41 concave lens ray diagram
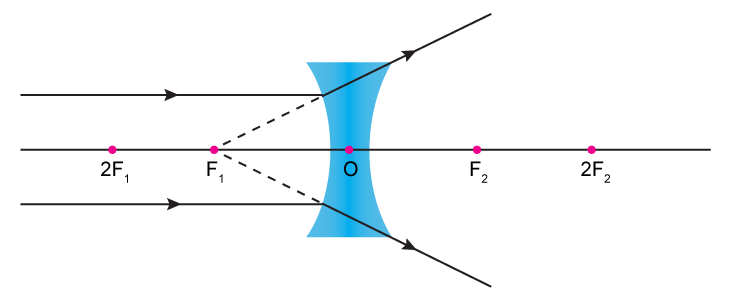
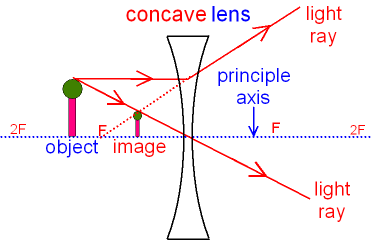
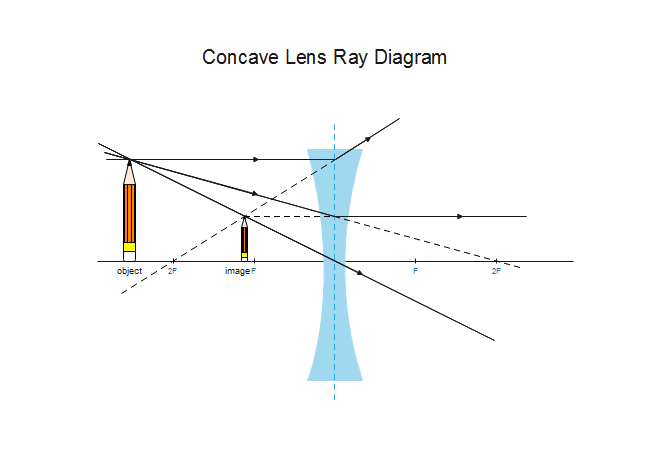
Ray diagram for an object viewed through a concave lens. For an object viewed through a concave. lens, light rays from the top of the object will be refracted. and will diverge. on the other side ... For a Concave lens,There are only 2 casesThey areObject is Placed at InfinityObject is Placed between Infinity and Optical CenterCase 1 - Object is Placed at infinityIn this Case, Object is kept far away from mirror (almost at infinite distance)So, we draw rays parallel to principal axisSince ray pa
A concave lens has a focal point {eq}f = 4 {/eq} cm. Display a ray diagram of a figurine placed at a distance {eq}d_o = 6 {/eq} cm from the lens. answer choices Answers:
Concave lens ray diagram
Ray Diagram for an Object Located at the Focal Point. Thus far we have seen via ray diagrams that a real image is produced when an object is located more than one focal length from a concave mirror; and a virtual image is formed when an object is located less than one focal length from a concave mirror (i.e., in front of F). But what happens ... Ray Diagrams for Concave Lenses. The ray diagrams for concave lenses inside and outside the focal point give similar results: an erect virtual image smaller than the object. The image is always formed inside the focal length of the lens. Shows how to draw the ray diagrams for locating the image produced by a concave lens and a convex mirror. You can see a listing of all my videos at my websit...
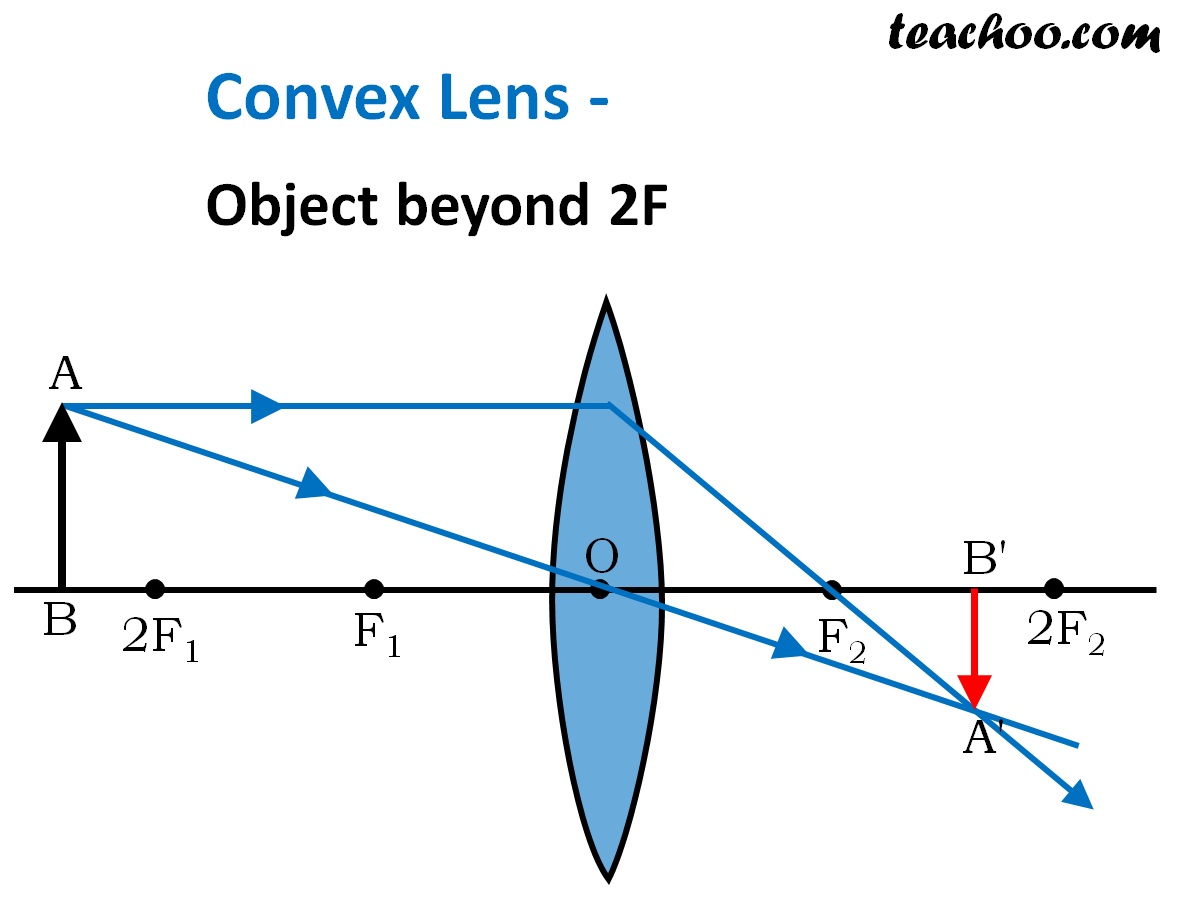
Concave lens ray diagram. http://www.physicshelp.caFree simple easy to follow videos all organized on our website The students can use a convex lens diagram to understand the ray's path after passing through a convex lens. The students may create a convex ray diagram by hand, but the process is lengthy, and at the same time, complicated. If the students fail to place the paths of the light properly, they may end up with a faulty convex lens ray diagram. The ray passing through the focal point becomes parallel to the principal axis after refraction by the lens. Ray diagram for concave lens. Image formation in convex lens Case 1:When object beyond 2F: In this case image will form between F and 2F, image will be real, inverted, smaller than the object. ... A concave lens ray diagram is a simple way of visualising the path that light rays take when passing through a concave lens. To draw a ray diagram you only need to draw two ray lines. This is sometimes referred to as "the two rules of refraction for diverging lenses".
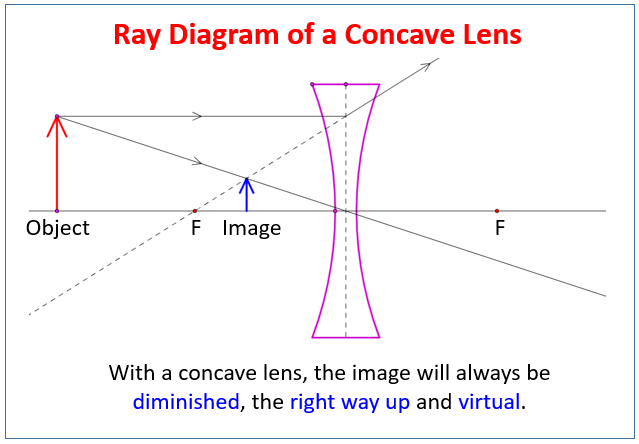
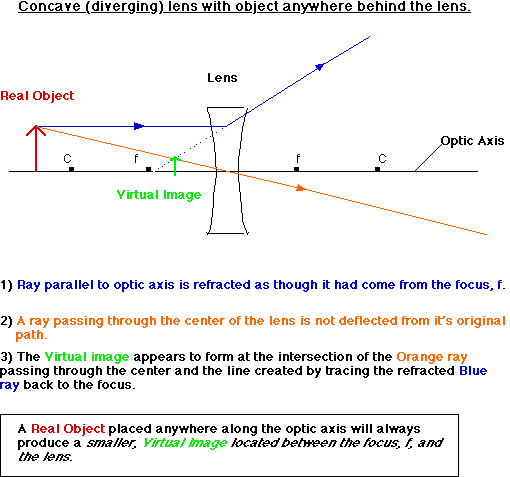
With a concave lens, the image will always be diminished, the right way up and virtual. Draw a ray diagram to show how an image is formed by a concave lens. Describe the properties of an image produced by a concave lens. Draw different ray diagrams with the object at different places in relation to the focus and find out where the image appears. The ray diagram above illustrates that the image of an object in front of a double concave lens will be located at a position behind the double concave lens. Furthermore, the image will be upright, reduced in size (smaller than the object), and virtual. This is the type of information that we wish to obtain from a ray diagram. A ray diagrams helps you understand the chara... This video shows you a simple method for drawing a ray diagram for a concave lens given the location of object. Hi ! In this animation of CONCAVE Lens, you get a good confidence to draw Ray Diagrams for various Object Positions. The aim is to have a clear understanding...
Draw a ray diagram to show how an image is formed by a concave lens. Draw a ray diagram for an object placed 60 cm from the surface of a convex lens with a focal length of 120 cm. Ray Diagrams for Concave Lenses The ray diagrams for concave lenses inside and outside the focal point give similar results. Concave Lens - Ray diagram Uses of Concave and Convex Lens Sign convention for Convex and Concave Lens Lens Formula Power of a lens NCERT Questions → Class 10. Chapter 10 Class 10 - Light - Reflection and Refraction (Term 1) Concepts NCERT Questions ... Concave Mirror Ray Diagram lets us understand that, when an object is placed at infinity, a real image is formed at the focus. The size of the image is much smaller compared to that of the object. When an object is placed behind the center of curvature, a real image is formed between the center of curvature and focus. A concave lens is thinner in the middle than it is at the edges. This causes parallel rays to diverge. A concave lens separates but appears to come from a principal focus on the other side of the lens. In the concave lens ray diagram, a concave lens is drawn as a vertical line with inward-facing arrows to indicate the shape of the lens. To create the diagram, a student should pick a point on ...
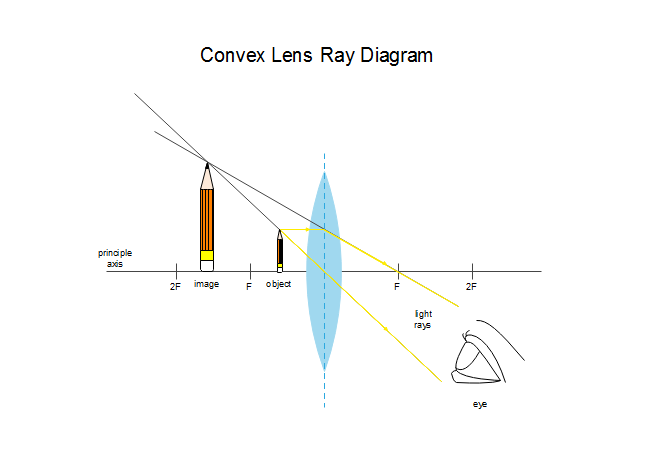
A convex lens is thicker in the middle than it is at the edges. Parallel light rays that enter the lens converge. They come together at a point called the principal focus. In a ray diagram, a ...
When a ray, passing through focus strikes concave or convex lenses, the reflected ray will pass parallel to the principal axis. Image Formation by Concave and Convex Lenses: Convex Lenses. When an object is placed at infinity, the real image is formed at the focus. The size of the image is much smaller than that of the object.
Shows how to draw the ray diagrams for locating the image produced by a concave lens and a convex mirror. You can see a listing of all my videos at my websit...
Ray Diagrams for Concave Lenses. The ray diagrams for concave lenses inside and outside the focal point give similar results: an erect virtual image smaller than the object. The image is always formed inside the focal length of the lens.
Ray Diagram for an Object Located at the Focal Point. Thus far we have seen via ray diagrams that a real image is produced when an object is located more than one focal length from a concave mirror; and a virtual image is formed when an object is located less than one focal length from a concave mirror (i.e., in front of F). But what happens ...

Whanake, (v) in Te Reo Maori means to move onwards, move upwards. This was taken at Piha, Auckland, New Zealand. Piha Beach is famous for it’s stunning beaches but beauty can be found on a clifftop on the way to the beach from the carpark. This photo was taken during a photo expedition when I was out of a job, so the fact that it was taken on a whim on the way to the beach resonates that “it’s not about the destination, it’s about the journey.†It matters not what stage of life we’re in as long as we keep moving and looking for inspiration.

Breathing is a process that allows you to get oxygen and, at the same time, eliminate carbon dioxide through exhalation. Only under special conditions, such as underwater, this last process is visible to the naked eye.

The Holy Mirror: Discovering Ourselves Through the Lens of Scripture...SAINT-SULPICE ART...spatial filter edge detection and to blend two images together..."magic" displayed the patter reverse with reflecting powerful light source

Image from page 234 of "The class-book of anatomy : designed for schools, explanatory of the first principles of human mechanism, as the basis of physical education" (1834)

🔴 If you want to use this image Please Follow me on insta ►►👉 https://tinyurl.com/y7fsmkjz

















0 Response to "41 concave lens ray diagram"
Post a Comment