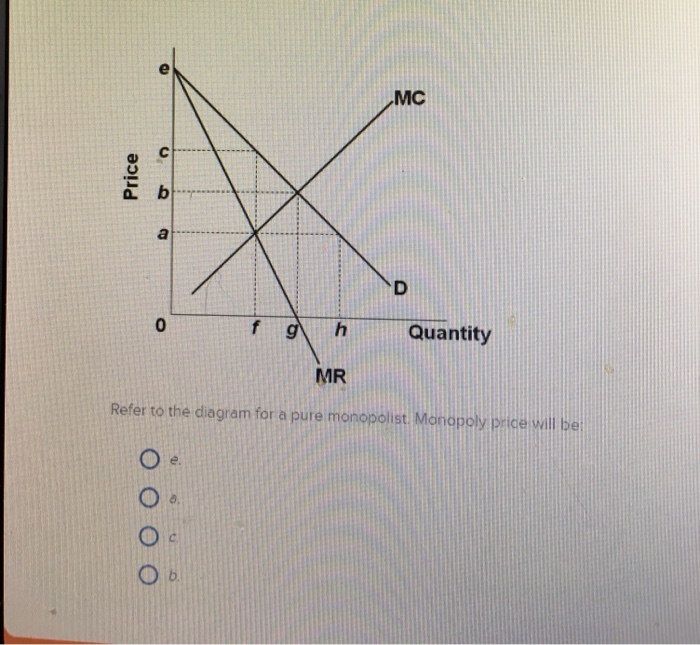
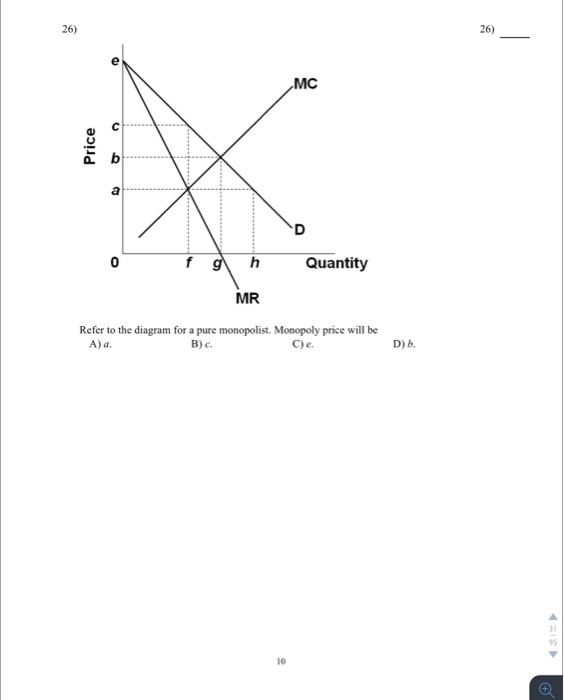
38 refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. monopoly price will be
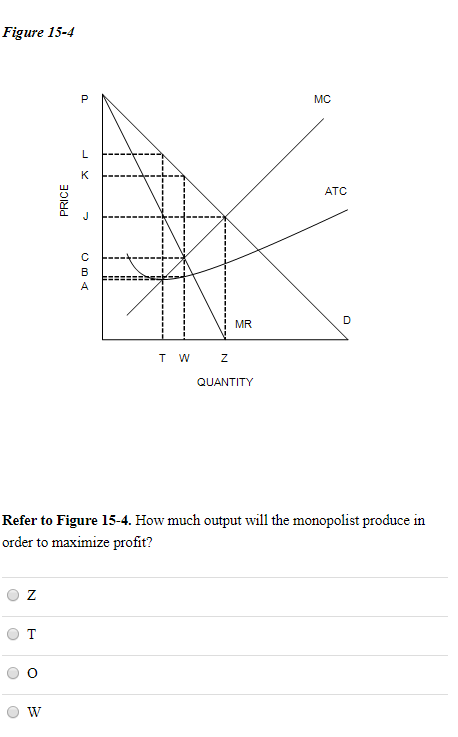
Solved Price Q g h Quantity MR Refer to the diagram for a ... Expert Answer 100% (1 rating) Monopoly price is M … View the full answer Transcribed image text: Price Q g h Quantity MR Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly output will be Multiple Choice o n. O between fand g where MR = MC. O Previous question Next question Refer to the following diagram for a pure monopoly: The ... Refer to the following diagram for a pure monopoly: The profit-maximizing quantity is: A. g, and the. Refer to the following diagram for a pure monopoly: The profit-maximizing quantity is: A. g, and the profit-maximizing price is e. B. h, and the profit-maximizing price is e. C. g, and the profit-maximizing price is f.
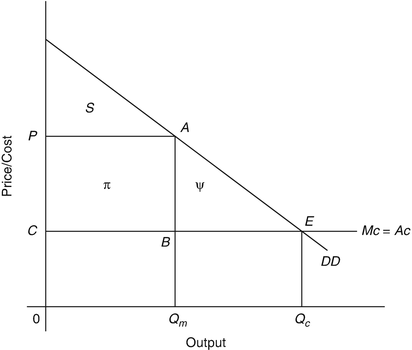
Solved Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist ... See the answer Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist. If the monopolist is unregulated, it will maximize profits by charging: A. a price above P 3 and selling a quantity less than Q 3. B. price P 3 and producing output Q 3. C. price P 2 and producing output Q 2. D. price P 1 and producing output Q 1.
Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. monopoly price will be
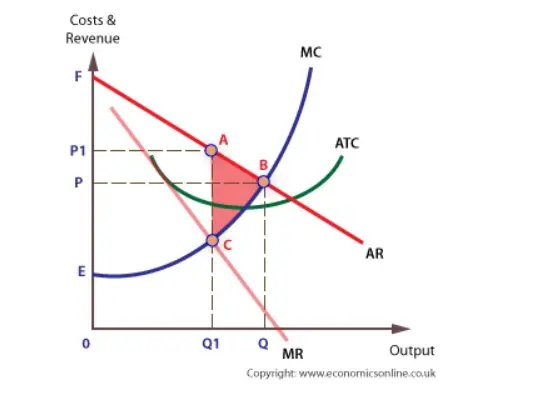
At its profit-maximizing output, a pure nondiscriminating... If a pure monopolist is producing more output than the mr = mc output: The demand curve faced by a nondiscriminating pure monopoly is; If a pure monopolist is operating in a range of output where demand is elastic: Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. monopoly output will be; If a pure monopolist is producing at that output where p = atc ... Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly price ... On the cost side of the profit equation, a pure monopolist does not differ from a perfect competitor. A pure monopolist is selling 10 units at a price of $10. If the marginal revenue of the 11th unit is $1, then the price of the 11th unit is The demand curve faced by a pure monopolist MICRO: CH. 13 Pure Monopoly Part II Flashcards | Quizlet Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly price will be c. Refer to the diagrams. Diagram (A) represents equilibrium price and quantity in a purely competitive industry. Picture is diagram (B) If the industry depicted in the graph comprises only one seller, the profit-maximizing price and quantity will be P3 and Q3.
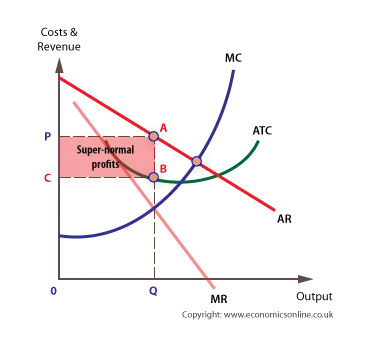
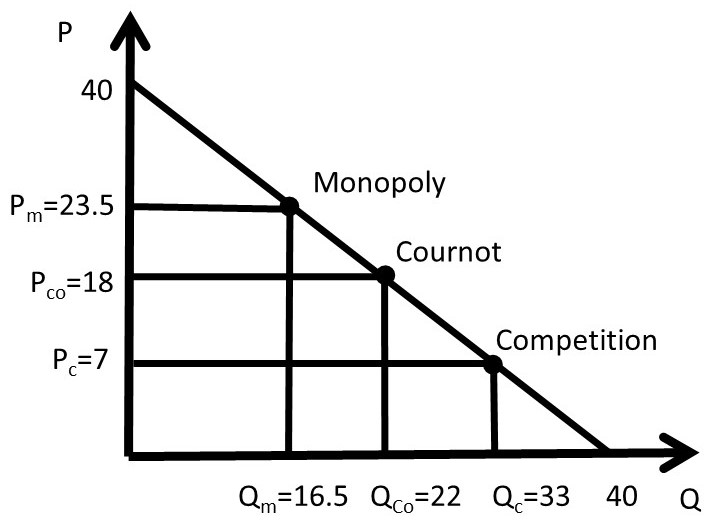
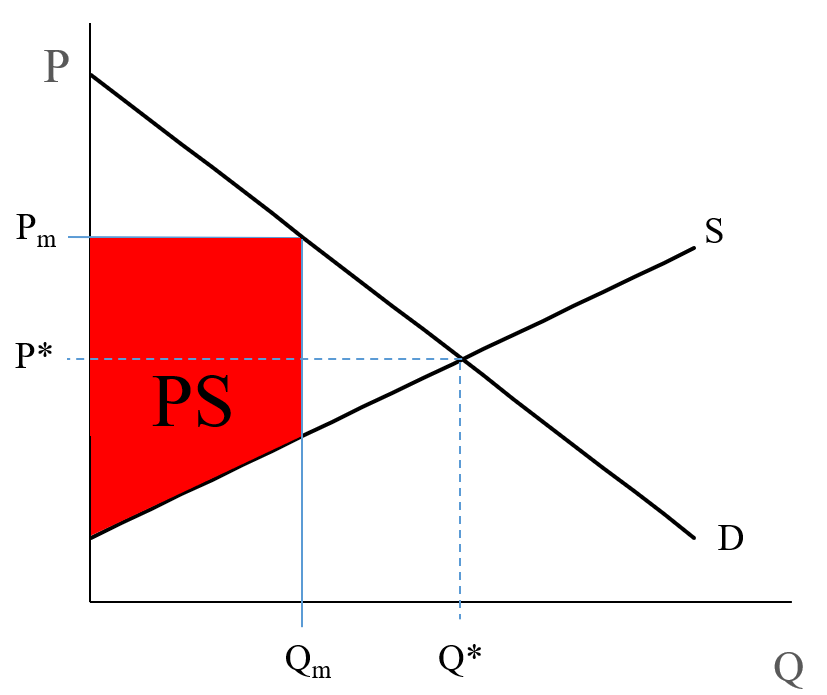
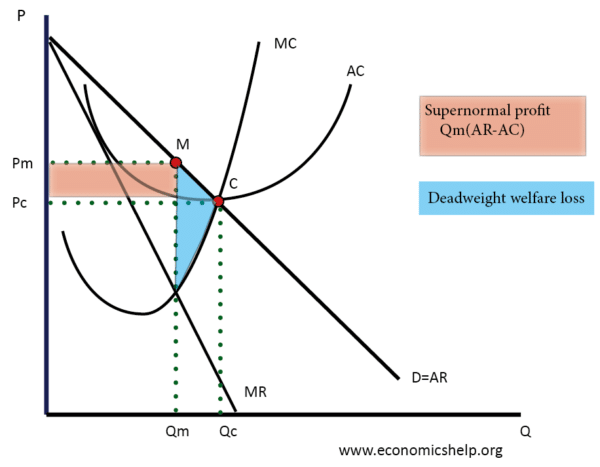
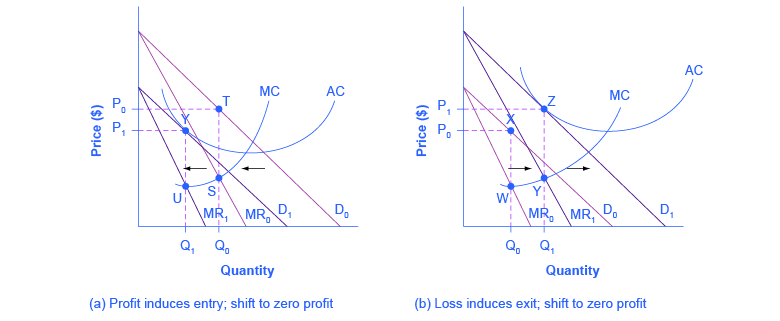
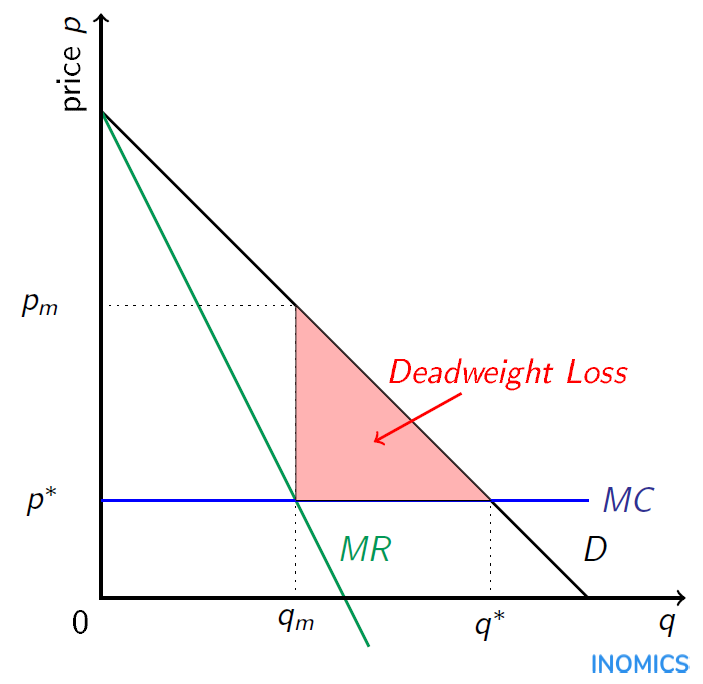
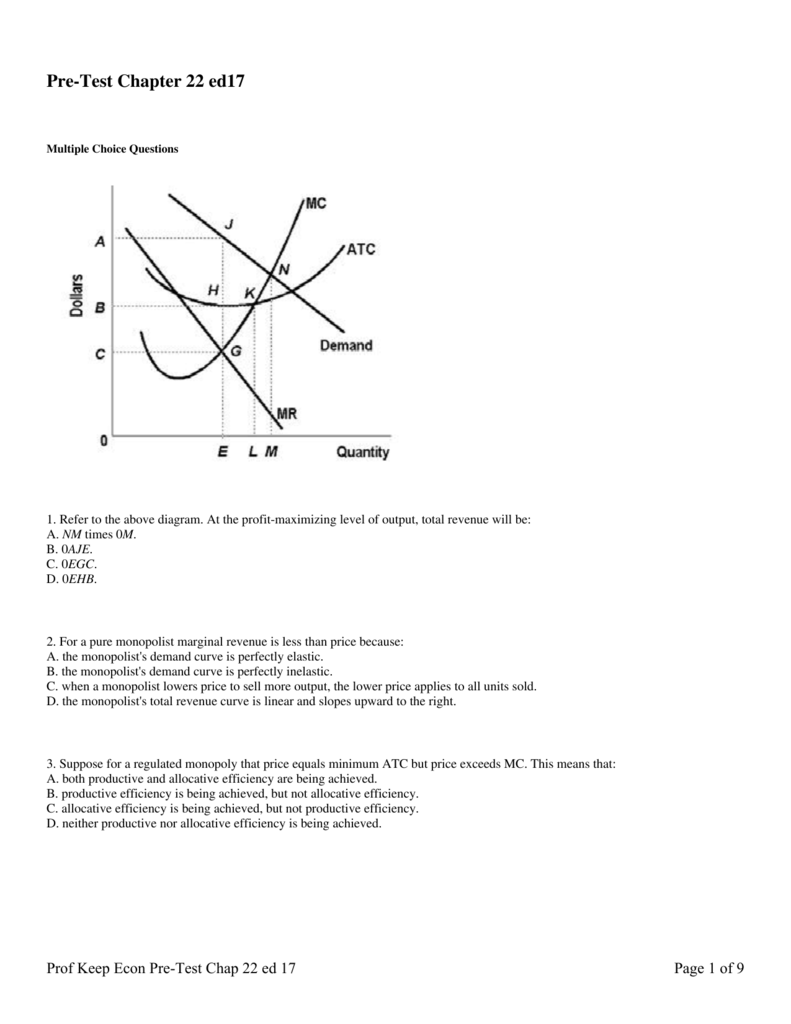
Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. monopoly price will be. DOC Chapter 7 Review Questions 9. Refer to the above diagram. At the profit-maximizing level of output, the firm will realize: A) an economic profit of ABHJ. B) an economic profit of ACGJ. C) a loss of GH per unit. D) a loss of JH per unit. 10. Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly price will be: A) e. B) c. C) b. D) a. 11. Solved > 121.Refer to the above graph for a pure:1637243 ... Question : 121.Refer to the above graph for a pure monopoly. A : 1637243. 121. Refer to the above graph for a pure monopoly. A profit-maximizing monopolist would set what price and quantity levels in the short run? A. P1 and Q1. B. P2 and Q3. C. P3 and Q2. D. P4 and Q1. Micro Chapter 12 Monopolies Flashcards - Quizlet In the short run, a monopolist's economic profits may be positive or negative depending on market demand and cost conditions Refer to the diagram. If this industry is purely monopolistic, the profit-maximizing price and quantity will be P3 and Q3 Refer to the diagrams. Firm A is a pure competitor and Firm B is a pure monopoly Diagram of Monopoly - Economics Help Monopoly Graph. A monopolist will seek to maximise profits by setting output where MR = MC. This will be at output Qm and Price Pm. Compared to a competitive market, the monopolist increases price and reduces output. Blue area = Deadweight welfare loss (combined loss of producer and consumer surplus) compared to a competitive market.
Refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist ... Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. monopoly price will be; Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. monopoly price will be: The demand curve faced by a nondiscriminating pure monopoly is; Refer to the diagram to the right. the firm represented in the diagram makes; Refer to the diagram. a shortage of 160 units would be encountered ... Refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist ... Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. monopoly price will be: The demand curve faced by a nondiscriminating pure monopoly is Suppose a pure monopolist is faced with the demand schedule Refer to the diagram. a shift of the aggregate demand curve from ad1 to ad0 might be caused by a (n) study.com › learn › microeconomics-questions-andMicroeconomics Questions and Answers - Study.com Suppose a monopolist faces the following demand curve: P=420-4Q. Marginal cost of production is constant and equal to $36, and there are no fixed costs. What is the value of the deadweight loss whe... The demand curve faced by a nondiscriminating pure monopoly is Refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. demand is elastic The practice of price discrimination is associated with pure monopoly because Which of the following best approximates a pure monopoly? Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. monopoly output will be
Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. If the ... PMI is the acronym for Private Mortgage Insurance often used by borrowers whose LTV (loan-to-value) ratio is less than 20 percent. Lenders must cease charging PMI when the LTV reaches Charging more interest than is legally allowed is known as Charging an interest rate that seats the legal maximum ceiling is known as › 37552359 › Economics_of_theEconomics of the Public Sector - Joseph E ... - Academia.edu Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link. qqmonreg Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist. Suppose a regulatory commission is created to determine a legal price for the monopoly. If the commission seeks to provide the monopolist with a "fair return," it will set price at: quizlet.com › 304346607 › chapter-12/13/14-flash-cardsChapter 12, 13, 14 Flashcards - Quizlet b. Assume that a pure monopolist and a purely competitive firm have the same unit costs. In the case of a pure monopolist, resources will be allocated c. Even though both monopolists and competitive firms follow the MC = MR rule in maximizing profits, there are differences in the economic outcomes because d.
PDF AP Unit 6 64. Refer to the above diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. At output Q average variable cost is QJ. True False 65. Refer to the above diagrams. Both firms are selling their products in purely competitive markets. True False 66. Refer to the above diagrams. The demand for Firm A's product is perfectly elastic. True False 67. Refer to the ...
Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist Suppose a ... 153. Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. Suppose a regulatory commission is created to determine a legal price for the monopoly. If the commission seeks to provide the monopolist with a "fair return," it will set price at A. P 1 . B. P 3 . C. P 2 . D. P 4 .
For a pure nondiscriminating monopolist, marginal revenue ... If a pure monopolist can price discriminate by separating buyers into two or more groups, Which is true of a price-discriminating pure monopolist? Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. monopoly price will be; Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. monopoly price will be: If a pure monopolist is producing more output than the mr = mc ...
Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist Monopoly ... Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly price will be:c. Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly output will:f . Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly profit:cannot be determined from the information given. In the short run a pure monopolist's profit:may be positive, zero, or negative.
Micro Final Flashcards - Quizlet Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly price will be A) c. B) a. C) e. D) b. A Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly output will be A) f. C) g. B) between f and g. D) h. A A pure monopolist is generally viewed as A) both productively and allocatively inefficient. B) productively inefficient but allocatively efficient.
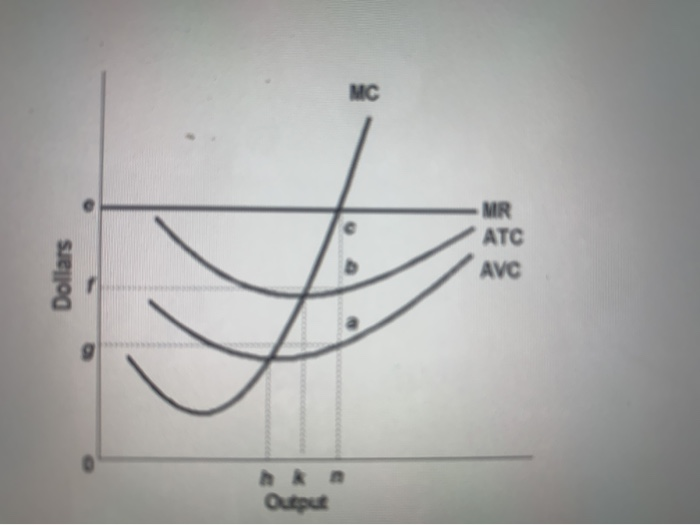
Solved MC Price D f h Quantity MR Refer to the diagram for ... MC Price D f h Quantity MR Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly profit Multiple Choice cannot be determined from the information given. will be ae per unit sold. will be ac per unit sold. will be bc per unit sold. Question: MC Price D f h Quantity MR Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist.
One feature of pure monopoly is that the monopolist is ... Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. Suppose a regulatory commission is created to determine a legal price for the monopoly. If the commission seeks to provide the monopolist with a "fair return," it will set price at:
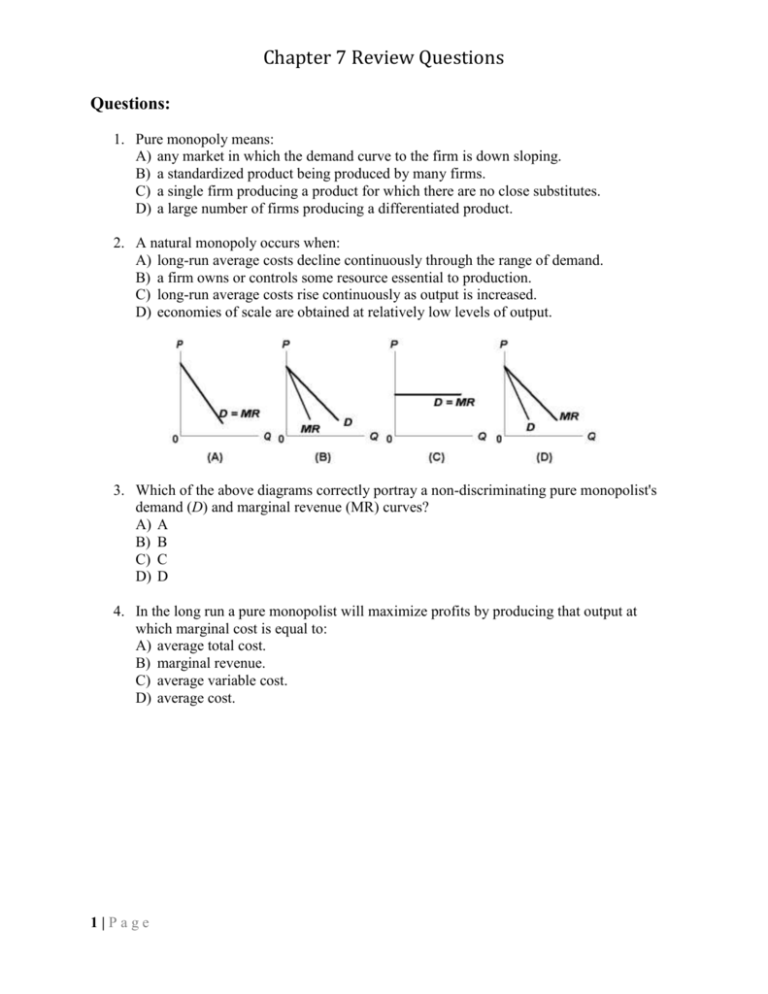
Refer to the above diagram for a nondiscriminating ... Pure monopoly means: a single firm producing a product for which there are no close substitutes.A monopolistic firm has a sales schedule such that it can sell 10 prefabricated garages per week at $10,000 each, but if it restricts its output to 9 per week it can sell these at $11,000 each.
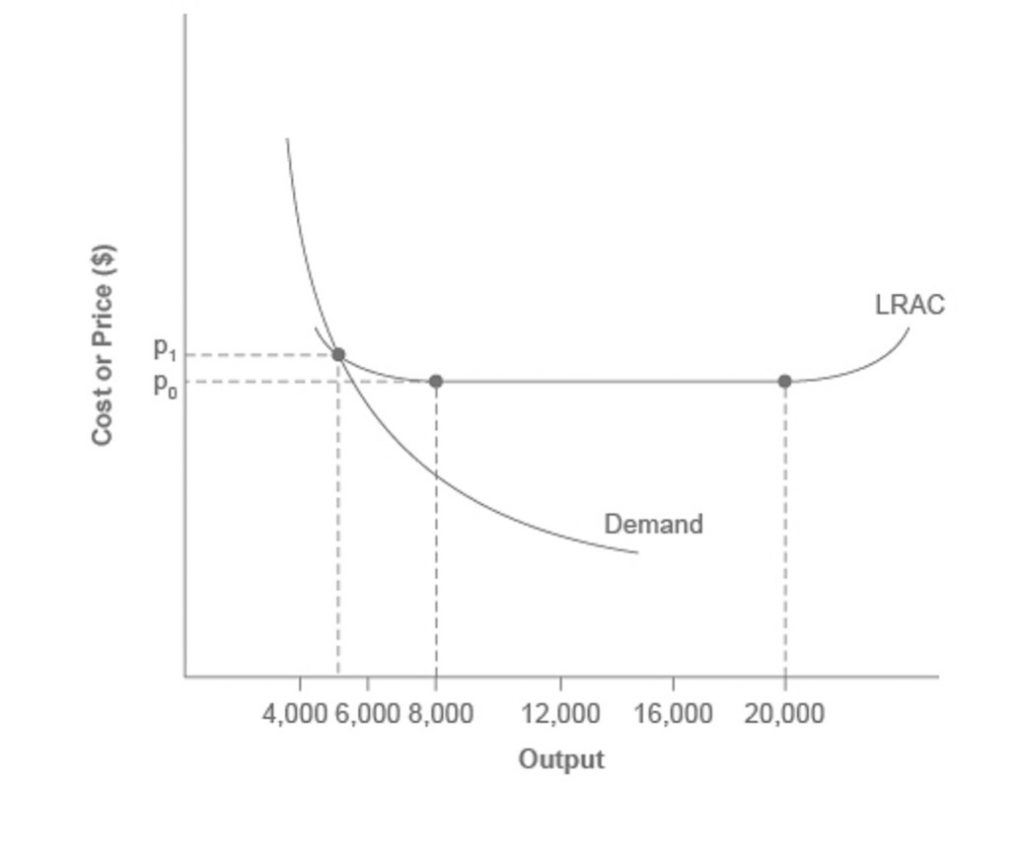
Micro Chapter 24 Flashcards | Quizlet The graph below shows the cost and revenue curves for a natural monopoly. Consider the following two policies: Policy 1 sets price at D=MC. Policy 2 sets price at D=ATC. A) both would result in the same level of output and price B) both would result in an inefficient allocation of resources relative to the unregulated result
ECON CH 12 Flashcards | Quizlet For a pure nondiscriminating monopolist, marginal revenue is less than price because; When a monopolist lowers price to sell more output, the lower price applies to all units sold. Refer to the diagram for a non discriminating monopolist.
Refer to the diagram for a natural monopolist. If a ... Refer to the diagram for a natural monopolist. If a regulatory commission set a maximum price of P the monopolist would. A) produce output Q_1 and realize an economic profit. B) produce output Q_3 and realize an economic profit. C) produce output Q_3 and realize a normal profit. D) close down in the short run.
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Profit_(economics)Profit (economics) - Wikipedia In this case, the monopolist can set its price at any level it desires, maintaining a substantial economic profit. In both scenarios, firms are able to maintain an economic profit by setting prices well above the costs of production, receiving an income that is significantly more than its implicit and explicit costs.
Solved 30.Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist ... D) f . 32. Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly profit: a.cannot be determined from the information given. b.will be ae per unit sold. c.will be bc per unit sold. d.will be ac per unit sold. 33.
Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist Monopoly ... Chapter 10 - Pure Monopoly 72. Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly profit: A. cannot be determined from the information given. B. will be ae per unit sold. C. will be bc per unit sold. D. will be ac per unit sold. 73. In the short run a pure monopolist's profit: A. will be maximized where price equals average total cost. B. may be positive, zero, or negative.
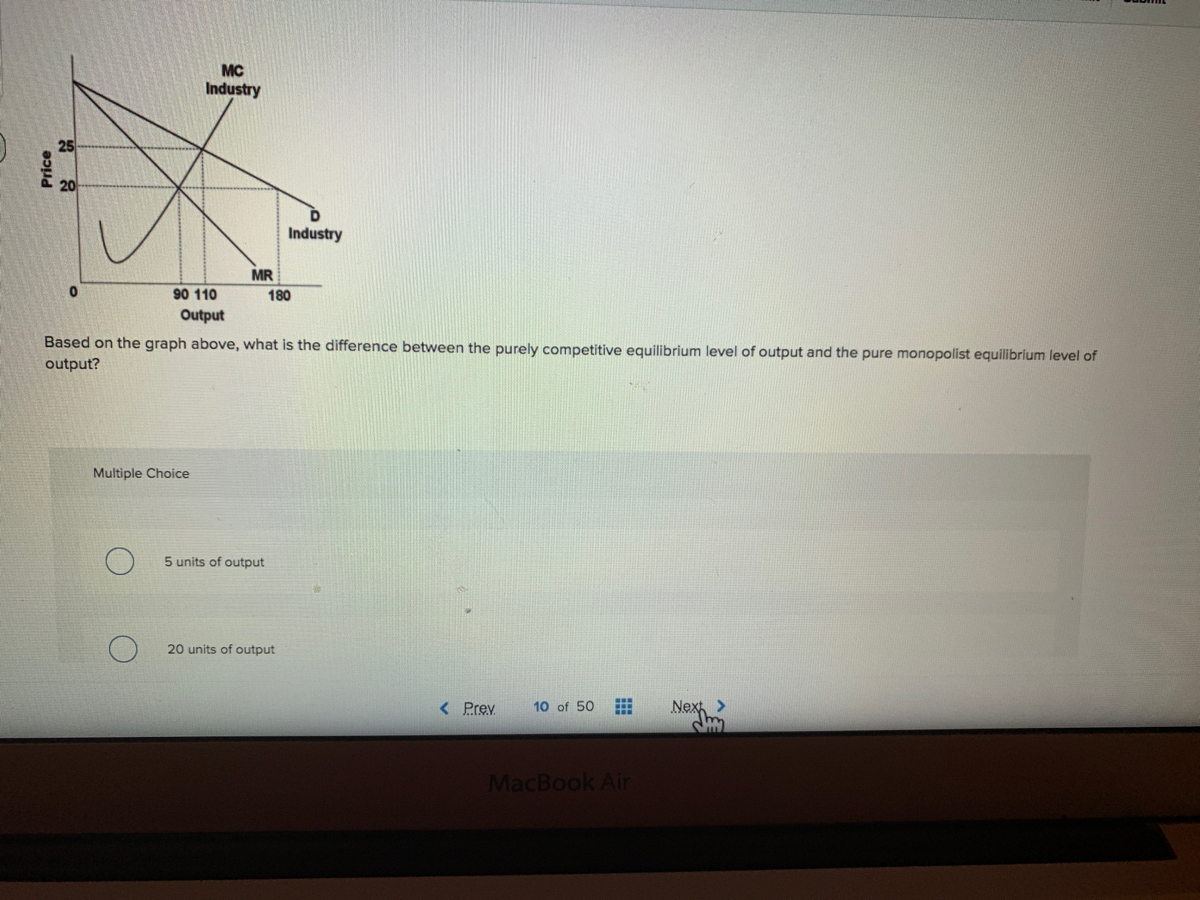
Refer to the diagram for a natural monopolist If a ... Refer to the demand and cost data for a pure monopolist given in the table. A nondiscriminating monopolist would earn maximum profits of A. $600. B. $500. C. $250. D. $100. I 314. Output Price Total Cost 0 $500 $250 1 300 260 2 250 290 3 200 350 4 150 500 5 100 680 Refer to the demand and cost data for a pure monopolist given in the table.
MICRO: CH. 13 Pure Monopoly Part II Flashcards | Quizlet Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly price will be c. Refer to the diagrams. Diagram (A) represents equilibrium price and quantity in a purely competitive industry. Picture is diagram (B) If the industry depicted in the graph comprises only one seller, the profit-maximizing price and quantity will be P3 and Q3.
Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly price ... On the cost side of the profit equation, a pure monopolist does not differ from a perfect competitor. A pure monopolist is selling 10 units at a price of $10. If the marginal revenue of the 11th unit is $1, then the price of the 11th unit is The demand curve faced by a pure monopolist
At its profit-maximizing output, a pure nondiscriminating... If a pure monopolist is producing more output than the mr = mc output: The demand curve faced by a nondiscriminating pure monopoly is; If a pure monopolist is operating in a range of output where demand is elastic: Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. monopoly output will be; If a pure monopolist is producing at that output where p = atc ...















0 Response to "38 refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. monopoly price will be"
Post a Comment