41 in an aggregate expenditures diagram, a lump-sum tax (t) will
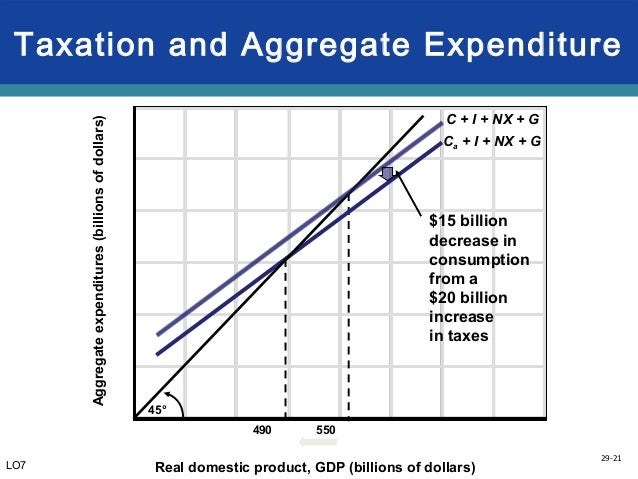
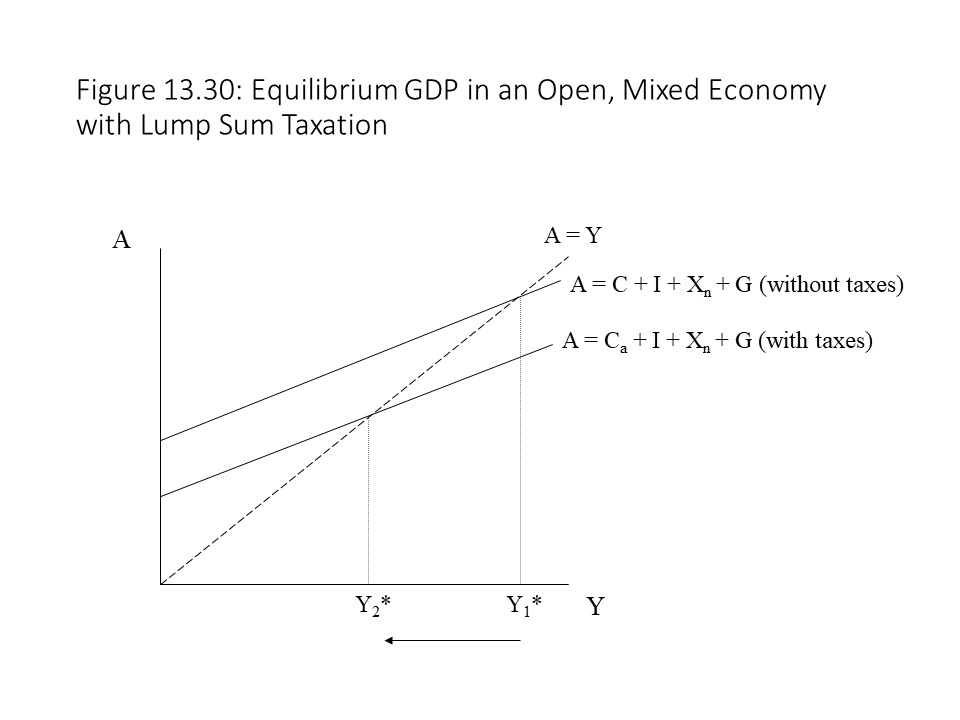
In a mixed open economy which of the following will affect ... In an aggregate expenditure diagram, C = a + c Y d , where the imposition of lump-sum tax decreases the disposable income. So a lump-sum tax shifts the C + I + X line downward by an amount equal to T * MPC, where MPC is denoted by 'c' and represents marginal propensity to consume. Answered: Planned expenditure function question… | bartleby Business Economics Q&A Library Planned expenditure function question with lump-sum tax Do all parts to the question (show your work) Assume in Fantasticland, MPC = 0.75, and autonomous consumption = $6000. %3D Planned investment = $2000, and planned government purchases = $5000. All Planned I and G are autonomous expenditures. Taxes ( T) is = $1000, and net exports = zero. %3D а.
Don't hesitate - Save time and Excel In an aggregate expenditure diagram a lump-sum tax (T) will :a)shift the C+Ig+Xn line upward by an amount equal Tb)shift the C+Ig+Xn line downward by an amount equal Tc)not affect the C+Ig+Xn lined) Shift the C+Ig+Xn line downward by an amount equal to T x MPC3 .
In an aggregate expenditures diagram, a lump-sum tax (t) will
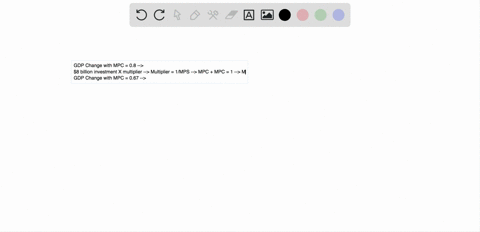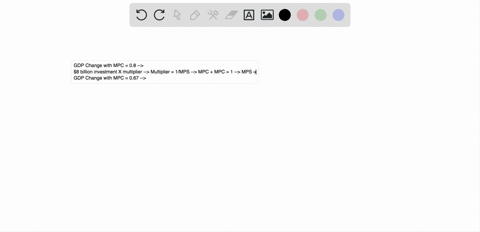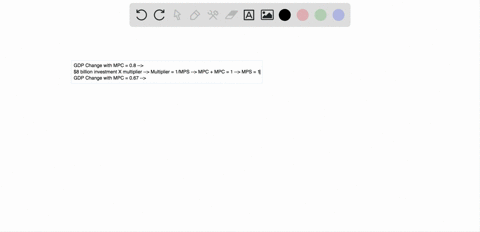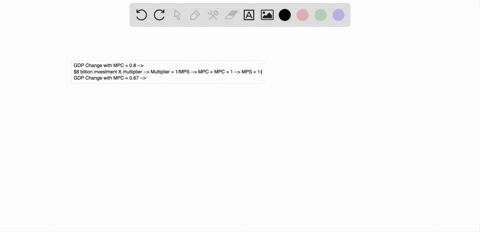
If a lump sum tax of 40 billion is imposed and the MPC is ... 182.In an aggregate expenditures diagram equal increases in government spending and in lump-sum taxes will: A. shift the aggregate expenditures line downward. B. shift the aggregate expenditures line upward. C. leave the aggregate expenditures line unchanged. D. reduce the equilibrium GDP. mbch10quiz If government increases lump-sum taxes by $20 billion and the economy's MPC is .6, then the: A. ... ln moving from a private closed to a mixed closed economy in the aggregate expenditures model, taxes: A. ... Refer to the above diagram. The Aggregate Expenditures Model - CAS The Investment Multiplier. The model of Aggregate Expenditures that we are currently considering is often called a Keynesian Model because it was first formulated by British economist John Maynard Keynes in his General Theory of Employment, Interest, and Money, published in 1936—at the height of the great depression. One of the central premises of Keynesian economics is the idea of a multiplier.
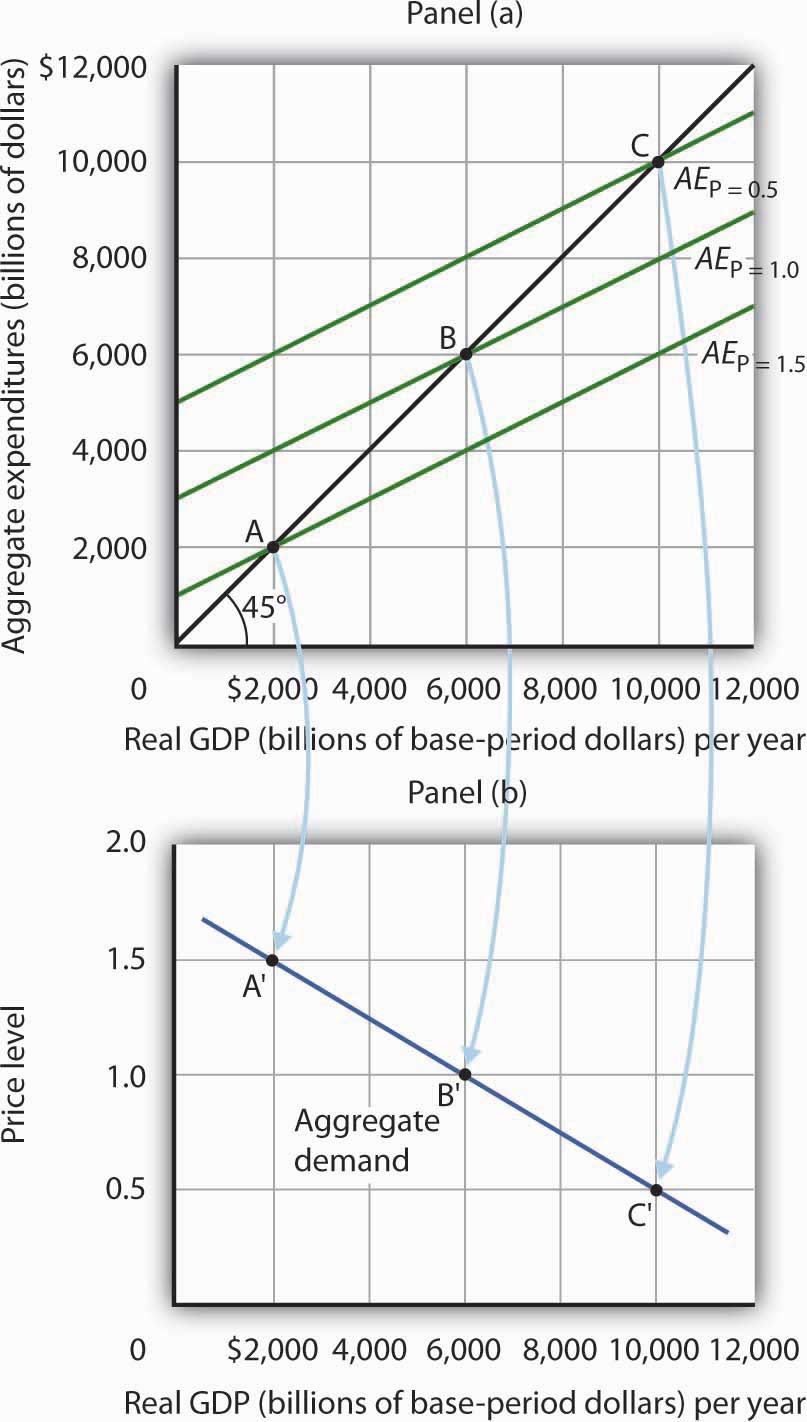
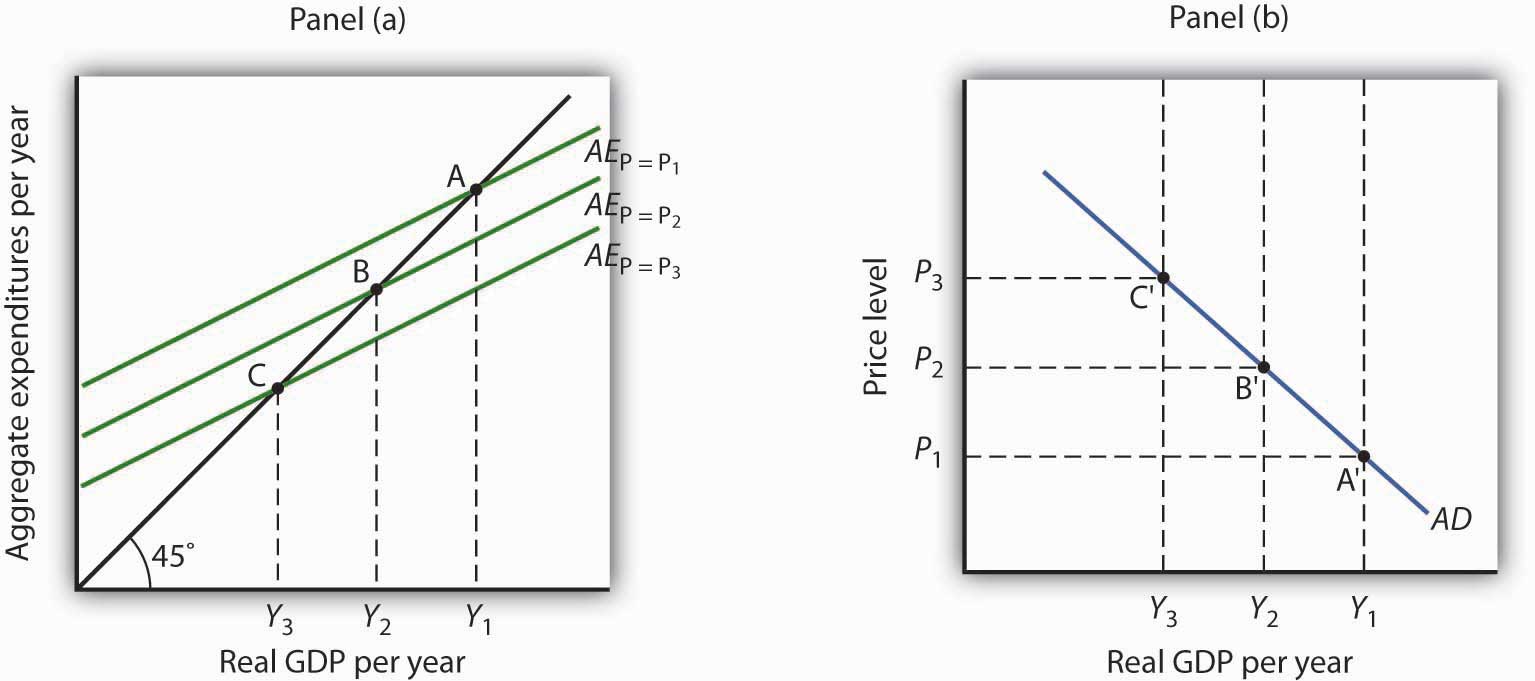
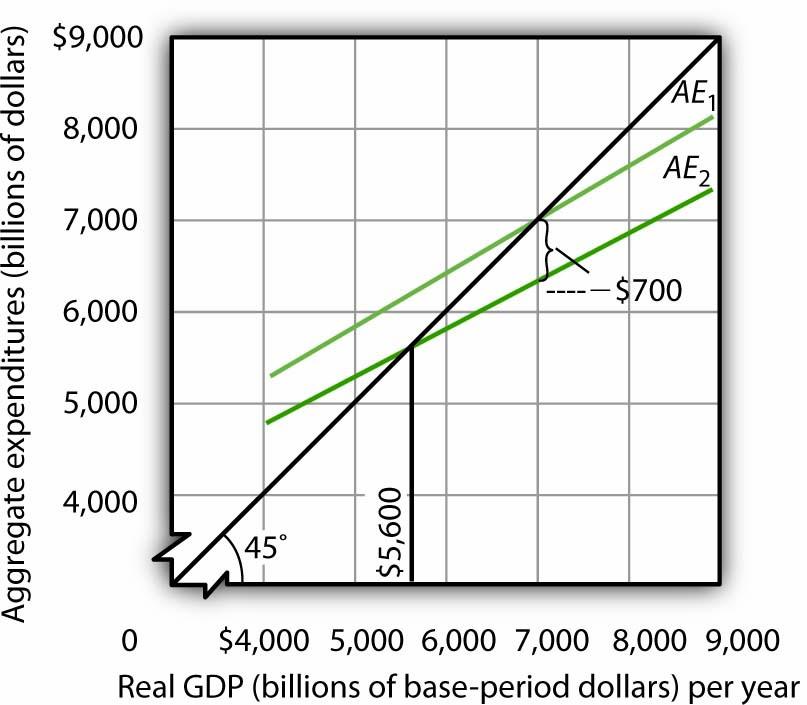
In an aggregate expenditures diagram, a lump-sum tax (t) will. Ch 11 economics - Subjecto.com In an aggregate expenditures diagram, a lump-sum tax (T) will. shift the C + Ig + Xn line downward by an amount equal to T × MPC. The effect of imposing a lump-sum tax is to. reduce the absolute levels of consumption and saving at each level of GDP but to not change the size of the multiplier Use the following to answer question 1 - Humble ISD In an aggregate expenditures diagram, a lump-sum tax (T) will: A) shift the C +1 + Xn line downward by an amount equal to T x MPC. B) shift the C +1 + Xn line upward by an amount equal to T. CHAPTER 9 MACRO TEST Flashcards - Quizlet In an aggregate expenditures diagram, a lump-sum tax (T ) will: a. not affect the C + Ig + Xn line. b. shift the C + Ig + Xn line upward by an amount equal to T. c. shift the C + Ig + Xn line downward by an amount equal to T. d. shift the C + Ig + Xn line downward by an amount equal to T × MPC. Click card to see definition 👆 D A8 Flashcards | Quizlet If government increases its tax revenues by $15 billion and the MPC is 2/3, then we can expect the equilibrium GDP to decrease by $30 billion. In an aggregate expenditures diagram, a lump-sum tax (T) will shift the C + Ig + Xn line downward by an amount equal to T × MPC.
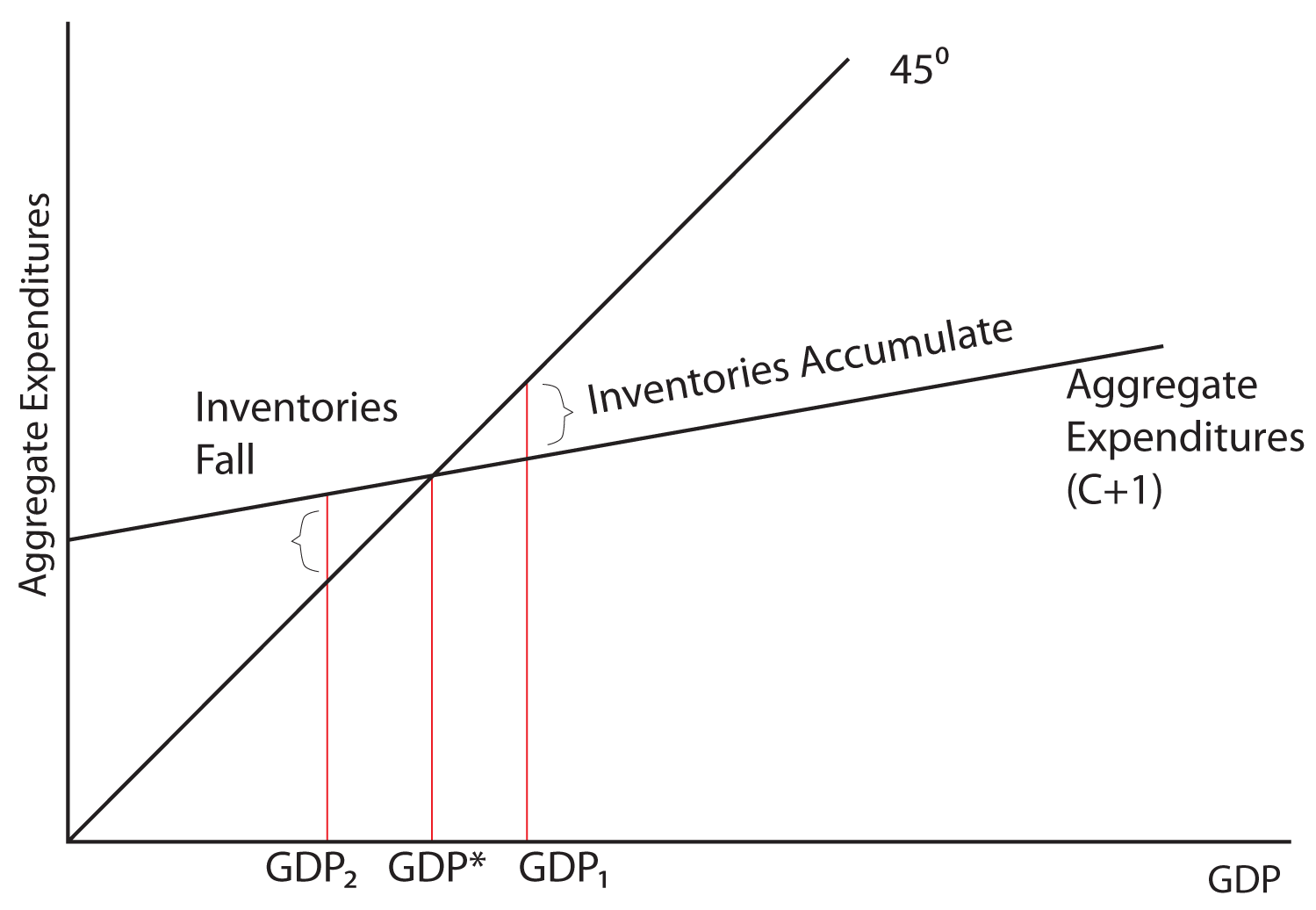
Econ chapter 11 Flashcards - Quizlet In an aggregate expenditures diagram, a lump-sum tax (T) will: $480 (Advanced analysis) If S = -60 + .25Y and Ig = 60, where S is saving, Ig is gross investment, and Y is gross domestic product (GDP), then the equilibrium level of GDP is: Wiring Diagram Trend in an aggregate expenditures diagram a lump-sum tax (t) will. 44 in an aggregate expenditures diagram, a lump-sum tax (t) will. Aggregate Expenditure: Investment, Government Spending ... Graphically, t… Written By Beth J. Reynolds March 15, 2022 Add Comment Edit. Chap 13 - University of Dayton By varying government expenditures and tax revenues, Congress can influence aggregate expenditure and economic activity. Keynesians are generally in favor of using fiscal policy to fine tune the economy. They point out that the most volatile component of aggregate demand is investment expenditure. quiz #3 Flashcards | Quizlet In an aggregate expenditures diagram, a lump-sum tax (T) will shift the C + Ig + Xn line downward by an amount equal to T × MPC. Suppose that unintended increases in inventories are occurring in a mixed closed economy.
Determination of National Income of a Country As found above, in the three sector economy with Government expenditure and lump-sum tax: Y = 1/1 - b (a - bT + I + G) where 7 is lump sum income tax. Now, a decrease in lump-sum income tax by ∆T will cause a change in income (that is, ∆Y). Increase in tax will reduce the disposable income and therefore the consumption demand. PDF Macro final exam study guide - True/False questions ... 5.If the MPC increases, the planned aggregate expenditure line on the Keynesian cross diagram becomes steeper. TRUE. 6.In a simple Keynesian model (with lump-sum taxes and a MPC of 0.8), if the government increases spending by $400 billion and increases taxes by $400 billion, output will increase by $400 billion. TRUE. Macro Q.5.docx - QUI Z IV 1. A lump-sum tax causes the ... In an aggregate expenditures diagram, a lump-sum tax (T) will: shift the C + I g + X n line downward by an amount equal to T × MPC. 17. An increase in taxes will have a greater effect on the equilibrium GDP: the larger the MPC. 18. In a private closed economy, when aggregate expenditures equal GDP: planned investment equals saving. 19. Homework for Chapter 10 10-2 (Key Question) What is the ... 10-3 Graphically depict the aggregate expenditures model for a private ... Assume now a lump-sum tax system is imposed such that the government collects.9 pages
The tax in the above economy is a A 10 percent ... 170.In an aggregate expenditures diagram, a lump-sum tax (T) will: A. not affect the C + I g + X n line. B. shift the C + I g + X n line upward by an amount equal to C. shift the C + I g + X n line downward by an amount equal to D. shift the C + I g + X n line downward by an amount equal to T × MPC. T. T.
Econ Chapter 11 Flashcards | Quizlet Lump Sum tax A tax of a constant amount/ a tax that yields the same amount of a tax revenue at each level of GDP. In an aggregate expenditures diagram, this will decrease C + Ig + Xn downward by an amount equal to it times MPC When government raises taxes it affects the aggregate expenditures in a public open economy by:
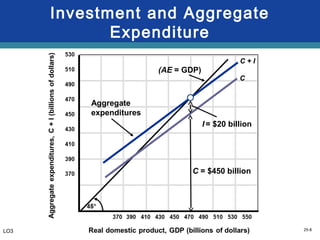
28.2 The Aggregate Expenditures Model - Principles of ... Equation 28.11 is the algebraic representation of the aggregate expenditures function. We shall use this equation to determine the equilibrium level of real GDP in the aggregate expenditures model. It is important to keep in mind that aggregate expenditures measure total planned spending at each level of real GDP (for any given price level).
Solved Refer to the diagram for a private closed economy ... D. Disposable income will decline by the amount of the tax and consumption at each level of GDP will decline by the amount of the tax multiplied by the MPC. 14. In an aggregate expenditures diagram, a lump-sum tax (T) will: A. not affect the C + I g + X n line. B. shift the C + I g + X n line upward by an amount equal to T.
PDF Macro Exam 2 Self Test -- T/F questions Dr. McGahagan Fill ... _____5.If the MPC increases, the planned aggregate expenditure line on the Keynesian cross diagram becomes flatter. _____6.In a simple Keynesian model (with lump-sum taxes and a MPC of 0.8), if the government increases spending by $400 billion and increases taxes by $400 billion, output will increase by $2000 billion.
PDF Macro final exam test bank - T/F questions Note that these ... 4.If investment increases, the planned aggregate expenditure line on the Keynesian cross diagram shifts upward 5.If the MPC increases, the planned aggregate expenditure line on the Keynesian cross diagram becomes flatter. 6.In a simple Keynesian model (with lump-sum taxes and a MPC of 0.8), if the government increases spending
Ch 11 economics - StudyHippo.com If a lump-sum tax of $40 billion is imposed and the MPC is .6, the saving schedule will shift. answer. downward by $16 billion. ... In an aggregate expenditures diagram, a lump-sum tax (T) will. answer. shift the C + Ig + Xn line downward by an amount equal to T × MPC. question. The effect of imposing a lump-sum tax is to.
Solved In an aggregate expenditures diagram, a lump-sum tax Economics. Economics questions and answers. In an aggregate expenditures diagram, a lump-sum tax (7) will 26 Multiple Choice shift the C+19+ Xnline downward by an amount equal to T. O shift the C+ lg* Xnline downward by an amount equal to TX MPC shift the C+/Xline upward by an amount equal to T.
In an aggregate expenditures diagram equal increases in ... 197. In an aggregate expenditures diagram equal increases in government spending and in lump-sum taxes will: A) shift the aggregate expenditures line downward. C) not affect the aggregate expenditures line. B) shift the aggregate expenditures line upward. D) reduce the equilibrium GDP. Answer: B Type: A Topic: 4 E: 185 MA: 185 198.
Determination of National Income in Three-Sector Economy Another method for calculating B m is by adding up the G m and T m, described as follows: B m = G m + T m. B m = 1/1-b + -b/1-b. B m = 1. The value of balanced budget multiplier (B m) is one. This implies that the change in national is exactly equal to the change in government expenditure and taxes simultaneously. Proportional Income Tax and ...
In an aggregate expenditures diagram, equal increases in ... In an aggregate expenditures diagram, equal increases in government spending and in lump-sum taxes will A)shift the aggregate expenditures line downward. B)shift the aggregate expenditures line upward. C)leave the aggregate expenditures line unchanged. D)reduce the equilibrium GDP.
Intermediate Macroeconomics - The Keynesian Model We begin with an accounting definition for aggregate expenditures because this is the heart of the Keynesian model. We will convert the accounting identity for aggregate expenditures into a model by first proposing an equilibrium condition in which aggregate output equals aggregate expenditures. ... T 0 = lump sum tax t = income tax rate ...
The Aggregate Expenditures Model - CAS The Investment Multiplier. The model of Aggregate Expenditures that we are currently considering is often called a Keynesian Model because it was first formulated by British economist John Maynard Keynes in his General Theory of Employment, Interest, and Money, published in 1936—at the height of the great depression. One of the central premises of Keynesian economics is the idea of a multiplier.
mbch10quiz If government increases lump-sum taxes by $20 billion and the economy's MPC is .6, then the: A. ... ln moving from a private closed to a mixed closed economy in the aggregate expenditures model, taxes: A. ... Refer to the above diagram.
If a lump sum tax of 40 billion is imposed and the MPC is ... 182.In an aggregate expenditures diagram equal increases in government spending and in lump-sum taxes will: A. shift the aggregate expenditures line downward. B. shift the aggregate expenditures line upward. C. leave the aggregate expenditures line unchanged. D. reduce the equilibrium GDP.
















0 Response to "41 in an aggregate expenditures diagram, a lump-sum tax (t) will"
Post a Comment