42 trigeminal nerve branches diagram
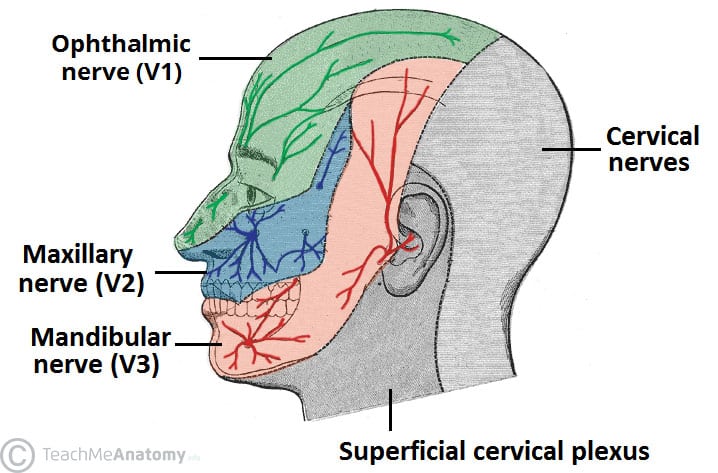
14 Jun 2021 — What are the trigeminal nerve branches? · Ophthalmic: This branch sends nerve impulses from the upper part of your face and scalp to your brain. "Trigeminal" = tri, and "-geminus" or twin, or thrice twinned derives from the fact that it has three major branches: Ophthalmic nerve (V1) 1st branch - sensory ...
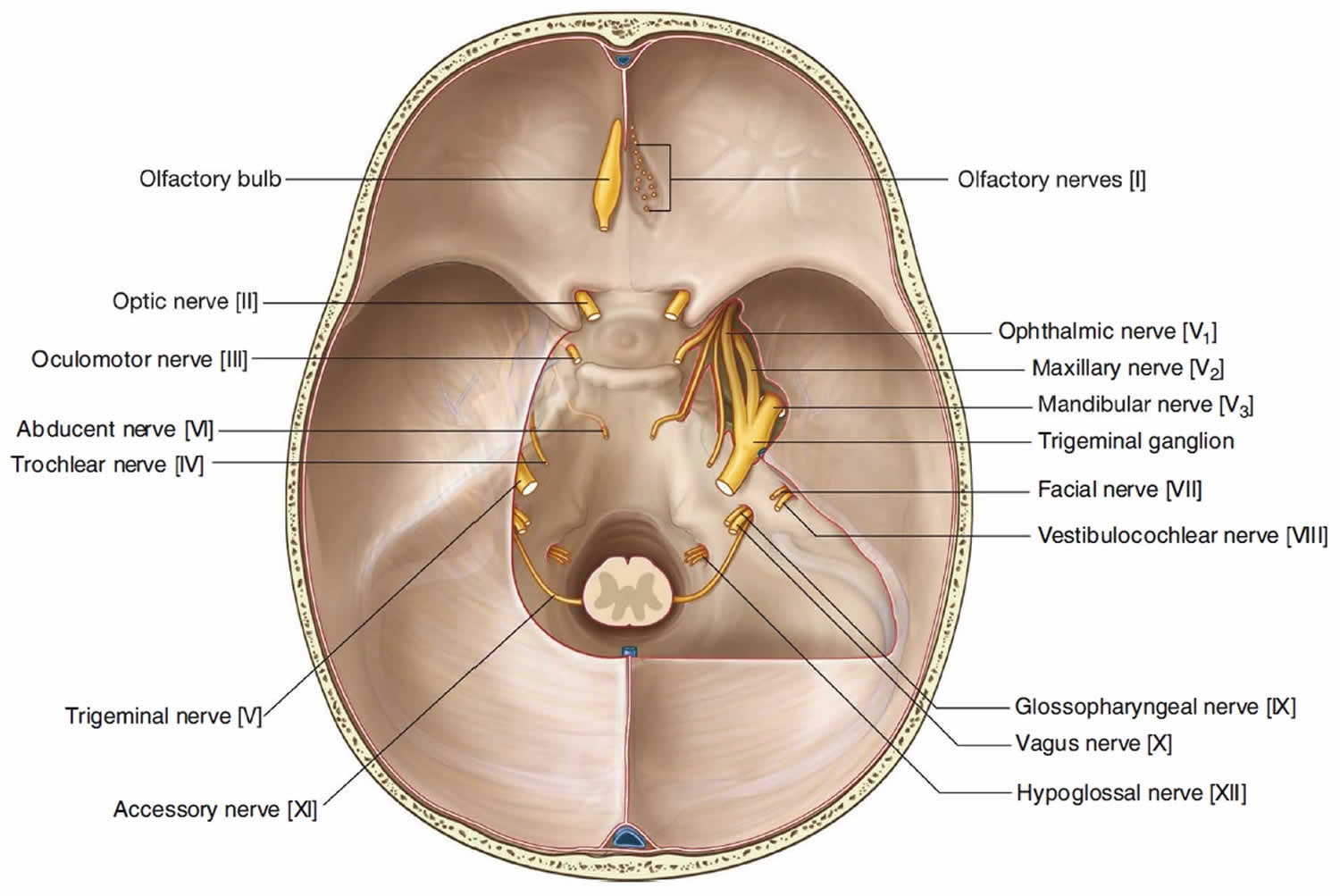
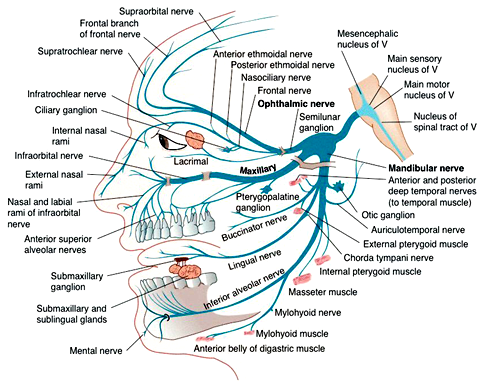
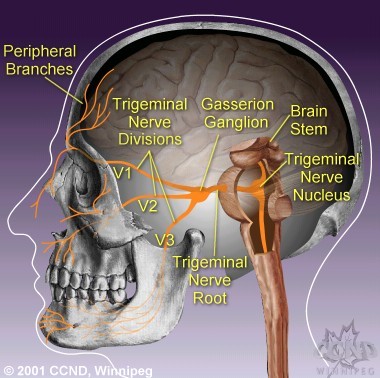
The trigeminal nerve, also known as the fifth (or V) cranial nerve, is a cranial nerve and its primary role is relaying sensory information from the face and head, although it does provide motor control to the muscles of mastication.It is both large and complicated and has multiple brainstem nuclei (sensory and motor) as well as many interconnections with other cranial nerves.
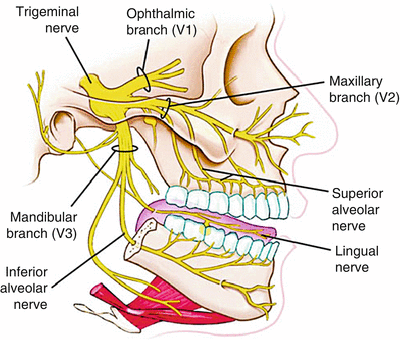
Trigeminal nerve branches diagram
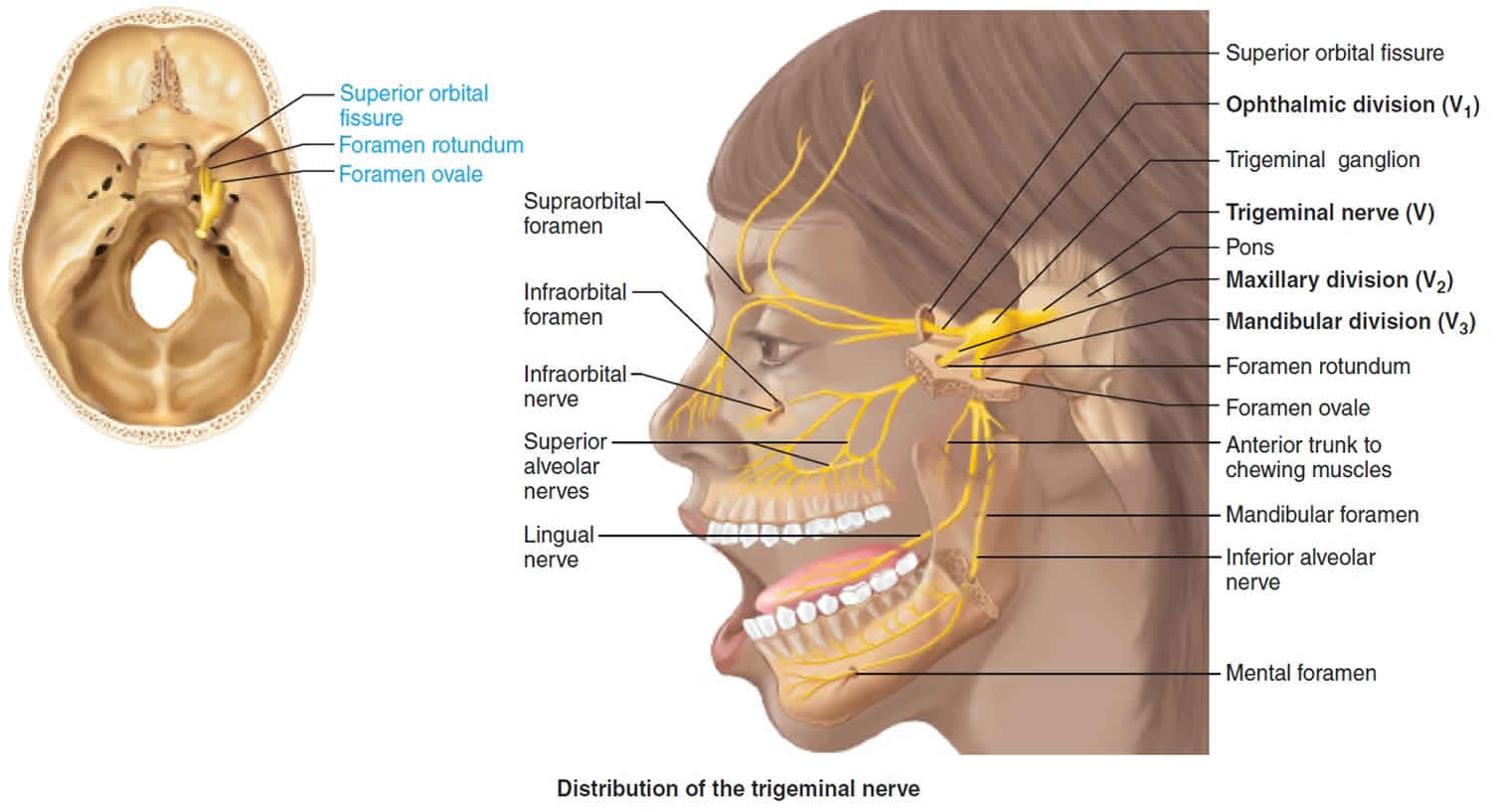
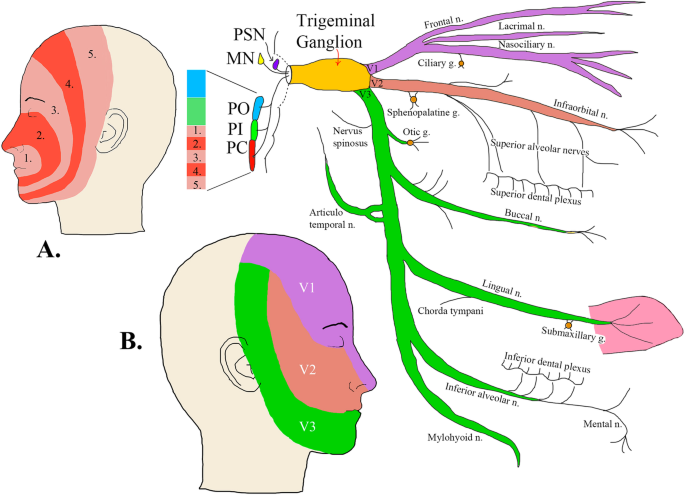
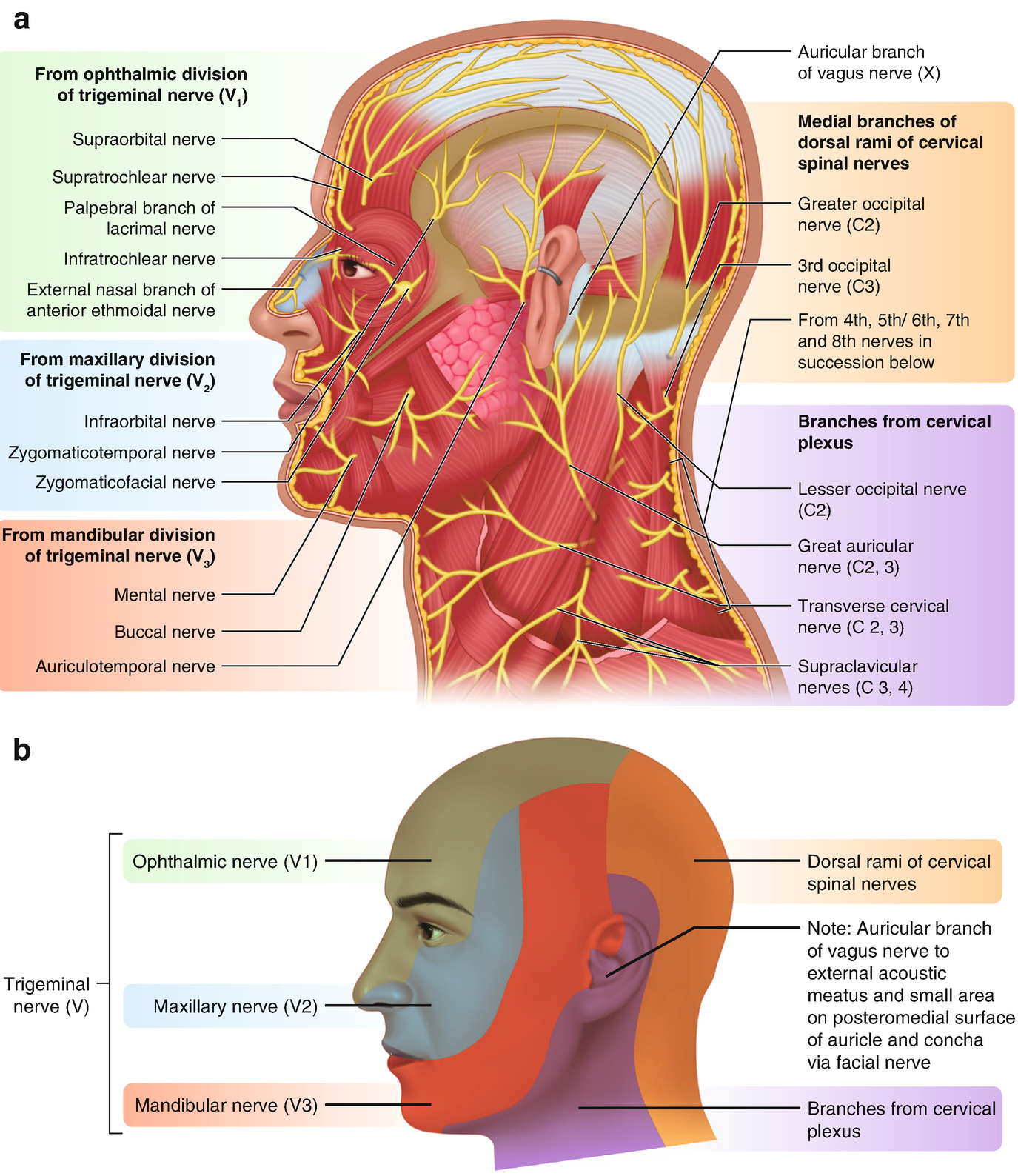
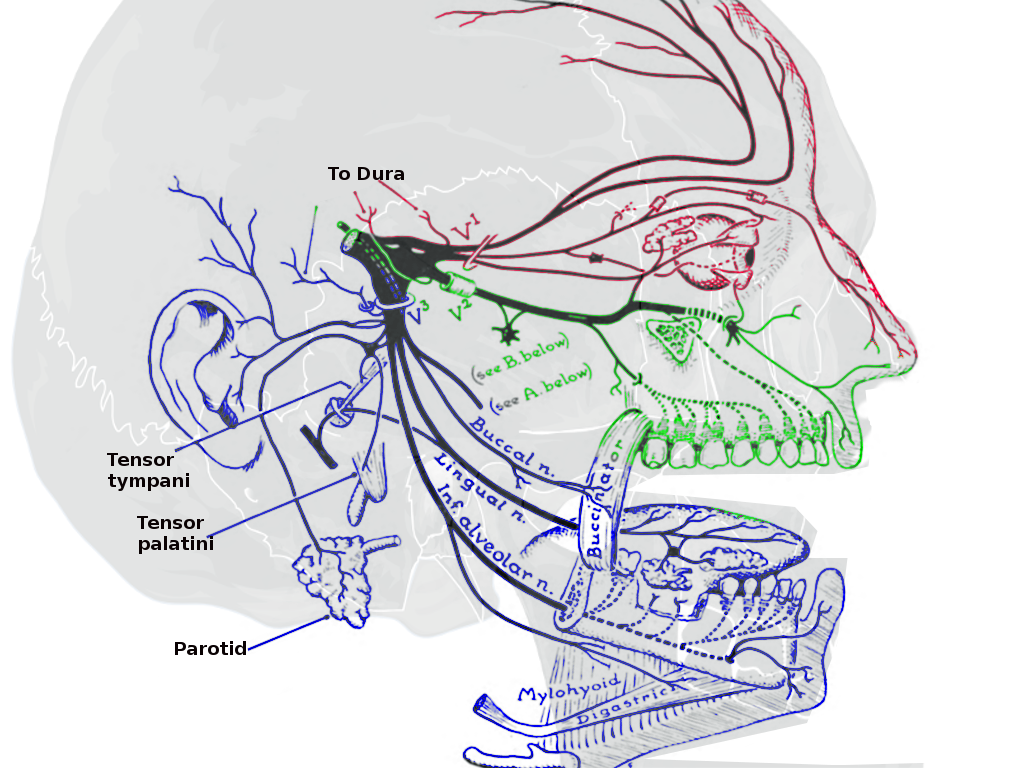
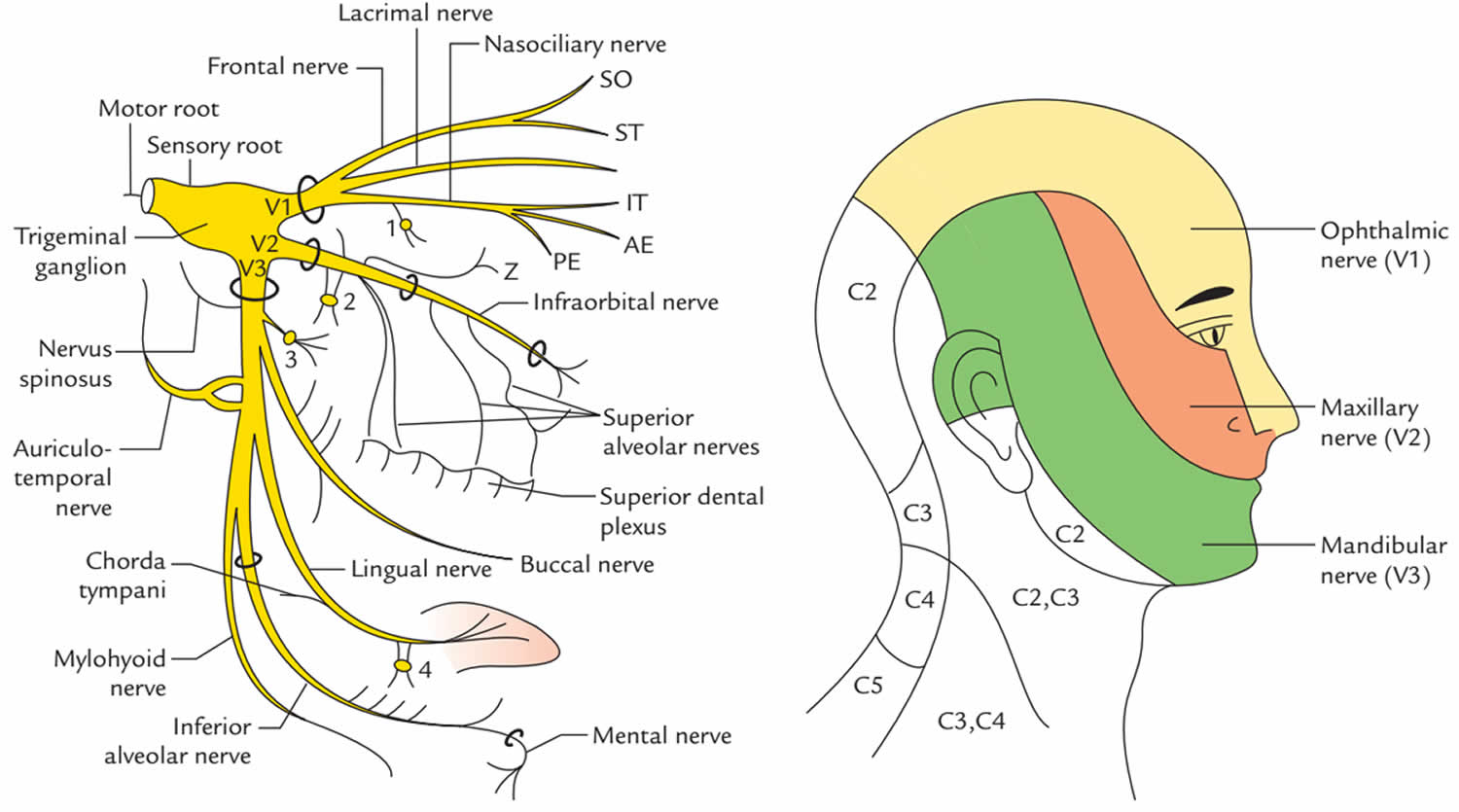
The trigeminal nerve is associated with derivatives of the 1st pharyngeal arch. Sensory: The three terminal branches of CN V innervate the skin, mucous membranes and sinuses of the face.Their distribution pattern is similar to the dermatome supply of spinal nerves (except there is little overlap in the supply of the divisions). Gross Anatomy. The trigeminal nerve is the largest and most complex of the 12 cranial nerves (CNs). It supplies sensations to the face, mucous membranes, and other structures of the head. It is the motor nerve for the muscles of mastication and contains proprioceptive fibers. The trigeminal nerve is the largest of the cranial nerves and can be further divided into three divisions: ophthalmic, maxillary, and mandibular. The ophthalmic division sends information from the scalp, forehead, and upper eye lids (the upper parts of the head) and is sensory in modality, of the general somatic sensory variety.
Trigeminal nerve branches diagram. The motor nerve branch of the trigeminal nerve is smaller than the sensory branches and exits from the brainstem through the root of the trigeminal nerve. Location . The trigeminal nerve roots and ganglion, like those of other cranial nerves, are located right outside the brainstem. The brainstem is the lower part of the brain that serves as ... The trigeminal nerve is the largest of the 12 cranial nerves. Its main function is transmitting sensory information to the skin, sinuses, and mucous membranes in the face. The three major branches of the trigeminal nerve—the ophthalmic nerve (V1), the maxillary nerve (V2) and the mandibular nerve (V3)—converge on the ...Sensory branches · Function · Trigeminal nucleus · Spinal trigeminal nucleus Branches of the trigeminal nerve. Print. Sections. Products and services. Trigeminal neuralgia results in pain occurring in an area of the face supplied by one or more of the three branches of the trigeminal nerve. There is a problem with information submitted for this request. Review/update the information highlighted below and resubmit the form.
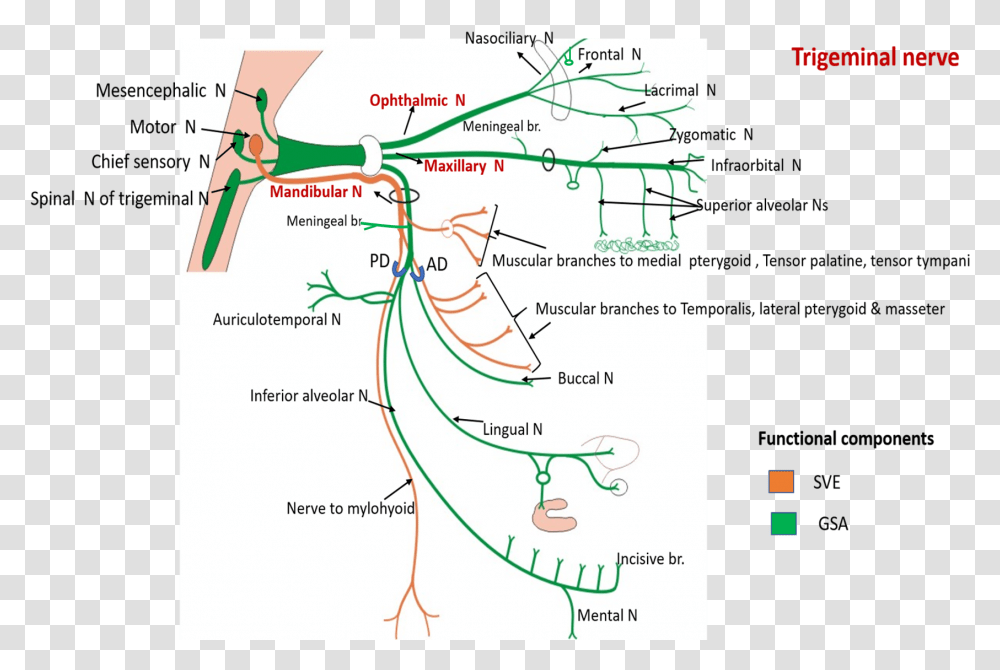
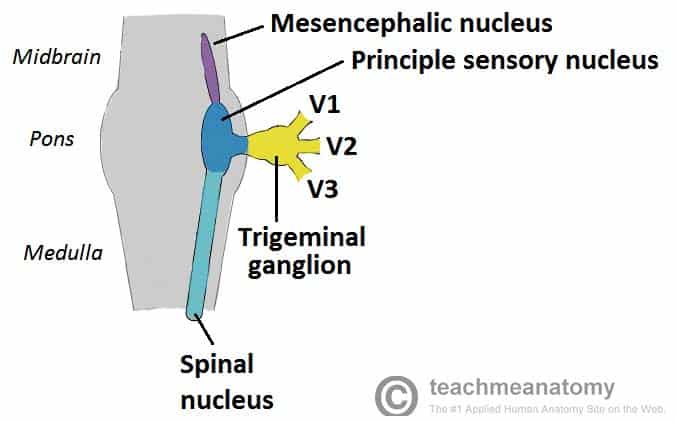
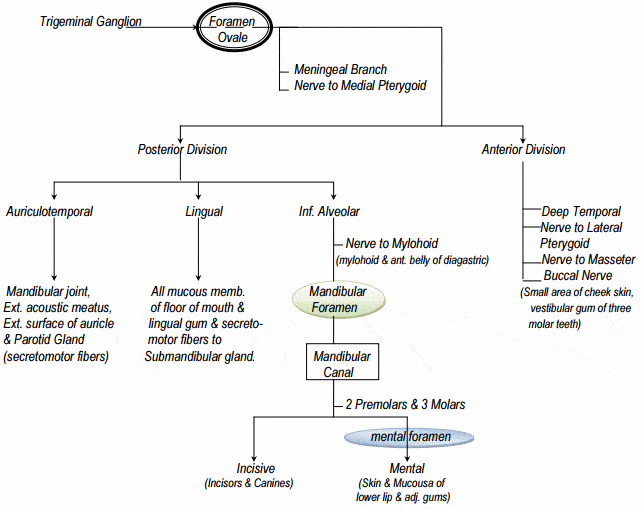
The trigeminal nerve is the fifth cranial nerve (CN V). Its primary function is to provide sensory and motor innervation to the face. The trigeminal nerve consists of three branches on either side that extend to different territories of the face. These branches join at the trigeminal ganglia which are located within the Meckel cave of the cranial cavity. The different branches are namely the ... Trigeminal nerve. The large trigeminal nerve or 5th cranial nerve has three branches: ophthalmic (V1), maxillary (V2), and mandibular (V3) divisions. Trigeminal nerve is a mixed nerve providing sensations of the face for touch, temperature, and pain from the upper, middle, and lower portions of the face, as well as the oral cavity, to the brain. The ophthalmic branch is the first division of the trigeminal nerve. It is a purely sensory nerve that carries afferent stimuli of pain, light touch, and temperature from the upper eyelids and supraorbital region of the face, up to the vertex of the head. The nerve also acts as a conduit for sympathetic fibers that require access to the ciliary body, lacrimal glands, cornea, and conjunctiva ... The trigeminal nerve is the largest of the cranial nerves and can be further divided into three divisions: ophthalmic, maxillary, and mandibular. The ophthalmic division sends information from the scalp, forehead, and upper eye lids (the upper parts of the head) and is sensory in modality, of the general somatic sensory variety.
Gross Anatomy. The trigeminal nerve is the largest and most complex of the 12 cranial nerves (CNs). It supplies sensations to the face, mucous membranes, and other structures of the head. It is the motor nerve for the muscles of mastication and contains proprioceptive fibers. The trigeminal nerve is associated with derivatives of the 1st pharyngeal arch. Sensory: The three terminal branches of CN V innervate the skin, mucous membranes and sinuses of the face.Their distribution pattern is similar to the dermatome supply of spinal nerves (except there is little overlap in the supply of the divisions).

Jual Terapi Akupunktur Untuk Nyeri Wajah Trigeminal Neuralgia Kab Magelang Klinik Pakualaman 2 Tokopedia



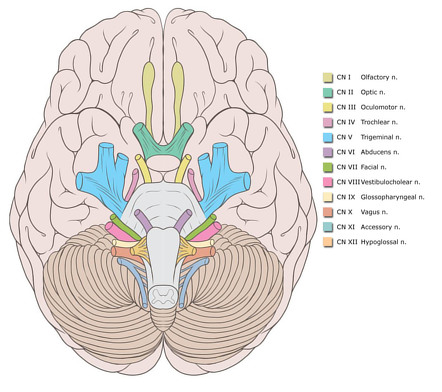

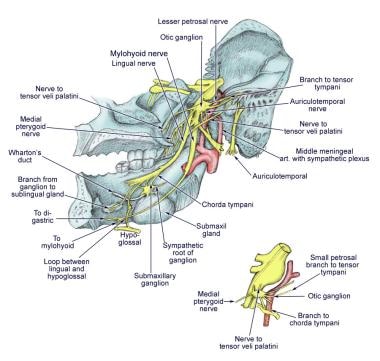
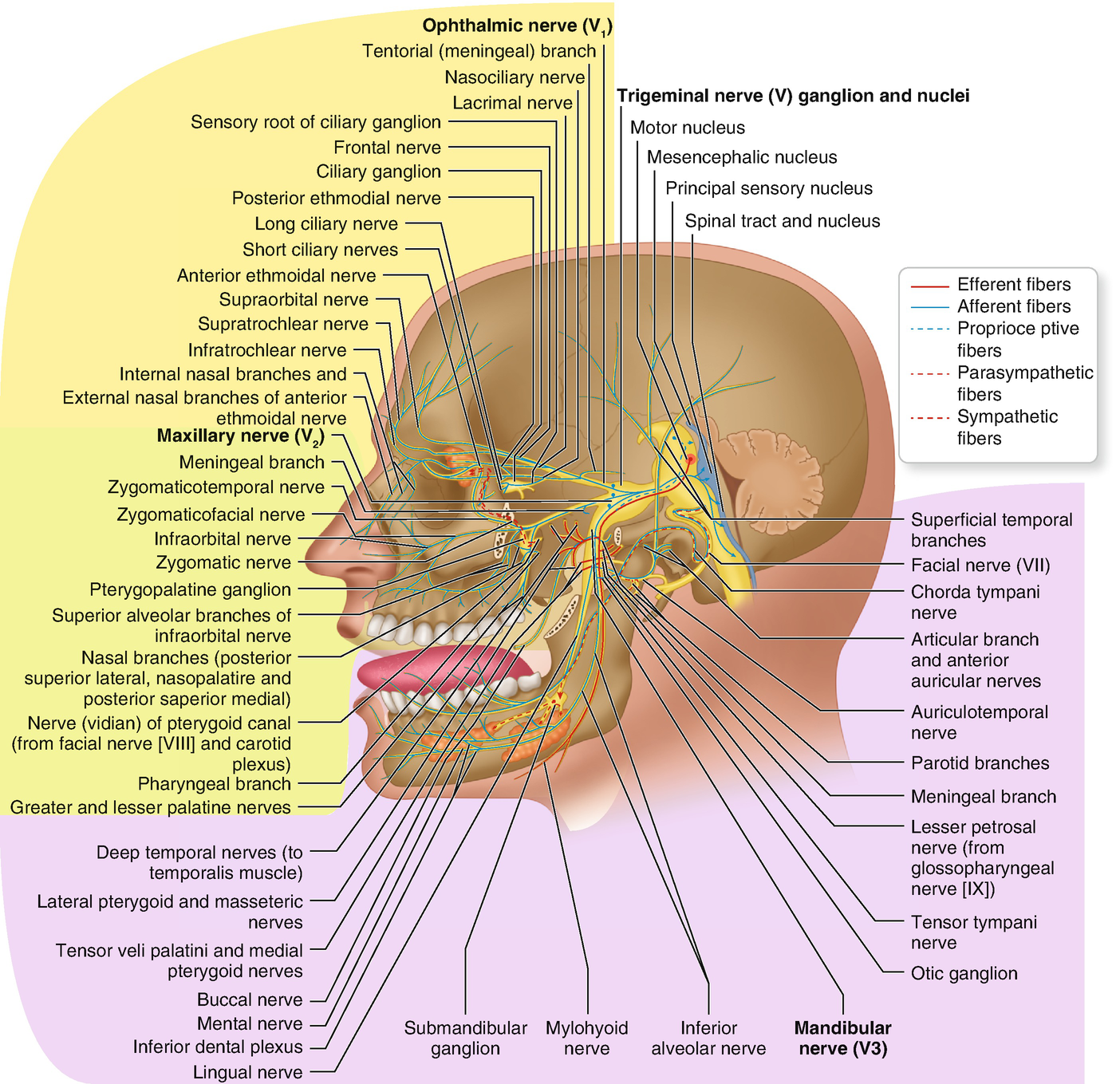
:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/nucleus-principalis-nervi-trigemini/trj4f9Y96F8ZxnclYEC0g_Principle_nucleus_of_trigeminal_nerve_02.png)

















0 Response to "42 trigeminal nerve branches diagram"
Post a Comment