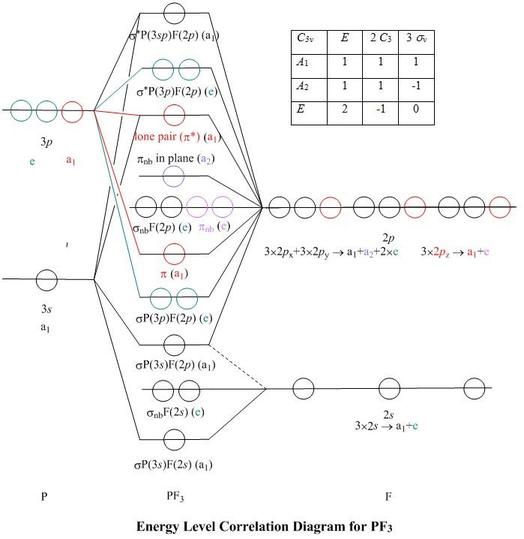
42 square planar orbital diagram
molecular orbital diagram for square planar complexes ... About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators ... Square Planar D Orbital Splitting Diagram - schematron.org ABSTRACT: The presentation of d-orbital splitting diagrams for square planar transition metal complexes in textbooks and educational. The crystal field theory can be extended to square-planar complexes, such as Pt ( NH3)2Cl2. The splitting of the d orbitals in these compounds is shown in the figure below. diagram. return to top.
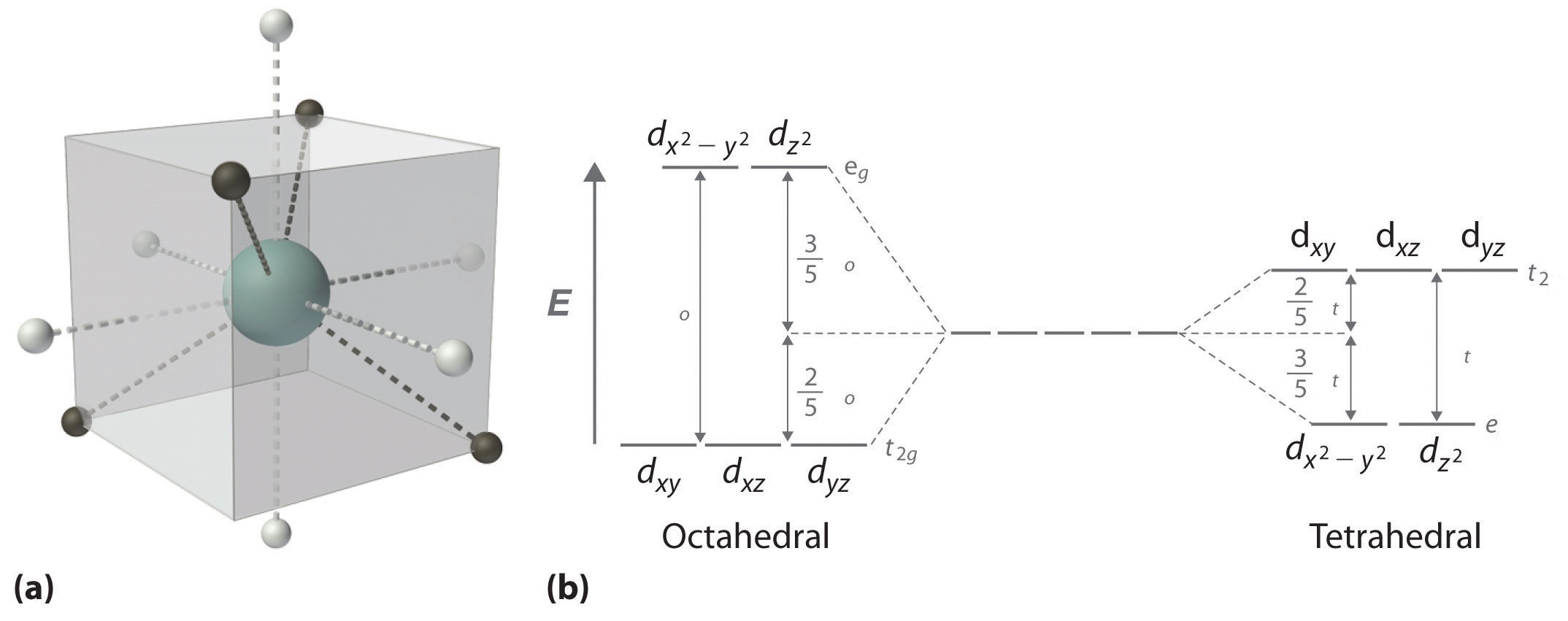
Crystal field theory - Wikipedia Square planar and other complex geometries can also be described by CFT. The size of the gap Δ between the two or more sets of orbitals depends on several factors, including the ligands and geometry of the complex. Some ligands always produce a small value of Δ, while others always give a large splitting.
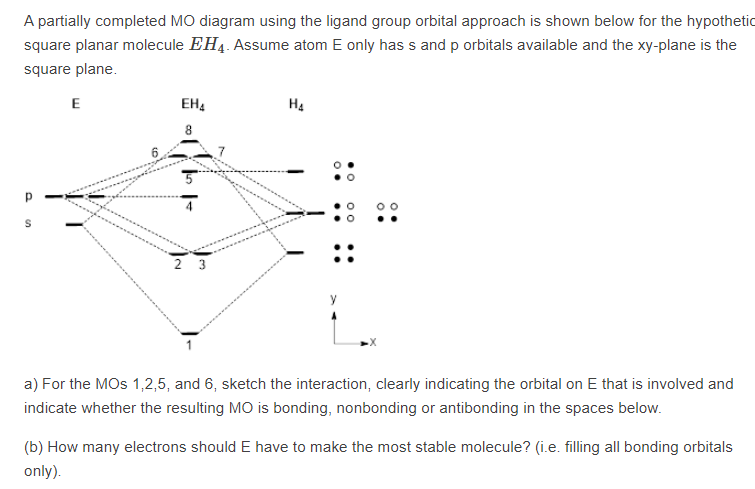
Square planar orbital diagram
Molecular Orbitals of Square-Planar Tetrahydrides | VIPEr This in-class activity walks students through the preparation of a molecular-orbital diagram for methane in a square-planar environment. The students generate ligand-group orbitals (LGOs) for the set of 4 H(1s) orbitals and then interact these with carbon, ultimately finding that such a geometry is strongly disfavored because it does not maximize H/C bonding and leaves a lone pair on C. Ch4 Molecular Orbital Diagram - Wiring Diagrams As can be seen from the energy diagram - four of the molecular orbitals. Generate the Molecular Orbitals for CH4 (Td), CH4 (D4h) and Cyclopropane using diagram between the bonding MOs of square planar and tetrahedral CH4. The molecular orbital description of bonding in methane does several things for us. D-orbital splitting diagrams - Berkeley D-orbital splitting diagrams Use crystal field theory to generate splitting diagrams of the d-orbitals for metal complexes with the following coordination patterns: 1. Octahedral 2. Tetrahedral 3. Trigonal bipyramidal 4. Square pyramidal d z2x2-y d xy d yzxz 5. Square planar d z2x2-y d xy d yzxz d z2 d x2-yxy d yz d xz d z2 d x2-y2 d xy d yz d ...
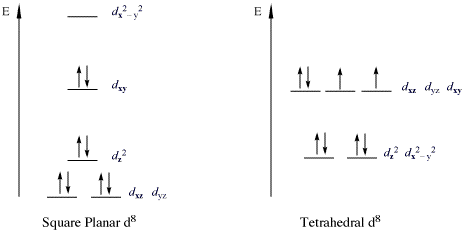
Square planar orbital diagram. Ch4 Molecular Orbital Diagram - schematron.org It uses 3-D pictorial presentations of molecular orbitals to elucidate organic reaction . As can be seen from the energy diagram - four of the molecular orbitals. Generate the Molecular Orbitals for CH4 (Td), CH4 (D4h) and Cyclopropane using diagram between the bonding MOs of square planar and tetrahedral CH4. Spin states (d electrons) - Wikipedia Spin states when describing transition metal coordination complexes refers to the potential spin configurations of the central metal's d electrons. In many these spin states vary between high-spin and low-spin configurations. These configurations can be understood through the two major models used to describe coordination complexes; crystal field theory and ligand field theory, … Transition Metal d-Orbital Splitting Diagrams: An Updated ... Here we provide a concise summary of the key features of orbital splitting diagrams for square planar complexes, which we propose may be used as an updated reference in chemical education. KEYWORDS: General Public Upper Division Undergraduate Inorganic Chemistry Textbooks Crystal Field/Ligand Field Theory MO Theory Transition Elements Cited By Tetrahedral vs. Square Planar Complexes - Chemistry LibreTexts The square planar geometry is prevalent for transition metal complexes with d 8 configuration. The CFT diagram for square planar complexes can be derived from octahedral complexes yet the dx2-y2 level is the most destabilized and is left unfilled. Contributors and Attributions Angad Oberoi (UCD), Justin Nuckles (UCD) StackExchange ( orthocresol)
Part 9(E): Ligand Field Theory (Mo Diagram Square Planar ... In this video, I have explained the detailed molecular orbital diagram for square planar complexes. Formation of sigma lgo and pi lgo have been discussed in ... What is the correct molecular orbital diagram for the d ... However, planar square complexes are drawn completely differently according to other approaches and this makes me doubt the validity of my diagram. To arrive to this diagram, I used the following table: [citation needed] As $\ce{NH3}$ is a σ only ligand, I am not taking into account the π interactions, for which there is a separate table. In ... square_planar_crystal_field_.pdf - square planar crystal ... square planar crystal field 1 square planar crystal field draw the square planar crystal field splitting diagram what d orbital is the most destabilised dx2-dy2 points at the lignads what is the second most destabilised dxy points between the ligands what d orbital is very stabilised dz^2 points at non of the ligands Bonding in Coordination Compounds: Crystal Field Theory ... In square planar molecular geometry, a central atom is surrounded by constituent atoms, which form the corners of a square on the same plane. The square planar geometry is prevalent for transition metal complexes with d 8 configuration. The CFT diagram for square planar complexes can be derived from octahedral complexes yet the dx2-y2 level is ...
PDF Coordination Chemistry II: Jahn-Teller, Square Planar ... diagram σ &π LFT Besureyou toderive know this how by considering π ║ , π σ, and separately ┴ TheAOMprovides interactionsonthe isanegative σ numberbecausethe in-phaseorbonding wayto estim energy +e σ ofthe Rem and interactionis favorable emberfor dx2-y2orbitals atetheim orbitals pactofmetal-ligand (onlyusedondorbitals!). eσ octahedral com interact 4.1.2: Introduction to Ligand Field ... - Chemistry LibreTexts Figure 4.1.2. 3: Diagram of d orbitals (left) and ligands (L1 and L2 on the right) along with their corresponding energy. The orbitals in the middle represent the bonding combination. Energy increases from bottom to top. Molecular Orbital Theory – Octahedral, Tetrahedral or Square ... the main features of molecular orbital theory for metal complexes are as follows: 1.the atomic orbital of the metal center and of surrounding ligands combine to form new orbitals, known as molecular orbitals. 2.the number of molecular orbitals formed is the same as that of the number of atomic orbitals combined. 3.the additive overlap results in … PDF Simple Molecular Orbitals - Sigma and Pi Bonds in ... - CPP An atomic orbital is located on a single atom. When two (or more) atomic orbitals overlap to make a bond we can change our perspective to include all of the bonded atoms and their overlapping ... orbital diagram and that would force us to fill in the bonding sigma MO and the anti-bonding sigma-star MO. What we gain in the bonding sigma MO, we ...
(PDF) Inorganic Chemistry by Miessler ~ 5th Edition ... This book is ideal for who want to use a strong molecular-orbital approach to explain structure and reactivity in inorganic chemistry. (PDF) Inorganic Chemistry by Miessler ~ 5th Edition | Arnab Patra - Academia.edu
GCE Chemistry A ALLOW diagram with missing C, O or Cl symbols. For × × • •C=O bond, ALLOW sequence ... Highest energy electron(s) in a p orbital/p sub-shell 1 ALLOW outer electron(s) in a p orbital/sub-shell BUT IGNORE p shell ALLOW electron configuration ends in p OR the last electron is in a p orbital ALLOW valence electron(s) in p orbital/sub-shell Total 8 . H032/01 Mark Scheme June …
Solved Hi! Can you please explain how to find both ... - Chegg Can you please explain how to find both the sigma and the pi bonds for a square planar orbital diagram? Expert Answer. Who are the experts? Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. 100% (2 ratings)
Square Planar D Orbital Splitting Diagram We find that the square planar complexes have the greatest crystal field splitting ligand field (left diagram) and the tetrahedral field (right diagram).D-orbital splitting diagrams Use crystal field theory to generate splitting diagrams of the d-orbitals for metal complexes with the following coordination patterns: 1. Octahedral 2. Tetrahedral 3.
Transition Metal d-Orbital Splitting Diagrams: An Updated ... The presentation of d-orbital splitting diagrams for square planar transition metal complexes in textbooks and educational materials is often inconsistent and therefore confusing for students. Here we provide a concise summary of the key features of orbital splitting diagrams for square planar complexes, which we propose may be used as an updated reference in chemical education.
complex ions - colour - chemguide The diagram shows the arrangement of the d electrons in a Cu 2+ ion before and after six water molecules bond with it. Whenever 6 ligands are arranged around a transition metal ion, the d orbitals are always split into 2 groups in this way - 2 with a higher energy than the other 3. The size of the energy gap between them (shown by the blue arrows on the diagram) varies with …
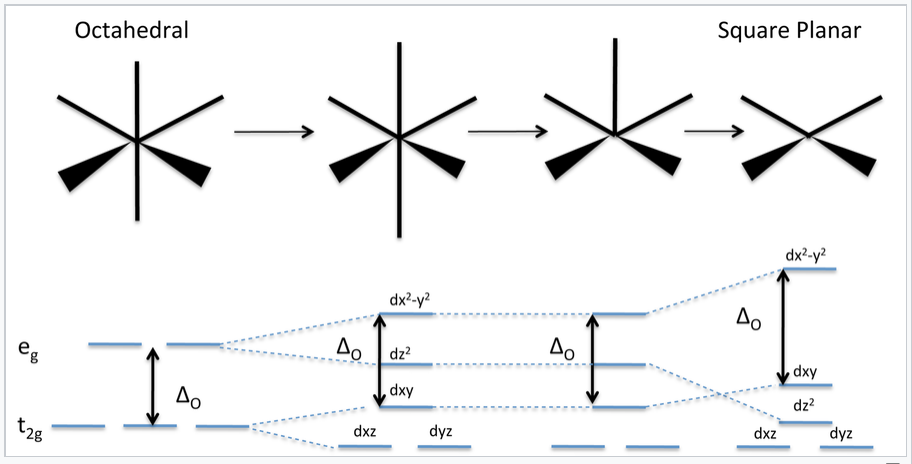
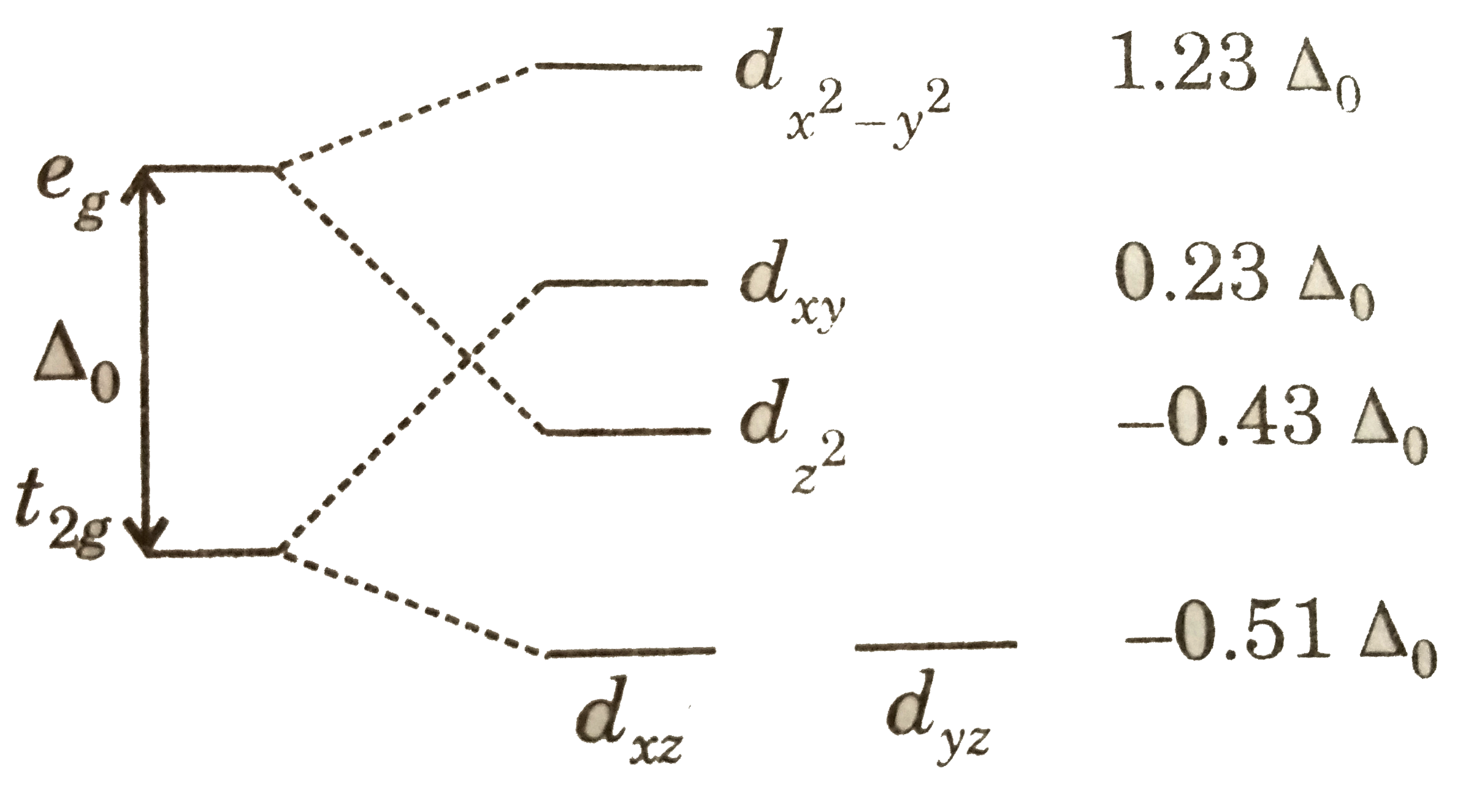
CHEM2P32 Lecture 11. Square and Tetrahedral Complexes The orbital splitting diagram for square planar coordination can thus be derived from the octahedral diagram. As ligands move away along the z-axis, d-orbitals with a z-component will fall in energy. The d z2 orbital falls the most, as its electrons are concentrated in lobes along the z-axis.
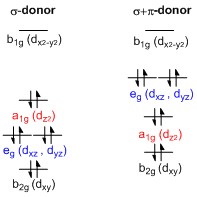
Why is PtCl4^2- square planar? | Socratic A good general rule is that if you have either square planar or tetrahedral, a low-spin complex generally forms square planar, and a high-spin complex generally forms tetrahedral. Platinum is not an exception to that statement. To see why, we should consider nickel, which is in the same group, whose complexes are tetrahedral sometimes and square planar other times.
PDF Lecture 6 4 coordinate complexes, summary, typical exam ... Walsh diagram for D4hTd n.b steric factors always favour Td(angles 109.5) Bond Square planar Tetrahedral Ni-N 1.68 Å 1.96 Å Ni-P 2.14 Å 2.28 Å Ni-S 2.15 Å 2.28 Å Ni-Br 2.30 Å 2.36 Å 4 (weakly) antibonding electrons 2 (weakly) antibonding electrons Typical bond lengths Factors controlling geometry 1) Sterics - large ligands favour Td
Aromaticity - Wikipedia In chemistry, aromaticity is a property of cyclic (ring-shaped), typically planar (flat) molecular structures with pi bonds in resonance (those containing delocalized electrons) that gives increased stability compared with other geometric or connective arrangements with the same set of atoms.Aromatic rings are very stable and do not break apart easily. ...
PDF CHE P7 M7 e-Text The ligand field splitting energy diagram for a square planar geometry can thus be derived from an octahedral diagram as shown below (Figure2). As the z-ligands move away, the ligands in the square plane move a little closer to the metal. Now, d-orbitals with a z-component will fall in energy. The d
Solved Label the d orbitals in the following d-orbital ... We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. 100% (45 ratings) The removal of a pair of ligands from the z-axis of an octahedron leaves four ligands in the x-y plane. …. View the full answer. Transcribed image text: Label the d orbitals in the following d-orbital energy diagram of a square-planar complex.
Tetrahedral and Square Planar Complexes | Introduction to ... The square planar geometry is prevalent for transition metal complexes with d 8 configuration. The CFT diagram for square planar complexes can be derived from octahedral complexes yet the dx2-y2 level is the most destabilized and is left unfilled. Terms degeneracyHaving the same quantum energy level.
Molecular Orbital Theory - Octahedral, Tetrahedral or ... Molecular Orbital Theory - Octahedral, Tetrahedral or Square Planar Complexes,molecular orbital theory for tetrahedral complexes pdf, molecular orbital diagram for tetrahedral complex, molecular orbital theory for octahedral complexes pdf, molecular orbital theory for square planar complexes pdf.
Square planar molecular geometry - WikiMili, The Best ... A general d-orbital splitting diagram for square planar (D 4h) transition metal complexes can be derived from the general octahedral (O h) splitting diagram, in which the d z 2 and the d x 2 −y 2 orbitals are degenerate and higher in energy than the degenerate set of d xy, d xz and d yz orbitals.
Square planar molecular geometry - Wikipedia A general d-orbital splitting diagram for square planar (D 4h) transition metal complexes can be derived from the general octahedral (O h) splitting diagram, in which the d z2 and the d x2−y2 orbitals are degenerate and higher in energy than the degenerate set of d xy, d xz and d yz orbitals.
D-orbital splitting diagrams - Berkeley D-orbital splitting diagrams Use crystal field theory to generate splitting diagrams of the d-orbitals for metal complexes with the following coordination patterns: 1. Octahedral 2. Tetrahedral 3. Trigonal bipyramidal 4. Square pyramidal d z2x2-y d xy d yzxz 5. Square planar d z2x2-y d xy d yzxz d z2 d x2-yxy d yz d xz d z2 d x2-y2 d xy d yz d ...
Ch4 Molecular Orbital Diagram - Wiring Diagrams As can be seen from the energy diagram - four of the molecular orbitals. Generate the Molecular Orbitals for CH4 (Td), CH4 (D4h) and Cyclopropane using diagram between the bonding MOs of square planar and tetrahedral CH4. The molecular orbital description of bonding in methane does several things for us.
Molecular Orbitals of Square-Planar Tetrahydrides | VIPEr This in-class activity walks students through the preparation of a molecular-orbital diagram for methane in a square-planar environment. The students generate ligand-group orbitals (LGOs) for the set of 4 H(1s) orbitals and then interact these with carbon, ultimately finding that such a geometry is strongly disfavored because it does not maximize H/C bonding and leaves a lone pair on C.
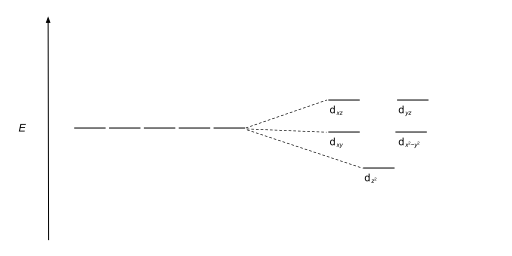









![d-orbital energy levels in planar [M II F 4 ] 2− , [M II (NH ...](https://pubs.rsc.org/image/article/2020/DT/d0dt02022b/d0dt02022b-f1_hi-res.gif)











0 Response to "42 square planar orbital diagram"
Post a Comment