40 brain and spinal cord diagram
The extension of the central nervous system is through the medulla oblongata, which continues as the spinal cord, by exiting the skull through the foramen magnum and continuing in the spinal column. This is where the spinal cord gives out nerves which form the peripheral nervous system.
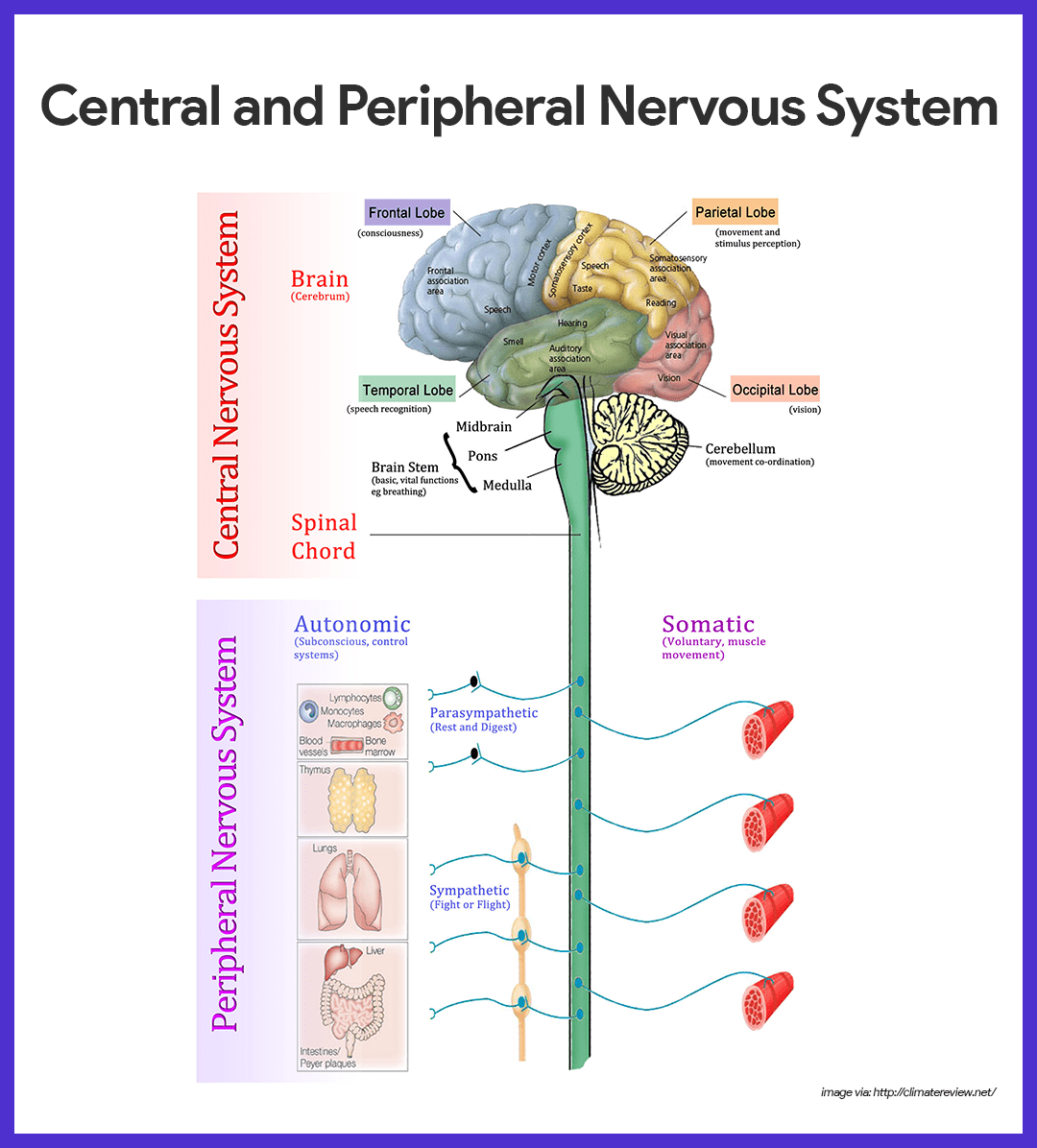
The brain stem begins inferior to the thalamus and runs approximately 7 cm before merging into the spinal cord. The brain stem centers produce the rigidly programmed, automatic behaviors necessary for survival. Positioned between the cerebrum and the spinal cord, the brain stem also provides a pathway for fiber tracts ...
The medulla oblongata is a roughly cylindrical mass of nervous tissue that connects to the spinal cord on its inferior border and to the pons on its superior border. The medulla contains mostly white matter that carries nerve signals ascending into the brain and descending into the spinal cord.
Brain and spinal cord diagram
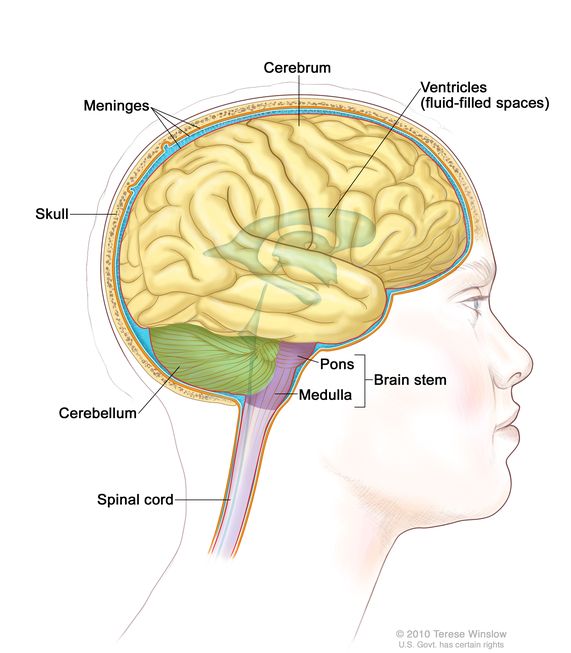
The brain is surrounded by a skull, which is made up of 22 bones - 14 are facial bones and 8 are cranial bones. The skull protects the brain from the frontal, lateral, and dorsal directions. The brain is confined within the cranium and covered by cerebrospinal fluid. The Cerebrospinal Fluid or CSF flows through the skull and spinal cord.
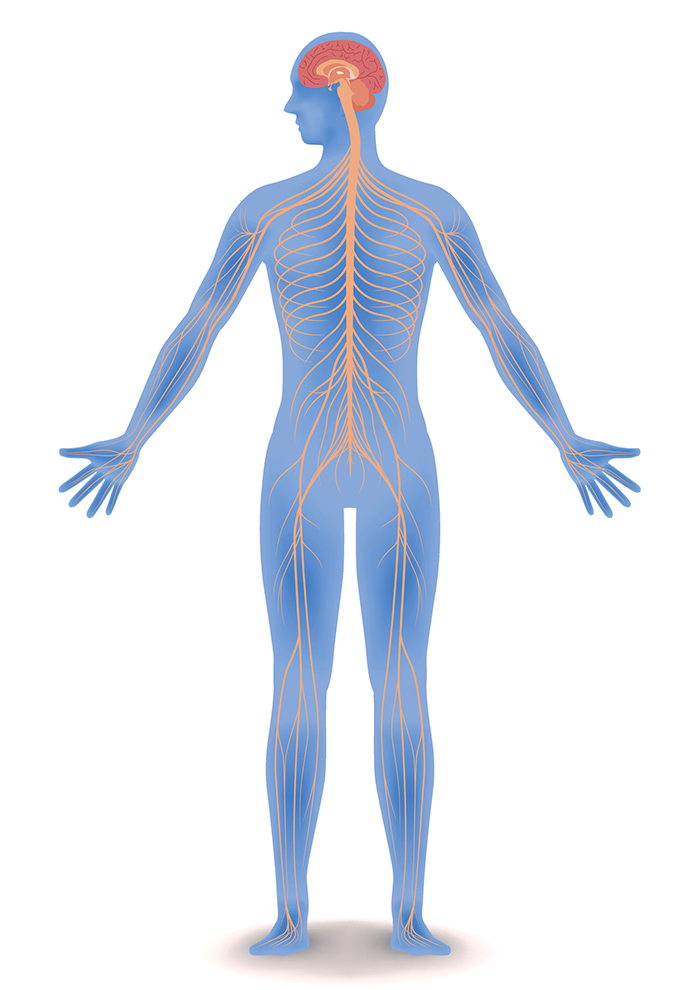
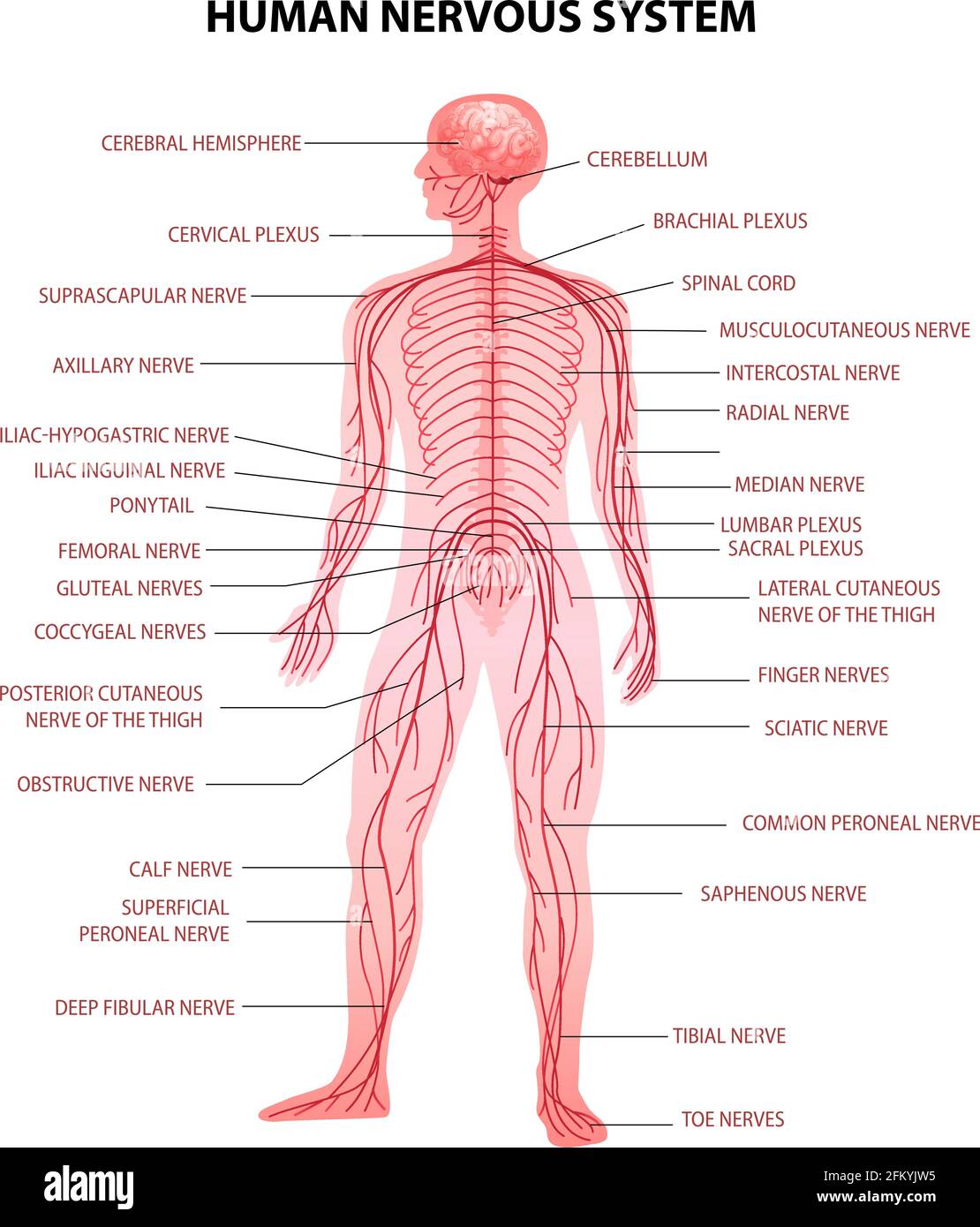
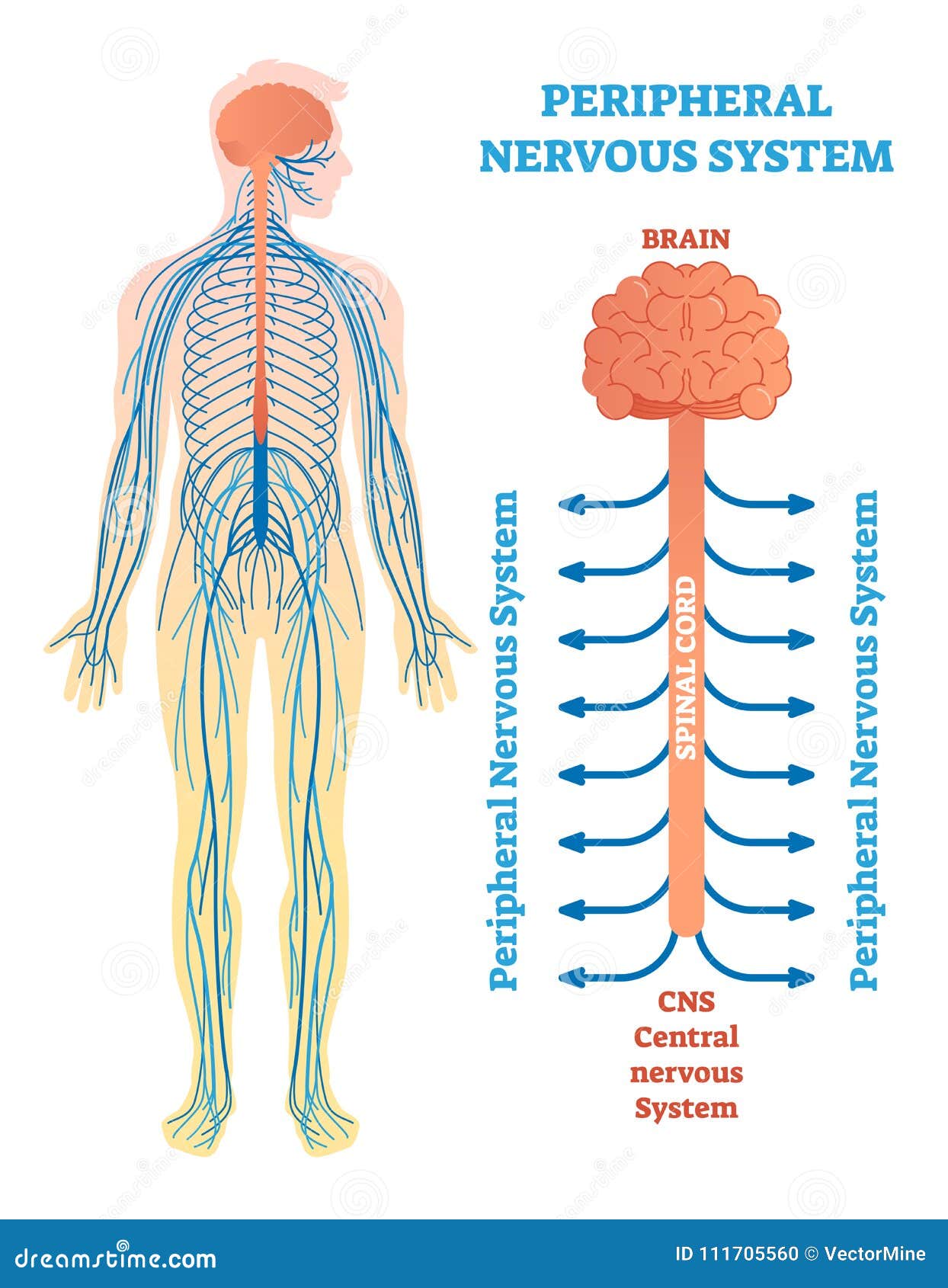
The brain and spinal cord (the CNS) function as the control center. They receive data and feedback from the sensory organs and from nerves throughout the body, process the information, and send commands back out. Nerve pathways of the PNS carry the incoming and outgoing signals.
The brain and its meninges are contained in a tough, bony protective structure, the skull. The spinal cord Spinal Cord The spinal cord is a long, fragile tubelike structure that begins at the end of the brain stem and continues down almost to the bottom of the spine. The spinal cord consists of bundles of nerve...
Brain and spinal cord diagram.
(11) This brain part controls involuntary actions such as breathing, heartbeats, and digestion. (12) cerebrum cerebellum brain stem spinal cord This part of the nervous system moves messages between the brain and the body.
Spinal Cord Controls simple reflexes Pathway to neural fibers Medulla Controls/regulates heartbeat and breathing To and from brain Reticular Formation Helps control arousal, responds to change in monotony Thalamus Relays sensory information, switchboard between sensory neurons and higher brain regions Deals with sight, hearing, touch, taste.
The CNS is the processing centre of the body and consists of the brain and the spinal cord. Both of these are protected by three layers of membranes known as meninges. For further protection, the brain is encased within the hard bones of the skull, while the spinal cord is protected with the bony vertebrae of our backbones.
The brain stem connects the spinal cord to the higher-thinking centers of the brain. It consists of three structures: the medulla oblongata, the pons, and the midbrain. The medulla oblongata is continuous with the spinal cord and connects to the pons above. Both the medulla and the pons are considered part of the hindbrain.
Spinal Cord Diagram. The spinal cord is one of the most important structures in the human body. In fact, it is the most important structure for any vertebrates. Anatomically, the spinal cord is made up is made up of nervous tissue and is integrated into the spinal column of the backbone.
The spinal cord is a single structure, whereas the adult brain is described in terms of four major regions: the cerebrum, the diencephalon, the brain stem, and the cerebellum. A person's conscious experiences are based on neural activity in the brain. The regulation of homeostasis is governed by a specialized region in the brain.
Function: Connects Vertebro-basilar system and Internal carotid system. Circle of Willis (Function) 1) To maintain COLLATERAL CIRCULATION in case of blockage of any of the components. 2) Equalizes blood flow to different parts of the brain. 3) Connects Vertebro-basilar system and Internal carotid system. Circle of Willis Defects.
Spinal Cord Brain Diagram. angelo. December 1, 2021. Brain And Spinal Cord Anatomy From The Merck Manual Home Healthbook Basic Anatomy And Physiology Brain Anatomy Medical Anatomy. Find Hd Draw A Labelled Diagram Of A Section Of Human Brain Human Brain Class 10 Hd Png Download To Search And Download Mor Human Brain Brain Diagram Brain.
A complete spinal cord injury means that there is a total blockage of signals from the brain to your sacral nerves. An incomplete spinal cord injury means there is some preservation of nerves from the brain to the lowest part of the spinal cord, the sacral level. The amount of movement and feeling that
Together with the brain and the spinal cord, the nerves constitute the nervous system. To distinguish the control centres from the information pathways, we divide the nervous system into two sub-systems (to see them, run your cursor over their names in the following diagram):
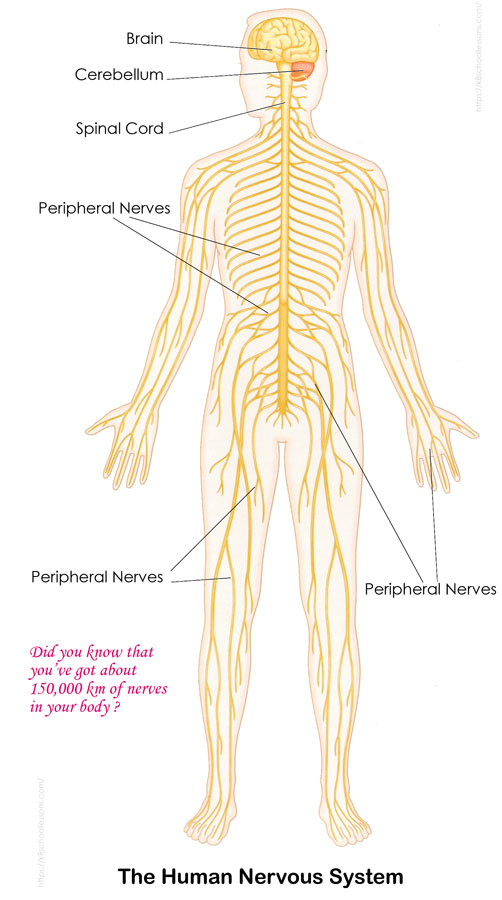
12 cranial nerves (diagram) Cranial nerves are peripheral nerves that emerge from the cranial nerve nuclei of the brainstem and spinal cord. They innervate the head and neck. Cranial nerves are numbered one to twelve according to their order of exit through the skull fissures.
The spinal motor neurons project out of the cord to the correct muscles via the ventral root. These connections control conscious movements, such as writing and running. Information also flows in the opposite direction resulting in involuntary movement. Sensory neurons provide feedback to the brain via the dorsal root.
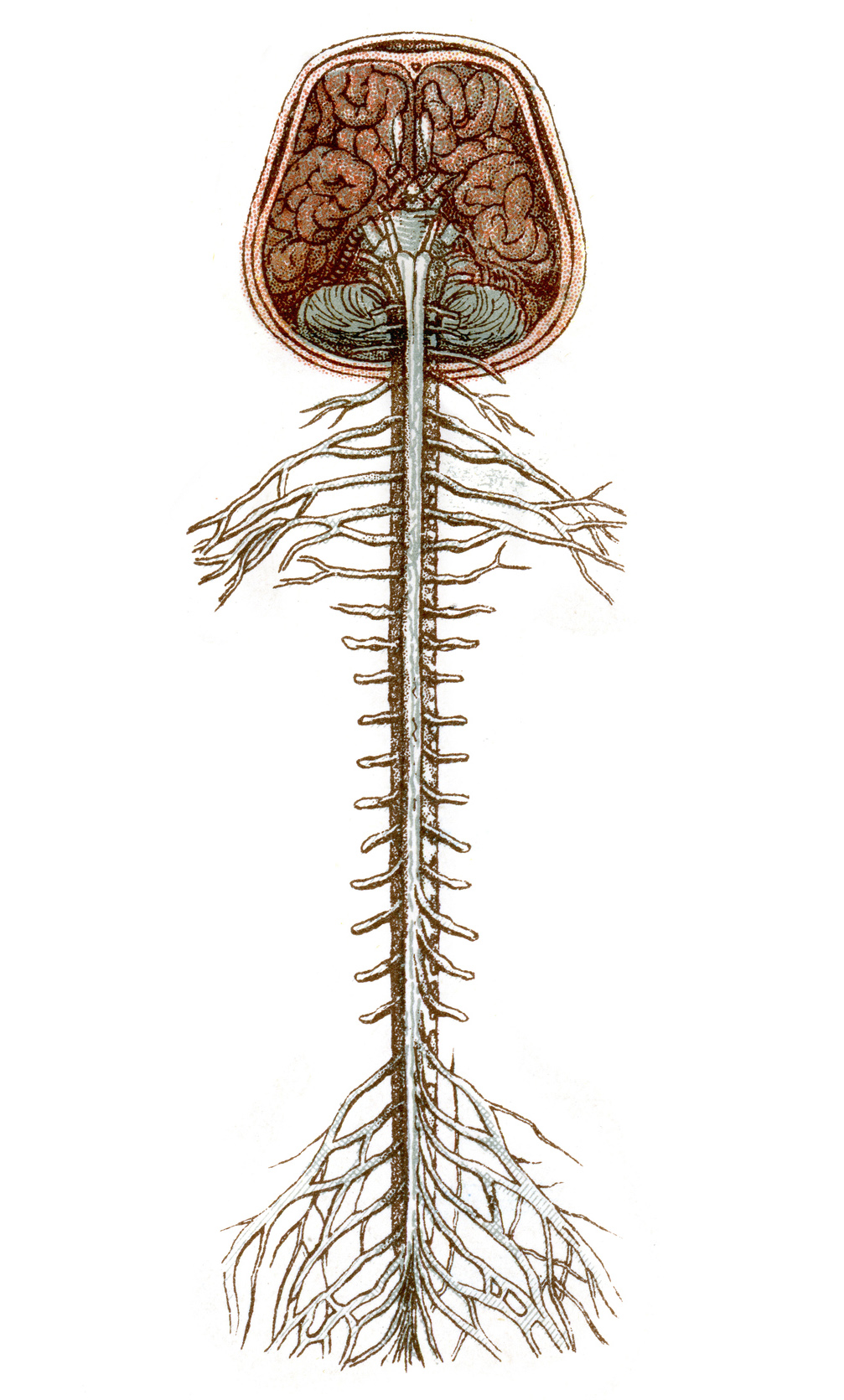
The spinal cord is a long, fragile tubelike structure that begins at the end of the brain stem and continues down almost to the bottom of the spine. The spinal cord consists of bundles of nerve axons forming pathways that carry incoming and outgoing messages between the brain Brain The brain's functions are both mysterious and remarkable ...
lower-motor neuron in the brain stem or spinal cord. The axon of the lower-motor neuron has direct control over skeletal muscle fibers. Stimulation of the lower- motor neuron always has an excitatory effect on the skeletal muscle fibers. Skeletal muscle Skeletal muscle Somatic motor nuclei of brain stem Lower motor neurons
Neural pathways that connect the brain and the spinal cord are called the ascending and descending tracts. They are responsible for carrying sensory and motor messages to and from the periphery. For example; this is how sensation from your fingertips reaches your brain and how conscious and reflexive actions return to your fingers.
Internal structure of the human brain Spinal Cord Protected by the vertebrae and cerebrospinal fluid. Nerves from the body parts enter the spinal cord as 31 pairs of spinal nerves. The spinal cord is the pathway for all the impulses that are conducted to and from the brain and also processes reflex actions.
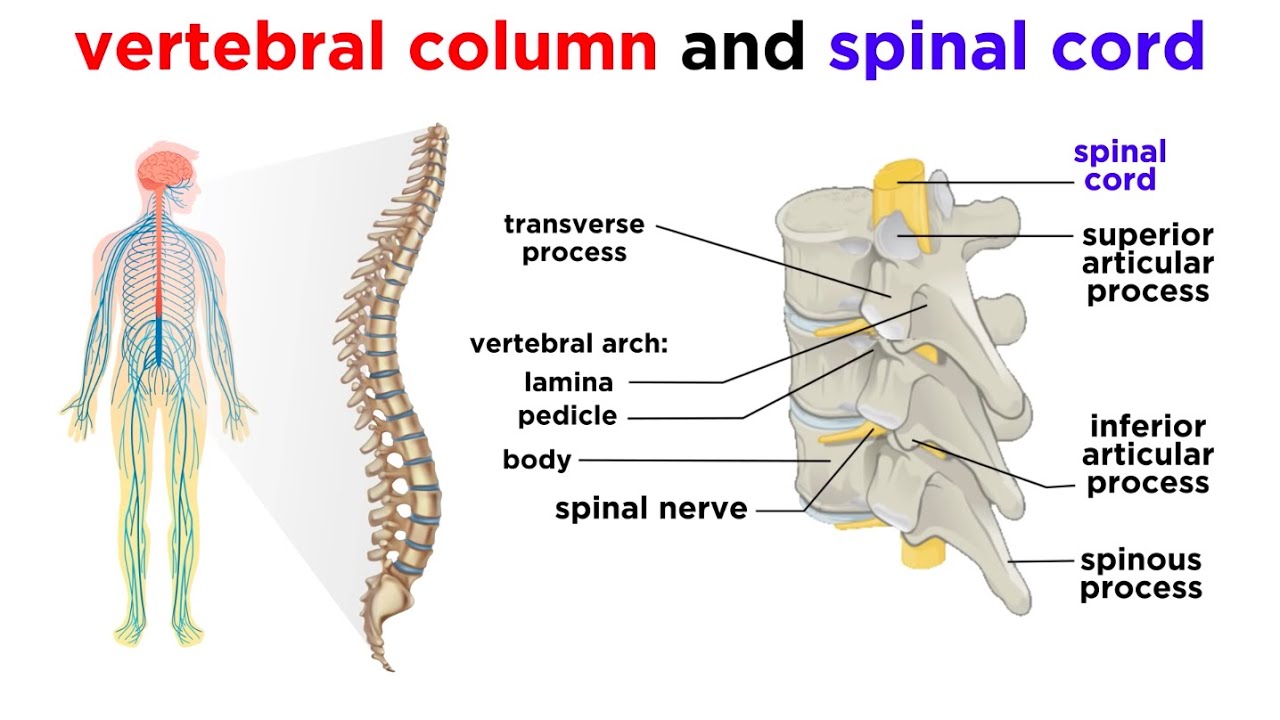
Spine and Nerves. The vertebral column's most important physiologic function is protecting the spinal cord, which is the main avenue for communication between the brain and the rest of the body ...
Ques. Briefly describe the difference between the brain and spinal cord. (3 marks) Ans: The brain and the spinal cord are part of the nervous system. They mainly differ in terms of functions, structure, and location. The brain is present inside the skull (cranium) while the spinal cord is protected by the vertebral column.
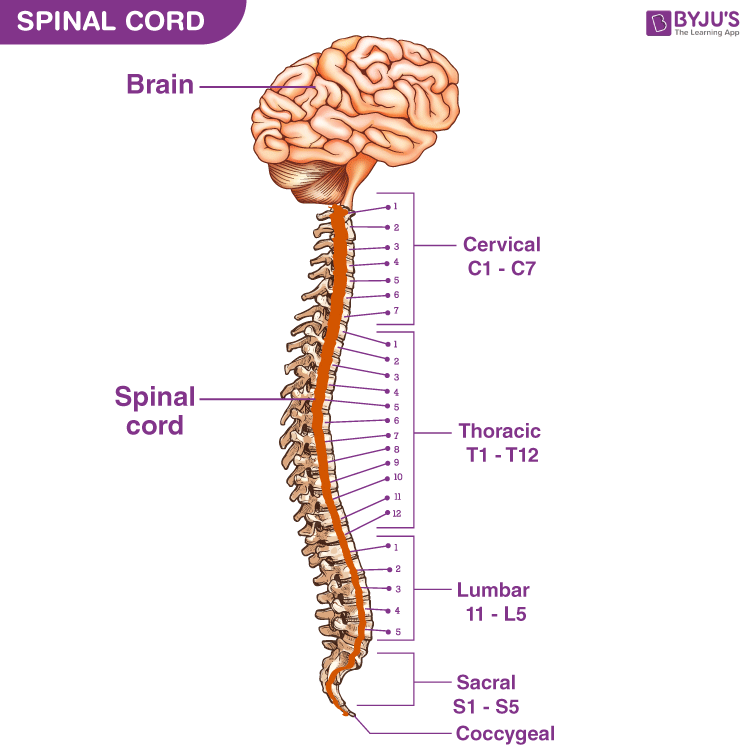
Human Spinal Cord: Structure and Effects (With Diagram) The human spinal cord is made up 31 segments. From each of these segments, a pair of spinal nerves takes origin. Hence there are 31 pairs of spinal nerves. Of 31 pairs: i. 8 belong to cervical segments. ii. 12 belong to thoracic segments.
central nervous system (CNS) consists of the brain and spinal cord; body's integration and interpretation center the CNS is composed mainly of interneurons peripheral nervous system (PNS) conssits of all parts of the nervous system outside the brain and spinal cord the PNS is composed mainly of sensory and motor nerurons
Ventricles are hollow cavities of the brain, that contain the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), which circulates within the brain and spinal cord. There are all together four ventricles in the human brain, that constitute the ventricular system, along with the cerebral aqueduct. They are known as, lateral ventricles, third ventricle, and fourth ventricle.
Spinal Cord Anatomy. In adults, the spinal cord is usually 40cm long and 2cm wide. It forms a vital link between the brain and the body. The spinal cord is divided into five different parts. Several spinal nerves emerge out of each segment of the spinal cord. There are 8 pairs of cervical, 5 lumbar, 12 thoracics, 5 sacral and 1 coccygeal pair ...
Brain And Spinal Cord Diagram Name angelo. November 28, 2021. Pin On Optometry . ... Nervous System For Kids Brain Spinal Cord Nerves Human Body Nervous System Human Nervous System Human Body Unit . In cord, diagram, name. Leave a Reply Cancel reply. You must be logged in to post a comment.


(246).jpg)
/what-is-the-peripheral-nervous-system-2795465-FINAL-b69e1bb803654212a83d9e68eb4847d0.png)



















:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/brain_spinal_cord-57fe96b15f9b5805c26d5072.jpg)


0 Response to "40 brain and spinal cord diagram"
Post a Comment