38 mo diagram of f2
Valence electrons in F2- = 15 It's molecular orbital confirguation will be Bond order = (Bonding electron - antibonding electron)/2 = 8-7/2 = 0.5 bond order No of sig …. View the full answer. Transcribed image text: 2. Draw an MO diagram for the valence electrons in the F2 ion. What is the bond order?
Molecular orbital diagram for c2. This video shows the mo diagrams of the c2 n2 o2 and f2 molecules. Molecular orbitals are formed combining similar atomic orbitals. Just because some chemical species shows integral value of bond order doesnt mean that it should exist. Molecular orbital diagram for the molecule oxygen o2.
Molecular orbital diagram for f2. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of. C would this ion exist. To further demonstrate the consistency of the lewis structures with mo. For the ion f2.
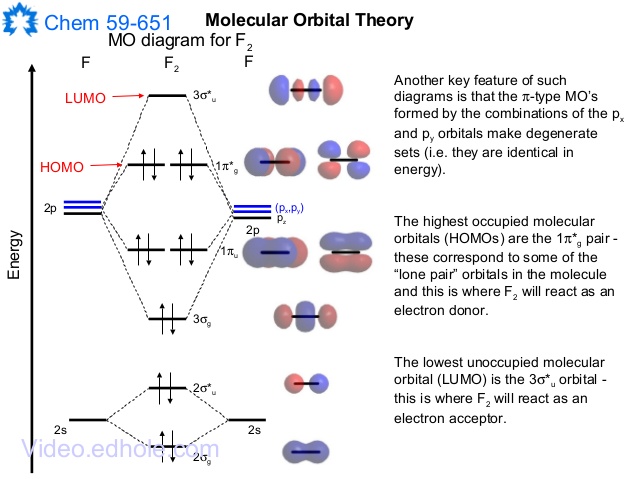
Mo diagram of f2
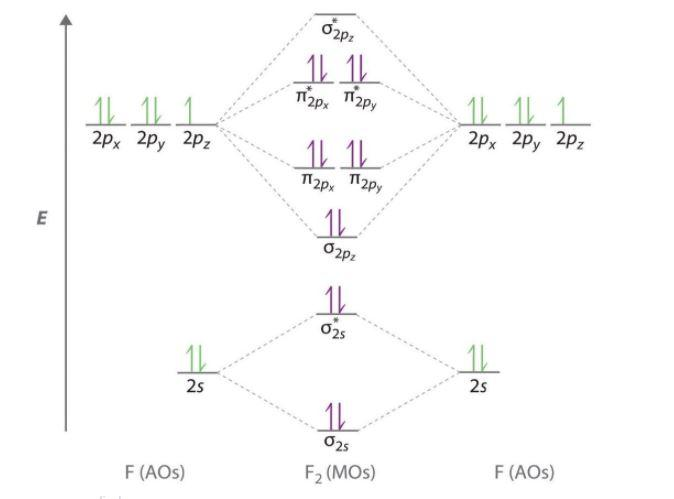
For example, an ns/ns overlap for a homonuclear diatomic molecule gives rise to a partial MO diagram like this: and an np/np overlap for O2 and F2 gives: So, the full MO diagram is: Thus, the valence electron configuration is: (σ2s)2(σ* 2s)2(σ2pz)2(π2px)2(π2py)2(π* 2px)2(π* 2py)2. Answer link.
mo bonding in f2 and o2 chemistry libretexts molecular orbitals mo are constructed from atomic orbitals in o 2 and f 2 there is a crossover of the sigma and the pi ortbials the relative energies of the sigma orbitals drop below that of the pi orbitals information from the mo diagram justify o2 s stability and show that it s bonding order is 2.
Draw an MO diagram for the valence electrons in F2. What is the bond order? How many o and π bonds are there? What is the HOMO and LUMO? What is the magnetism of the species? FREE Expert Solution 83% (476 ratings) Sign up for free to view this solution Sign up for free. 582,038. students enrolled. 97%. ...
Mo diagram of f2.
This is the molecular orbital diagram for the homonuclear diatomic Be2+, . electrons would be in a bonding orbital, we would predict the Li2 molecule to be . Explain why the relative energy levels diagrams for Li2, Be2, B2, C2, N2 are different The molecular orbital theory of Li2 to F2 gives a graphical explanation.
A bare molecular orbital diagram is presented and you must drag the correct orbitals and labels onto the diagram. Molecular orbital diagram for f2. The other molecular orbital produced s h h shows a decrease in electron density between the nuclei reaching a value of zero at the midpoint between the nuclei where there is a nodal plane.
Answer (1 of 6): Here is the solution, > * For O2 molecule, > * For F2 molecule, Thanks for reading.
12 Mar 2017 — Total no. of electrons in N2+ : 13 · Its electronic configuration is : σ1s² σ*1s² σ2s² σ*2s² π 2py² [π2pz² σ2px1 ] · Bond order = 1/2[Nb-Na], where, Nb=no. of ...
Draw an MO diagram for the valence electrons in F2^- ion. What is the bond order? How many o and π bonds are there? What is the HOMO and LUMO? What is the magnetism of the species? FREE Expert Solution 88% (20 ratings) Sign up for free to view this solution Sign up for free. 586,797. students enrolled ...
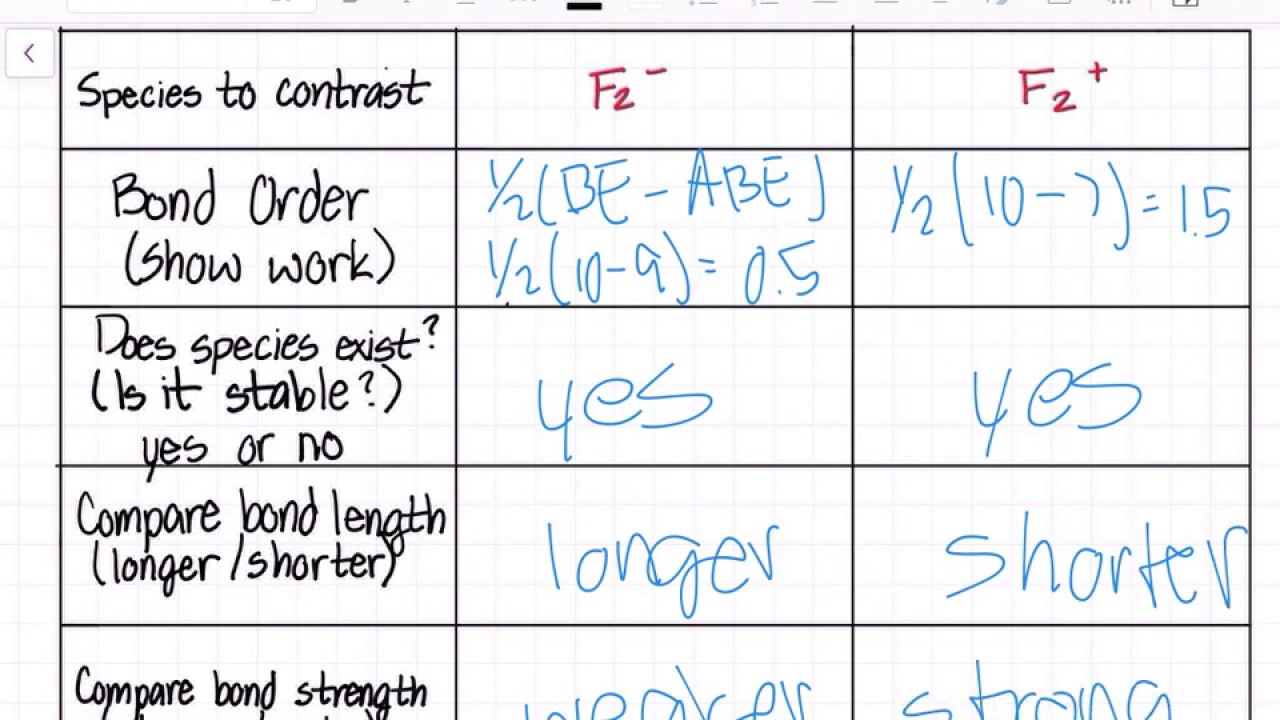
Arrange the following in order of decreasing stability. a blank molecular orbital diagram (part a 1 figure) has been provided to you. rank the fluorine species from most to least stable. to rank items as equivalent, overlap them. f2, f2+, f2-
Draw molecular orbital diagram for F 2 molecule. Also, gives its electronic configuration, bond order and magnetic property. Hint: The Molecular Orbital Theory (MOT) explains the formation of the molecule in a better way than Valence Bond Theory (VBT). The bond order calculations are feasible using MOT and so is the description of electronic ...
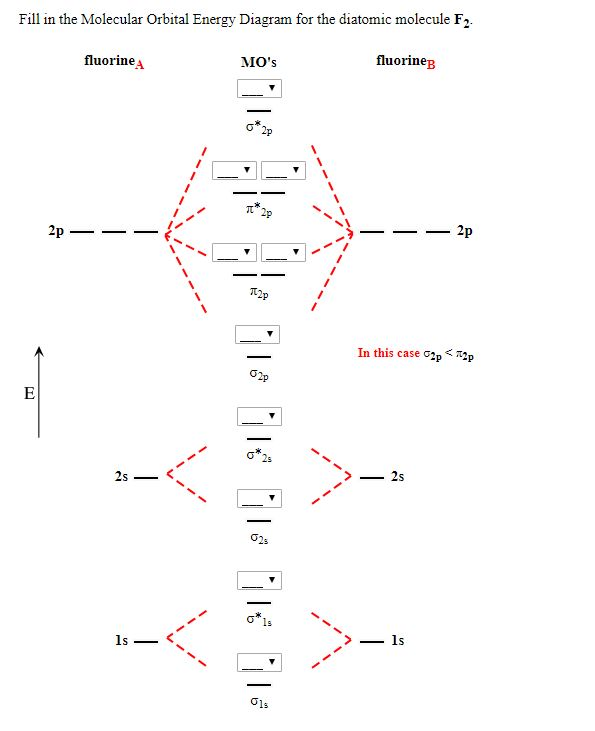
Draw the molecular orbital (MO) electron diagram for the F2 molecule. Be sure your diagram contains all of the electrons in the molecule, including any core electrons. Who are the experts? Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high.
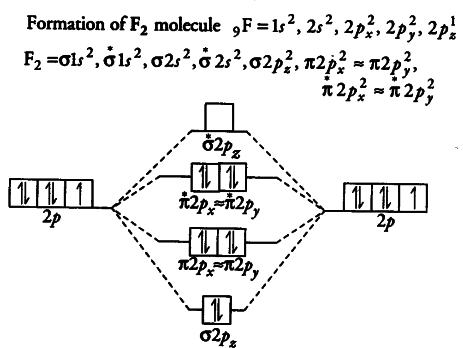
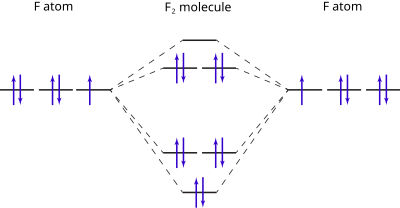
When we make the molecular orbital energy level diagram of f2 molecule then, we will get this configuration: 1σs 2, 1σ*s 2, 2σs 2, 2σ* 2, σ2pz 2, π2p x 2, π2p y 2, πp x * 2, π2p y * 2. From this electronic configuration, we can see that there are a total of ten bonding molecular orbitals and eight antibonding molecular orbitals.
MO Diagram for HF The AO energies suggest that the 1s orbital of hydrogen interacts mostly with a 2p orbital of fluorine. The F 2s is nonbonding. H-F nb σ σ* Energy H -13.6 eV 1s F -18.6 eV -40.2 eV 2s 2p So H-F has one σ bond and three lone electron pairs on fluorine
Even rather simple molecular orbital (MO) theory can be used to predict from the bottom of the diagram because this is how MO diagrams are constructed, from N2, O2, F2, Ne2 the complexity of the molecular orbitals develop in two ways. Page 1. MO Diagrams for Elements Li2 through Ne2. (Don't memorize.) Li2 through N2. O2 through Ne2.
MO Diagrams. Now we're ready to look at MO diagrams for the first row series. Note that the molecules that aren't common and stable might still be more stable in the gas phase than single atoms. For instance, in a gas of Li metal, diatomic molecules will form. The figure shows a summary of the energy levels, so we can see how they change.
The valence electrons = 14; BO = 0.5* (8-6) = 1. The bond order is commonly used to signify the bond stability. Higher bond order indicates more stability and vice versa. Thus, is the most stable. is diamagnetic while and are paramagnetic in nature. Further Explanation: MO diagram:
F2 Molecular Orbital (MO) Diagram. As per molecular orbital (MO) theory, all the constituent atoms in a molecule contribute to the formation of molecular orbitals. These MOs are a linear combination of the atomic orbitals. Thus, the electrons in a molecule are not individually assigned to atomic orbitals but to molecular orbitals. Let us have a ...
Click here👆to get an answer to your question ️ 37. Draw molecular orbital diagram for F2 molecule. Also, give its electronic configuration, bond order and magnetic property. 138. Solve the following:
Molecular orbital diagram for n2 o2 c2 f2 also h2o. Electronic configuration of c2 molecule is σ 1s2 σ1s2 σ2s2 σ2pz 2 2px 1 2py orbital s what is the origin of differences between mo schemes o₂ and n₂ chemistry stack exchange c2 2 lewis structure how to draw the for c2 2 youtube figure orbital correlation diagram for homonuclear ...
Using the Molecular Orbital Model to Explain Why Some Molecules Do Not Exist. This molecular orbital model can be used to explain why He 2 molecules don't exist. Combining a pair of helium atoms with 1s 2 electron configurations would produce a molecule with a pair of electrons in both the bonding and the * antibonding molecular orbitals. The total energy of an He 2 molecule would be ...
Answer (1 of 4): The atomic number of fluorine is 9, so a (neutral) F2 molecule has a total of 18 electron, or 14 valence electrons (excluding the four 1s electrons). The (F2)- ion has one more valence electron, or 15. The orbital diagram for a diatomic molecule is To find the bond order, add th...
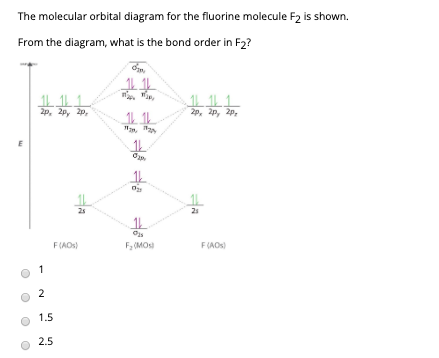
Identify the MO diagram for F2. F2 valence e−: diagram A 6 diagram A 8 diagram A 10 diagram B 12 diagram B 14 Solution In B2, C2, and N2, the 𝜎2𝑝 orbital is higher in energy than the 𝜋2𝑝 orbitals as shown in diagram A.
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of ...
#3. Draw the MO diagram for `O_2^+` This is a bit of a curveball, but a perfectly valid problem. Recall that a cation indicates a loss of `1` electron. `O_2^+` is just the ionized form of `O_2`; that is, it's `O_2` with `1` missing electron. The MO diagram will be the same as the MO diagram of `O_2`, except with `1` less electron.
When two fluorine atoms bond, the sigma(2p) bonding molecular orbitals are lower in energy than the pi(2p) bonding orbitals.F2(2+) has a bond order of 2, so ...
This video is about MO Diagram #2 - F2
As discussed in class the MO diagram for B 2 shows that it has two unpaired electrons (which makes it paramagnetic) and these electrons are in bonding molecular orbitals resulting in the equivalent bond strength of one bond. As discussed in class it is not a bond. This example was covered in class to show the rare exception that this single bond is a bond.






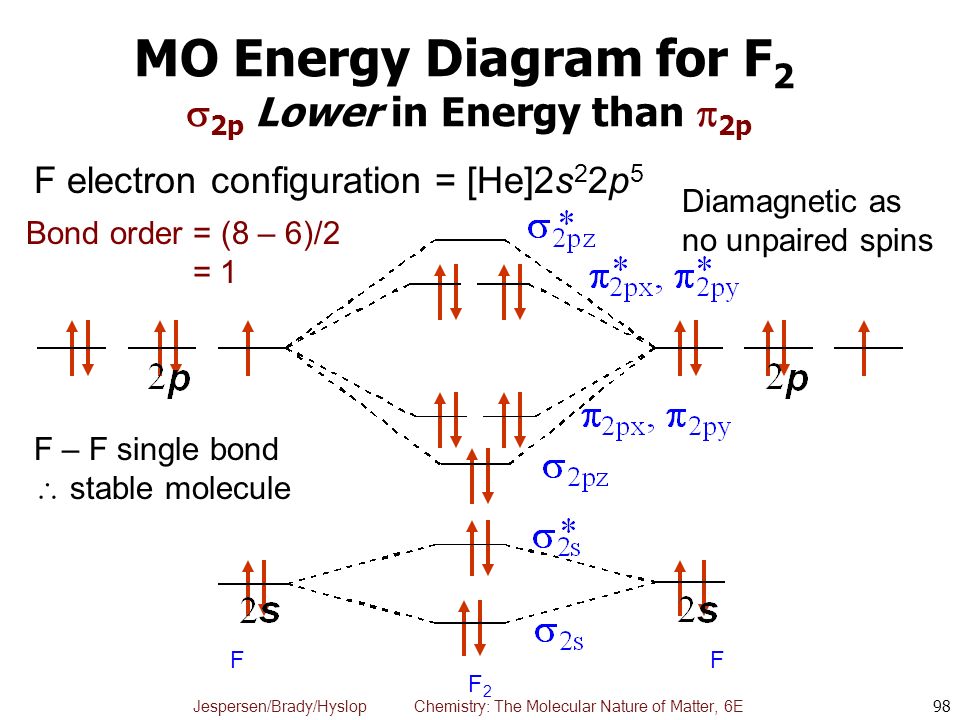

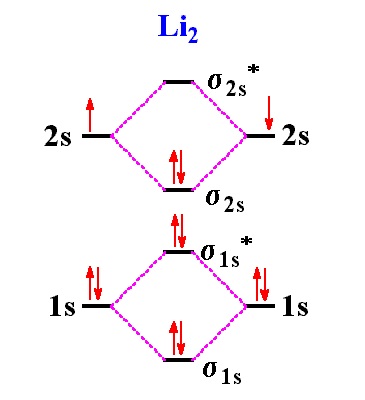
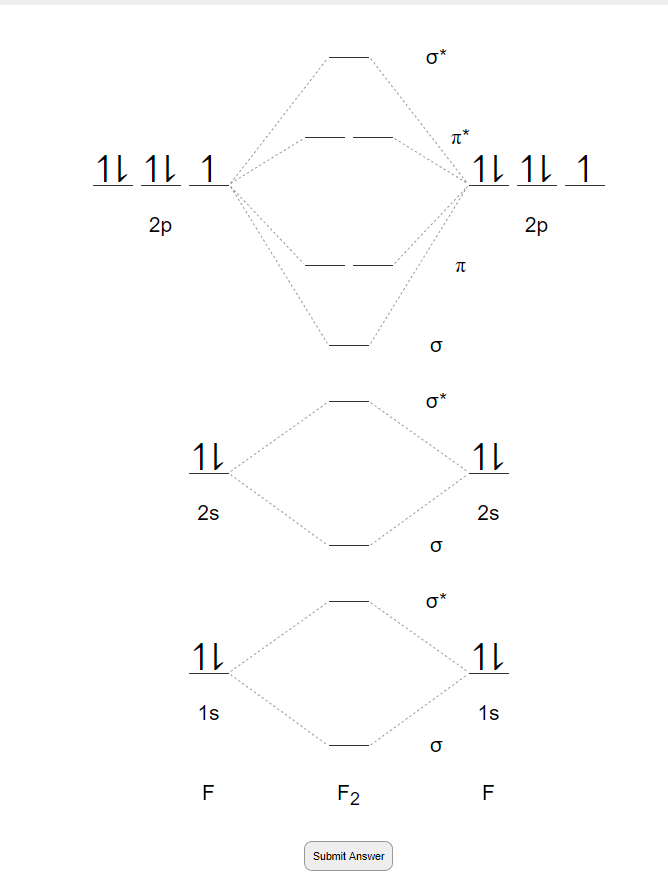
![Expert Answer] Draw the molecular orbital diagram for F2 and ...](https://hi-static.z-dn.net/files/dae/d7baa23a1d4a2ea2c90e0a703e2fd41d.jpg)

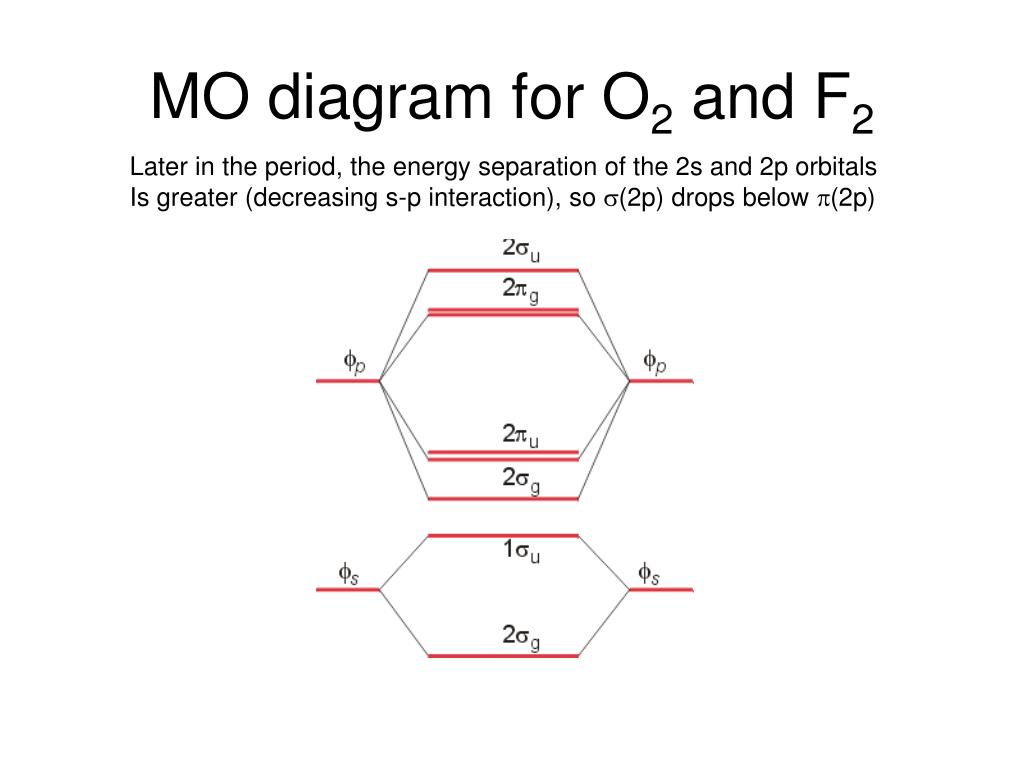


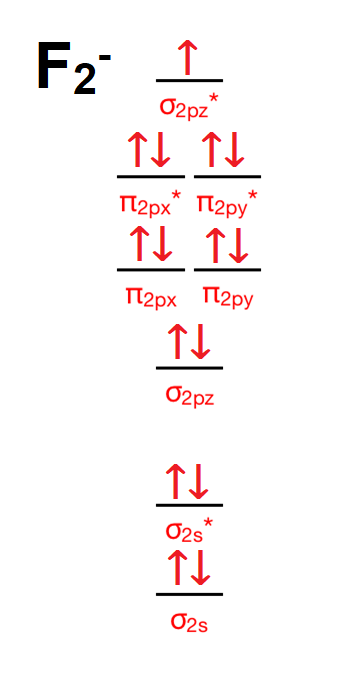
![Expert Answer] Draw the molecular orbital diagram for F2 and ...](https://hi-static.z-dn.net/files/d7a/d377148aa5469a29270f608aa4d77ef6.png)




0 Response to "38 mo diagram of f2"
Post a Comment