41 free body diagram of a pulley
Free Body Diagram Examples. Now we will explain the FBD concept, using the following free body diagram example problem as shown in Fig. 1. A 50 kg stationary box must be pulled up a 30 degree inclined by a pulley system. Free-Body Diagram Example Problem 3 Bank robbers have pushed a 1000 [kg] safe to a second-story floor-to-ceiling window. They plan to break the window, then lower the safe 4.0 [m] to their truck. Not being too clever, they stack up 600 [kg] of furniture, tie the rope between the safe and the furniture, and place the rope over a pulley.
Using the pulley system illustrated to the right below as an example, the basic method for discussed. As in Lessons 15, 16 and 17, the basic method is to draw a free body diagram of the forces involved, write an expression for the net force, and then solve for the acceleration. In a pulley system two masses are strung over a pulley. Note that ...

Free body diagram of a pulley
Pulley#1 Pulley#2 Do a free body diagram on Pulley #2. Find the tension on each string. Ü L L. Ù H. á L Û° F Ú° L Ù Û° E Ú° L Ü L Û L Ú. Û Ù Ú. Û Ù Ú H Ù. à ß ß E Ú H Ù. ß Ý Û L Ú L. , Û L. A 5.0‐kg block is placed on top of a 10‐kg block. A horizontal force Pulleys and Tension ProblemSum of Forces in Inclined Frames of ReferencePulleys, Tension, and Extension SpringsForces Subscripts ConvectionTwo-Force Members... FREE-BODY DIAGRAMS (Section 5.2) 2. Show all the external forces and couple moments. These typically include: a) applied loads, b) support reactions, and, c) the weight of the body. Idealized model Free-body diagram (FBD) 1. Draw an outlined shape. Imagine the body to be isolated or cut "free" from its constraints and draw its outlined shape.
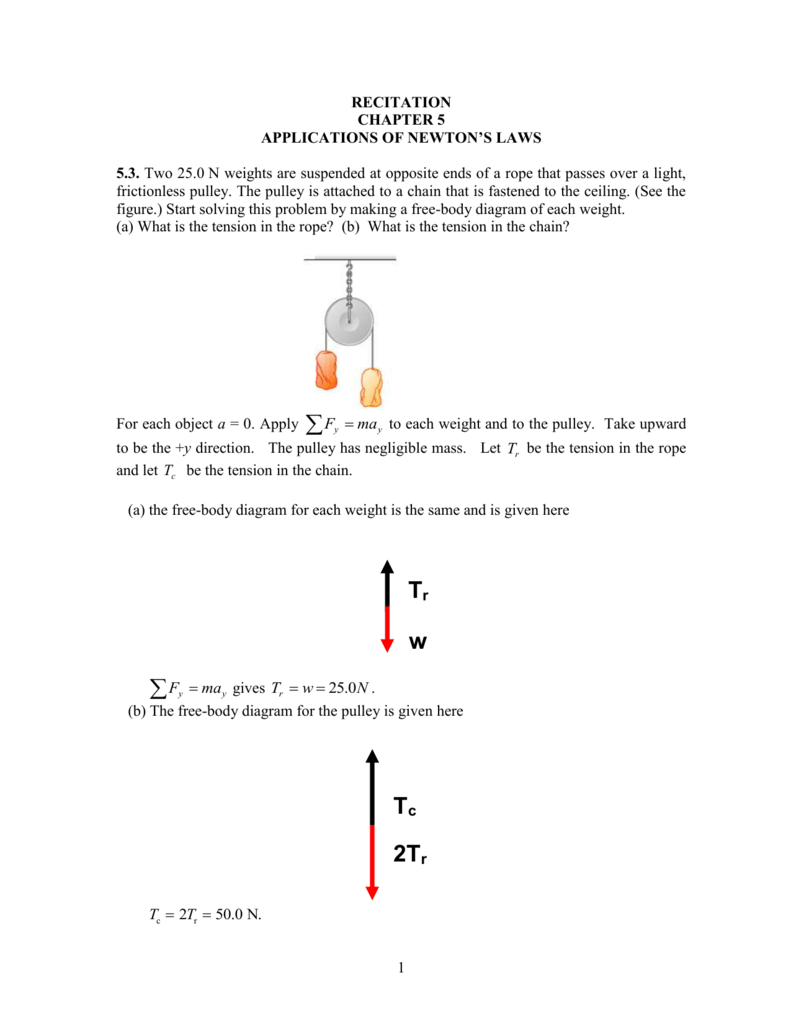
Free body diagram of a pulley. Figure 5.32 (a) The free-body diagram for isolated object A. (b) The free-body diagram for isolated object B. Comparing the two drawings, we see that friction acts in the opposite direction in the two figures. Because object A experiences a force that tends to pull it to the right, friction must act to the left. Because object B experiences a component of its weight that pulls it to the … • Free Body Diagram Establish your coordinate system and draw the particle’s free body diagram showing only external forces. These external forces usually include the weight, normal forces, friction forces, and applied forces. Show the ‘ma’vector (sometimes called the inertial force) on a separate diagram. Free body diagrams The mechanical advantage of a pulley system can be analysed using free body diagrams which balance the tension force in the rope with the force of gravity on the load. In an ideal system, the massless and frictionless pulleys do not dissipate energy and allow for a change of direction of a rope that does not stretch or wear. Figure 5.6: A diagram for the system of two objects and a pulley. Figure 5.7: Free-body diagrams if there is no friction. (a) The free-body diagram of the red box. (b) An appropriate coordinate system for the red box. (c) The free-body diagram of the red box, with force components aligned with the coordinate system. (d) and (e), a
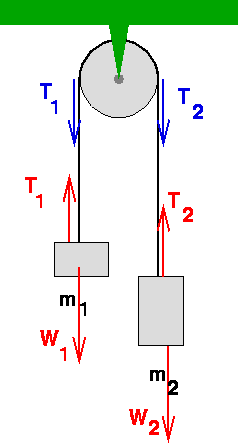
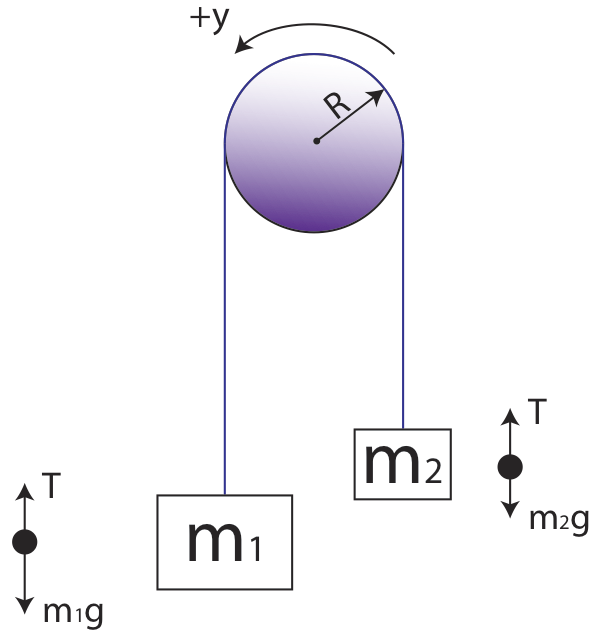
placed over a pulley as indicated in the diagram below. There are TWO free-body diagrams since there are two masses in this problem. M 1 M 2 Pulley X Y W 1 T 1 W 2 T 2 Free-Body Diagram for M 1 Free-Body Diagram for M 2 i) W 1 is the force of gravity on mass M 1 and W 2 is the force of gravity on mass M 2. W 1 = M 1 g and W 2 =M 2 g. ii) T 1 is ... Analyzing it with free-body diagrams (for me the most complicated subject in mechanics I can think of) is at least tricky if not impossible. ... For a pulley aligned with the coordinate system and a 90 degree turn, a different diagonal element will then have the ##-T## term]. 14.12.2021 · Neither of these scenarios look much like a "pulley" to me - they look like spools. Neither are stable/in equilibrium. Are they free-floating in space? I don't see how you can "pre-load" something that isn't fixed. Anyway, no, the two scenarios are not equivalent: the torques applied to the spool are different. 5,112. sysprog said: Yes, the first drawing is in incorrect; the second diagram is a free-body diagram; there is no real apparatus involved -- it's an abstraction; your remark about Physics seems to me to be overly restrictive. A free body diagram has one free body and depicts all of the forces acting on that body.
To further test your understanding of free-body diagrams, see our force problems, which include problems where you need to draw free-body diagrams of objects that move up an incline, hang from ropes attached to the ceiling, and hang from ropes that run over pulleys. For each problem, we provide a step-by-step guide on how to solve it. 21.12.2021 · By definition, the orbit (bony orbit or orbital cavity) is a skeletal cavity comprised of seven bones situated within the skull.The cavity surrounds and provides mechanical protection for the eye and soft tissue structures related to it.. The bones that make up the orbit contain several foramina and fissures through which important neurovascular structures (such as the optic … Figure 5.32 (a) The free-body diagram for isolated object A. (b) The free-body diagram for isolated object B. Comparing the two drawings, we see that friction acts in the opposite direction in the two figures. Because object A experiences a force that tends to pull it to the right, friction must act to the left. Because object B experiences a component of its weight that pulls it to the left ... Because the string is assumed to be massless and the pulley is assumed to be massless and frictionless, the tension T A in the string is uniform and equal in magnitude to the pulling force of the string on the block. The free-body diagram on block 1 is shown in Figure 8.41(a). 1 2 . 3 P (a) (b) (c) (d) ˆ j T A ,1 B m 1 g ,2 m 2 g T B
Use the free body diagram of the pulley (Figure 4) to answer the Pre-Lab Questions. 1. Draw a free body diagram for M1. 2. Draw a free body diagram for M2. 3. Apply Newton's 2nd Law to write the equations for M1 and M2. You should get two equations with Tension in the string, weight for each mass and accelerations for each mass (a1.
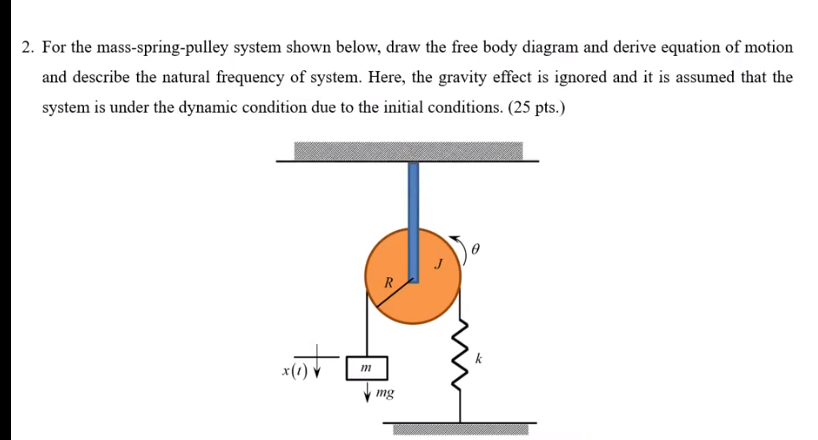
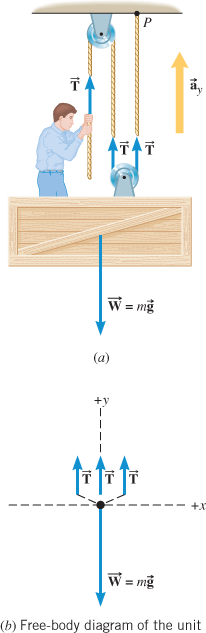
• Free body diagram for each element ... • Assume that the pulley is ideal –No mass and no friction –No slippage between cable and surface of cylinder (i.e., both move with same velocity) –Cable is in tension but does not stretch • Draw FBDs and write equations of motion
From the perspective of a free-body diagram the compound pulley system could be replaced by tying two ropes to the load and pulling up on each with a force equal to the effort. The disadvantages of pulleys, in contrast to machines that use rigid objects to transfer force, are slipping and stretching.
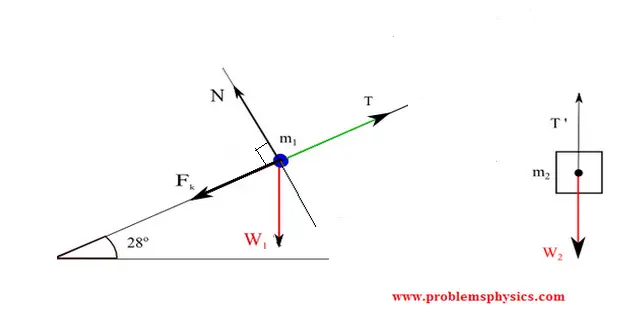
The free-body diagrams for the two objects are shown below. Because the parallel component of gravity on m 1 exceeds the sum of the force of gravity on m 2 and the force of friction, the mass on the inclined plane (m 1 ) will accelerate down it and the hanging mass (m 2 ) will accelerate upward.
Department of Mechanical Engineering Force equilibrium (mechanical eql.) (Mechanical) equilibrium requires that the concurrent forces that act on the body satisfy The particle in a equilibrium system must satisfy Since both must be satisfied, the material point then must have zero acceleration, a = 0 R =∑F =0 R =∑F =m.a
Step 2 – Draw a free-body diagram of the pulley. A complete free-body diagram of the pulley, shown in Figure 11.3 (a), reflects that fact that the center-of-mass of the pulley remains at rest, so the net force must be zero. There is still a non-zero net torque, about an axis through the center of the pulley and perpendicular to the page,
free-body-diagrams. T From the above discussions, we have the three equations: This is less than that in case 1 as we predicted. 9. Atwood's machine. Atwood's machine involves one pulley, and two objects connected by a string that passes over the pulley. In general, the two objects have different masses. a a. 10. Re-analyzing the Atwood's ...
Coordinate systems and Common acceleration - Pulley in Physics. For an ideal pulley, the tension is the same throughout the rope (therefore the same symbol T in both diagrams). This is generally a common consideration for pulley tension problems. The acceleration a of each subject is indicated. The cart accelerates to the right when the ...
Download scientific diagram | (a) A two-pulley belt drive. (b) Free body diagrams of the belt on the driver and driven pulleys from publication: Microslip friction in flat belt drives | The ...
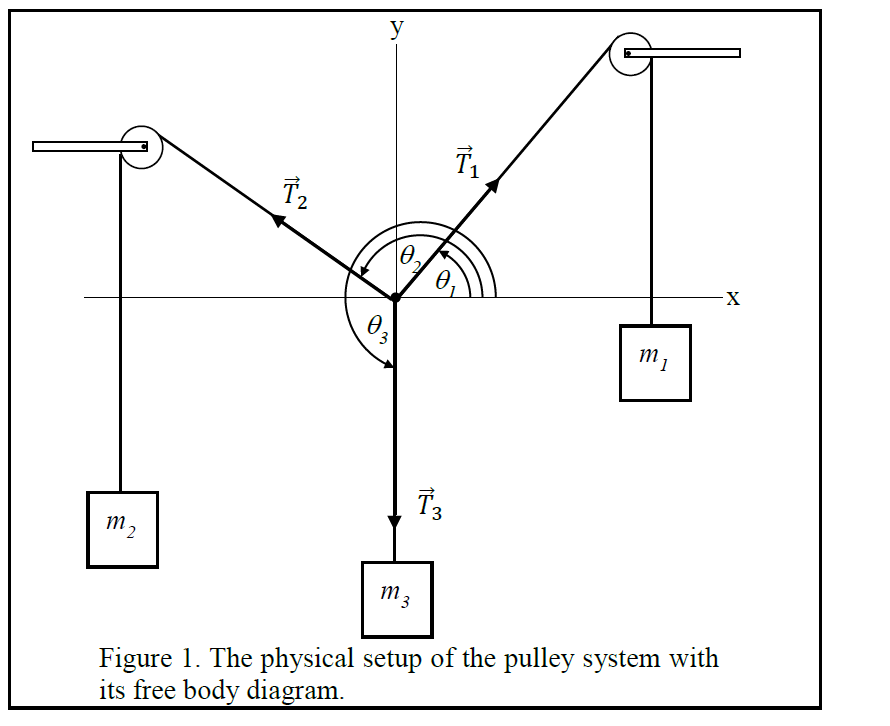
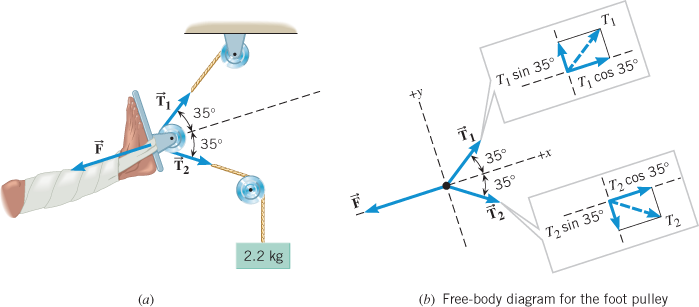
B) free body diagram of point P; three forces (upper part of figure below) 1) Tension T 1 2) Tension T 2 3) Tension T 3 Example 8 : A system with two blocks, an inclined plane and a pulley A) free body diagram for block m 1 (left of figure below) 1) The weight W 1 exerted by the earth on the box.
A free body diagram is defined as an illustration that depicts all the forces acting on a body, along with vectors that are applied by it on the immediate environs. Apart from the acting forces and subsequent work done, the moment magnitudes are also considered to be a part of such diagrammatic representations.
Making accurate free body diagrams for a system of blocks connected by string and pulleys is an important step towards writing the correct equations of motio...
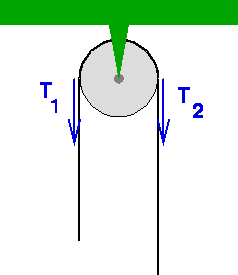
Feb 26, 2016 · Is there any difference between the free body diagram of fixed pulley and movable pulley? Not particularly. The main thing is that you can assume the fixed pulley isn't accelerating, so all forces on it must sum to zero. A movable pulley may or may not be accelerating. is it true that fixed pulley has T1 and T2, but movable has T2 on both sides ...
What would the free-body diagram of the balance of forces be for a rope and a pulley: a. For the rope turned 90 degrees? b. For the rope turned 180 degrees? 3. Experiment! Strings, Tension and Pulleys An ideal pulley is one that simply changes the direction of the tension. A man is holding a box at a constant height off the ground by means of a ...
4.11.2021 · Also shown below is the free-body diagram of the object which shows the tension forces, T, acting in the string. As you can see, the tension forces come in pairs and in opposite directions: Following Newton's Second Law of Motion, we can then express the summation of forces using the free-body diagram of the object, as shown on the right side of the illustration …
We can draw the free body diagram of bob at a as shown in figure 1.43. The force acting on the bob is it's weight mg and tension T of the string. Tenstion T is resolved in two components T cos θ and T sin θ as shown in figure 1.43. we can write the equation of motion. T cos θ = mg T sin θ = mv2/r.
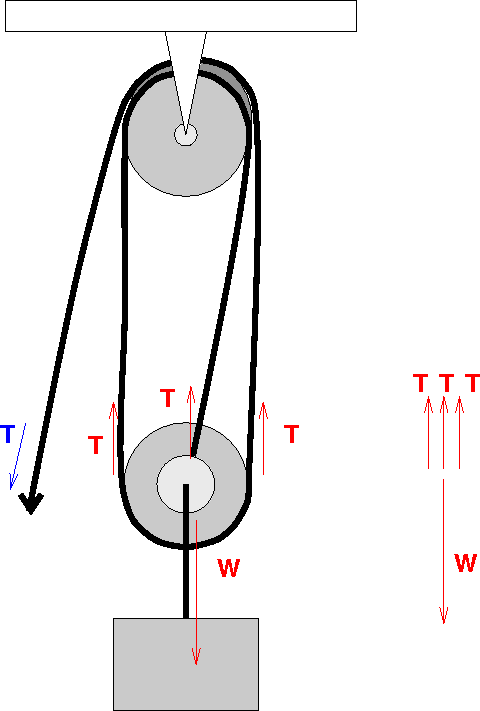
Free Body Diagram Practice M1 M2 FBD of Mass 1: F T FBD of the movable pulley: W 1 W 2 + W pulley F T F T Tension Forces (F T ) are equal throughout the system. Create a FBD for the pulley system pictured below.
FREE-BODY DIAGRAMS (continued) 3. Label loads and dimensions: All known forces and couple moments should be labeled with their magnitudes and directions. For the unknown forces and couple moments, use letters like A x, A y, M A, etc.. Indicate any necessary dimensions. Idealized model Free-body diagram
FREE-BODY DIAGRAMS (Section 5.2) 2. Show all the external forces and couple moments. These typically include: a) applied loads, b) support reactions, and, c) the weight of the body. Idealized model Free-body diagram (FBD) 1. Draw an outlined shape. Imagine the body to be isolated or cut "free" from its constraints and draw its outlined shape.
Pulleys and Tension ProblemSum of Forces in Inclined Frames of ReferencePulleys, Tension, and Extension SpringsForces Subscripts ConvectionTwo-Force Members...
Pulley#1 Pulley#2 Do a free body diagram on Pulley #2. Find the tension on each string. Ü L L. Ù H. á L Û° F Ú° L Ù Û° E Ú° L Ü L Û L Ú. Û Ù Ú. Û Ù Ú H Ù. à ß ß E Ú H Ù. ß Ý Û L Ú L. , Û L. A 5.0‐kg block is placed on top of a 10‐kg block. A horizontal force






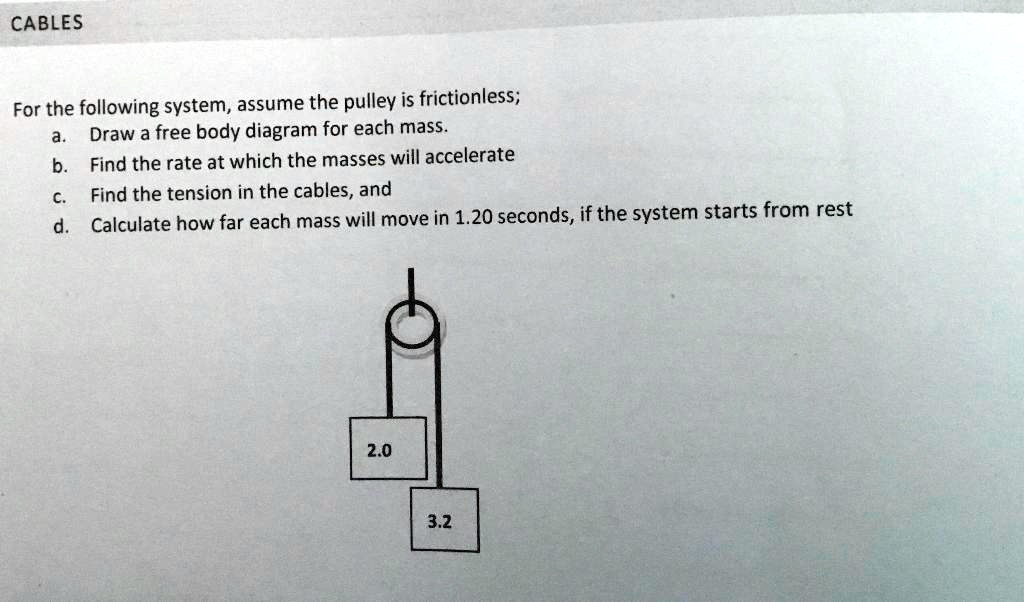
















0 Response to "41 free body diagram of a pulley"
Post a Comment