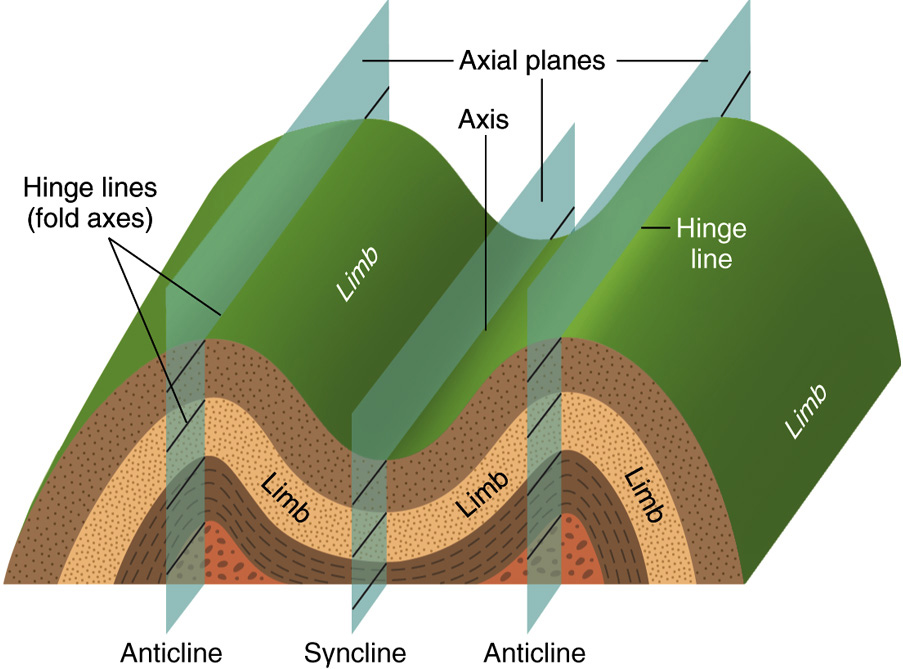
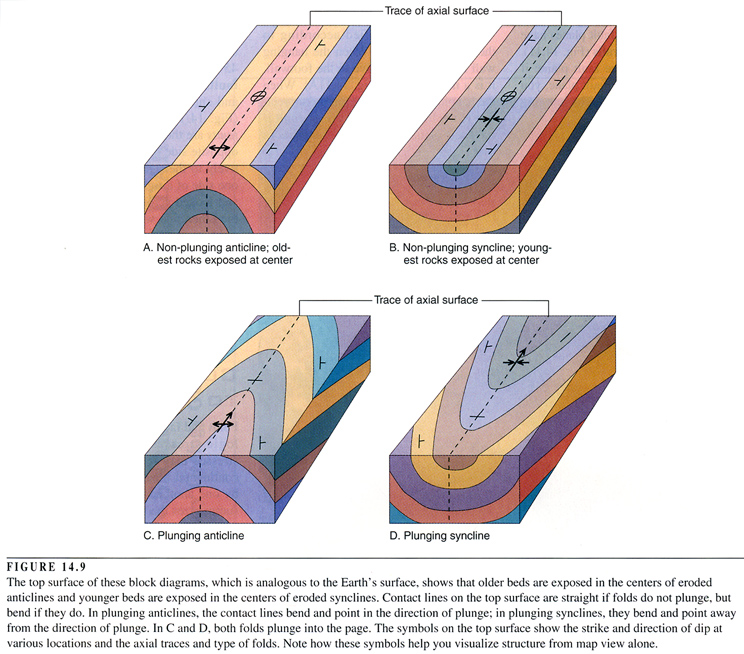
41 anticline and syncline diagram
Anticline and syncline diagram. In structural geology an anticline is a type of fold that is an arch like shape and has its oldest beds at its core whereas a syncline is the inverse of a anticline. Synclines are folds in which each half of the fold dips toward the trough of the fold. Anticlines and synclines form in sections of the crust that are undergoing compression, places where the crust is being pushed together. Plunging Anticlines and Synclines. A plunging anticline or a plunging syncline is one that has its axis tilted from the horizontal so that the fold is plunging into the earth along its length.
If the younging direction is away from the inside of the fold, then the fold is an anticline. In areas of mild deformation like the Rocky Mountain foothills, where the rocks are regionally the right way up, anticlines are antiforms; the terms can be used more or less interchangeably. Similarly, in such areas synclines are also synforms.
Anticline and syncline diagram
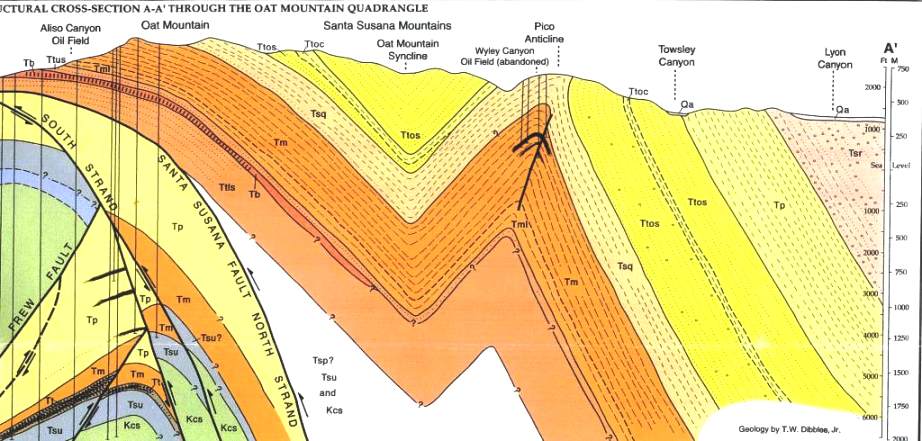
Anticlines and synclines form in sections of the crust that are undergoing compression, places where the crust is being pushed together. Plunging Anticlines and Synclines. A plunging anticline or a plunging syncline is one that has its axis tilted from the horizontal so that the fold is plunging into the earth along its length. • anticlines and synclines - plunge out eventually, don't go on forever • domes and basins - very broad features within continental interiors • complex folds - the result of very ductile behavior. Fig. 7.11. Types of folds. Fig. 7.15a. A series of anticlines & synclines Diagram of a syncline and an anticline. In structural geology, a syncline is a fold with younger layers closer to the center of the structure. A synclinorium (plural synclinoriums or synclinoria ) is a large syncline with superimposed smaller folds.
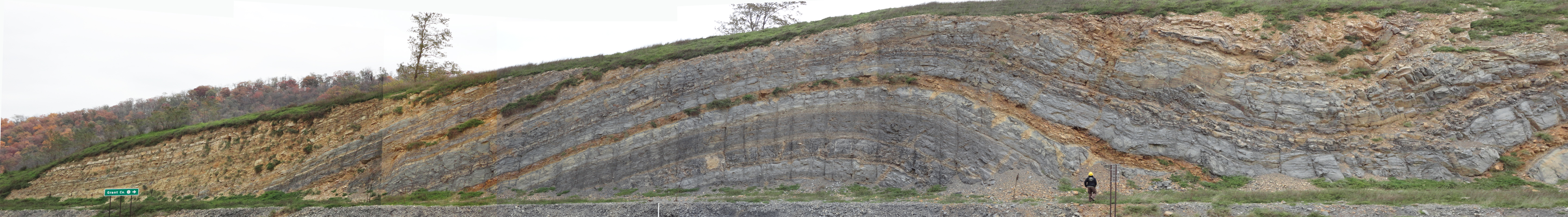
Anticline and syncline diagram. Block diagram of an Anticline and Syncline. Hinge Line is the same as.Geologic Structures Diagrams (Depending upon your printer, you may have to adjust your page and/or printer settings to make a print out of the following diagrams. These adjustments may include things like page orientation, page reduction (80% vs. Acetate 54 (Figure 14-13) Syncline and Anticline. C 1992 West Publishing Company . This diagram depicts an adjacent ANTICLINE and SYNCLINE with their representative FOLD AXIS and AXIAL PLANES. The shallow structure in Kokyar Anticline slightly differs from the deep one; the former is a compressional anticline and the latter is a fault-bent folding anticline (Figures 4.21b-d). The shallow trap area and closure increase upward; for example, N 1 x 3 trap area is 37.64 km 2 and the closure is 350 m. Anticline and syncline (Diagram by Phyllis Newbill) Anticlines are folds in which each half of the fold dips away from the crest. Synclines are folds in which each half of the fold dips toward the trough of the fold. You can remember the difference by noting that anticlines form an "A" shape, and synclines form the bottom of an "S."
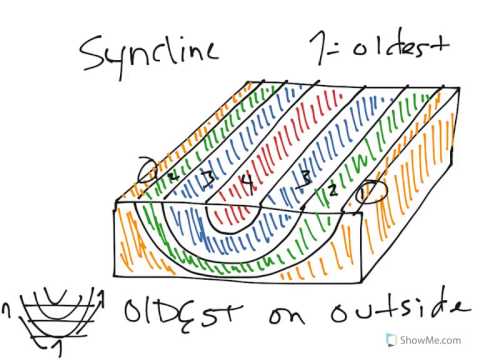
Plunging Syncline Block Diagram. The three broad classes of folds are (1) anticlines, (2) synclines and (3) Figure 4: Schematic diagrams illustrating horizontal and plunging anticlines. stream cut. A block diagram is a Block Diagrams & Nomenclature Plunging synclines plunge in the direction the "V" opens. Plunging anticlines plunge in the. There are three main types of folds: anticlines, synclines, and monoclines. Anticline. An anticline is a fold that is convex: it curves like a rainbow. "A" is for "anticline," and the capital letter "A" represents the shape of the fold. Figure 22. Anticline showing fold hinge line and strike and dip symbols. For the block diagrams below identify the fold using all relevant fold descriptors (note the letter 'A' is the oldest rock and 'D' is the youngest). A A B B C C D D ... Nonplunging, symmetrical syncline Plunging, symmetrical anticline igneous intrusion Anticline (monocline) Normal Fault A syncline is a concave geological fold, with layers that dip downward toward the center of the structure. This arrangement is opposite to that of an arching anticline. Provided that the syncline has not been overturned, strata within synclines have progressively younger rock layers toward the center of the syncline, with the youngest layer at the fold's center or hinge, mirrored by the same ...
Syncline and anticline Syncline and anticline are terms used to describe folds based on the relative ages of folded rock layers. A syncline is a fold in which the youngest rocks occur in the core of a fold (i.e., closest to the fold axis), whereas the oldest rocks occur in the core of an anticline. Source for information on Syncline and Anticline: World of Earth Science dictionary. Syncline Anticline Figure 6.12 Full Alternative Text 1. Below each block diagram in Figure6.12, label the type of fold as either an anticline or a syncline. 2. The plane extending through each block diagram is called axial plane plunging and non- plunging folds. First cut it in half so you have a syncline and an anticline. To show the outcrop pattern of an anticline cut a thin slice from the top to expose the layers underneath. To show the outcrop pattern of plunging folds cut the sponge roll obliquely. Doubly plunging fold patterns in a table A P 1 minute Anticline Diagram A syncline is created by the downfolding of rock layers until a trough is formed. In a syncline, the youngest rock layers are found in the center. Syncline Syncline Diagram Syncline Anticlines and synclines can be symmetrical, asymmetrical or asymmetrical overturned. An asymmetrical overturned fold occurs when one limb is ...
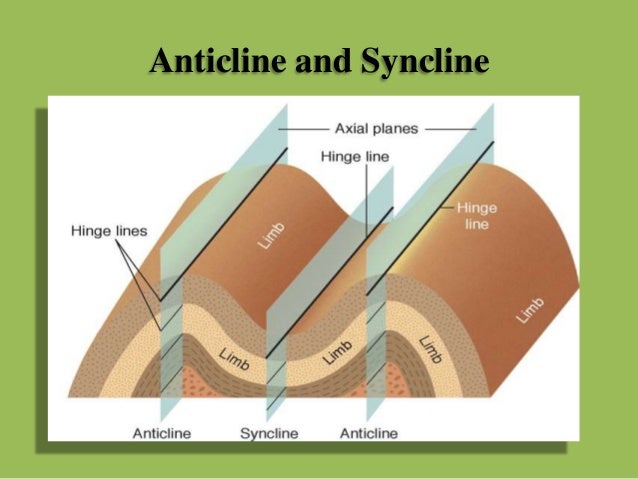
1.3 Folds on Block Diagrams Figure 6 shows a schematic diagram of an anticline with key components labeled. First, observe that the anticline is symmetrical; both limbs dip the same amount, but in opposite directions. In a way, you can consider fold limbs to be two sets of inclined strata which dip in different.
A plunging fold is a fold that is tilted downwards in space, parallel to the fold hinge plane. Figure 26. Plunging anticline (left) and plunging syncline (right). The interactive diagrams are linked below. Interactive SketchUp diagram of a plunging anticline: Interactive SketchUp diagram of a plunging syncline:
Anticline Block Diagram. In terms of geologic structures, the up folds are called anticlines and the down folds are In block diagrams like those shown below, the top of the block is the. A block diagram is a combination of Block Diagrams & Nomenclature anticline. Contrary to the syncline, the rock beds dip away from the fold axis, and the.
vnticline) and synclines open up (think swncline) and monoclines just have one limb. In GY 111, we more or less ignore monoclines, so the rest of this lecture (and all of the Chapter 6 exercises) will be restricted to anticlines and synclines. Once you understand the basic difference between anticlines and synclines, the rest of
Anticlines arch upward, and synclines sink downward. Source: Randa Harris (2015) CC BY-SA 3.0. view source. A monocline is a simple fold structure that consists of a bend in otherwise horizontal rock layers. Anticlines and synclines are more common than monoclines. An anticline fold is convex up: the layered strata dip away from the center of ...
Monoclines, anticlines, and synclines are the three basic types of folds. Here they are shown in block diagrams, as well as in diagrams showing their essential geometry: the relationship of the strata to the axial surface. Anticlines and Synclines. Anticlines (upfolds) and synclines (downfolds) are very common geologic structures that form in ...
Anticlines and Synclines. The most basic types of folds are anticlines and synclines. Anticlines are "up" folds; synclines are "down" folds. In box diagrams like these, the top of the box is the horizontal surface of the earth, the map view. The other two visible sides of the box are cross-sections, vertical slices through the crust. The ...
syncline is toward the open end of the V-shaped pattern of diverging formations. Figure 5.8 shows both cases. An anticline that plunges In opposite directions is a doubly plunging anticline, and a syncline that plunges in opposite directions is a doubly plunging syncline. Variations of doubly plunging folds arc the structural dome
In structural geology, an anticline is a type of fold that is an arch-like shape and has its oldest beds at its core, whereas a syncline is the inverse of an anticline. A typical anticline is convex up in which the hinge or crest is the location where the curvature is greatest, and the limbs are the sides of the fold that dip away from the hinge. Anticlines can be recognized and differentiated ...
Anticlines and synclines are the most common up-and-down folds that result from compression. An anticline has a ∩-shape, with the oldest rocks in the center of the fold. A syncline is a U-shape, with the youngest rocks in the center of the fold. Domes and basins are often considered types of folds.
Diagram of an anticline. In structural geology, an anticline is a fold that is convex up and has its oldest beds at its core. The term is not to be confused with. This Diagram depicts some of the differences between Asymmetrical, Symmetrical, and Folds typically occur in anticline-syncline pairs. Cross-sectional diagram of an anticline.
Diagram of a syncline and an anticline. In structural geology, a syncline is a fold with younger layers closer to the center of the structure. A synclinorium (plural synclinoriums or synclinoria ) is a large syncline with superimposed smaller folds.
• anticlines and synclines - plunge out eventually, don't go on forever • domes and basins - very broad features within continental interiors • complex folds - the result of very ductile behavior. Fig. 7.11. Types of folds. Fig. 7.15a. A series of anticlines & synclines
Anticlines and synclines form in sections of the crust that are undergoing compression, places where the crust is being pushed together. Plunging Anticlines and Synclines. A plunging anticline or a plunging syncline is one that has its axis tilted from the horizontal so that the fold is plunging into the earth along its length.
























0 Response to "41 anticline and syncline diagram"
Post a Comment