39 d orbital energy level diagram
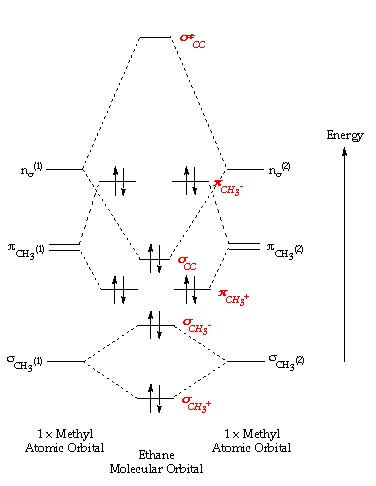
The molecular, sp 3 orbitals are arranged in a tetrahedron, with bond angles of 109.5 o. Each of the 1s orbitals of H will overlap with one of these hybrid orbitals to give the predicted tetrahedral geometry and shape of methane, CH 4. Hybridization also changes the energy levels of the orbitals. The 2s orbital of carbon is lower in energy than the 2p orbitals, since it is more penetrating. The molecular orbital energy- level diagram that results is constructed by putting the molecular orbitals in order of increasing number of internuclear nodal planes, the orbital with no such nodal plane lying at lowest energy and the orbital with nodal planes between all the atoms lying at highest energy. A molecular orbital diagram, or MO ...
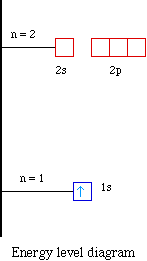
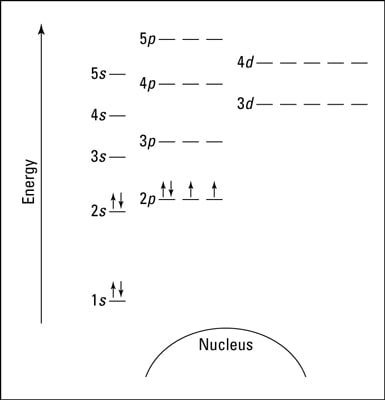
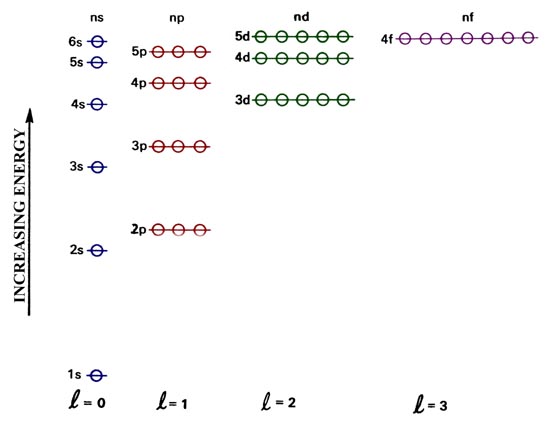
The Aufbau principle tells you that the lowest-energy orbitals fill first, but the specific order isn't sequential in a way that's easy to memorize. See Resources for a diagram showing the filling order. Note that the n = 1 level only has s orbitals, the n = 2 level only has s and p orbitals, and the n = 3 level only has s, p and d orbitals.
D orbital energy level diagram
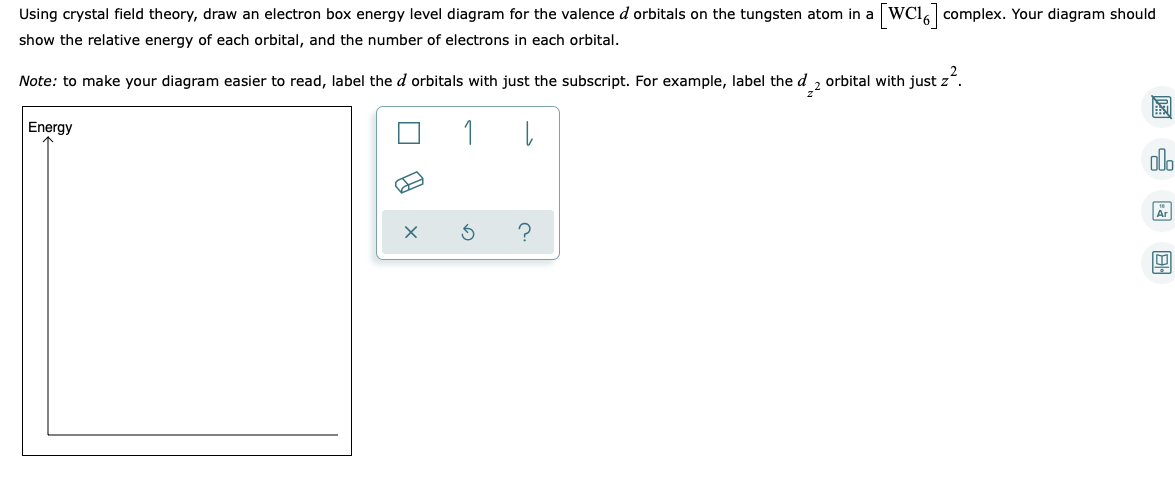
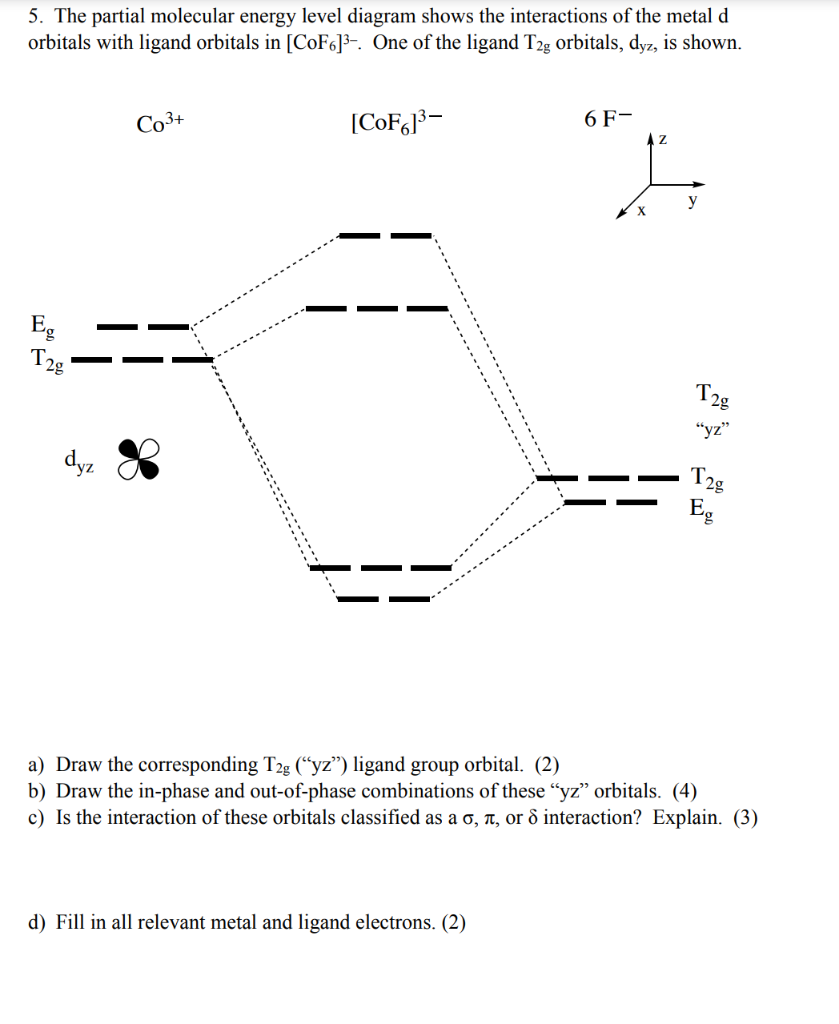
The diagram (not to scale) summarises the energies of the orbitals up to the 4p level. The oddity is the position of the 3d orbitals. They are shown at a slightly higher level than the 4s - and so it is the 4s orbital which will fill first, followed by all the 3d orbitals and then the 4p orbitals. Orbital Energy Level Diagram for O2. Energy Level Diagrams: Some Important Observations. The energy level diagram can help us deduce that the energy of the subshells of a specific shell is not equal. The energies of 2s and 2p, for example, are different. The subshell with the lowest value of I has the lowest energy in a given shell. 2s (I = 0) has lower energy than 2p (I = 1) in the second ... For each of the complexes (Co (NH3)6]3+ and [CoF6]3- (a) Draw an orbital energy level diagram that shows how the d-orbitals are split (ignore any Jahn-Teller distortion that might be present) and assign the appropriate labels (t2g, eg, e, or t2) to the d-orbitals. (b) Show how these orbitals are occupied by electrons and state whether each ...
D orbital energy level diagram. with the. d. orbital being one level lower than the energy level it is on. orbital diagram for arsenic see more ideas approximately from diagram electron configuration gallery & create your house design images related to pictures as well help you in locating the solution are seeking about itOrbital diagram for arsenic. Like all ligand-metal interaction diagrams, the energy levels of the ligands by themselves are shown on one side. The metal's electronic energy levels are shown on the other side. The result of their interaction, a metal-ligand complex, is shown in the middle. The d orbital splitting diagram is shown in a box. 9 May 2021 — The energy difference between the two d orbital levels is ... Like all ligand-metal interaction diagrams, the energy levels of the ligands ... Stable electronic configurations: MO Energy Level Diagrams Reviewed ... Ligand (σ- and π*) orbitals and metal d-orbitals are shown.) Simplified MO energy ...37 pages
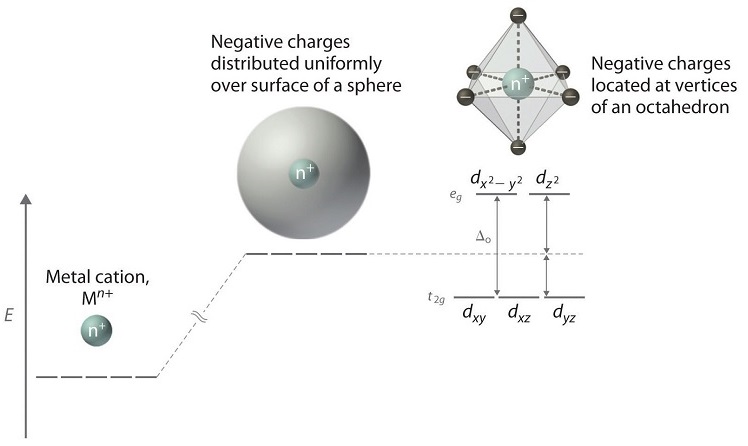
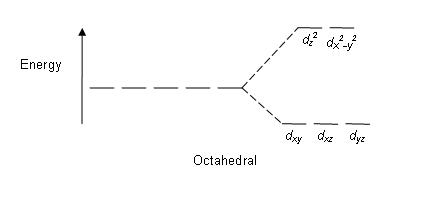
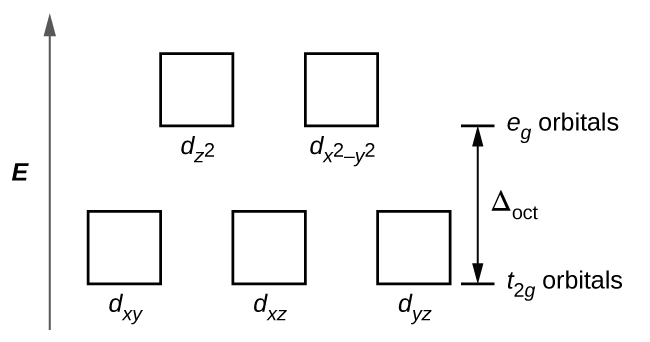
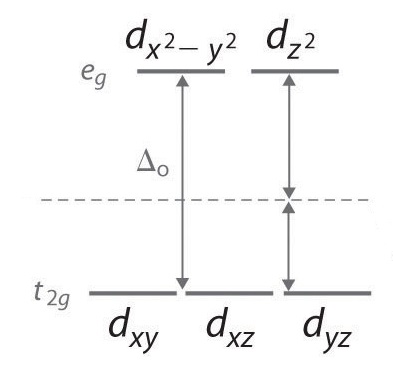
• The energy increase of the e g orbitals and the energy decrease of the t 2g orbitals must be balancedrelative to the energy of the hypotheticalsphericalfield(aka the barycenter).• The energy of each of the two orbitals of the e g set rises by +3/5 o (+6 Dq) while the energy of eachof the three t 2g orbitalsfallsby ‐2/5 o(‐4Dq). • Thisresults inno netenergy changefor the system: Your diagram should show the relative energy of each orbital, and the number of electron in each orbital. Question: Using crystal field theory, draw an electron box energy level diagram for the valence d orbital on the cobalt atom in a [CoBr_6]^3- complex. Your diagram should show the relative energy of each orbital, and the number of electron ... The s-orbital has the azimuthal quantum number value of 0, the p-orbital has a value of 1, and the d-orbital has two and f-orbital 3. The orbital energy levels of these are varied, s-orbital having the lowest energy level and f-orbital being the highest, summed up as s < p <; d < f. Each orbital has four lobes. Notice that each of the lobes is pointing ... you will have come across this diagram which shows the arrangement of the d electrons in a Cu 2+ ion before and after six water molecules bond with it. Notice that all of the d orbitals are now at a higher energy than in the uncombined ion due to the repulsions. But notice also that they are split into two groups. The ...
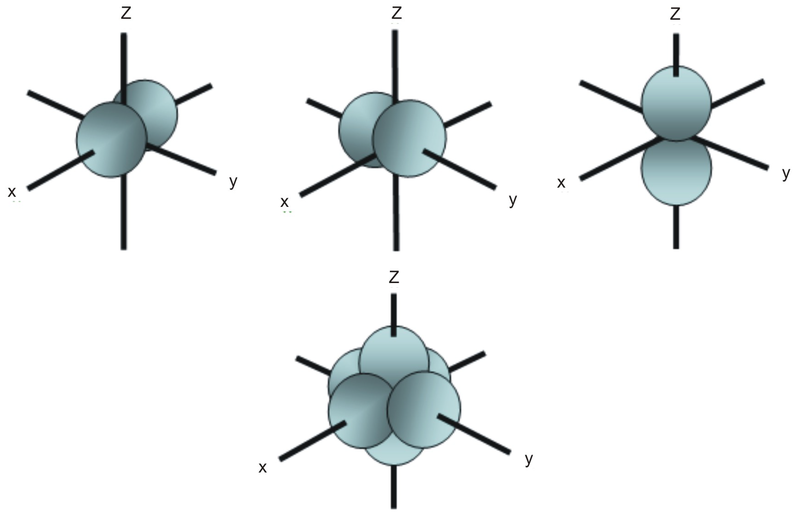
11 Oct 2021 · 1 answer(a) The complex ion, [Ni(en)3]2+ is octahedral. Since en is a strong ligand there is pairing of electrons. Number of unpaired electrons = n ... Figure 6.27 "Orbital Energy Level Diagram for the Hydrogen Atom" shows that the energy levels become closer and closer together as the value of n increases, as expected because of the 1/n 2 dependence of orbital energies. Figure 6.27 Orbital Energy Level Diagram for the Hydrogen Atom. At the first energy level, the only orbital available to electrons is the 1s orbital. However, at the second level, there are also orbitals called 2p orbitals in addition to the 2s orbital. Unlike an s orbital, a p orbital points in a particular direction. The one shown below points up and down the page. At any one energy level, we have three absolutely equivalent p orbitals pointing mutually ... Molecular Orbital Energy Diagrams. The relative energy levels of atomic and molecular orbitals are typically shown in a molecular orbital diagram . For a diatomic molecule, the atomic orbitals of one atom are shown on the left, and those of the other atom are shown on the right.
Below is a blank energy level diagram which helps you depict electrons for any specific atom. At energy level 2, there are both s and p orbitals. The 2s has lower energy when compared to 2p. The three dashes in 2p subshells represent the same energy. 4s has lower energy when compared to 3d. Therefore, the order of energy level is as follows: sd
The energy of an orbital depends on the shape and size of the orbital. In a multiple-electron system, the shielding effect also influences the orbital's energy. Energies of orbitals are quantized as per quantum mechanics. Thus, there are only selected energy levels available, which an electron can occupy. An electron residing in a particular ...
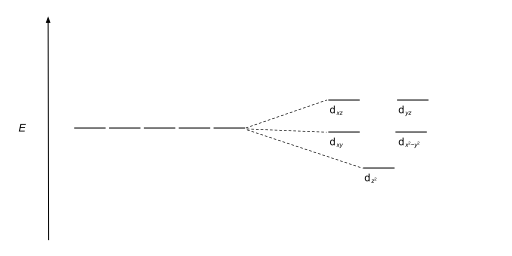
Any orbital in the xy plane has a higher energy level. There are four different energy levels for the square planar (from the highest energy level to the lowest energy level): d x 2-y 2, d xy, d z 2, and both d xz and d yz. Figure 6: Splitting of the degenerate d-orbitals (without a ligand field) due to an square planar ligand field.
Therefore, the electron energy levels of these five d-orbitals in mechanics forming a set five-fold degenerate energy level and the shape diagram dimensions of these orbitals identify by the principal, azimuthal, magnetic, spin quantum number or numbers of the atom for physics or chemistry courses.
Energy-Level Diagrams. Because electrons in the σ 1 s orbital interact simultaneously with both nuclei, they have a lower energy than electrons that interact with only one nucleus. This means that the σ 1 s molecular orbital has a lower energy than either of the hydrogen 1s atomic orbitals. Conversely, electrons in the \( \sigma _{1s}^{\star } \) orbital interact with only one hydrogen ...
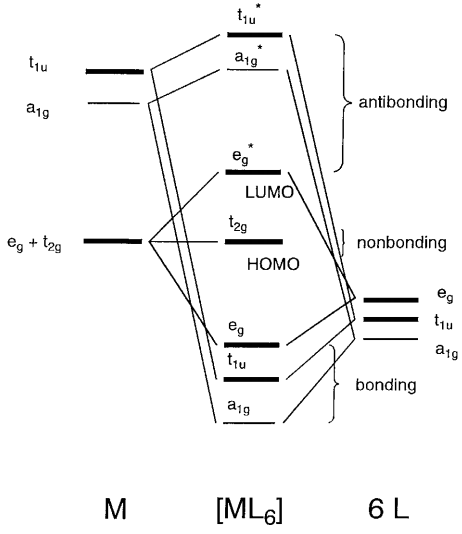
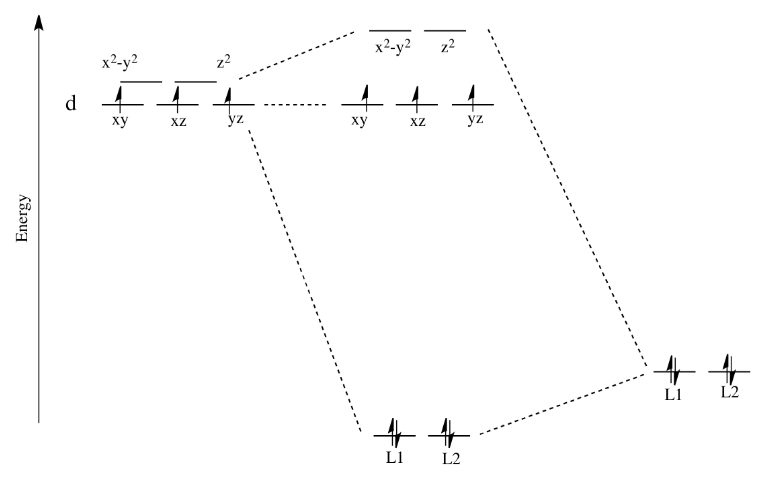
• that raises the energy of the d-orbitals! • The d-orbitals are anti-bonding or at best non-bonding. • The stability of the bonding comes from the ligand
A P-Orbital in the second energy level is a 2p orbital ( 2p(x), 2p(y), 2p(z) ) A P-Orbital in the third energy level is a 3p orbital ( 3p(x), 3p(y), 3p(z) ) etc. In addition, the third and subsequent energy levels each contain five D-Orbitals, the fourth and subsequent energy levels contain seven F-Orbitals and so on.
There are 2 h atoms on the outside. Character table for the the point group d3h. Molecular Orbital Energy Level Diagram Britannica For examplea molecular orbital diagram or mo diagram is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals lcao molecular orbital method in particular.
FIGURE 3.33 A typical d molecular orbital energy-level diagram for a heteronuclear diatomic molecule AB the relative contributions of the atomic orbitals to the molecular orbitals are represented by the relative sizes of the spheres and the horizontal position of the boxes. In this case, A is the more electronegative of the two elements. The molecular orbital energy-level diagrams of ...
The octahedral ion [Fe(NO2)6]3−, which has 5 d-electrons, would have the octahedral splitting diagram shown at right with all five electrons in the t2g level.Overview of crystal field theory · Crystal field stabilization energy
Download scientific diagram | Energy level ordering of d -orbitals in (a) tetrahedral and (b) octahedral crystal field environments. from publication: ...
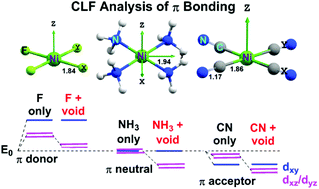
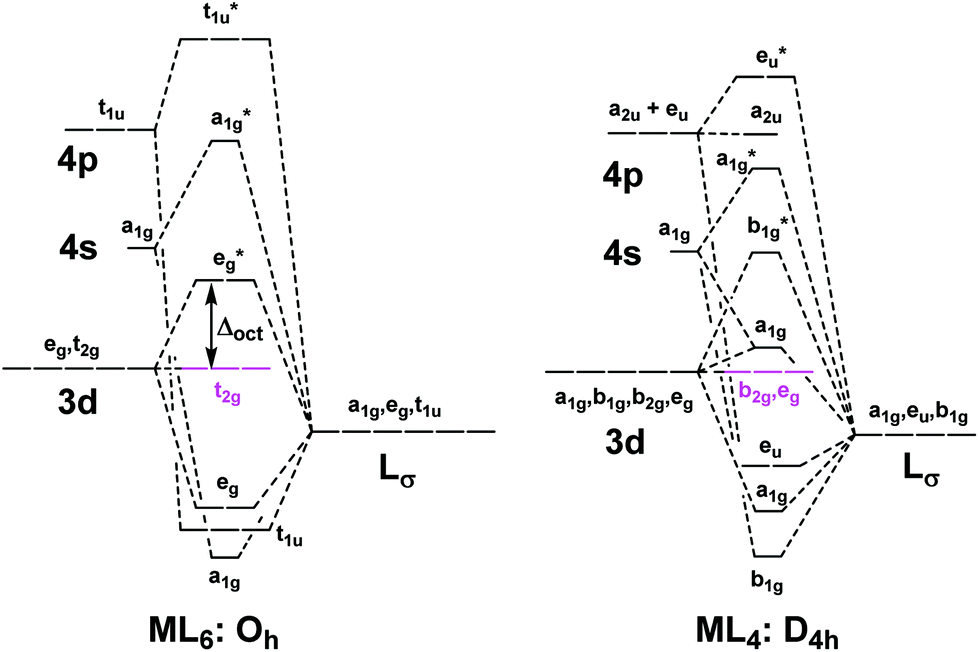
The overall molecular orbital energy level diagram for this type of π-bonding in octahedral complexes can be shown as: Figure 21. The generation of π and σ-molecular orbitals in octahedral complexes. Buy the complete book with TOC navigation, high resolution images and
Answer to: Draw an orbital energy-level diagram showing the configuration of the d-electrons on the metal ion in the complex NiCl42- (tetrahedral)....1 answer · Top answer: The given coordination complex ion is [NiCl4]2−[NiCl4]2−. The central metal atom in {eq}{\left[...
The overall molecular orbital energy level diagram for σ-bonding in octahedral complexes can be shown as: Figure 10. The formation of σ-molecular orbitals (bonding, antibonding and non-bonding) in octahedral complexes of transition metals. Buy the complete book with TOC navigation,
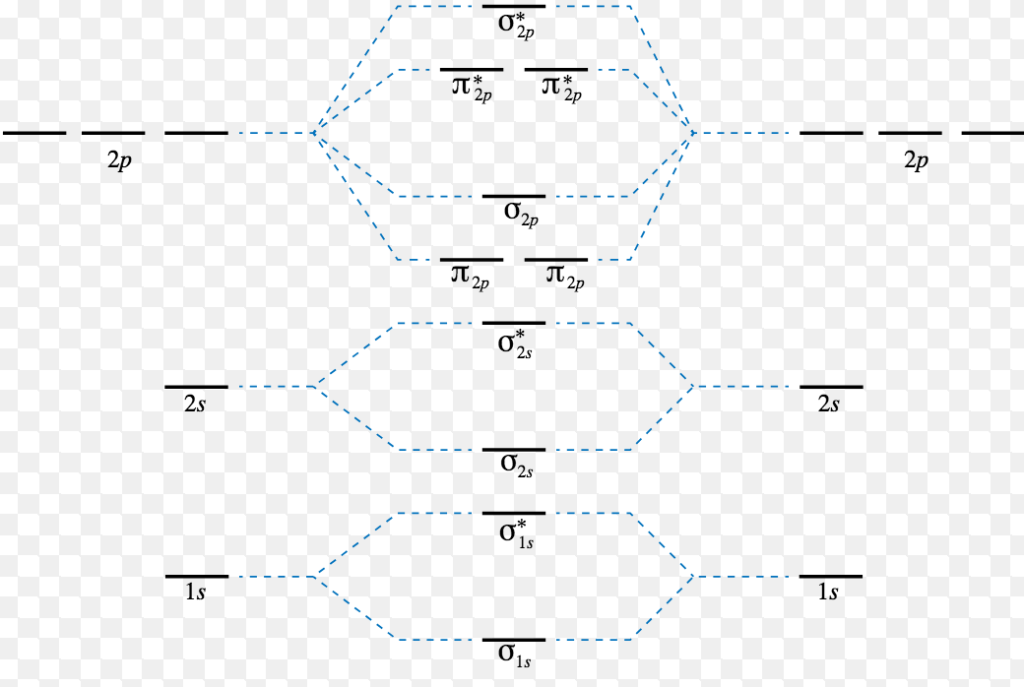
Energy level diagram for Molecular orbitals. The first ten molecular orbitals may be arranged in order of energy as follow: σ (1s) <σ ∗ (1s) < σ(2s) <σ ∗ (2s) < π(2p x) = π(2p y) < σ(2p z) < π ∗ (2p x) =π ∗ (2p y) <π ∗ ( 2p z) Relationship between electronic configuration and Molecular behaviour. 1) Stability of molecules in terms of bonding and antibonding electrons ...
This video explains s, p, d, and f orbitals, sublevels, and their shapes. It discusses the 4 quantum numbers n, l, ml, and ms. n represents the energy leve...
molecular orbital energy-level diagram for the NO molecule. We assume that orbital order is the same as that for N2. The bond order is 2.5. Figure 9.42: The molecular orbital energy-level diagram for both the NO+ and CN-ions. Figure 9.43: A partial molecular orbital energy-level diagram for the HF molecule.
A molecular orbital is a region of space in a covalent species where electrons are likely to be found. The combination of two atomic orbitals always forms two molecular orbitals; the bonding molecular orbital, which is _____ in energy, and the antibonding molecular orbital, which is _____ in energy, than the original atomic orbitals.
Molecular Orbital Theory: Energy level diagram for molecular orbitals. Molecular orbital theory was put forward by Hund and Mullikan in 1932. This theory is modern and more rational. This theory assume that in molecules, atomic orbitals lose their identity and the electrons in molecules are present in new orbitals called molecular orbitals.
For each of the complexes (Co (NH3)6]3+ and [CoF6]3- (a) Draw an orbital energy level diagram that shows how the d-orbitals are split (ignore any Jahn-Teller distortion that might be present) and assign the appropriate labels (t2g, eg, e, or t2) to the d-orbitals. (b) Show how these orbitals are occupied by electrons and state whether each ...
Orbital Energy Level Diagram for O2. Energy Level Diagrams: Some Important Observations. The energy level diagram can help us deduce that the energy of the subshells of a specific shell is not equal. The energies of 2s and 2p, for example, are different. The subshell with the lowest value of I has the lowest energy in a given shell. 2s (I = 0) has lower energy than 2p (I = 1) in the second ...
The diagram (not to scale) summarises the energies of the orbitals up to the 4p level. The oddity is the position of the 3d orbitals. They are shown at a slightly higher level than the 4s - and so it is the 4s orbital which will fill first, followed by all the 3d orbitals and then the 4p orbitals.

















0 Response to "39 d orbital energy level diagram"
Post a Comment