with NGT, IGR, and T2D from each ethnic group.
Now that you know how your body handles glucose with insulin and glucagon, you are ready to understand diabetes. Diabetes is classified into three types: Type 1, Type 2 and gestational diabetes. Type 1 (also called juvenile diabetes or insulin-dependent diabetes) is caused by a lack of insulin. This type is found in five percent to 10 percent ...
The relationship between lipid levels and diabetes is further complicated by the apparently causal link between statin therapy and increased risk of type 2 diabetes. ... (DIAGRAM) consortium, including 34,840 case and 114,981 control ... in up to 42,854 participants from the Meta-Analyses of Glucose and Insulin-related traits Consortium (MAGIC) ...
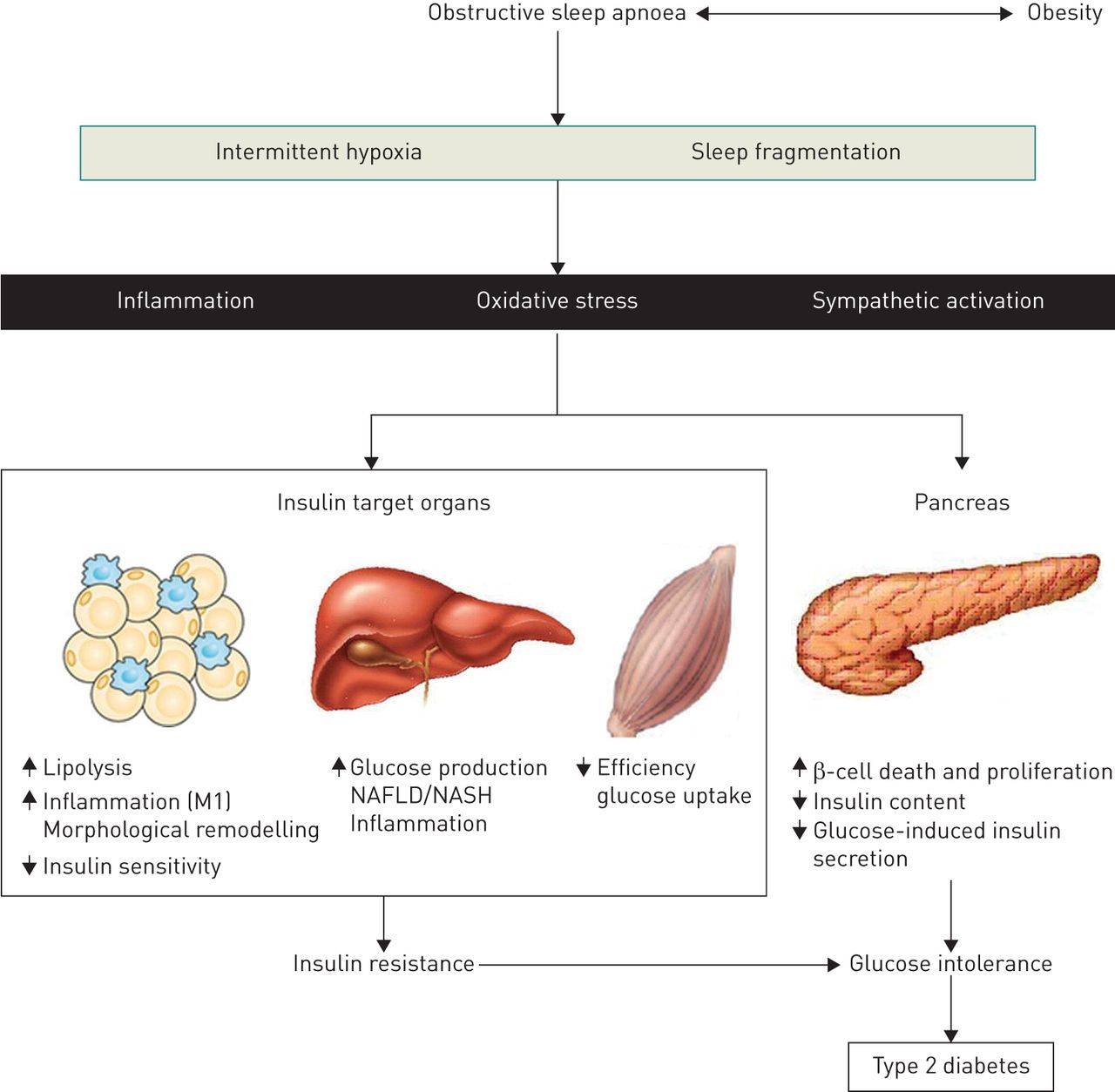
Sleep Apnoea Insulin Resistance And Diabetes The First Step Is In The Fat European Respiratory Society
from the DIAGRAM (DIAbetes Genetics Replication And Meta-analysis) consortium andupto133,010individuals without diabetes for insulin s ecretion and sensitivity from the MAGIC (Meta-Analyses of Glucose and Insulin-related traits Consortium) and GENESIS (GENEticS of Insulin Sensitivity) studies. Eight of 21 associations between
To investigate the relationship between BMI and GA/A1c ratio stratified by degree of insulin secretory function and insulin resistance, patients were classified into 3 groups based on the American Diabetes Association 2011 guidelines: T2D (A1c≥6.5%), increased risk for diabetes (A1c = 5.7-6.4%, described as prediabetes hereon), and normal ...
Diabetes is a disease caused by a breakdown in the glucose metabolic process resulting in abnormal blood glucose fluctuations. Traditionally, control has involved external insulin injection in response to elevated blood glucose to substitute the role of the beta cells in the pancreas which would otherwise perform this function in a healthy individual.
The relationship between glucose and insulin levels was examined in a prospective study of 153 pregnant patients without diabetes who underwent a standard 50 gm glucose challenge test. One hundred eighteen women had normal screening results (glucose level <140 mg/dl) and 35 had abnormal screening values but a normal oral glucose tolerance test.
relationship between insulin and glucose diagram 🙆remission. Because diabetics have a suppressed immune system, simple infections can sometimes be the first sign of the disease
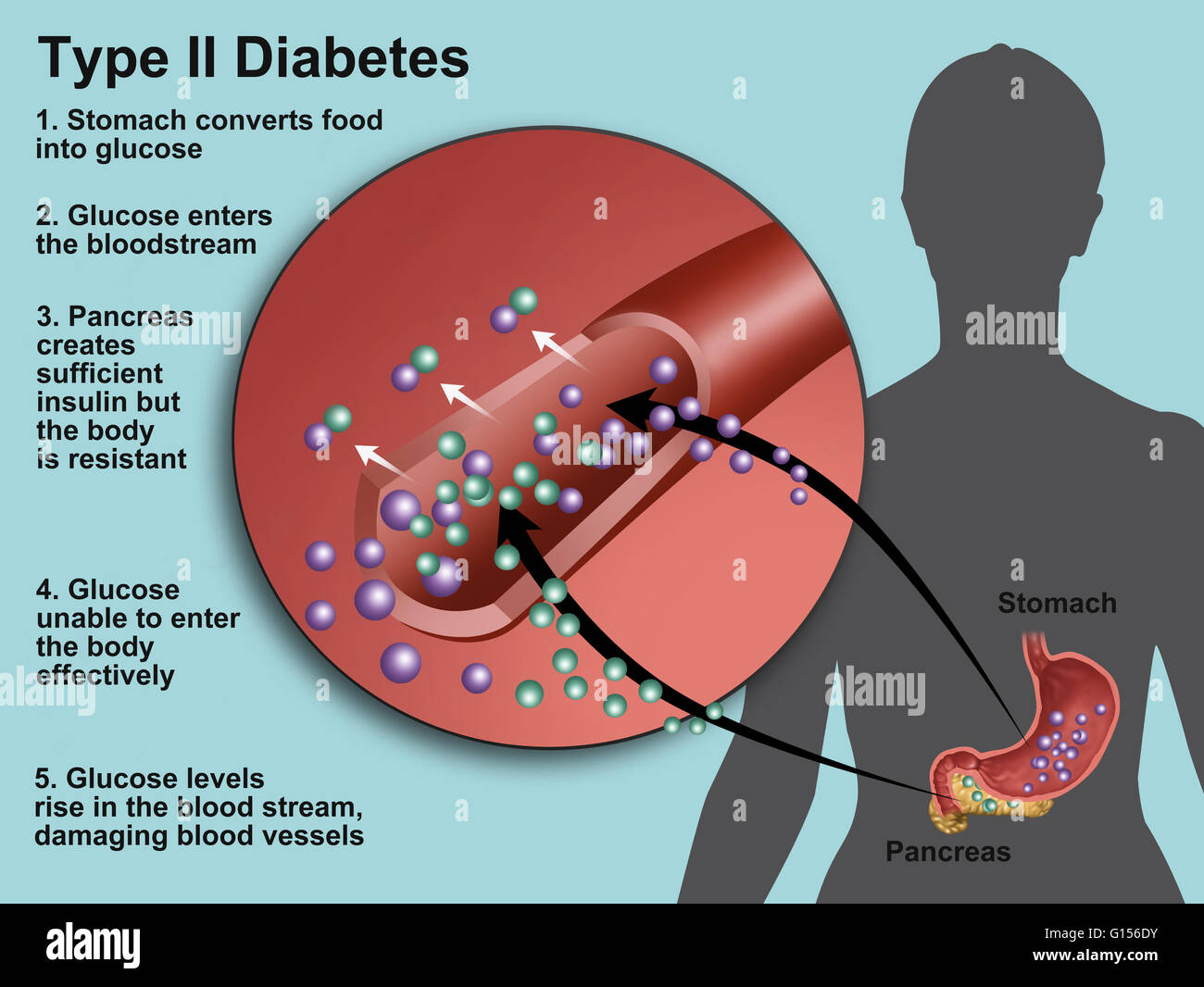
Insulin is a key player in developing type 2 diabetes. This vital hormone—you can’t survive without it—regulates blood sugar (glucose) in the body, a very complicated process. Here are the high points: The food you eat is broken down into blood sugar. Blood sugar enters your bloodstream, which signals the pancreas to release insulin.
In this activity you will examine the relationship between glucose and insulin in the human body. You are going to use the STELLA® glucose-insulin models developed for the activity to simulate different types of glucose release into the bloodstream and the insulin secreting response of the pancreas.
Mar 30, 2021 · Insulin is a natural hormone produced by the beta cells in the pancreas that helps to regulate blood sugar levels. The insulin producing beta cells monitors the blood sugar to ensure it is constant. If your blood glucose increases after taking carbohydrate foods, your body will stimulate the beta cells to produce insulin.
Diagram the feedback relationship of blood glucose and the hormones insulin and glucagon. INSULIN: - blood glucose levels rise - pancreas releases insulin ( beta cells) - in response to the insulin, target cells take up glucose and the liver converts glucose to glycogen GLUCAGON:
Insulin and glucagon work in what’s called a negative feedback loop. During this process, one event triggers another, which triggers another, and so on, to keep your blood sugar levels balanced.






















0 Response to "41 relationship between insulin and glucose diagram"
Post a Comment