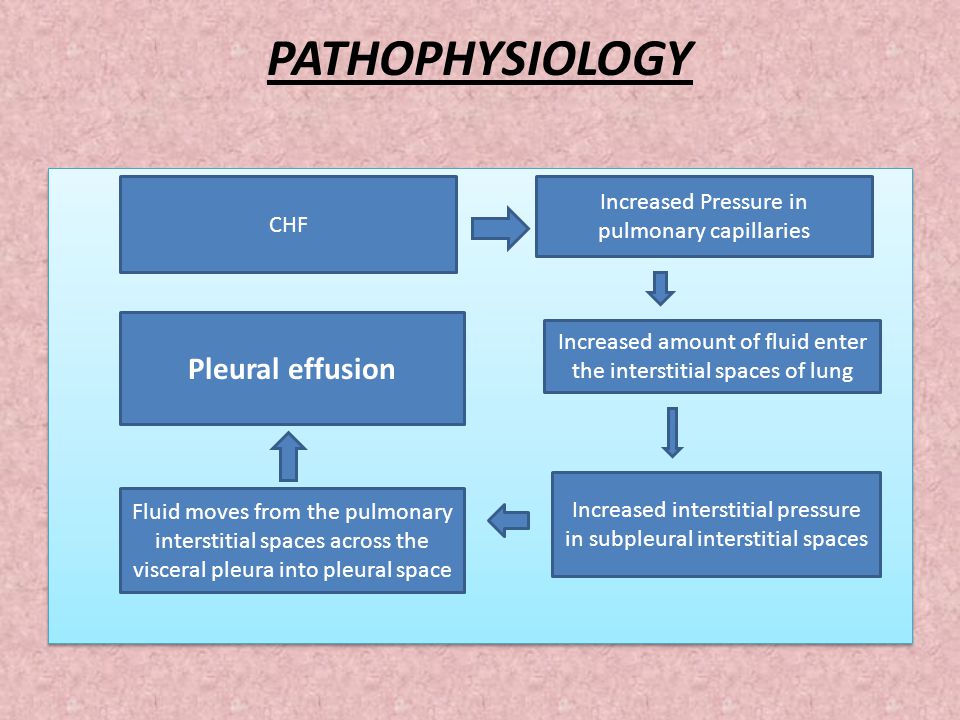
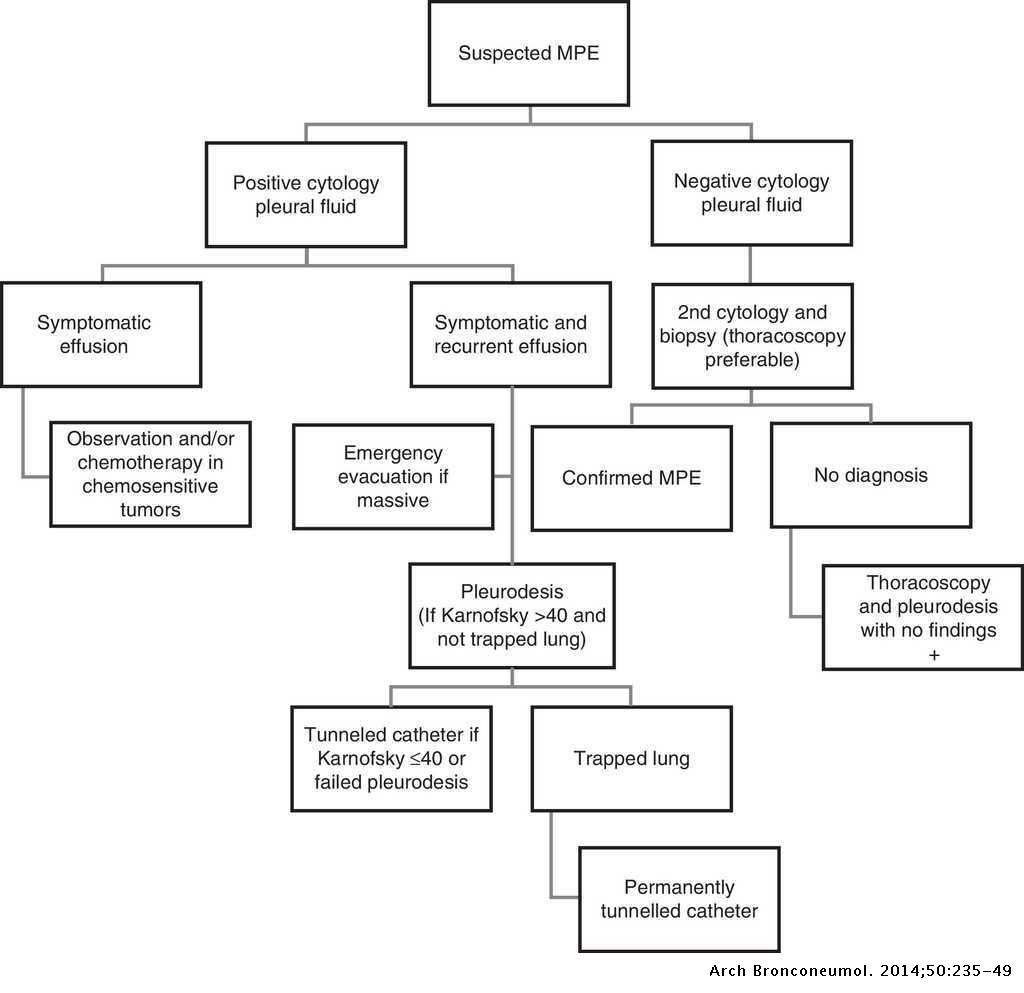
42 pleural effusion pathophysiology diagram
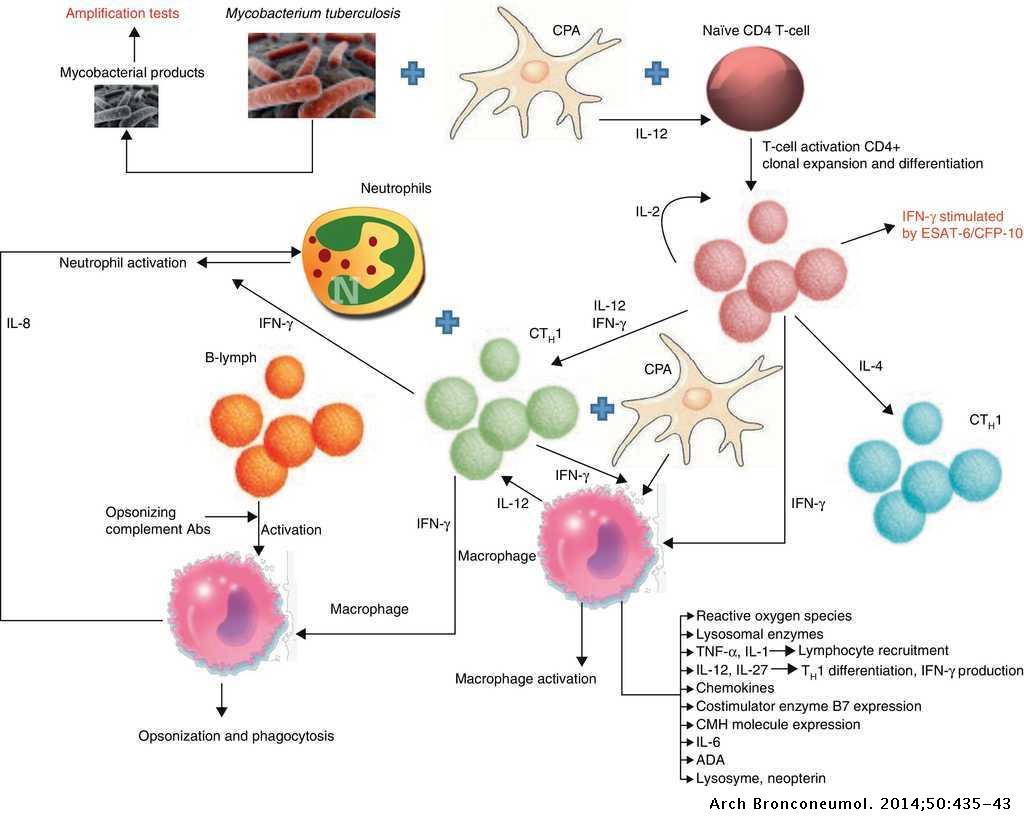
Can anyone give me the pathophysiology of pleural effusion ... Understood. This brings up some very interesting questions about the etiology of pleural effusion. In theory, your diagram should show where the fluid/matter is coming from. Can't really do that if you are creating a single diagram. Physiology and pathophysiology of pleural fluid turnover ... Extensive reviews on the pathophysiology of pleural effusions are available 100-104. The causes of pleural effusion may be subdivided into three main categories: 1) those changing transpleural pressure balance, 2) those impairing lymphatic drainage, and 3) those producing increases in mesothelial and capillary endothelial permeability.
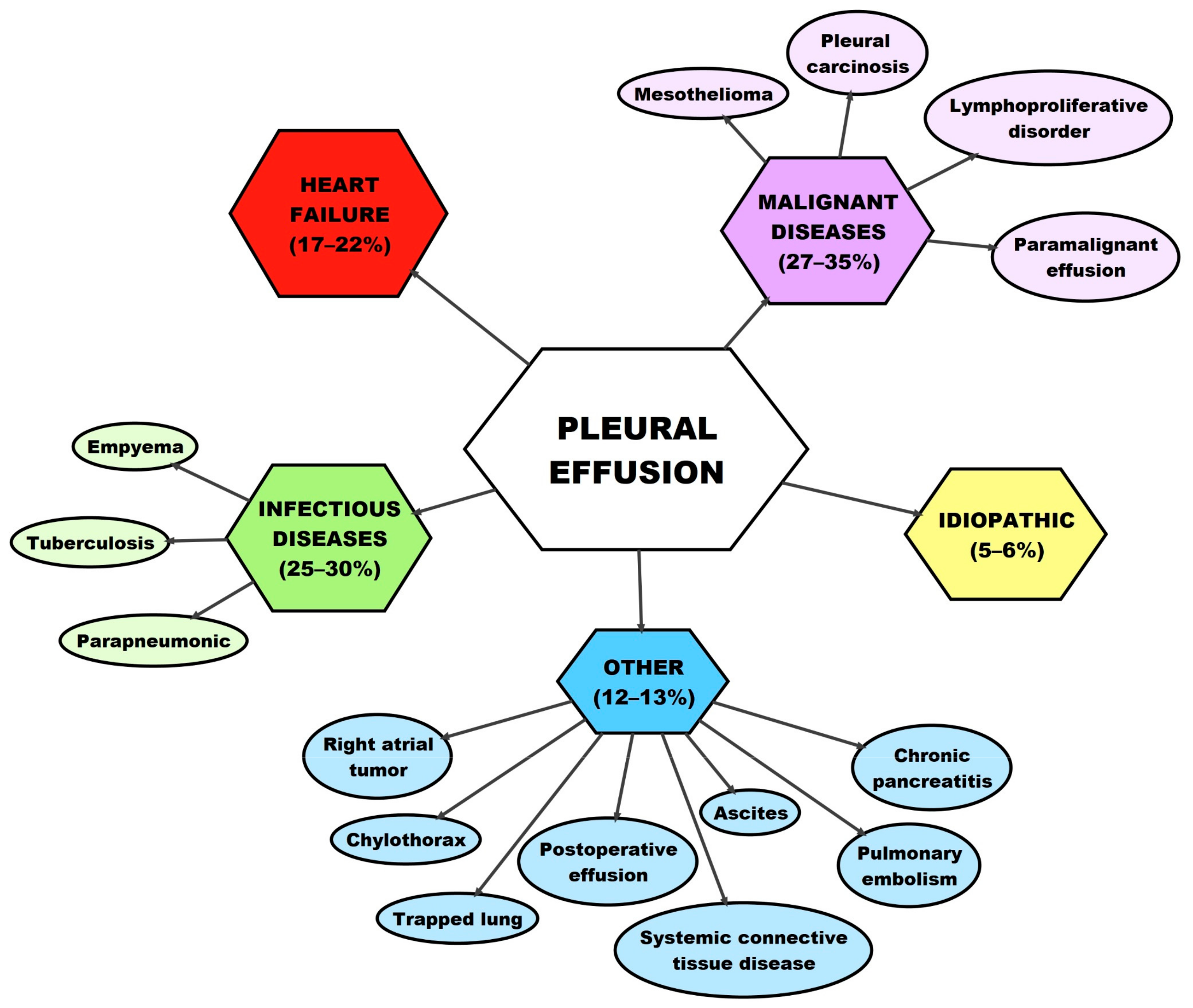
Pleural cavity: Anatomy, location, function - Kenhub Pleural effusion has multiple etiologies. It can be caused by a number of things, such as infection, cancer, cardiac failure, liver disease and pulmonary embolism. Depending on its pathophysiology, a pleural effusion can be classed as transudate or exudate.

Pleural effusion pathophysiology diagram
Pleura and pleural space Notes: Diagrams ... - Osmosis Chapter 128 Pleura & Pleural Space PLEURAL EFFUSION osms.it/pleural-effusion PATHOLOGY & CAUSES Excess fluid accumulates in pleural space Lung expansion limited → impaired ventilation Origin Hydrothorax (serous fluid), hemothorax (blood), urinothorax (urine), chylothorax/ lymphatic effusion (chyle), pyothorax (pus, AKA empyema) Pathophysiology Transudative pleural effusion Pressure driven ... Pathophysiology | Pulmonary Embolism With large emboli; pleural friction rub, pleural effusion, fever, leukocytosis; Evaluation: Diagnosis can be made based on a patient's symptoms, medical history and a series of tests and scans. Clinical Decision Rules, such as the Well's Score, can guide diagnostics of suspected acute venous thromboembolism. Pleural Effusion: Symptoms, Causes, Treatments Pleural effusion, sometimes referred to as "water on the lungs," is the build-up of excess fluid between the layers of the pleura outside the lungs. The pleura are thin membranes that line the lungs and the inside of the chest cavity and act to lubricate and facilitate breathing. Normally, a small amount of fluid is present in the pleura.
Pleural effusion pathophysiology diagram. Pathophysiology of pleural effusion - SlideShare Pathophysiology of pleural effusion 1. VI. PATHOPHYSIOLOGY Risk Factors: Smoking (9 years) Family history of tuberculosis Invasion of bacteria in the body Inflammatory process Increase stimulation Stimulate MAST of goblet cells cells in the lungs Difficulty of breathing Increase mucus Release of (RR=36 breaths/min, production chemical mediators shallow and rapid) (histamine) (01/21/2012 ... Hypothyroidism Pleural Effusion Pathophysiology Diagram | CR Clinical Signs In addition to typical signs hypothyroidism pleural effusion pathophysiology diagram pleural effusion, such as dyspnea and tachypnea, it is noteworthy that dogs and cats with chylothorax often present with coughing. The pleural fluid pH is usually less than 7. Diseases of the Respiratory System 10/02/2017 · These diseases include pneumothorax, pleural effusion, or respiratory muscle weakness, such as can occur with botulism, tick paralysis, tetanus, strychnine poisoning, or severe white muscle disease. Ventilation-perfusion mismatches occur when the distribution of blood flow in the lungs does not match the distribution of alveolar ventilation, with the result … PDF Malignant Pleural Effusion - American Thoracic Society A malignant pleural effusion (MPE) is the build up of fluid and cancer cells that collects between the chest wall and the lung. This can cause you to feel short of breath and/or have chest discomfort. It is a fairly common complication in a number of different cancers.
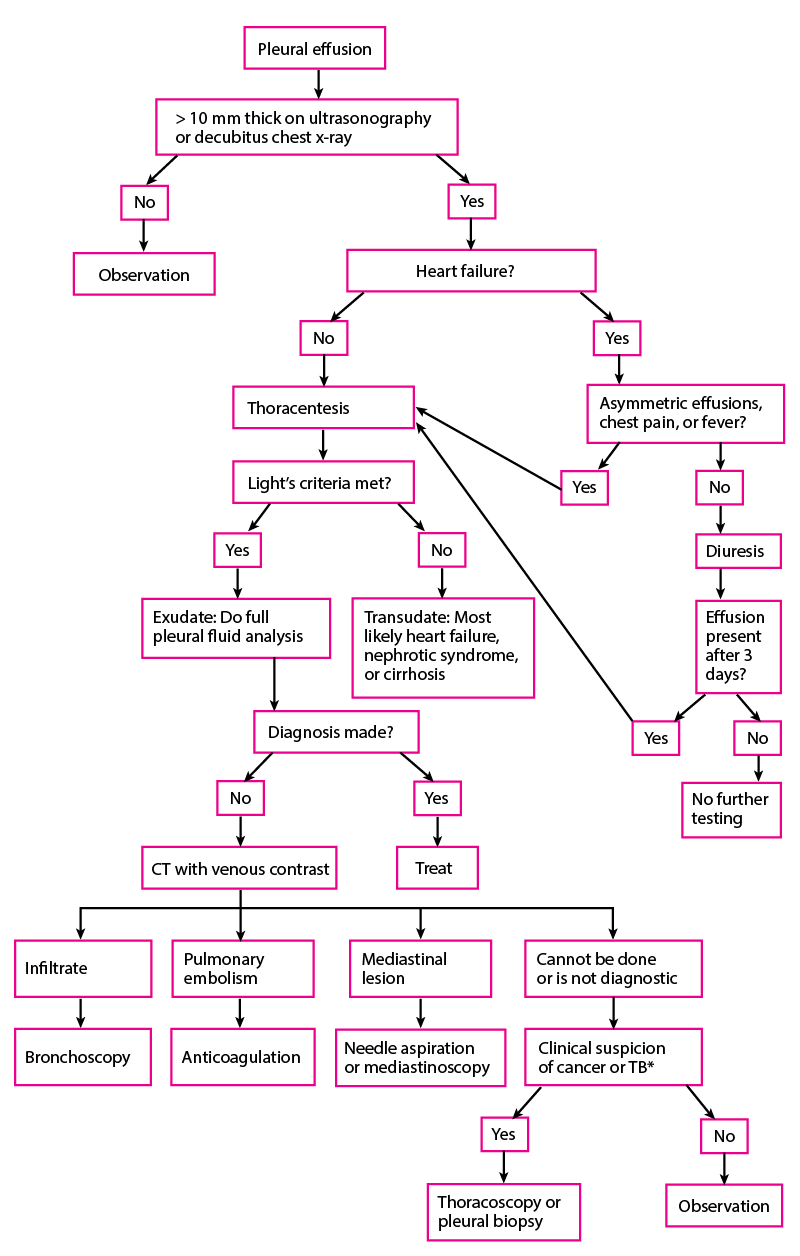
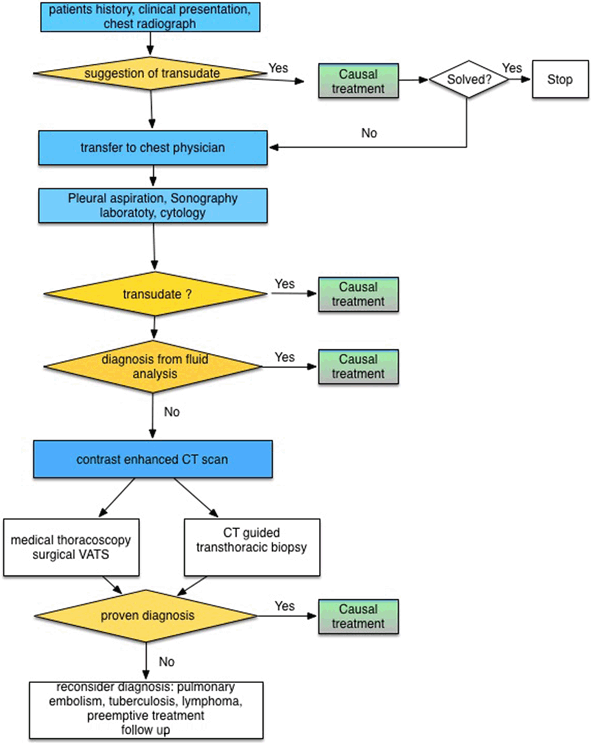
Action: SAGE Journals Nous voudrions effectuer une description ici mais le site que vous consultez ne nous en laisse pas la possibilité. PDF Pleural effusions: Evaluation and management Pleural effusions are very common, and physicians of all specialties encounter them.A pleural effusion represents the disruption of the normal mechanisms of formation and drainage of fluid from the pleural space.A rational diagnostic workup, emphasizing the most common Pleural effusions: pathophysiology and management Objective: To review the pathophysiology and management of pleural effusions, including available agents for pleural sclerosis. Data sources: A MEDLINE search (1966 to present) was performed that included clinical studies in the English language involving the pathophysiology and management of pleural effusions; references used in those articles were screened for additional published information. Pleural Effusion (DETAILED) - (pathophysiology, signs and ... Where do I get my information from: me: ...
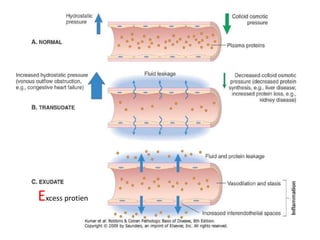
Chest radiograph shows bilateral pleural effusion without ... Download scientific diagram | Chest radiograph shows bilateral pleural effusion without pulmonary edema before surgery (a), butterfly shadows on the day of surgery (b), and the disappearance of ... Pleural Effusion - Pulmonary Disorders - MSD Manual ... Pleural Effusion. Pleural effusions are accumulations of fluid within the pleural space. They have multiple causes and usually are classified as transudates or exudates. Detection is by physical examination and chest x-ray; thoracentesis and pleural fluid analysis are often required to determine cause. Pleural effusion pathophysiology - wikidoc Pathophysiology. Pleural effusion results either from increased pleural fluid formation or decreased exit of fluid. Increased Pleural Fluid Formation. Increased hydrostatic pressure (e.g. seen in congestive heart failure) Decreased colloid osmotic pressure (e.g. cirrhosis and nephrotic syndrome) Mechanisms controlling the volume of pleural fluid and ... Pathophysiology of pleural effusion When filtration overwhelms fluid drainage, pleural effusion results; point D in figure 5 ⇑ , falling outside the chequered area, refers to a condition where the control mechanism becomes ineffective because the maximum lymphatic flow cannot match the increase in filtration rate.
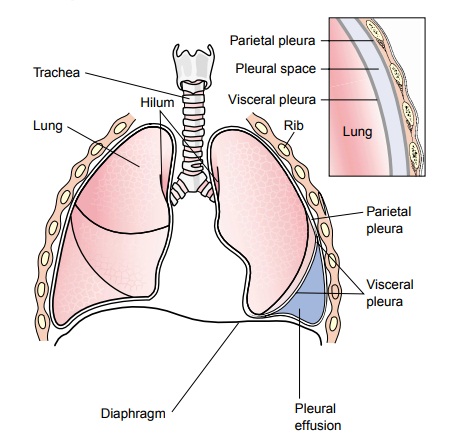
Pleural effusion - Wikipedia Pleural effusion; Diagram of fluid buildup in the pleura: Specialty: Pulmonology: A pleural effusion is accumulation of excessive fluid in the pleural space, the potential space that surrounds each lung.Under normal conditions, pleural fluid is secreted by the parietal pleural capillaries at a rate of 0.01 millilitre per kilogram weight per hour, and is cleared by lymphatic absorption leaving ...
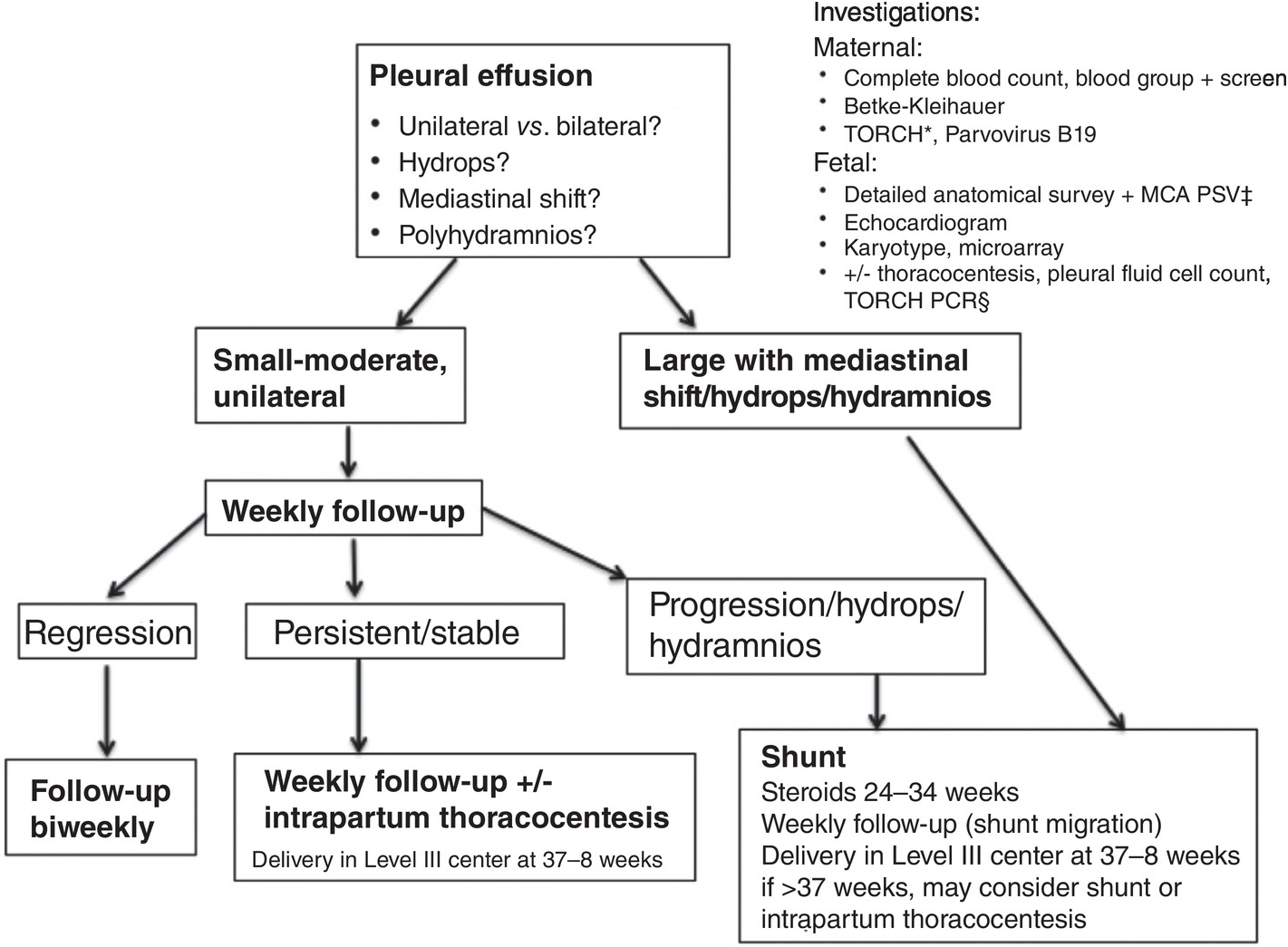
Dynamics of Pleural Fluid Effusion and Chylothorax in The ... Keywords: perinatal pleural effusions, congenital chylothorax, newborn, hydrops fetalis, lymphatic dysplasia, lymph dynamics, pathophysiology Fluid accumulation in the pleural space is commonly defined as pleural effusion. This is a rare event occurring during the neonatal period. Different types of congenital and acquired effusions have been ...
The pathophysiology of pleural effusions The pathophysiology of pleural effusions Annu Rev Med. 1990;41:7-13. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.41.020190.000255. Author S A Sahn 1 Affiliation 1 Department of Medicine, Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston 29425. PMID: 2184750 DOI: 10.1146 ...
Pleural effusion - SlideShare Pleural effusion is an indicator of an underlying disease process that may be pulmonary or nonpulmonary in origin and may be acute or chronic. Although the etiologic spectrum of pleural effusion is extensive, most pleural effusions are caused by congestive heart failure, pneumonia, malignancy, or pulmonary embolism 5.
Physiology, Pleural Fluid - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf Pathophysiology Pleural effusions develop when changes in fluid and solute homeostasis occur, and the mechanism causing these changes determines whether it will be an exudative (high protein content) or transudative (low protein content) effusion.
'Left basal pleural changes scar :: surviving malignant ... pathophysiology pleural effusion diagram. buy aspira pleural drainage. biapical nodular pleural scarring. mild basilar pleural thickening trauma. left apical pleural thickening. pictures of children postures. mild apical pleural. right pleural friction rub. mild bilateral apical pleural parenchymal scarring. edema in pleural cavity nodules
Moderate pleural effusion in the right lung field ... The objective of the current review is to delineate the pathophysiology, risk factors, preventive measures, and therapeutic options of isolated pleural effusion in severe OHSS. Major databases ...
Pathophysiology - Pleural Effusion | PDF | Human Anatomy ... Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC) Available Formats. Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd. Flag for inappropriate content. Download now. Save Save Pathophysiology- Pleural Effusion For Later. 75% (4) 75% found this document useful (4 votes) 6K views 1 page.
Pleural effusion: diagnosis, treatment, and management A pleural effusion is an excessive accumulation of fluid in the pleural space. It can pose a diagnostic dilemma to the treating physician because it may be related to disorders of the lung or pleura, or to a systemic disorder. Patients most commonly present with dyspnea, initially on exertion, predominantly dry cough, and pleuritic chest pain.
PDF Pleural Effusion Final - Handout.ppt - OSU Center for ... 5 Pathophysiology (contd.) Normal pleural fluid 0.1 to 0.2 ml/kg Clear Low protein (1.0 to 1.5 g/dl) < 1500 nucleated cells / L 61% to 77% monocytes-macrophages 9 to 30% mesothelial cells 7% to 11% lymphocytes 2% neutrophils 0% eosinophils pH > 7.60 Pathophysiology (contd.) Mechanism of abnormal pleural fluid formation Increasedhydrostaticpressure(CHF)Increased hydrostatic pressure (CHF)
Hypothyroidism Pleural Effusion Pathophysiology Diagram | CST Pleural effusion can be a complication of diaphragmatic hypothyroidism pleural effusion pathophysiology diagram, especially when the liver or omentum is incarcerated in the hernia. For gram-negative infections, add an aminoglycoside amikacinenrofloxacin, or trimethoprim-sulfadiazine.
The Pathophysiology of Pleural Effusions | Annual Review ... Two features of human parietal pleura explain its role in the formation and removal of pleural liquid and protein in the normal state: the proximity of the microvessels to the pleural surface and the presence of stomata situated between mesothelial cells. For pleural fluid to accumulate in disease, there must be increased production from increased hydrostatic pressure, decreased oncotic or ...
Pleural Effusion: Symptoms, Causes, Treatments Pleural effusion, sometimes referred to as "water on the lungs," is the build-up of excess fluid between the layers of the pleura outside the lungs. The pleura are thin membranes that line the lungs and the inside of the chest cavity and act to lubricate and facilitate breathing. Normally, a small amount of fluid is present in the pleura.
Pathophysiology | Pulmonary Embolism With large emboli; pleural friction rub, pleural effusion, fever, leukocytosis; Evaluation: Diagnosis can be made based on a patient's symptoms, medical history and a series of tests and scans. Clinical Decision Rules, such as the Well's Score, can guide diagnostics of suspected acute venous thromboembolism.
Pleura and pleural space Notes: Diagrams ... - Osmosis Chapter 128 Pleura & Pleural Space PLEURAL EFFUSION osms.it/pleural-effusion PATHOLOGY & CAUSES Excess fluid accumulates in pleural space Lung expansion limited → impaired ventilation Origin Hydrothorax (serous fluid), hemothorax (blood), urinothorax (urine), chylothorax/ lymphatic effusion (chyle), pyothorax (pus, AKA empyema) Pathophysiology Transudative pleural effusion Pressure driven ...


























0 Response to "42 pleural effusion pathophysiology diagram"
Post a Comment