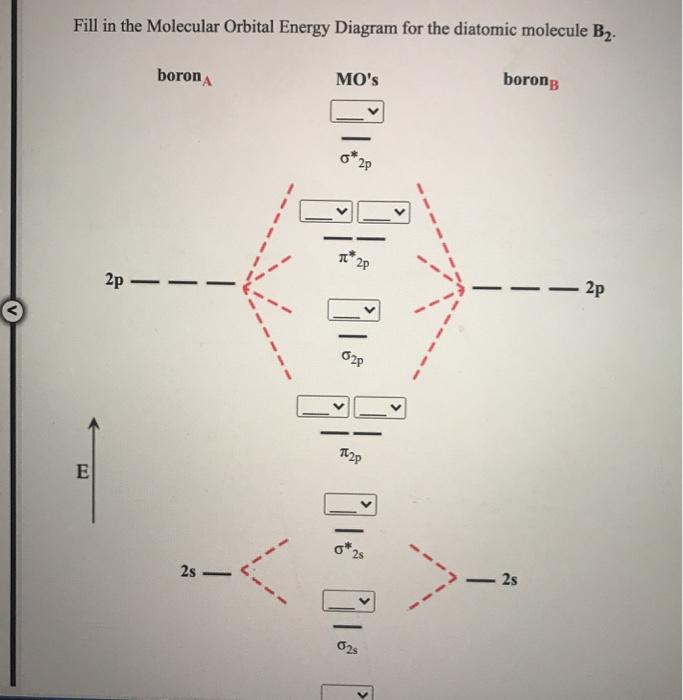
41 boron molecular orbital diagram
Boron exists in the earth's crust to the extent of only about 10 ppm (about the same abundance as lead). The pure element is shiny and black. It is very hard and in extremely pure form is nearly as hard as diamond, but much too brittle for practical use. At high temperatures it is a good conductor but at room temperature and below is an insulator. In an addition reaction the number of σ-bonds in the substrate molecule increases, usually at the expense of one or more π-bonds. The reverse is true of elimination reactions, i.e.the number of σ-bonds in the substrate decreases, and new π-bonds are often formed.Substitution reactions, as the name implies, are characterized by replacement of an atom or group (Y) by another atom …
Includes carbon, oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, phosphorus, chlorine, boron, beryllium, chlorine, fluorine, and hydrogen elements with six lone pair orbitals and six pear-shaped orbitals. Also contains 26 pear-shaped sigma bonds and six short bonds. Contents: Qty Element Holes 1 Carbon 4 1 Oxygen 4 1 Nitrogen 4 1 Sulfur 6 1 Phosphorus 5 1 Chlorine 4
Boron molecular orbital diagram
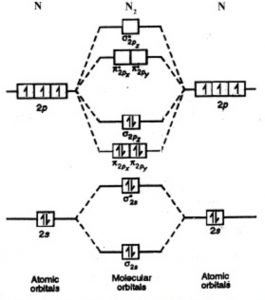
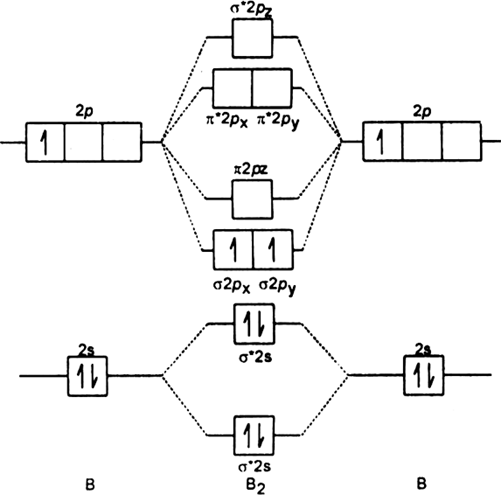
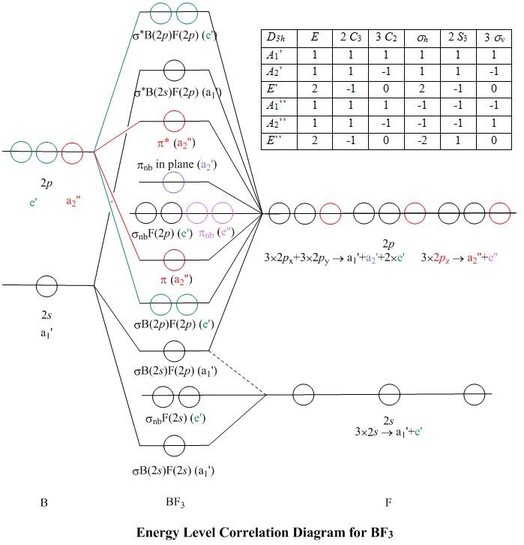
The molecular orbital diagram representing this order of energy levels is shown in fig. Fig. No. 5 Order of Energy Levels for Boron, Carbon, Nitrogen etc. This kind of energy reversal is due to mixing of 2s and 2p orbitals where the energy difference is very close, that is, for B, C, and N atoms. Molecular orbital diagram practice worksheet A chemical bonding of several metallabenzenes and metallabenzynes was studied via an adaptive natural density partitioning (AdNDP) algorithm and the induced magnetic field analysis. A unique chemical bonding pattern was discovered where the M=C (M: Os, Re) double bond coexists with the delocalized 6c-2e π-bonding elements responsible for aromatic properties of the investigated complexes.
Boron molecular orbital diagram. The population analysis for the HOMO levels reveals that only p orbitals of Br contribute to the HOMO of [B 14 Br 14] 2− and [B 16 Br 16] 2− clusters, while significant contribution from p orbitals of boron cage appears for the HOMOs in the case of X = Cl or F. The lack of mixing between Br and B orbitals most likely originates from the ... A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electron pairs between atoms.These electron pairs are known as shared pairs or bonding pairs, and the stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atoms, when they share electrons, is known as covalent bonding. Bottom-up graphene nanoribbons (GNRs) have recently been shown to host nontrivial topological phases. Here, we report the fabrication and characterization of deterministic GNR quantum dots whose orbital character is defined by zero-mode states arising from nontrivial topological interfaces. Topological control was achieved through the synthesis and on-surface assembly of three distinct ... Hence it promotes two electrons into two of the 3d orbitals one from 3s and one from 3p x. Thus formed six half filled sp 3 d 2 hybrid orbitals are arranged in octahedral symmetry. Each fluorine atom uses is half-filled 2p z orbitals for the bond formation. SF 6 is octahedral in shape with bond angles equal to 90 o.
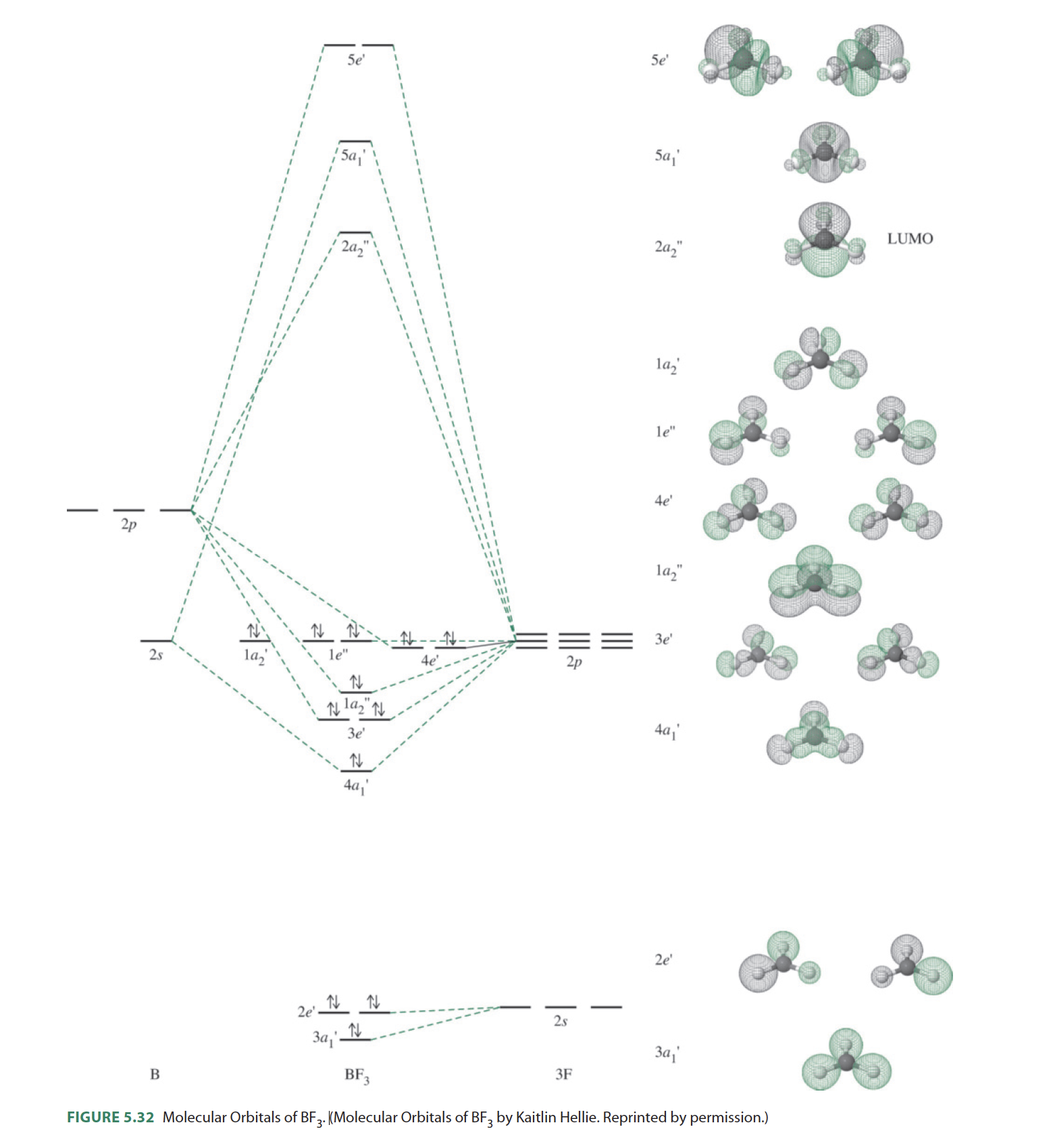
Assertion: Fluorine molecule has bond order one. Reason: The number of electrons in the antibonding molecular orbitals is two less than that in bonding molecular orbitals. Protons, neutrons, electrons fluorine-19 004. If playback doesn't begin shortly, try restarting your device. The molecular orbital diagram of BeCl2 will be drawn by combining atomic orbitals of beryllium atom and group orbitals of chlorine atom having similar energy and symmetry around a molecular axis. The 3s group orbitals of chlorine atom will remain non-bonding because their energy is very low as compared to the 2s and 2p atomic orbitals of ... Nov 18, 2021 · Molecular geometry and molecular shape will be the same for the molecules with 0 lone pair; which is the case of BCl3. Molecular Orbital Diagram of BCl3. Molecular orbital diagrams give us an idea about the mixing of orbitals in molecules. Let’s look into the MO diagram of boron trichloride. Boron Trichloride or BCl3 is a nonpolar compound because of its symmetrical structure ie; Trigonal Planar. The B-Cl bond itself is polar because of the difference in electronegativity of Boron (2.04) and Chlorine (3.16) atoms and all three B-Cl bonds lie at 120 degrees to each other. As a result, the dipole moment of each B-Cl bond is canceled ...
Nov 26, 2021 · Molecular Geometry of BF3. Each molecule has its shape that can be represented after finding out their electrons hybridized in various types of s-orbital and p-orbital like sp2, sp3, sp. As you found the molecule BF3 is sp2 hybridized (in the presence of 3 orbitals) with 1 boron atom and 3 atoms of fluorine. 40 the partial (valence-level) orbital diagram for a 3+ ion is shown below. Written By Christine J. Bell. Friday, November 26, 2021 Add Comment Edit. Electron configurat ion s of transit ion metal elements Hydrogen Z 1. Lithium Z 3. Ce 3 Xe4f 1. JEE Advanced 2023 Physics Syllabus includes topics under the broad categories of General Physics, Mechanics, Thermal Physics, Electromagnetic waves, Optics, among others. JEE Advanced 2023 Chemistry Syllabus covers topics including the States of Matter: Gases and Liquids, Atomic Structure, Chemical Bonding, and Molecular Structure, among others. Oct 26, 2021 · Molecular design. In our molecular design, we aim at aligning CT and LE states to enable spin–orbit coupling between excited triplet and excited singlet states and to promote fast RISC 33,34,35 ...
The Bohr Model of Magnesium (Mg) has a nucleus that contains 12 neutrons and 12 protons. This nucleus is surrounded by three-electron shells named K-shell, L-shell, and M-shell. The outermost shell in the Bohr diagram of Magnesium contains 2 electrons that also called valence electrons. Write the full orbital diagram for magnesium. Orbital Diagram: The subatomic particle that occupies most of ...
Incongruent melting occurs when a solid substance does not melt uniformly, so that the chemical composition of the resulting liquid is not the same as that of the original solid. During incongruent melting a new solid of different composition forms. In addition, phase diagram s provide valuable information about melting, casting, crystallization, and other phenomena.
Gallium is a chemical element with the symbol Ga and atomic number 31. Discovered by French chemist Paul-Émile Lecoq de Boisbaudran in 1875, Gallium is in group 13 of the periodic table, and has similarities to the other metals of the group (aluminium, indium, and thallium).. Elemental gallium is a soft, silvery metal at standard temperature and pressure.In its liquid state, it becomes ...
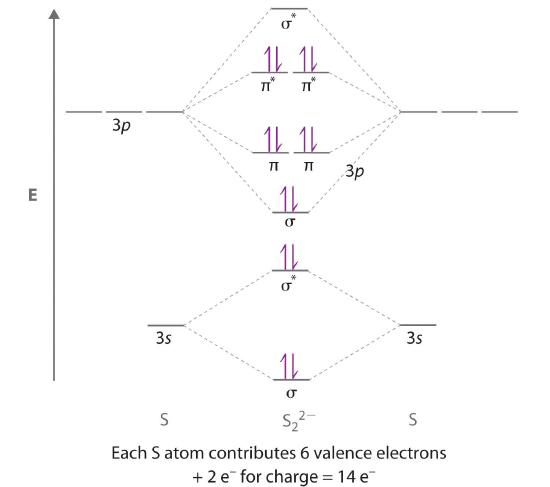
Of the 36 electrons associated with 12 boron atoms, 26 reside in 13 delocalized molecular orbitals; the other 10 electrons are used to form two- and three-centre covalent bonds between icosahedra. The same motif can be seen, as are deltahedral variants or fragments, in metal borides and hydride derivatives, and in some halides.
Molecular Orbitals diagram of Phosphorus Trifluoride (PF3) molecule. The molecular orbital diagram helps with determining how chemical bond formation is taking place. Also, it helps with figuring out how mixing and overlapping have taken place to produce four new hybrid orbitals.
Molecular orbital diagram for o2- ion 1918 (Venn's diagram is from 1904), named for English logician John Venn (1834-1923) of Cambridge, who explained them in the book "Symbolic Logic" (1881). 1834, introduced by English physicist and chemist Michael Faraday (suggested by the Rev. William Whewell, English polymath), coined from Greek ion ...
According to the Aufbau principle, the electrons of an atom occupy quantum levels or orbitals starting from the lowest energy level, and proceeding to the highest, with each orbital holding a maximum of two paired electrons (opposite spins). Electron shell #1 has the lowest energy and its s-orbital is the first to be filled.
Electronic Configuration in Periods. The period of the element is the value of n, the primary quantum number, for the valence shell. The number of electrons that can be accommodated by different energy levels varies. 2n2, where n is the energy level, is the greatest number of electrons that a given energy level can allow.
(The same conclusion can be drawn from an orbital correlation diagram or a Dewar-Zimmerman analysis.) For the more common "normal" electron demand Diels–Alder reaction, the more important of the two HOMO/LUMO interactions is that between the electron-rich diene's ψ 2 as the highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO) with the electron ...
CH2N2 Lewis Structure, Molecular Geometry, Hybridization, and Polarity. Diazomethane (CH2N2) is an explosive yellow gas. It is transported in the liquid phase and has a musty odor. If inhaled, it is highly toxic. In this diazomethane molecule, the methylene is attached to the diazo group, thus forming this simple diazo compound.
Molecular Orbital: Example Questions. Construct a molecular orbital diagram for each geometry Which of the following are true: 1. The positively charged carbon atom contributes four valence electrons to the molecular orbitals of the methyl cation. 2. The lowest unoccupied orbital for the planar methyl cation is an sp2 hybrid orbital. 3.
When you take the second period on the periodic table, so here we are on the second period, lithium has one valence electron, beryllium has two, boron has three, carbon has four, nitrogen has five, oxygen has six, fluorine seven, and neon eight. And so you have more orbitals in a second energy level.
Boron is a chemical element with the symbol B and atomic number 5. In its crystalline form it is a brittle, dark, lustrous metalloid; in its amorphous form it is a brown powder. As the lightest element of the boron group it has three valence electrons for forming covalent bonds, resulting in many compounds such as boric acid, the mineral borax, and the ultra-hard crystal boron carbide.
6. There is one p orbital on boron but there is no adjacent atom with another p orbital. Add it to the molecular orbital diagram as a non-bonding molecular orbital. 7. There are a total of 6 electrons to add to the molecular orbital diagram, 3 from boron and 1 from each hydrogen atom. sp Hybrid Orbitals in BeH2 1.
Sep 22, 2021 · Electron configurations and orbital diagrams are used to show the arrangement of electrons in shells (levels), subshells (sublevels) and orbitals for specific atoms. Write complete electron configurations and abbreviated orbital diagrams for each of the elements given below. Circle the valence electrons in your complete electron configurations.
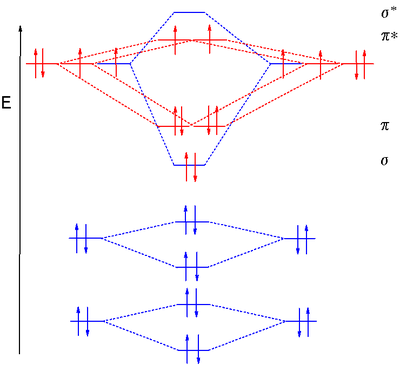
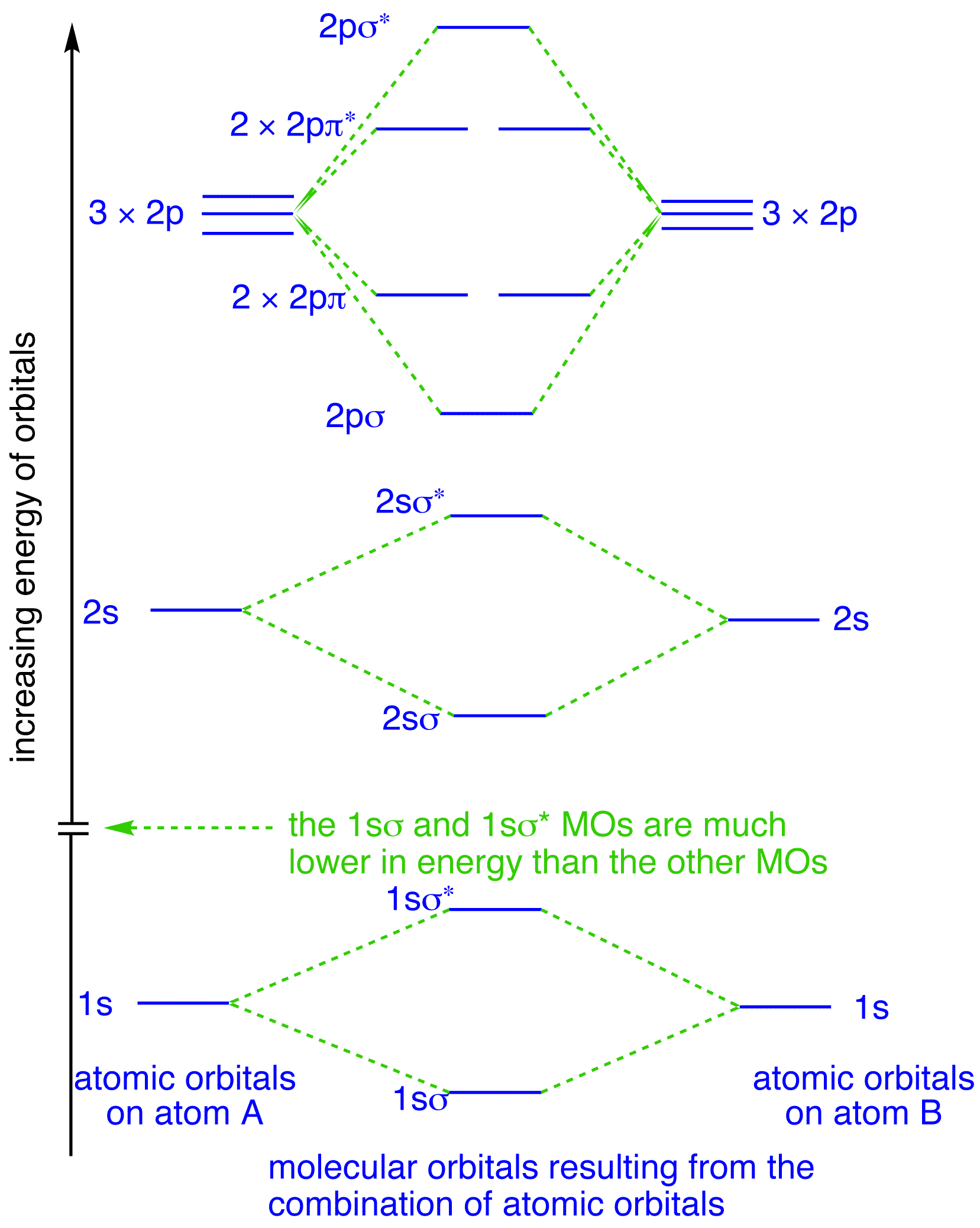
Molecular orbital diagram s are diagram s of MO energy levels, shown as short horizontal lines in the center, flanked on the sides by constituent AO energy levels for comparison, with the energy levels ranging from low energy at the bottom to high energy at the top. A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms ...
A nitrogen atom has seven electrons. In the ground state, they are arranged in the electron configuration 1s 2 2s 2 2p 1 x 2p 1 y 2p 1 z.It therefore has five valence electrons in the 2s and 2p orbitals, three of which (the p-electrons) are unpaired. It has one of the highest electronegativities among the elements (3.04 on the Pauling scale), exceeded only by chlorine (3.16), oxygen (3.44 ...
Graphite (/ ˈ ɡ r æ f aɪ t /), archaically referred to as plumbago, is a crystalline form of the element carbon with its atoms arranged in a hexagonal structure.It occurs naturally in this form and is the most stable form of carbon under standard conditions.Under high pressures and temperatures it converts to diamond.Graphite is used in pencils and lubricants.
unit iv: chemical bonding and molecular structure Valence electrons, ionic bond, covalent bond, bond parameters, Lewis structure, polar character of covalent bond, valence bond theory, resonance, geometry of molecules, VSEPR theory, concept of hybridization involving s, p and d orbitals and shapes of some simple molecules, molecular orbital ...
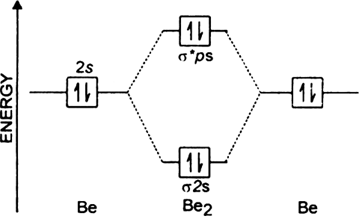
Beryllium is a chemical element with the symbol Be and atomic number 4. It is a steel-gray, strong, lightweight and brittle alkaline earth metal.It is a divalent element that occurs naturally only in combination with other elements to form minerals. Notable gemstones high in beryllium include beryl (aquamarine, emerald) and chrysoberyl.It is a relatively rare element in the universe, usually ...
How many valence electrons does boron have? You must recognize that the second principal energy level consists of both the 2 s and the 2 p sublevels and so the answer is three. In fact, the number of valence electrons goes up by one for each step across a period until the last element is reached. 1 Draw a Bohr Model of Beryllium Draw a Bohr ...
Chapter 9: models of chemical bonding. lewis dot symbols ionic bonding metallic bonding covalent bonding polar bonds electronegativity. lewis symbols. practice. give lewis dot symbols for:. oxide ion. magnesium. sodium ion. nitrogen. fluorine. argon. boron. 128 views download presentation. chapter #9 models of chemical bonding. 9.1) atomic properties and chemical bonds 9.2) the ionic bonding ...
A chemical bonding of several metallabenzenes and metallabenzynes was studied via an adaptive natural density partitioning (AdNDP) algorithm and the induced magnetic field analysis. A unique chemical bonding pattern was discovered where the M=C (M: Os, Re) double bond coexists with the delocalized 6c-2e π-bonding elements responsible for aromatic properties of the investigated complexes.
Molecular orbital diagram practice worksheet
The molecular orbital diagram representing this order of energy levels is shown in fig. Fig. No. 5 Order of Energy Levels for Boron, Carbon, Nitrogen etc. This kind of energy reversal is due to mixing of 2s and 2p orbitals where the energy difference is very close, that is, for B, C, and N atoms.



















0 Response to "41 boron molecular orbital diagram"
Post a Comment