40 orbital diagram of carbon
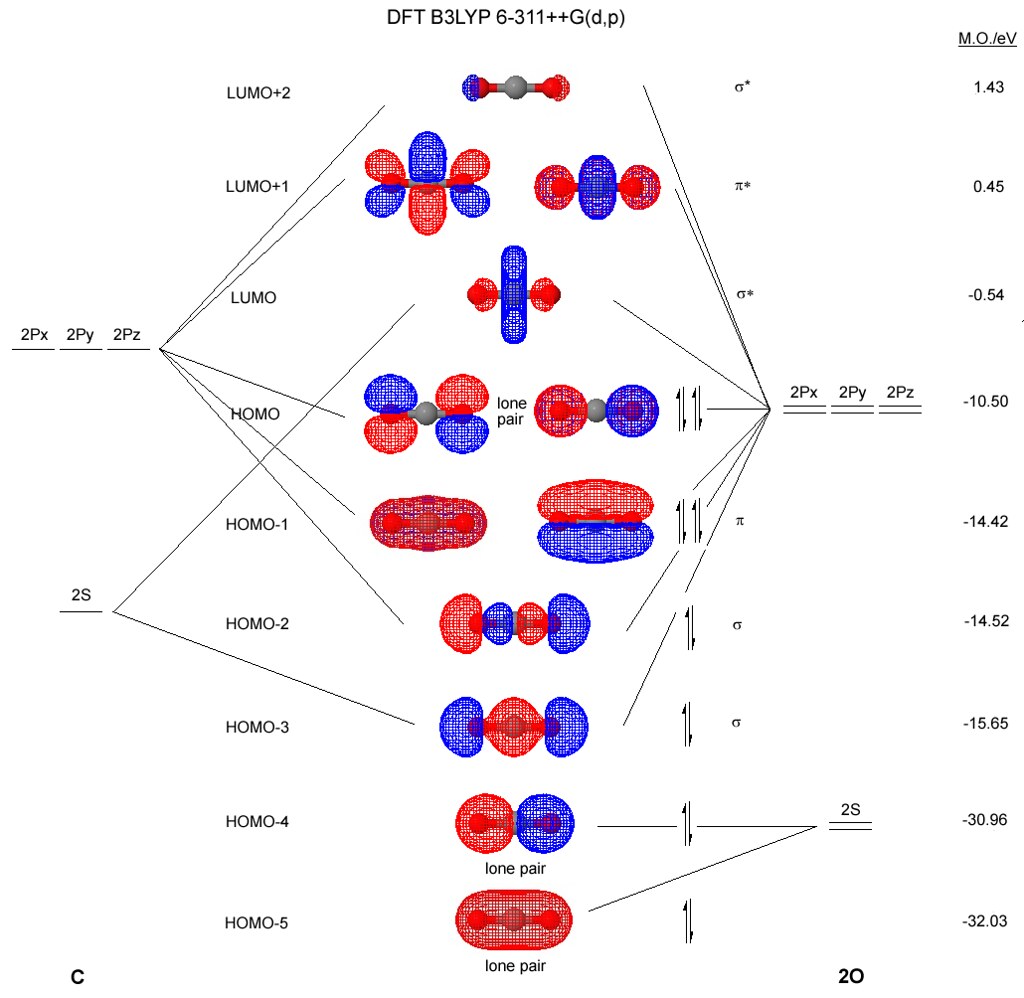
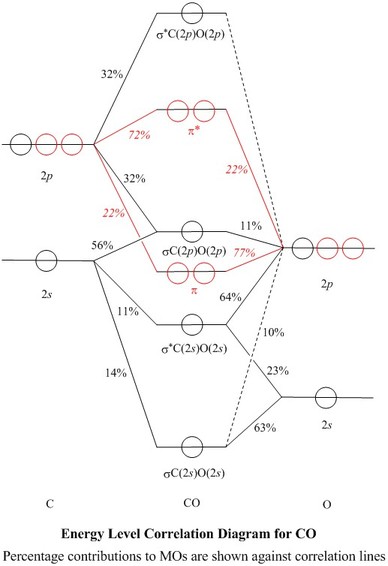
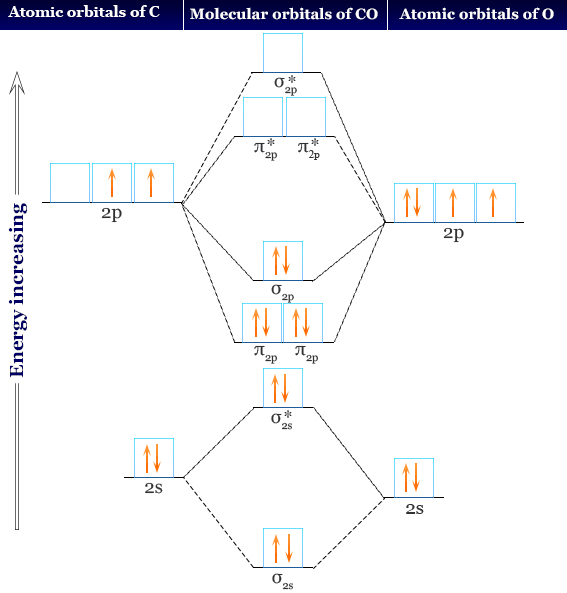
An isolated sp hybridized carbon atom for viewing. A bonded carbon atom would need orbital overlap for each orbital present, spa, spb, 2pz and 2px. There remain two 2p orbitals which are perpendicular to the two sp hybrid orbitals and to each other. Each 2p orbital extends along its entire axis with opposite phase in each lobe. 2pz 2px Molecular Orbital Diagram of CO. To understand the bonding in metal carbonyls, we need to first learn the Molecular Orbital \(\left( {{\rm{MO}}} \right)\) diagram of carbon monoxide. There are ten electrons in the carbon monoxide ligand.
The four valence electrons on carbon can be added to the energy diagram ( ). Each of the hydrogens has one valence electron in its 1 s orbital ( ). These will pair up with the carbon electrons to form four s (sigma) bonds. These are called sigma bonds (Greek for s) because they are formed from hybridized orbitals, which result from s orbitals.
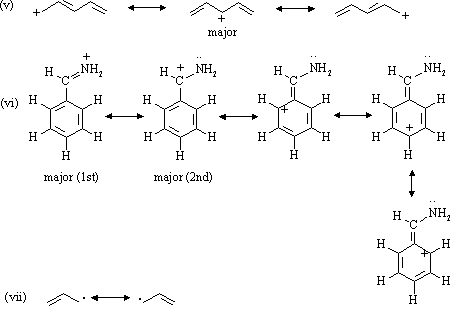
Orbital diagram of carbon
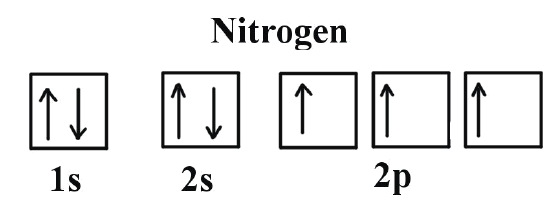
Orbital diagram of Lithium (Li) 4: Orbital diagram of Beryllium (Be) 5: Orbital diagram of Boron (B) 6: Orbital diagram of Carbon (C) 7: Orbital diagram of Nitrogen (N) 8: Orbital diagram of Oxygen (O) 9: Orbital diagram of Fluorine (F) 10: Orbital diagram of Neon (Ne) 11: Orbital diagram of Sodium (Na) 12: Orbital diagram of Magnesium (Mg) 13 ... Orbital-orbital Interactions and Symmetry Adapted Linear Combinations; ... Molecular orbitals in Carbon Monoxide. CONTROLS > Click on the CO molecular orbitals in the energy level diagram to display the shapes of the orbitals. Explore bonding orbitals in other small molecules. Electron configuration of carbon (C) atom through orbital diagram Atomic energy levels are subdivided into sub-energy levels. These sub-energy levels are called orbital. The sub energy levels are expressed by 'l'. The value of 'l' is from 0 to (n - 1). The sub-energy levels are known as s, p, d, f.
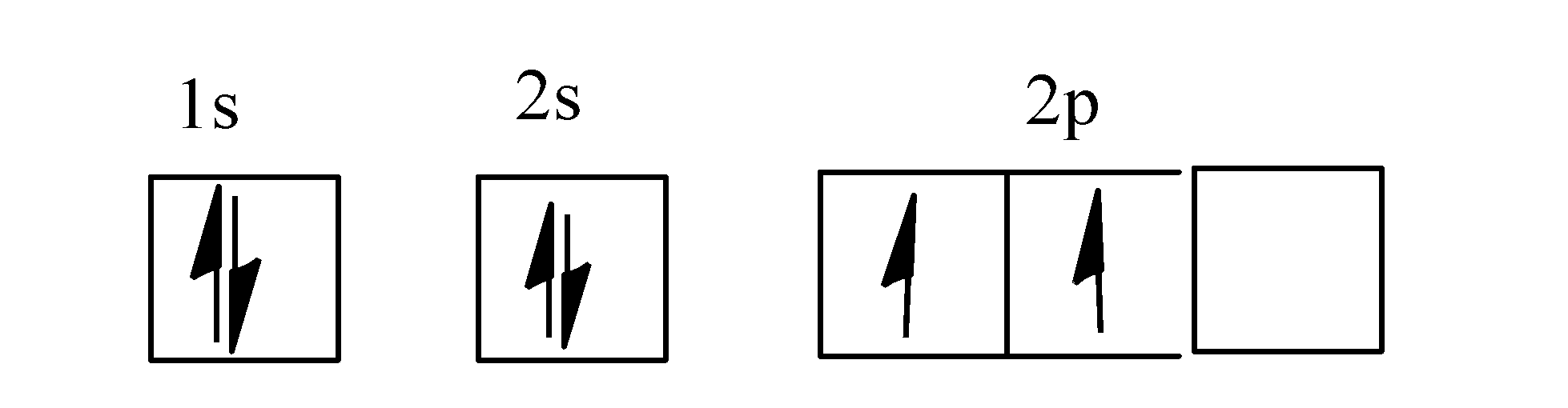
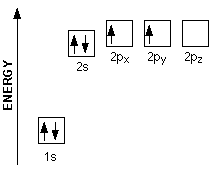
Orbital diagram of carbon. If we look at the valence shell configuration of carbon, we find two paired electrons in the 2s orbital, and two unpaired electrons in the 2p X and 2p Y orbitals, one in each: 2s 2p X 2p y 2p z Potential energy In order to fulfill the octet rule, carbon must use its 4 valence electrons when bonding to other atoms. However, only unpaired ... What is the orbital diagram for carbon? Electronic Configuration: Electronic configuration is the distribution of electrons in the atomic orbitals like s,p,d,f, ...1 answer · Top answer: The atomic number of carbon,C is 6. Its full ground state electronic configuration is as follows: C=1s22s22p2C=1s22s22p2 Its orbital... Each carbon has two sigma bonds, one to hydrogen and one to carbon, and two π bonds (the second and third bonds of the triple bond). Looking at the orbital diagram above, two p-orbitals must be removed from the hybridization pool to make the triple bond. This leaves one s and one p-orbital, leaving two sp orbitals. Orbital diagram involves the distribution of the electrons in the orbitals i.e. s, p , d and f-subshells. - An orbital can have a maximum of two electrons and ...1 answer · Top answer: Hint:. Orbital diagram is the filling of the electrons into different orbitals according to the number of electrons present in an atom and an orbital ...
Atomic Orbital Diagram for Iron(Fe) Iron ion(Fe 2+,Fe 3+) electron configuration. Ground state electron configuration of iron(Fe) is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 3d 6 4s 2.The electron configuration shows that the last shell of iron has two electrons and the d-orbital has a total of six electrons. The suggested molecular orbital electronic configuration of Co is : KK (sigma_2s)^2 (sigma _ (2s))^2, (pi_ (2px))^2 (pi_ (2py))^2 (sigma_ (2pz))^2. Experimentally determined bond length in CO and CO^+ are 112.8 pm and 111.5 pm . What is an orbital energy diagram? Orbital diagrams are a pictorial description of electrons in an atom. Ethane, a two carbon molecule with a single-bond between the carbons, is the simplest alkane. To understand the hybridization, start by thinking about the orbital diagram of the valence electrons of atomic, unhybridized carbon. The electron configuration for carbon is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 2. An orbital box diagram can be written as well. Boxes, or horizontal lines represent the orbitals, arrows represent the electrons, and if an orbital is full, the electrons must be of opposite spin-one arrow pointing up and the other one pointing down.
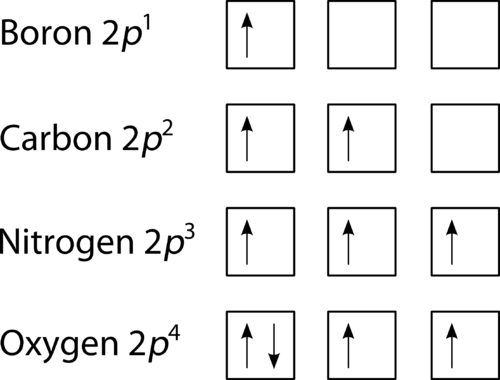
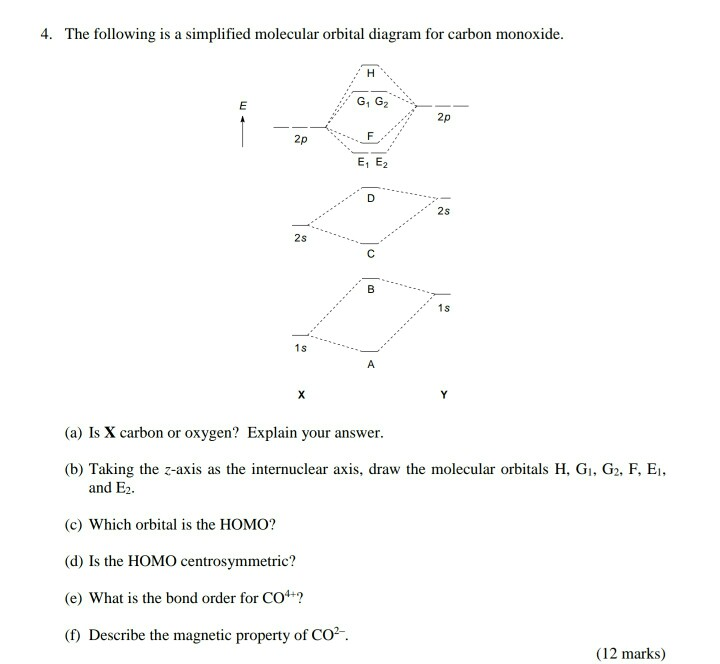
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of ... A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining MO diagrams can explain why some molecules exist and others do not. . combinations such as CO and NO show that the 3σg MO is higher in energy. Click on the CO molecular orbitals in the energy level diagram to display the shapes of the orbitals. What is the orbital diagram for carbon? With beryllium (Z = 4), the 2s sublevel is complete and the 2p sublevel begins with boron (Z = 5). Since there are three 2 p orbitals and each orbital holds two electrons, the 2p sublevel is filled after six elements….Second Period Elements. The atomic number of carbon is 6, which is also the number of The orbital diagram shows how the electrons are arranged within each sublevel. rule, each orbital must contain one electron each with the same spin, before.
see more informative chemistry lectureshttps://youtu.be/iZhZRWNonVshttps://youtu.be/3bQ2YZVCRqUhttps://youtu.be/PEkZoDgbMdIhttps://youtu.be/FMsg4LDrjkohttps:...
Finally, add the valence electrons to the molecular orbital diagram. Each carbon has 4 and each hydrogen 1 for a total of 12 electrons. Ethyne, sp hybridization with two pi bonds 1. 2. Ethyne, HCCH, is a linear molecule. Each carbon atom makes 2 sigma bonds and has no lone
Dot diagrams are very different to orbital diagrams, but they're still very easy to understand. They consist of the symbol for the element in the center, surrounded by dots indicating the number of valence electrons. For example, carbon has four valence electrons and the symbol C, so it is represented as:
The second diagram corrects this by realizing there are two unused p orbitals on the carbon. The valence electron configuration of "O" is ["He"] 2s^2 2p^4. To accommodate the two lone pairs and the bonding pair, it will also form three equivalent sp^2 hybrid orbitals.
In the nickel (Ni) ground-state electron configuration, the eight electrons of the 3d orbital are located in the d xy, d yz, d zx, d x2-y2, and d z2 sub-orbitals. The d-orbital has five sub-orbitals. The sub-orbitals are d xy, d yz, d zx, d x2-y2, and d z2. Each sub-orbital can have a maximum of two electrons.
The orbital diagram can be derived from the elemental carbon's (C) electron (e-) configuration. C is configured as a helium (He) core as [He]2s^2 2p^2, 2, 4. A Lewis dot structure would have a C ...
The element carbon has 6 electrons in total and one of the main things that many users might not know is the symbol by which it is represented. The symbol of carbon is written as 6. Carbon Electron Dot Diagram. If we talked about the electronic configuration of the element then, carbon is an element whose electronic configuration is given as 1s ...
MO Diagram for HF The AO energies suggest that the 1s orbital of hydrogen interacts mostly with a 2p orbital of fluorine. The F 2s is nonbonding. H-F nb σ σ* Energy H -13.6 eV 1s F -18.6 eV -40.2 eV 2s 2p So H-F has one σ bond and three lone electron pairs on fluorine
The orbital diagram shows how the electrons are arranged within each sublevel. The maximum number of electrons allowed in an orbital is #2# , each with opposite spins (Pauli's exclusion principle). In a neutral carbon atom, the #"1s"# sublevel has one orbital with two electrons with opposite spins, represented by the arrows pointing in opposite ...
Carbon is making 2 s and 2 p bonds to the oxygen atoms. The 2 s bonds indicate that there are 2 equivalent molecular orbitals formed. To form 2 hybrid molecular orbitals, we need to mix 2 atomic orbitals, an s orbital and a p orbital. The resulting hybrid orbitals are called sp hybrids. sp 3 Hybridization.
Carbon is the sixth element with a total of 6 electrons. In writing the electron configuration for carbon the first two electrons will go in the 1s orbital. Since 1s can only hold two electrons the next 2 electrons for C goes in the 2s orbital. The remaining two electrons will go in the 2p orbital.
Molecular Orbital Diagram of Carbon Molecule Video Lecture from Chapter Nature of Chemical Bond of Subject Chemistry Class 11 for HSC, IIT JEE, CBSE & NEET.W...
Electron configuration of carbon (C) atom through orbital diagram Atomic energy levels are subdivided into sub-energy levels. These sub-energy levels are called orbital. The sub energy levels are expressed by 'l'. The value of 'l' is from 0 to (n - 1). The sub-energy levels are known as s, p, d, f.
Orbital-orbital Interactions and Symmetry Adapted Linear Combinations; ... Molecular orbitals in Carbon Monoxide. CONTROLS > Click on the CO molecular orbitals in the energy level diagram to display the shapes of the orbitals. Explore bonding orbitals in other small molecules.
Orbital diagram of Lithium (Li) 4: Orbital diagram of Beryllium (Be) 5: Orbital diagram of Boron (B) 6: Orbital diagram of Carbon (C) 7: Orbital diagram of Nitrogen (N) 8: Orbital diagram of Oxygen (O) 9: Orbital diagram of Fluorine (F) 10: Orbital diagram of Neon (Ne) 11: Orbital diagram of Sodium (Na) 12: Orbital diagram of Magnesium (Mg) 13 ...




















0 Response to "40 orbital diagram of carbon"
Post a Comment