38 refer to the diagram. demand is relatively inelastic:
Categories: Core Diagram comments. Refer to the Diagram. In the P1p2 Price Range, Demand is: bus 115 quiz 1 - coursepaper 2 the u s demand for british pounds is awnsloping because a higher dollar price of pounds means british goods are cheaper to americans. This is only a preview. This is only a preview.
17. Refer to the above diagram and assume that price declines from $10 to $2. The coefficient of price elasticity of demand (midpoints formula) relating to this change in price is about: A. .25 and demand is inelastic. B. 1.5 and demand is elastic. C. 1 and demand is unit elastic. D. .67 and demand is inelastic.
Demand for a good is relatively inelastic if the PED coefficient is less than one ... the nominal price and quantity mean that demand curves have different ...
Refer to the diagram. demand is relatively inelastic:
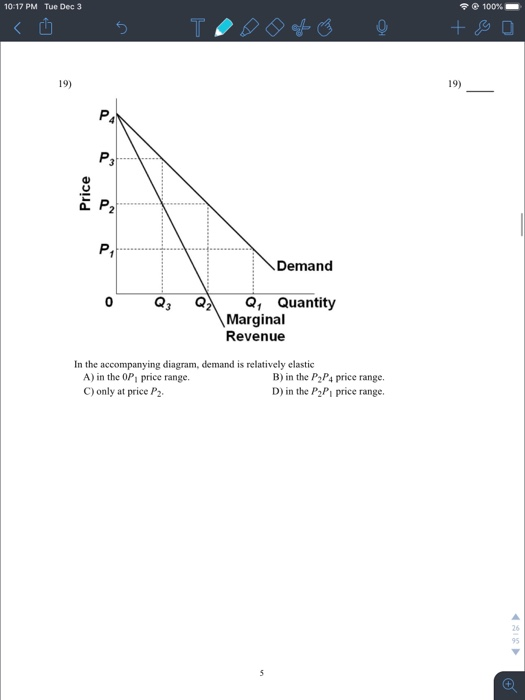
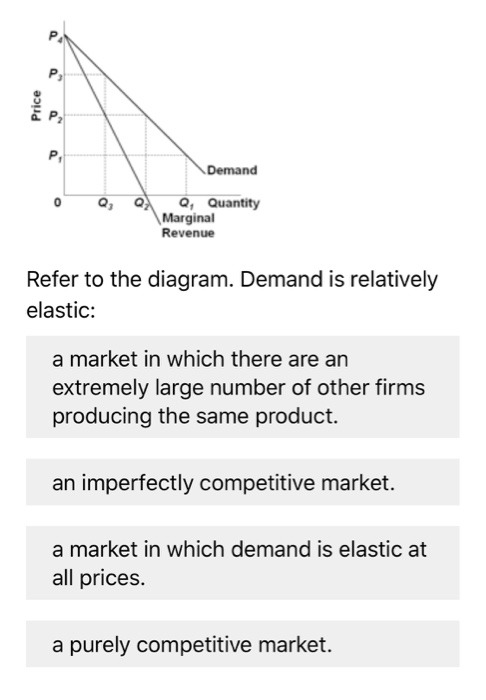
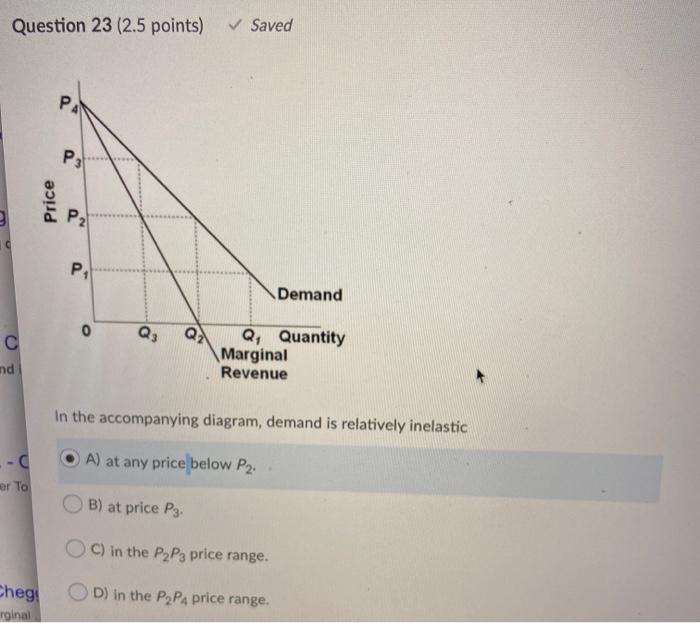
Refer to the above diagram. Demand is relatively elastic: A. in the P2P1 price range. B. in the 0P1 price range. C. in the P2P4 price range. D. only at price P2. in the P2P4 price range. 25. Refer to the above diagram. Demand is relatively inelastic: A. at price P3. B. at any price below P2. C. in the P2P4 price range. D. in the P2P3 price range. at any price below P2. 26. The demand curve ...
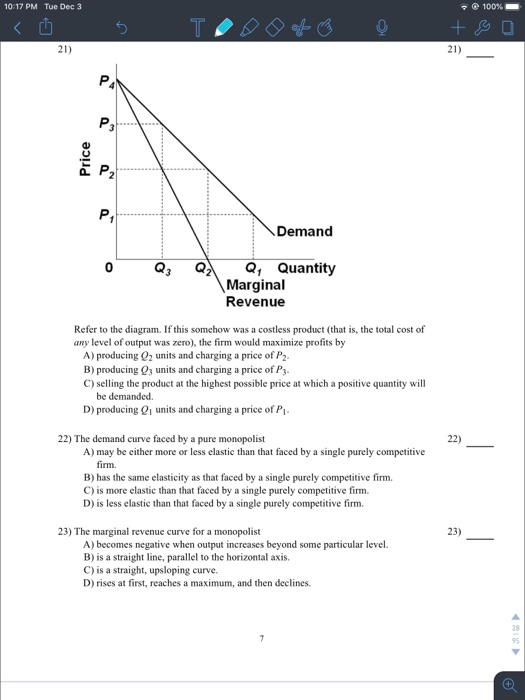
Demand is relatively inelastic: A) at price P3. B) at any price below P2. C) in the P2P4 price range. D) in the P2P3 price range. Answer: B. 37. Refer to the above diagram. If this somehow was a costless product (that is, the total cost of any level of output was zero), the firm would maximize profits by: A) selling the product at the highest ...
Refer to the above diagram. Demand is relatively elastic: A) in the P2P1 price range. C) in the P2P4 price range. ... the 0P1 price range. D) only at price P2 . C . 36. Refer to the above diagram. Demand is relatively inelastic: A) at price P3. B) at any price below P2. C) in the P2P4 price range. D) in the P2P3 price range. ...
Refer to the diagram. demand is relatively inelastic:.
Between the prices of $10 and $8, the price elasticity of demand is (use the midpoint formula): A).5: B).9: C) 1.11: D) 2: 2: Use the following diagram to answer the next question. (14.0K) Refer to the diagram. Suppose total revenue at price P 3 is the same as at price P 2. Then, over the price range from P 2 to P 3, demand is: A) relatively ...
Refer to the above diagram. Demand is relatively elastic: a) in the P2P1 price range. b) in the 0P1 price range. c) in the P2P4 price range. Rating: 5 · 2 reviews
In the accompanying diagram demand is relatively elastic marginal revenue the qualitative difference between areas q1 bc q2 and p1p2 ba in the diagram measures. In the p 2 p 3 price range. This problem has been solved. In the p2h price range. B at all points where the demand curve lies above the horizontal axis.
The coefficient of cross elasticity of demand is D1 is more elastic than D2. Refer to the diagram and assume a single good. If the price of the good decreases from $6.30 to $5.70, consumer expenditure would: decrease if demand were only D2. Refer to the data. The price elasticity of demand is relatively elastic: in the $6-$4 price range.
5. The demand schedules for such products as eggs, bread, and electricity tend to be: A. perfectly price elastic. B. of unit price elasticity. C. relatively price inelastic. D. relatively price elastic. 6. The demand for autos is likely to be: A. less elastic than the demand for Honda Accords. B. more elastic than the demand for Honda Accords.
Refer to the diagram and assume a single good. If the price of the good increased from $5.70 to $6.30 along D1, the price elasticity of demand along this portion of the demand curve would be: 1.2.
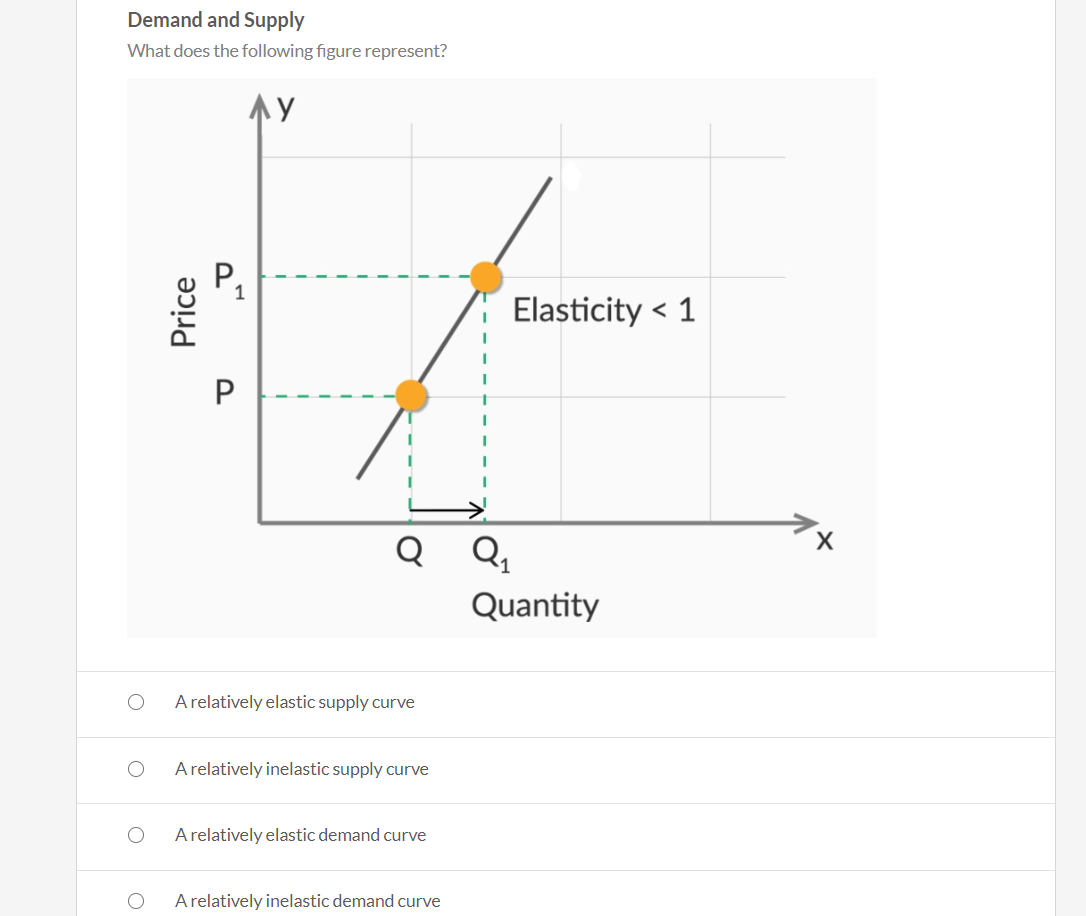
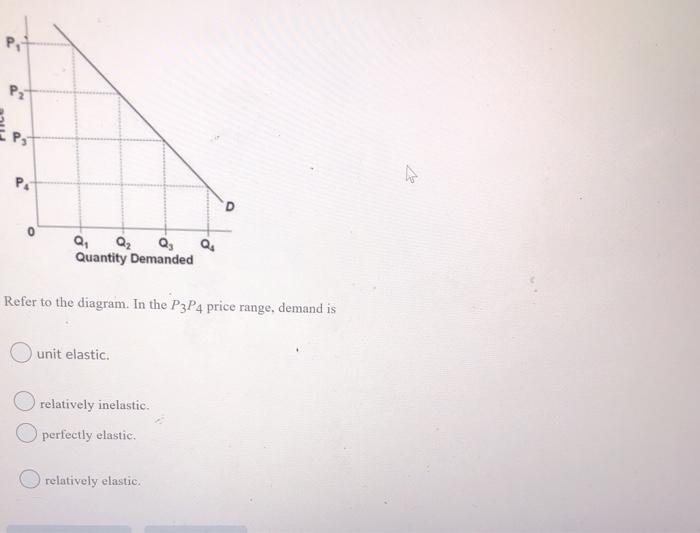
(Straight-line demand curve) Refer to the above diagram. In the P1P2 price range demand is: C. relatively elastic. Refer to the above diagram. In the P3P4 price range demand is: B. relatively inelastic. The total-revenue test for elasticity. C. does not apply to supply because price and quantity are directly related.
Refer to the above diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. Marginal revenue will be zero at output: A. ... charge a higher price where individual demand is inelastic and a lower price where individual demand is elastic. C. ... Refer to the above diagram. Demand is relatively inelastic: A. at price P 3. B. at any price below P 2. C.
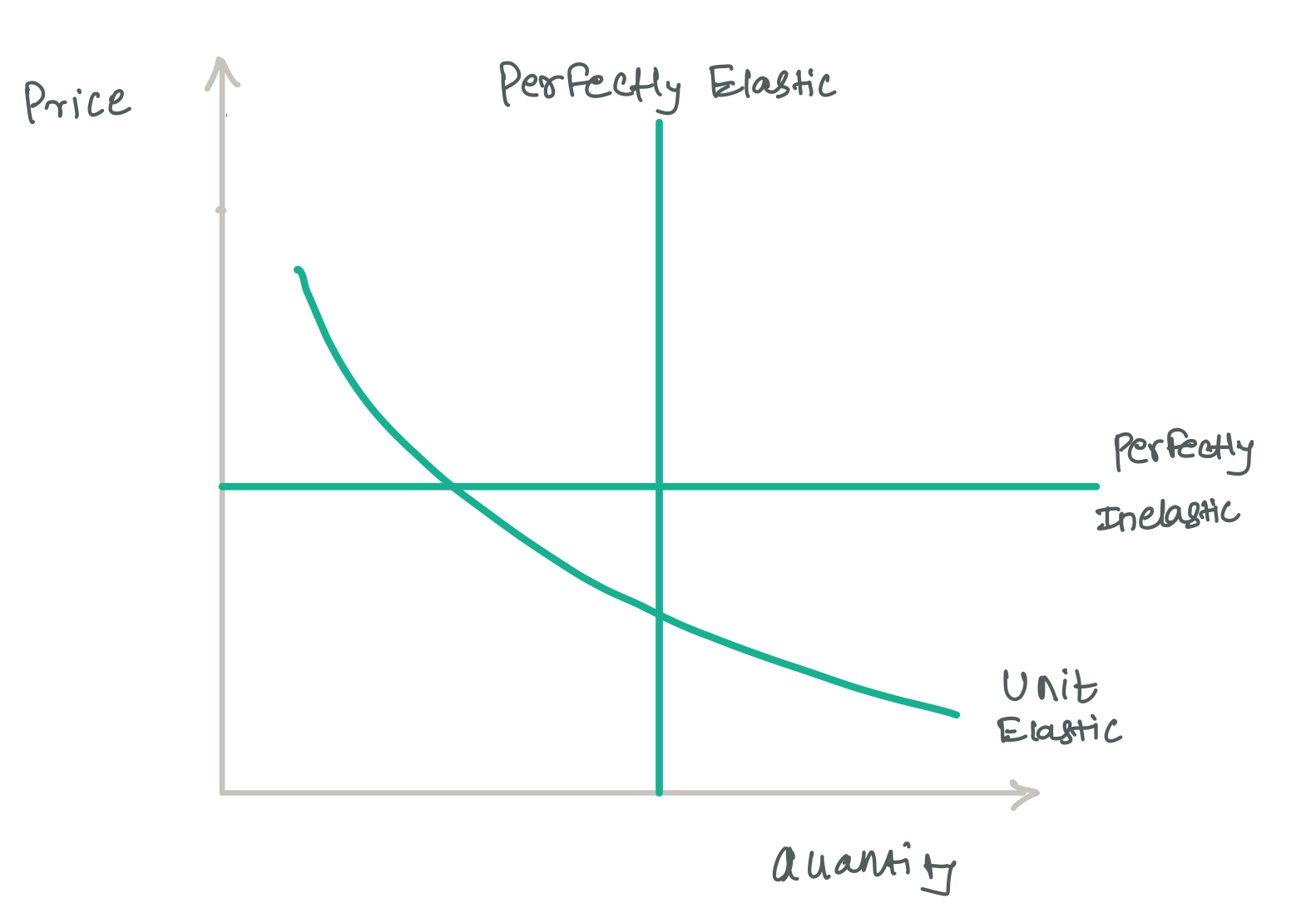
Since the demand curve is downward sloping, either ∆P or ∆Q will be negative. Therefore, the calculated value for elasticity has negative sign. On the basis of mid-point formula we may compute arc price elasticity. If E p > 1 demand is said to be elastic; if E p = 1 demand is unitary elastic and it E p < 1 demand is inelastic. Consider ...
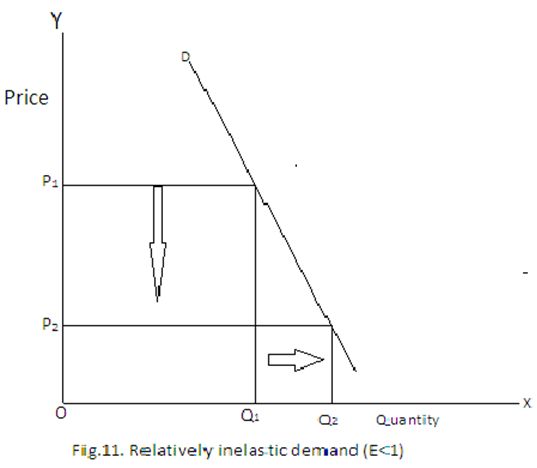
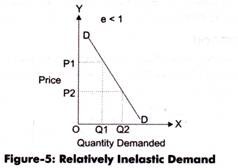
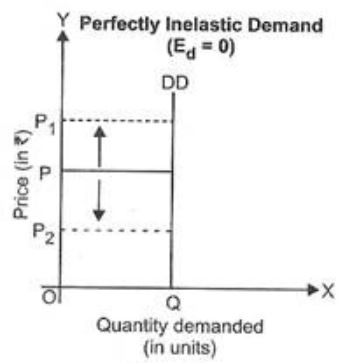
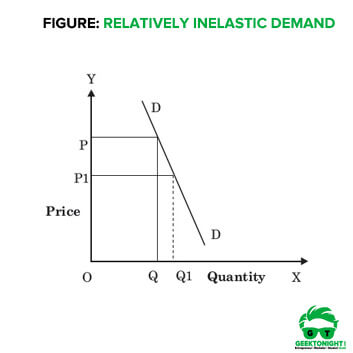
4. Relatively Inelastic Demand: Relatively inelastic demand is one when the percentage change produced in demand is less than the percentage change in the price of a product. For example, if the price of a product increases by 30% and the demand for the product decreases only by 10%, then the demand would be called relatively inelastic.
The demand curve of relatively inelastic demand is rapidly sloping, which is shown in Figure. Relatively Inelastic Demand In Figure, DD is the demand curve that slopes steeply with a fall in price. When price falls from OP to OP1, the demand rises from OQ to OQ1. However, the rise in demand QQ1 is less than the fall in price PP1.
The price elasticity of demand is relatively inelastic: ... Refer to the diagram, which is a rectangular hyperbola, that is, a curve such that each ...
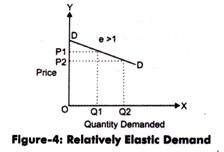
Relatively Inelastic Demand. Unitary Elastic Demand. Problem on PED. DEMAND FORECASTING . Relatively Elastic Demand Curve. Example: - There are commodities for which a small change in price will drastically reduce the amount of the commodity demanded. For example, air-travel for vacationers is very sensitive to price. An increase in the air fare will lead the vacationer to choose another mode ...
Inelastic demand is when a buyer's demand for a product does not change as much as its change in price. When price increases by 20% and demand decreases by only 1%, demand is said to be inelastic. This situation typically occurs with everyday household products and services. Products and Services A product is a tangible item that is put on ...
Economics. Economics questions and answers. Picture Refer to the diagram. In the P3P4 price range, demand is: of unit elasticity. relatively inelastic. relatively elastic. perfectly elastic. Refer to the diagram. In the P3P4 price range, demand is: of unit elasticity. relatively inelastic. relatively elastic. perfectly elastic.
An example of an inelastic demand curve is shown below. This diagram highlights the changes in expenditure for a producer that occurs when there is a small price rise in a market with inelastic demand. When a demand curve is relatively inelastic, it means that consumers are price insensitive to changes. In this instance, a price rise leads to a ...
b) perfectly inelastic over all ranges of output. ... Demand is relatively inelastic: a) at ... Image: Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist.
Refer to the diagram. Between the prices of $10 and $8, the price elasticity of demand is. .9. The cross elasticity of demand between two goods is reported to be +0.2. This implies that: 2 goods are substitues. The supply of product X is inelastic (but not perfectly inelastic) if the price of X rises b.
Refer to the above data. The price elasticity of demand is relatively inelastic: ... (Straight-line demand curve) Refer to the above diagram.
36. Refer to the above diagram. Demand is relatively inelastic: A) at price P3. B) at any price below P2. C) in the P2P4 price range. D) in the P2P3 price range. 37. Refer to the above diagram. If this somehow was a costless product (that is, the total cost of any level of output was zero), the firm would maximize profits by: A) selling the ...
"Inelastic demand" is a term that economists use to refer to a situation where demand for an item remains the same, no matter how far its price rises or falls. It's important to understand this concept if you're learning about economics.
When a firm is on the inelastic segment of its demand curve, it can: A. increase total revenue by reducing price. B. decrease total costs by decreasing price. C. increase profits by increasing price. D. increase total revenue by more than the increase in total cost by increasing price. 10-4 Chapter 10 - Pure Monopoly 21. Refer to the above diagram.
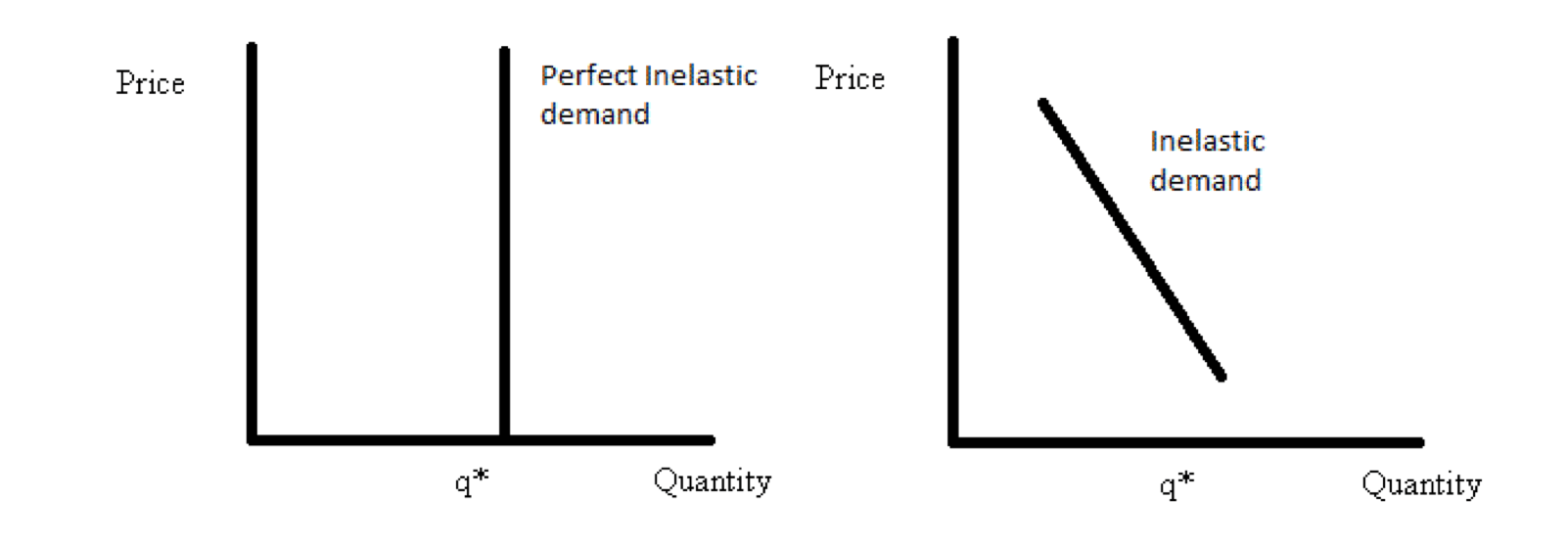
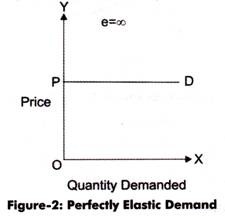
The basic formulate for the price elasticity of demand coefficient is. B. percentage change in quantity demanded/ ... A perfectly inelastic demand schedule. Rating: 5 · 1 review
perfectly inelastic. D. perfectly elastic. 4. R-1 F24033. Refer to the above diagram. Demand is relatively inelastic: A. at price P3. B. at any price below P2. C. in the P2P4 price range ... Refer to the above long-run cost diagram for a firm.
The basic formulate for the price elasticity of demand coefficient is. percentage change in quantity demanded/ percentage change in price. The demand for a product is inelastic with respect to price if. consumers are largely unresponsive to a per unit price change. We will write a custom essay on Ch 6 Elasticity specifically for you.
(Supposed to be a graph) In the accompanying diagram, demand is relatively inelastic a.) at price P3. b.) at any price below P2. c.) in the P2P4 price range. d.) in the P2P3 price range. b.) at any price below P2. (Supposed to be a graph) Refer to the diagram. If this somehow was a costless product (that is, the total cost of any level of output was zero), the firm would maximize profits by a ...
Refer to the above diagram. Demand is relatively elastic: in the P2P4 price range. Refer to the above diagram. Demand is relatively inelastic: at any price below P2. Refer to the above diagram. If this somehow was a costless product (that is, the total cost of any level of output was zero), the firm would maximize profits by:
Refer to the diagram and assume a single good. ... Refer to the data. The price elasticity of demand is relatively elastic: in the $6-$4 price range. Rating: 5 · 1 review
Refer come the diagram.Suppose total revenue in ~ price P3 is the very same as at price P2. Then, over the price selection from P2 come P3, need is: A) relatively elastic: B) relatively inelastic: C) unit elastic: D) perfectly elastic: 3: Suppose that a 2% boost in income in the economy decreases the quantity of devices demanded by 1% in ...
Refer to the two diagrams for individual firms. Figure 1 pertains to: a purely competitive firm. ... Refer to the diagram. Demand is relatively inelastic:. Rating: 5 · 2 reviews
35. Refer to the above diagram. Demand is relatively elastic: A. in the P2P1 price range. B. in the 0P1 price range. C. in the P2P4 price range. D. only at price P2. 36. Refer to the above diagram. Demand is relatively inelastic: A. at price P3. B. at any price below P2. C. in the P2P4 price range. D. in the P2P3 price range. 10-9 Chapter 10 ...



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_final_Graph2_Why_We_Splurge_When_Times_Are_Good_Feb_2020-1701a9a5d903401ba85edd21132b7f33.jpg)
/inelastic-demand-definition-formula-curve-examples-3305935-final-5bc4c3c14cedfd00262ef588.png)









/dotdash_Final_How_Does_Price_Elasticity_Affect_Supply_Feb_2020-01-08f0b93e209c4c27a601d6a376dd6aff.jpg)

0 Response to "38 refer to the diagram. demand is relatively inelastic:"
Post a Comment