37 free body diagram terminal velocity
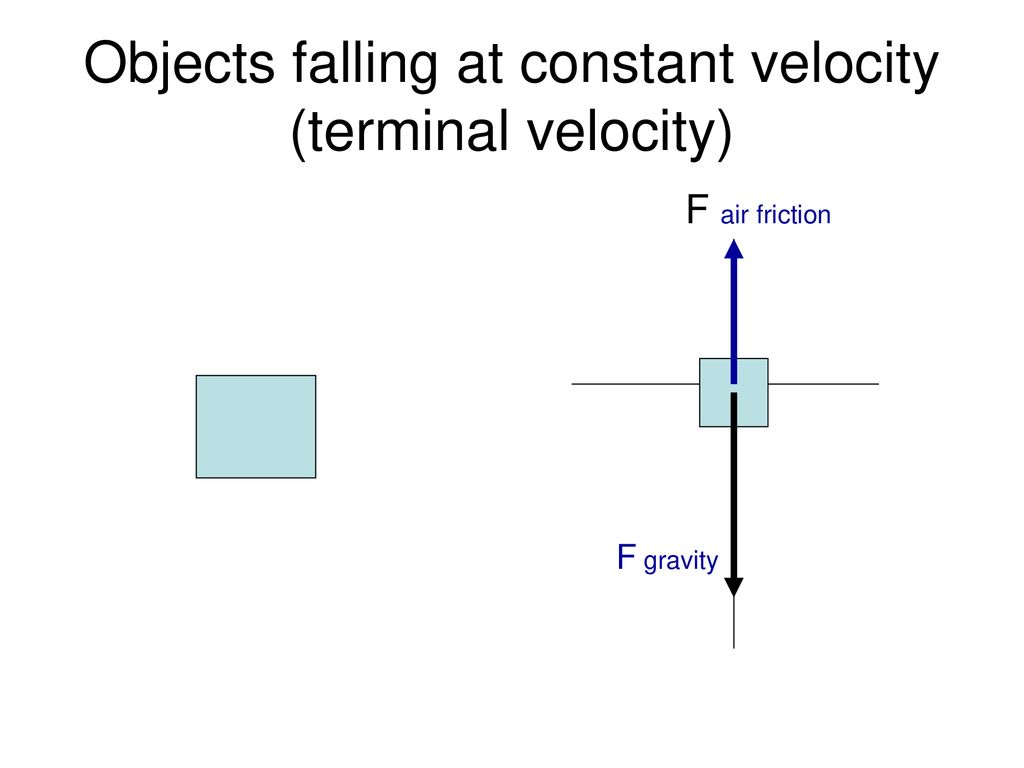
I have been testing out the Aerodynamic Physics (Deadly Reentry + Drag + Flight) mod, and i have been having some trouble with speeds. I am playing with a speed mod allowing me to fly 360 m/s usually, but no mather how aerodynamic i make my builds they won't go any faster than 120 m/s. Any advice on how to raise this speed? Draw a free body diagram of a meteor that is falling towards earth at terminal velocity. F air F gravity Net Force = 0 N The meteor is falling down, but its net force is 0 N! There is no acceleration!
Hi! I haven't taken a physics course before but my roommate has - during recent discussions the topic of surface tension and falling came up. Specifically we disagreed over the outcome of a car falling off of a bridge. My intuition tells me that the car (and any passengers inside) would be better off hitting the water at a slower speed, regardless of if they were still accelerating as they fell. My roommate, if I understood them correctly, contended that the impact force was somehow related to t...

Free body diagram terminal velocity
Free Body Diagrams a.k.a. Force Diagrams Free Body Diagram A free body diagram is a picture representation of all forces acting on an object. We use arrows to represent the forces and indicate their direction and magnitude. Magnitude expressed by number and arrow size. Transcribed image text: Nora has just parachuted out of an airplane(t), and she and her parachute have reached a constant terminal velocity. The free-body diagram for Nora and the parachute shown below is correct, and includes the weight force and a drag force due to air resistance (which acts a lot like friction). Explanation: This is because at terminal velocity, the ball stops accelerating and the net force on the ball is zero. For the net force to be zero, equal and opposite forces must act on the ball, so that their resultant force is zero. That is F₁ + F₂ = 0 ⇒ F₁ = -F₂ Since F₁ = 20 N, then F₂ = -F₁ = -20 N
Free body diagram terminal velocity. A free-body diagram is a diagram that is modified as the problem is solved. Normally, a free body diagram consists of the following components: The number of forces acting on a body depends on the specific problem and the assumptions made. Commonly, air resistance and friction are neglected. Terminal velocity and free fall are two related concepts that tend to get confusing because they depend on whether or not a body is in empty space or in a fluid (e.g., an atmosphere or even water). Take a look at the definitions and equations of the terms, how they are related, and how fast a body falls in free fall or at terminal velocity under different conditions. Drawing Free-Body Diagrams. Free-body diagrams are diagrams used to show the relative magnitude and direction of all forces acting upon an object in a given situation. A free-body diagram is a special example of the vector diagrams that were discussed in an earlier unit. These diagrams will be used throughout our study of physics. "The terminal velocity of a falling human being with arms and legs outstretched is about 120 miles per hour (192 km per hour) — slower than a lead balloon, but a good deal faster than a feather!" 53 m/s: The terminal velocity of a falling body occurs during free fall when a falling body experiences zero acceleration. This is because of the ...
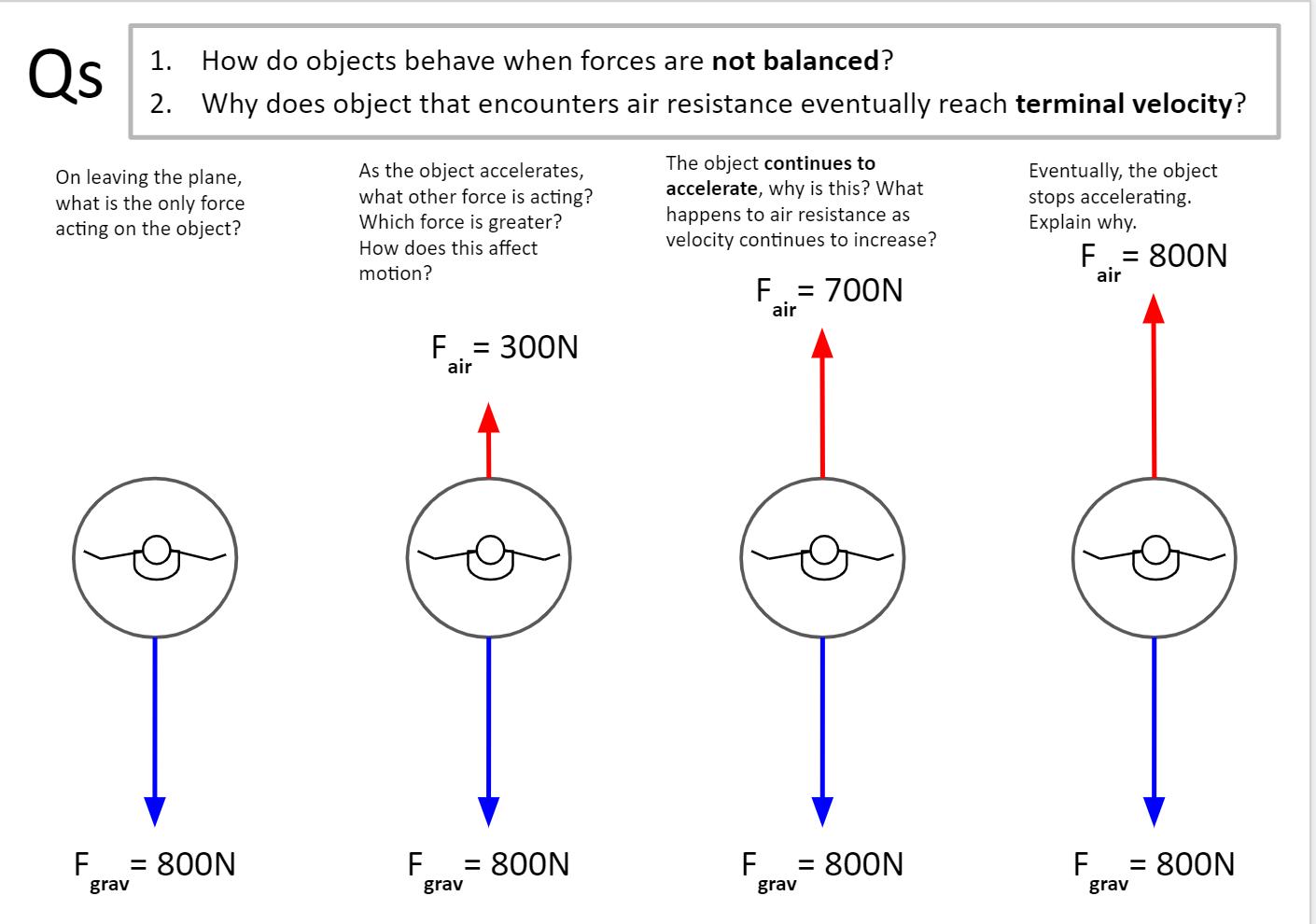
Your free body diagram is correct, The object isnt at constant velocity though, because it is being accelerated by gravity. The net force on the object is gravity. If there is no net force, or the net force = 0, then the velocity is constant. Im sorry I can't explain this better to you. Mar 24, 2005 #11 ramollari 437 1 jen333 said: AH!! I see.... For example, if I was dropped out of a plane and my starting velocity is higher than my terminal velocity would I eventually decelerate to terminal velocity? The free-body diagram of this object with the positive direction downward is shown in Figure. Newton's second law in the vertical direction gives the differential equation mg−bv = mdv dt, m g − b v = m d v d t, where we have written the acceleration as dv/dt. d v / d t. As v increases, the frictional force - bv increases until it matches mg. I recently saw the movie Crank where the main character had to constantly engage or intake adrenaline to slow down a mortal injection of poison of some sort. Spoiler Alert: >!In the end he fell from the sky at an incredible height (like a few miles) with no parachute with his back pointing nadir. He falls on the roof of a VW car and bounces up quite a distance (maybe 25 feet).!< Obviously that's all fiction. But I was wondering if it was real, would he really bounce? And to make the cal...
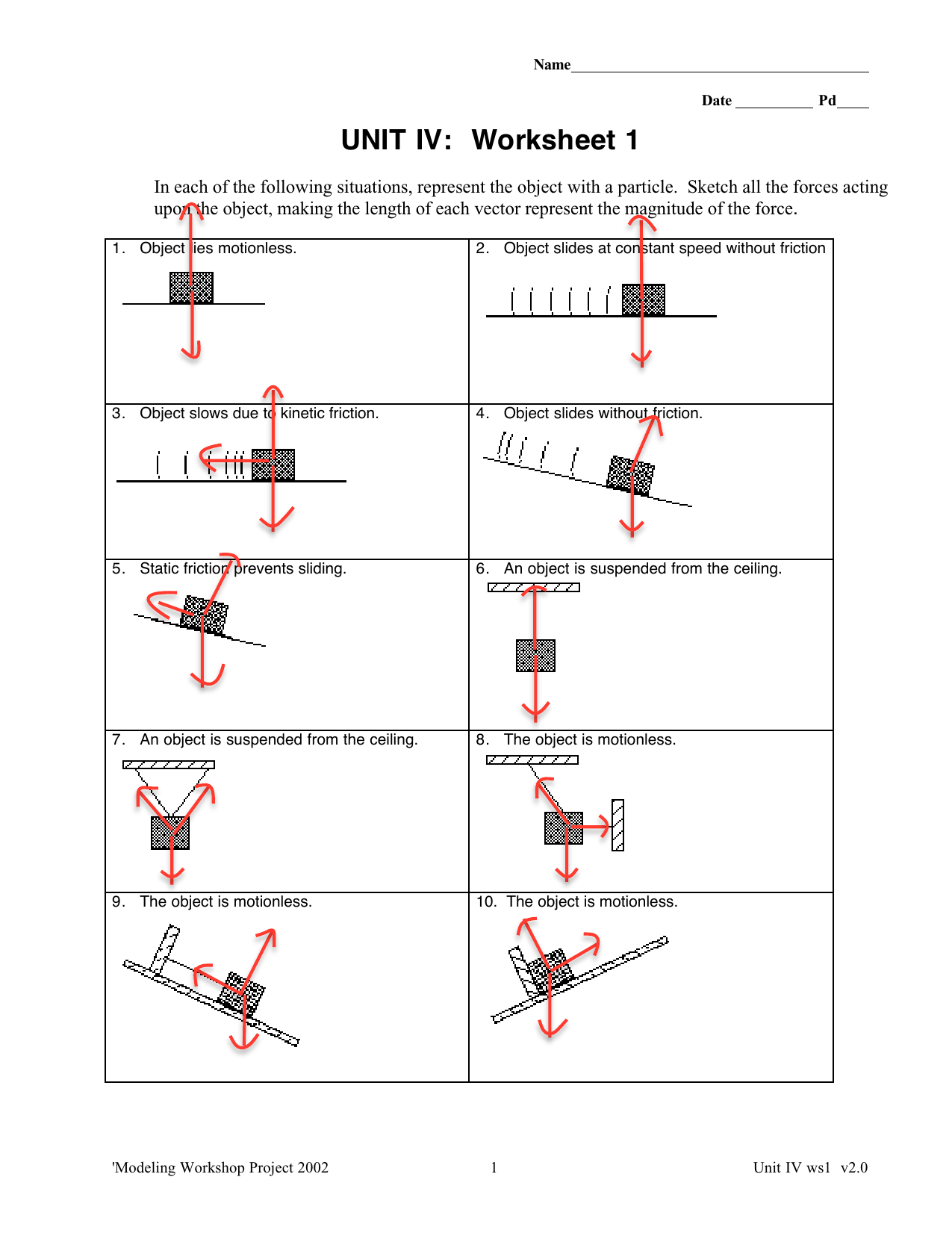
Worksheet #1 Free Body or Force diagrams… Drawing Free-Body Diagrams . Free-body diagrams are diagrams used to show the relative magnitude and direction of all forces acting upon an object in a given situation. A free -body diagram is a special example of the vector diagrams; these diagrams will be used throughout your study of physics. PhysicsLAB: Freebody Diagrams. In each case, a rock is acted on by one or more forces. On a sheet of paper, draw an accurate vector diagram showing all forces acting on the rock, and no other forces. Use a ruler, and do it in pencil so you can correct mistakes. Refer to the following information for the next two questions. A free body diagram (FBD) is a tool that helps us understand the total effect of all the forces acting on an object. There are a few steps that you should ... Terminal Velocity A rock is falling at a constant speed. This is called the object's terminal velocity. 1. Draw a FBD. He's landing on concrete
With a net force of zero the skydiver must be in , but they are not in because they are not static (motionless). Instead they are in , which means that they are moving, but the motion isn’t changing because all the forces are still balanced (net force is zero). This concept is summarized by , which tells us that an object’s motion will notchange unless it experiences a net force. Newton’s first law is sometimes called the Law of Inertia because is the name given to an object’s tendency to resist changes in motion. applies to objects that are not moving and to objects that are already moving. Regarding the skydiver, we are applying Newton’s First Law to (back and forth, up and down), but it also holds for the effect of on changes in rotational motion. Changes in motion are known as accelerations and we will learn more about how net forces cause translational accelerations in upcoming chapters.
A free-body diagram is a representation of an object with all the forces that act on it. The external environment (other objects, the floor on which the object sits, etc.), as well as the forces that the object exerts on other objects, are omitted in a free-body diagram. Below you can see an example of a free-body diagram:
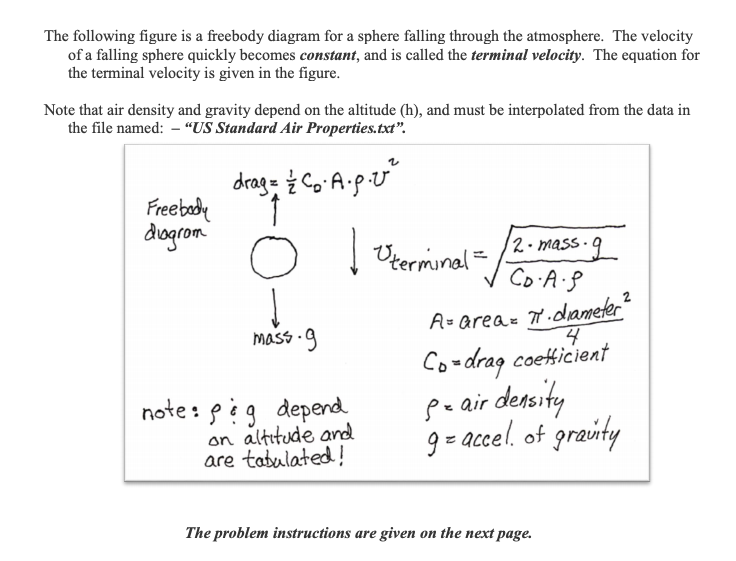
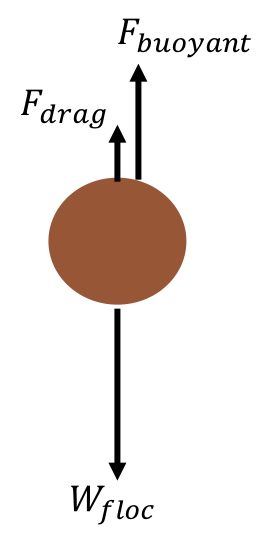
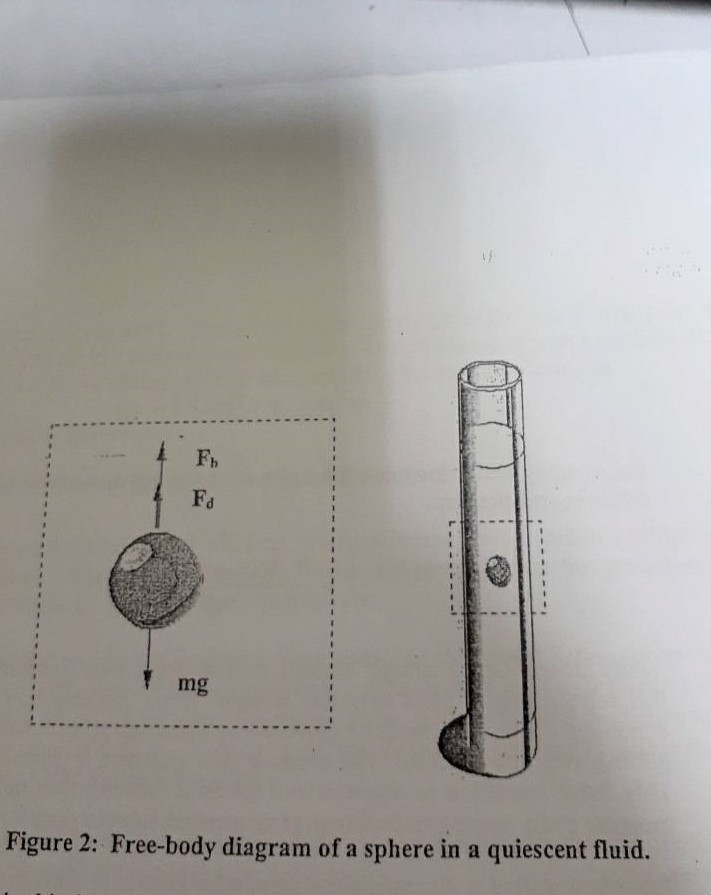
Draw the free body diagram for the sphere when it is falling at its terminal velocity. Derive a simple equation for the expected terminal velocity, in terms of the sphere's diameter D, the sphere's density Pshp and the fluid's density Pfluid. (7) Question: Question B2 Consider a sphere falling in a liquid.
Cheers fellas.
What situation does a free body diagram illustrate? A)The skydiver has landed on the ground. B) The skydiver has just jumped from the plane and hasn't released his parachute. C)The skydiver hasn't deployed his parachute and is falling at terminal velocity D) The skydiver has opened his parachute and is falling toward the ground at a constant ...
A ball is falling at terminal velocity. Which free body diagram shows the ball falling at termainal velocity 2 See answers Heyitsdaedae Heyitsdaedae so I hope that diagram gives u a great view at it nessa314 nessa314 Hey guys! I just took the quiz and the correct answer is the picture below!
Correct answers: 2 question: A ball is falling at terminal velocity. Terminal velocity occurs when the ball is in equilibrium and the forces are balanced Which free body diagram shows the ball falling at terminal velocity? F 20 N air F 5N air F, 20 N F, 20 N F 20 N ca O F 30 N
Air Resistance Questions questions make two free body diagrams for falling coffee filter: one at the instant when it is released and the other after it is Sign inRegister Sign inRegister Home My Library Courses You don't have any courses yet. Books You don't have any books yet. Studylists You don't have any Studylists yet. Recent Documents
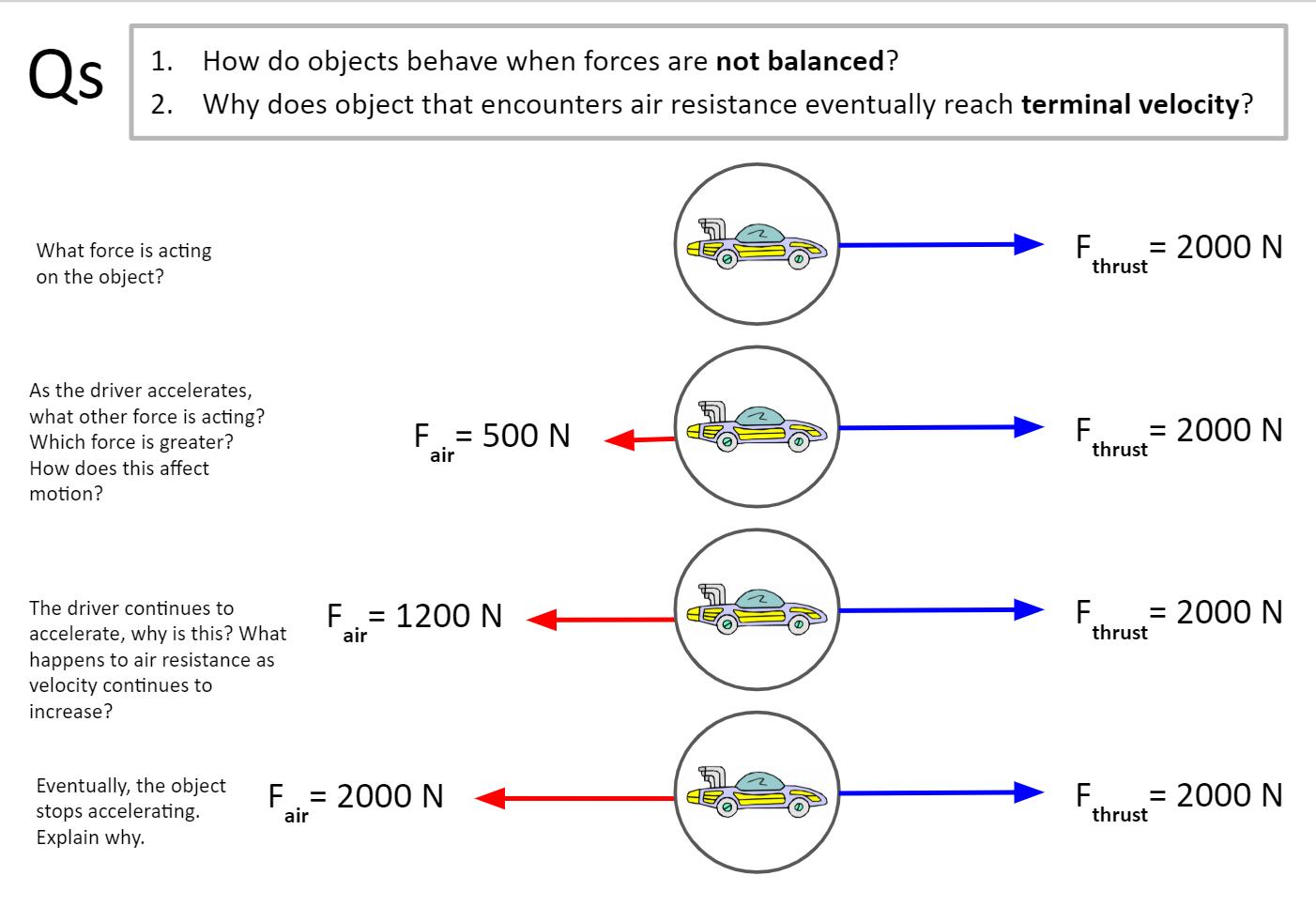
In a previous unit, it was stated that all objects (regardless of their mass) free fall with the same acceleration - 9.8 m/s/s. This particular acceleration value is so important in physics that it has its own peculiar name - the acceleration of gravity - and its own peculiar symbol - g. But why do all objects free fall at the same rate of acceleration regardless of their mass? Is it because they all weigh the same? ... because they all have the same gravity? ... because the air resistance is the same for each? Why? These questions will be explored in this section of Lesson 3.
Which free body diagram shows the ball falling at terminal velocity? A free body diagram with one force pointing downward labeled F Subscript g Baseline 20 N. A free body diagram with 2 forces: the first pointing downward labeled F Subscript g Baseline 20 N and the second pointing upward labeled F Subscript air Baseline 20 N.
approaching terminal velocity. Students will be able to draw free-body diagrams for objects falling in the presence of air objects approaching terminal velocity, and objects falling at terminal velocity. Students will be able to draw free-body diagrams depicting that a greater force of air resistance is required to balance out the greater
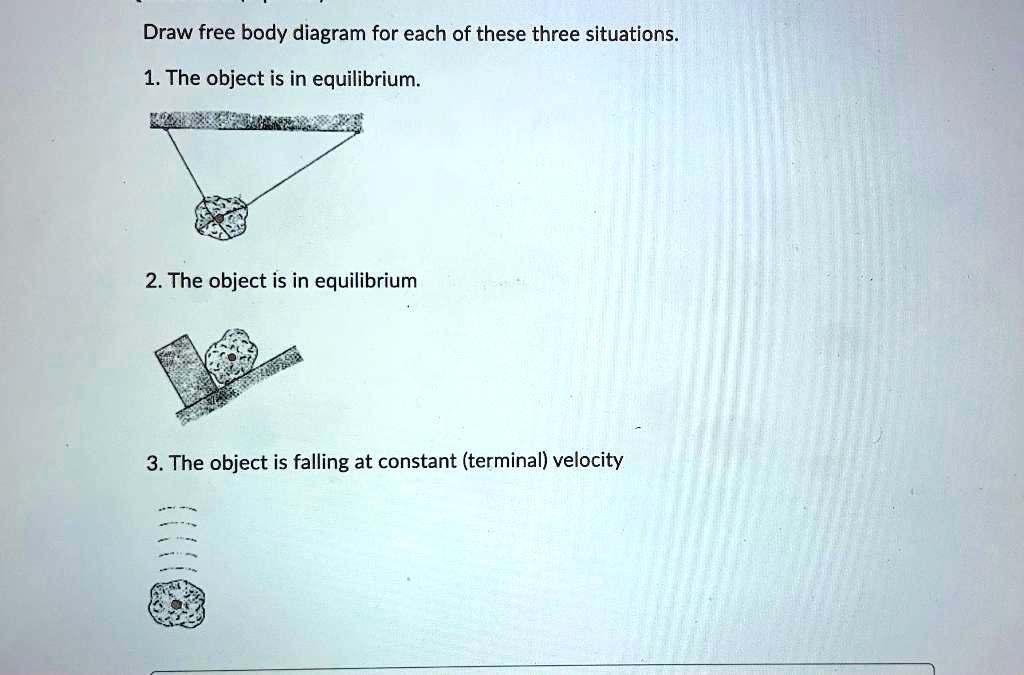
Construct free-body diagrams for the various situations described below. 1. A book is at rest on a table top. Diagram the forces acting on the book. 2. A girl is suspended motionless from a bar which hangs from the ceiling by two ropes. Diagram the forces acting on the girl. 3. An egg is free-falling from a nest in a tree. Neglect air ...
Free Body Diagrams. A free body diagram shows all the vector forces and their direction acting on an object; The dot in the middle represents the object; ... Terminal velocity is the point when a persons weight equals the air resistance force. At terminal velocity: There is no net force F air = -F w;
obtaining its orthogonal components from each velocity component. Figure 1 shows the free body diagram of the idealized skydiver a few seconds after leaving the airplane. The system of coordinates chosen associates the x direction with the horizontal and y direction with the vertical.
Figure 5.32 (a) The free-body diagram for isolated object A. (b) The free-body diagram for isolated object B. Comparing the two drawings, we see that friction acts in the opposite direction in the two figures. Because object A experiences a force that tends to pull it to the right, friction must act to the left. Because object B experiences a component of its weight that pulls it to the left ...
Edit: Seems my misconception stemmed from not factoring in thin atmosphere = less resistance/higher velocity on the way down. Thanks everyone!
If so, how would one calculate it?
lets say you were falling into the ocean but you were in the middle of a gigantic raindrop. When the raindrop hits the ocean, I am assuming the surface tension issue goes away because you are now basically already in the ocean as the ocean merges with the droplet, and you just begin to decelerate without "hitting" anything.
A 5 kg mass is being pushed across a rough table at a constant velocity by a constant force, F = 15 N, which acts at an angle θ = 37º to the horizontal. What is the magnitude of the frictional force? The numerical value of the normal now equals 40 N 49 N 58 N 61 N What is the coefficient of friction between the mass and the surface?
velocity of the sphere relative to the fluid, and d is the diameter of the sphere. Using this equation, along with other well-known principle of physics, we can write an expression that describes the rate at which the sphere falls through a quiescent, viscous fluid. To be begin we must draw a free body diagram (FBD) of the sphere. That is we must
Construct free-body diagrams for the following physical situations. Label all forces (e.g, Fgrav, Fnorm, Fapp, Ffrict, Fair, Ftens, etc. ). a. A physics book rests upon a level table. b. A skydiver is falling and has reached a terminal velocity. c. A large crate is being pushed leftward at a constant velocity. d. A sledder has reached
Explanation: This is because at terminal velocity, the ball stops accelerating and the net force on the ball is zero. For the net force to be zero, equal and opposite forces must act on the ball, so that their resultant force is zero. That is F₁ + F₂ = 0 ⇒ F₁ = -F₂ Since F₁ = 20 N, then F₂ = -F₁ = -20 N
Transcribed image text: Nora has just parachuted out of an airplane(t), and she and her parachute have reached a constant terminal velocity. The free-body diagram for Nora and the parachute shown below is correct, and includes the weight force and a drag force due to air resistance (which acts a lot like friction).
Free Body Diagrams a.k.a. Force Diagrams Free Body Diagram A free body diagram is a picture representation of all forces acting on an object. We use arrows to represent the forces and indicate their direction and magnitude. Magnitude expressed by number and arrow size.






















0 Response to "37 free body diagram terminal velocity"
Post a Comment