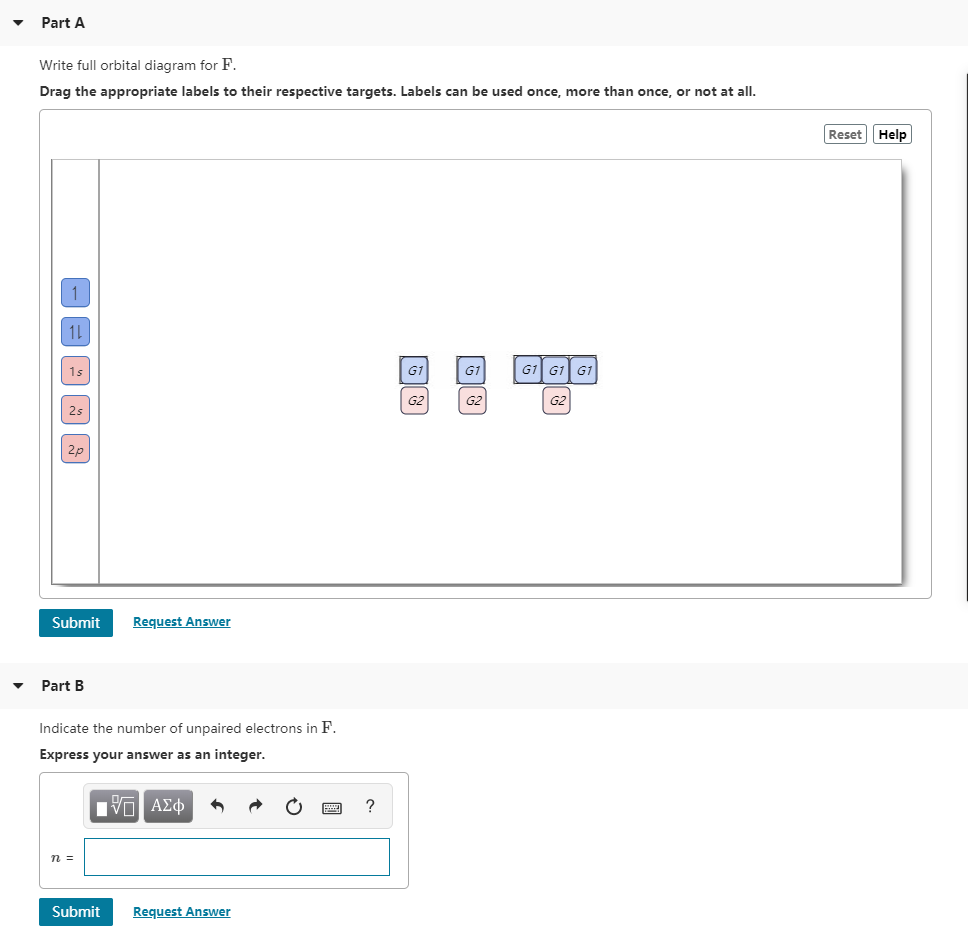
40 write full orbital diagram for f.
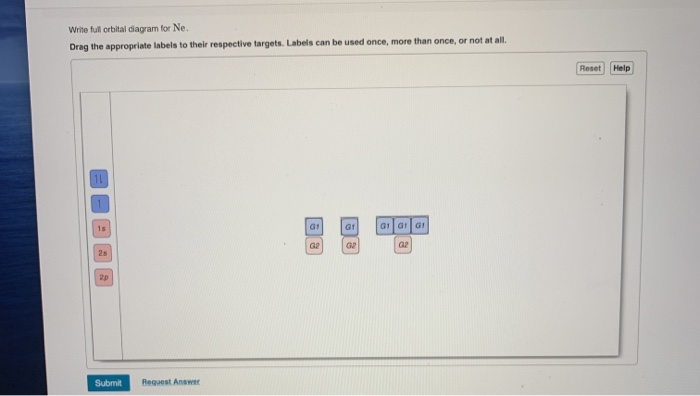
Transcribed image text: Part A Write the full orbital diagram for F. Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. Labels can be used once, more than once, or not at all. Reset Help 11 1s G1 G1 G1 G1 G1 G2 G2 G2 2s 2p Write the full orbital diagram for C. Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. Orbital Filling Diagram Electron Configuration Electron Dot Diagram a. Boron b. Silicon c. Sulfur d. Calcium e. Iodine f. Rubidium g. Chromium h. Gallium Where are the Electrons? Write the full electron configuration, short-hand electron configuration, and fill in the orbital diagrams, for the following elements. 1.
11. Write full orbital diagrams and indicate the number of unpaired electrons for each element. a) P: b) K: c) He: d) Al: 12. Write full orbital diagrams and indicate the number of unpaired electrons for each element. a) F: b) Be: c) B: d) Cl: 13. Write the noble gas electron configuration for the following elements. a) Nb: b) Se: c) Ca: d) Zn: 14.

Write full orbital diagram for f.
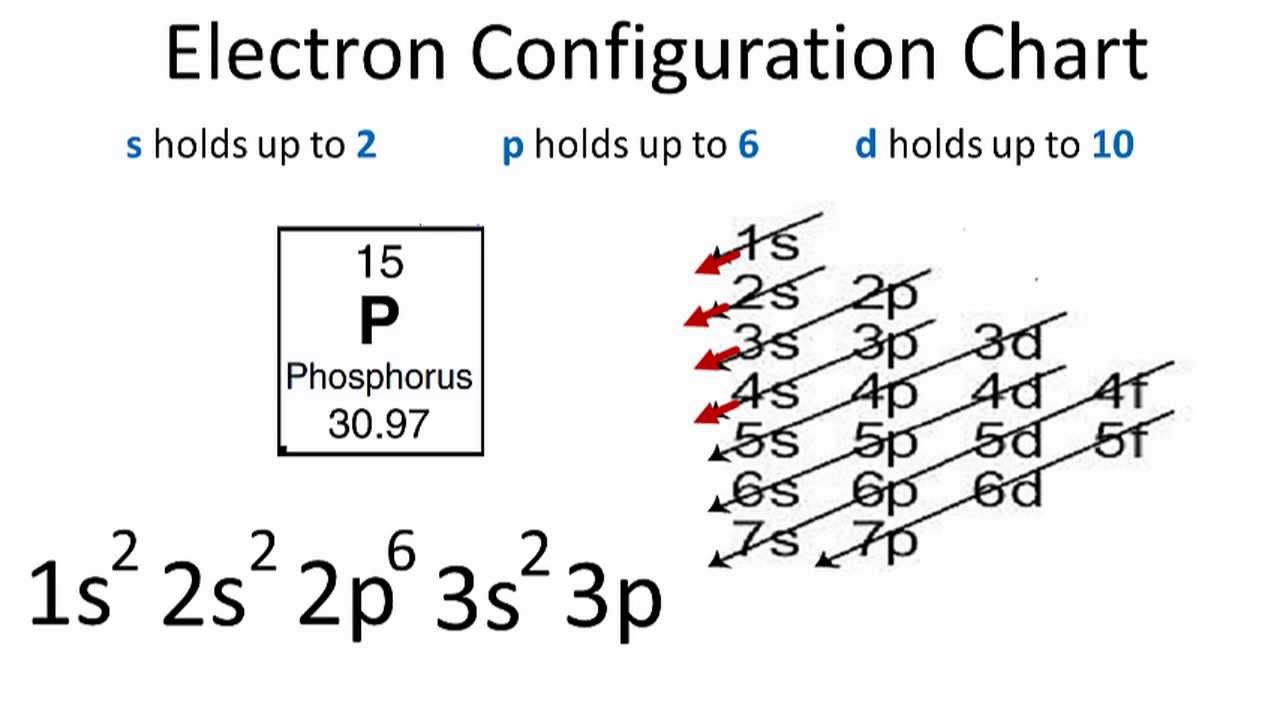
4. Each sublevel has increasing odd numbers of orbitals available. s = 1, p = 3, d = 5, f = 7. Each orbital can hold only two electrons and they must be of opposite spin. An s-sublevel holds 2 electrons, a p-sublevel holds 6 electrons, a d-sublevel holds 10 electrons, and an f-sublevel holds 14 electrons. For Strontium:a) Write the full electron configuration.b) Write the condensed electron configuration.c) Predict the common ion for Strontium.d) Write the con... This chemistry video tutorial provides a basic introduction into orbital diagrams and electron configuration. It explains how to write the orbital diagram n...
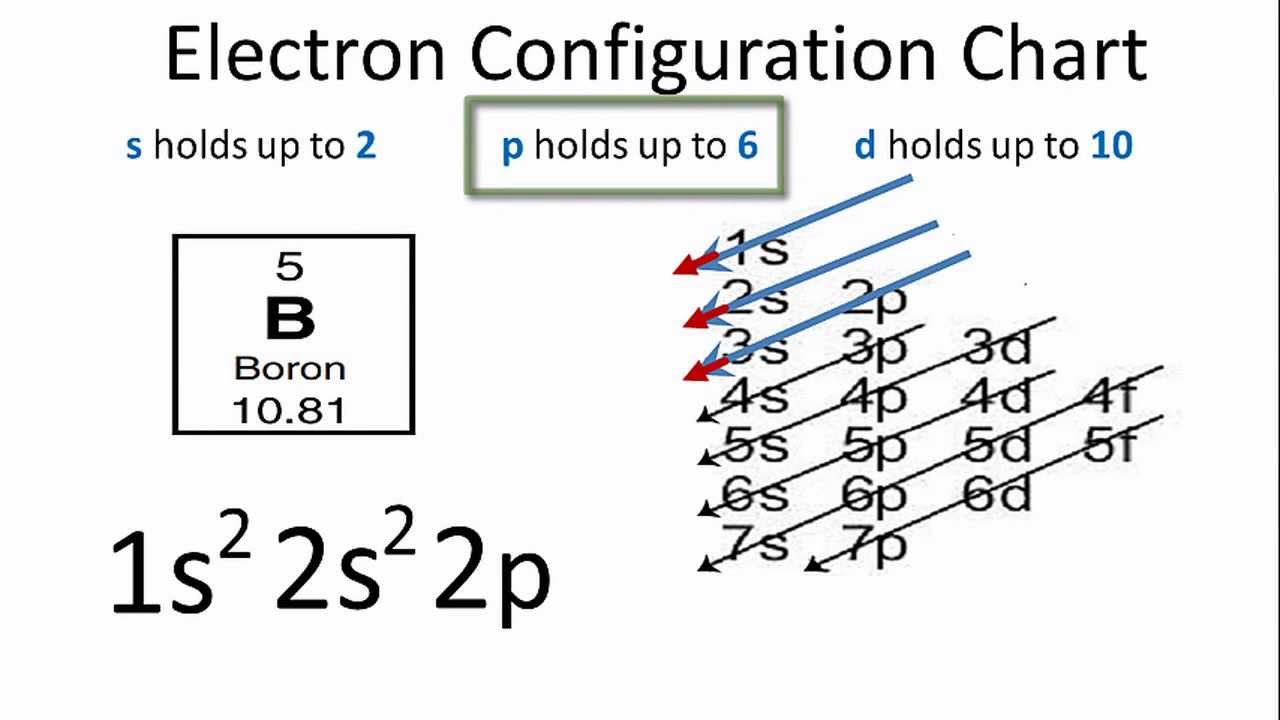
Write full orbital diagram for f.. The first number is the principal quantum number (n) and the letter represents the value of l (angular momentum quantum number; 1 = s, 2 = p, 3 = d and 4 = f) for the orbital, and the superscript number tells you how many electrons are in that orbital. Orbital diagrams use the same basic format, but instead of numbers for the electrons, they ... How to Write the Electron Configuration for Fluorine. Fluorine is the ninth element with a total of 9 electrons. In writing the electron configuration for fluorine the first two electrons will go in the 1s orbital. Since 1s can only hold two electrons the next 2 electrons for F go in the 2s orbital. An orbital diagram is a different way to show the electron configuration of an atom. It symbolizes the electron as an arrow in a box that represents the orbital. The orbital for a hydrogen atom: (is a box with 1s under it and an H next to it. It has one arrow in it facing up) The orbital diagram of fluorine is as follows: In an atom of fluorine, there are nine electrons and they are distributed as shown in the orbital diagram.Transcribed image text: Part A Write the full orbital diagram for F. Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. Labels can be used once, more than once, or not at all. Reset Help 11 1s G1 G1 G1 G1 G1 G2 G2 G2 2s 2p Write the full ...
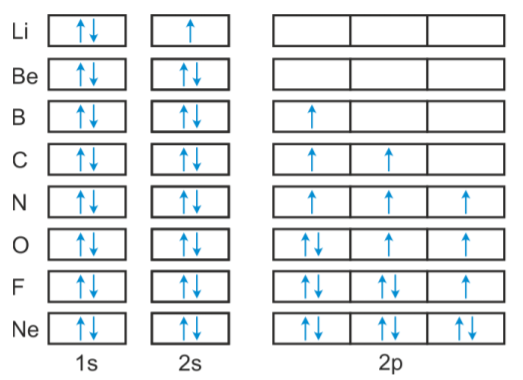
Use this tool to draw the orbital diagram. 3d. 4p. Draw orbital diagrams for the following elements. Write the electron configuration (full, and in core notation). 1. scandium. ↑↓. ↑↓. ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓. ↑↓. Contrary to what you may have seen, for Sc and the remaining elements, the 4s is not lower in energy than the 3d. In fact ... Orbital diagram of Hydrogen (H) 2: Orbital diagram of Helium (He) 3: Orbital diagram of Lithium (Li) 4: Orbital diagram of Beryllium (Be) 5: Orbital diagram of Boron (B) 6: Orbital diagram of Carbon (C) 7: Orbital diagram of Nitrogen (N) 8: Orbital diagram of Oxygen (O) 9: Orbital diagram of Fluorine (F) 10: Orbital diagram of Neon (Ne) 11 ... Write full orbital diagrams and indicate the number of unpaired electrons fo… 04:14. Write the full orbital diagram for each element. a. N b. F c… 02:16. Write the full orbital diagram for each element. \begin{equation} \beg… 03:30. Draw orbital-filling diagrams for the following atoms. ... The orbital filling diagram for helium. The electron configuration for helium is 1s². This means that we have two electrons in the 1s orbital, which looks like this: This diagram is exactly the same as the one for hydrogen, except that there's a second arrow added to the 1s orbital. This represents the second electron in the 1s orbital, and ...
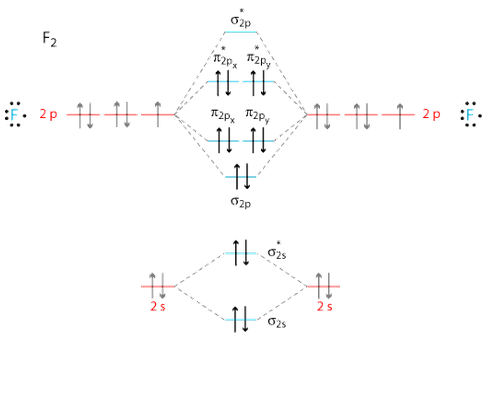
How to Write an Electron Configuration. The symbols used for writing the electron configuration start with the shell number (n) followed by the type of orbital and finally the superscript indicates how many electrons are in the orbital. For example: Looking at the periodic table, you can see that Oxygen has 8 electrons. Transcribed image text: Part A Write full orbital diagram for F. Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. Labels can be used once, more than once, or not at all. Reset Help @@@BE G1G1GT Submit Request Answer - Part B Indicate the number of unpaired electrons in F. Express your answer as an integer. Orbital Filling Diagrams •Each box represents an orbital which can hold a max of 2 e- •Aufbau principal -each electron occupies the lowest energy orbital available; German for "build up" •Electrons are notated with an arrow -Up arrow goes first then, down arrow -Arrows represent the opposing spin of electrons 5.2 Quantum Theory & The Atom Molecular Orbital Diagrams simplified. Megan Lim. Oct 26, 2016 · 3 min read. Drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry. The first major step is understanding ...
Orbital Diagram For Carbon - Materials Free Full. electron configuration for fluorine f terpconnect electron configuration notation the remaining five electrons will go in the 2p orbital therefore the f electron configuration will be 1s 2 2s 2 2p 5. What Is An Orbital Diagram - Functional Block Diagram Examples Originalstylophone.
The 3dx² - y² orbital looks exactly like the first group, except that that the lobes are pointing along the x and y axes, not between them. The 3dz² looks like a p orbital wearing a doughnut around its waist. f ORBITALS. At the fourth and higher levels, there are seven f orbitals in addition to the 4s, 4p, and 4d orbitals.
Full Orbital Diagram: Full orbital diagram demonstrates the organization of the electron in an orbital. The electrons arrangement follows the Pauli, Hunds, and also Aufbau rules.
In writing the electron configuration for Calcium the first two electrons will go in the 1s orbital. Since 1s can only hold two electrons the next 2 electrons for Calcium go in the 2s orbital. The next six electrons will go in the 2p orbital. The p orbital can hold up to six electrons. We'll put six in the 2p orbital and then put the next two ...
Correct Part F Indicate the number of unpaired electrons in it. Express your answer as an integer. ANSWER: ANSWER: = 0 Correct Part G Write full orbital diagram for. Use the buttons at the top of the tool to add orbitals. Click within the orbital to add electrons.
Answer to: (a) Write the full orbital diagram for F. (b) Indicate the number of unpaired electrons in it. By signing up, you'll get thousands of...
Complete an orbital diagram for scandium (Sc). Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. Labels can be used once, more than once, or not at all. Part C Electron configurations are a shorthand form of an orbital diagram, describing which orbitals are occupied for a given element.
Write the full orbital diagram for element. F. close. Start your trial now! First week only $4.99! arrow_forward. Question. Write the full orbital diagram for element. F. check_circle Expert Answer. Want to see the step-by-step answer? See Answer. Check out a sample Q&A here.
Neon atoms are the 2nd period of the periodic table and an element of the 18-group. The electron configuration of neon ends in a p-orbital. Therefore, it is a p-block element. The melting point of a neon atom is 24.56 K (−248.59 °C, −415.46 °F) and the boiling point is 27.104 K (−246.046 °C, −410.883 °F).
Write the orbital diagram for sulfur and determine its number of unpaired electrons. Electron configuration: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p4. Orbital diagram: 1s= 1 up 1 down. 2s= 1 up 1 down. 2p= 1 up 1 down 1 up 1 down 1 up 1 down. 3s= 1 up 1 down. 3p= 1 up 1 down 1 up 1 up. ... Write the full orbital diagram for each element. A.) N B.) F C.) Mg D.) Al.
The atomic number of carbon is 6, which is also the number of positively charged protons its atomic nuclei. If the atom is neutral, it will have the same number of negatively charged electrons. Its electron configuration is "1s"^2"2s"^2"2p"^2". The orbital diagram shows how the electrons are arranged within each sublevel. The maximum number of electrons allowed in an orbital is 2, each with ...
This chemistry video tutorial provides a basic introduction into orbital diagrams and electron configuration. It explains how to write the orbital diagram n...
For Strontium:a) Write the full electron configuration.b) Write the condensed electron configuration.c) Predict the common ion for Strontium.d) Write the con...
4. Each sublevel has increasing odd numbers of orbitals available. s = 1, p = 3, d = 5, f = 7. Each orbital can hold only two electrons and they must be of opposite spin. An s-sublevel holds 2 electrons, a p-sublevel holds 6 electrons, a d-sublevel holds 10 electrons, and an f-sublevel holds 14 electrons.
















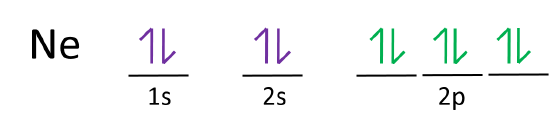

/800px-Orbital_representation_diagram.svg-589bd6285f9b58819cfd8460.png)

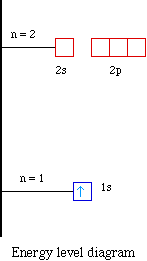
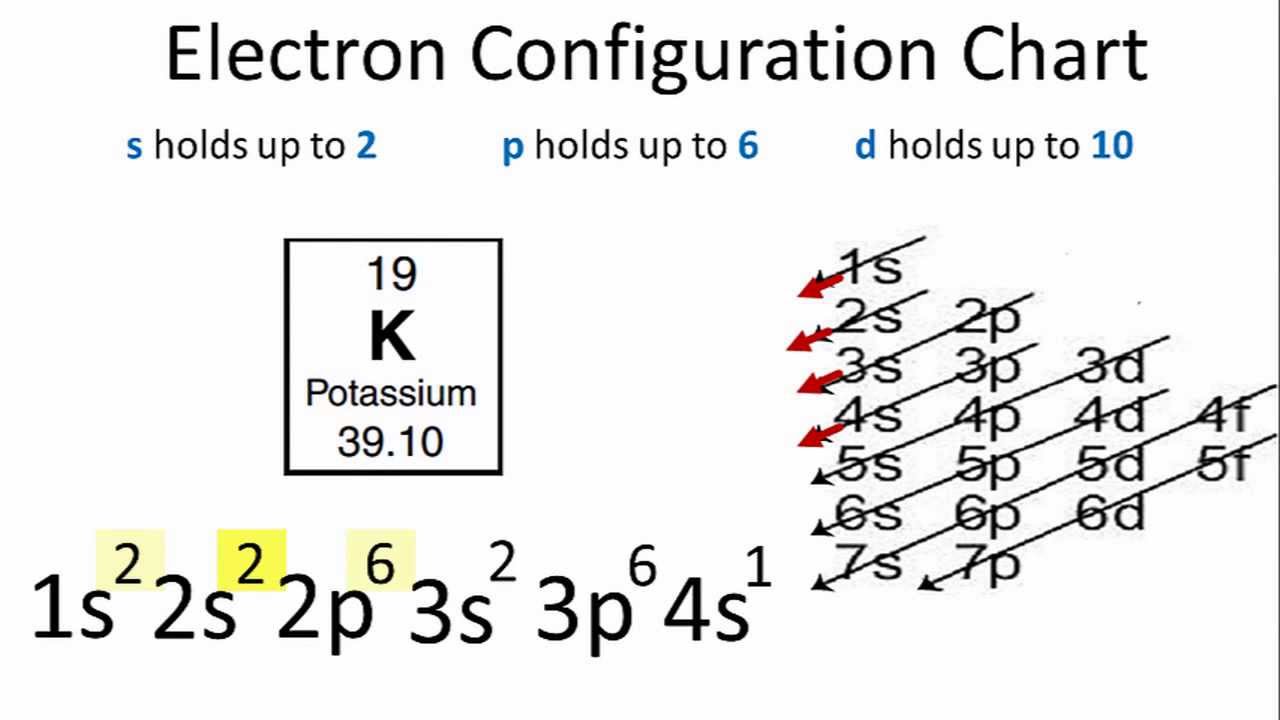






0 Response to "40 write full orbital diagram for f."
Post a Comment