42 space-time diagram
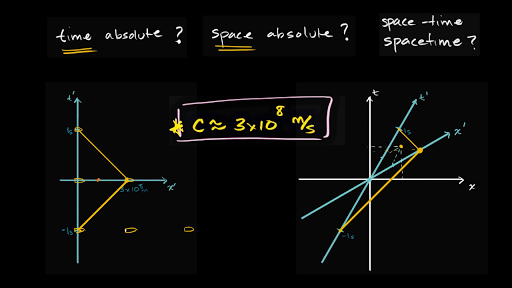
Introduction to special relativity and Minkowski spacetime diagrams. Including multiple observers in the "most obvious" way led to some problems. Let's see how we can start to solve those problems by introducing (what we'll later call) Minkowski spacetime diagrams. This is the currently selected item. Here's a little primer on spacetime diagrams to finish off our journey through Einstein's relativity. We need to get back to other topics._____...
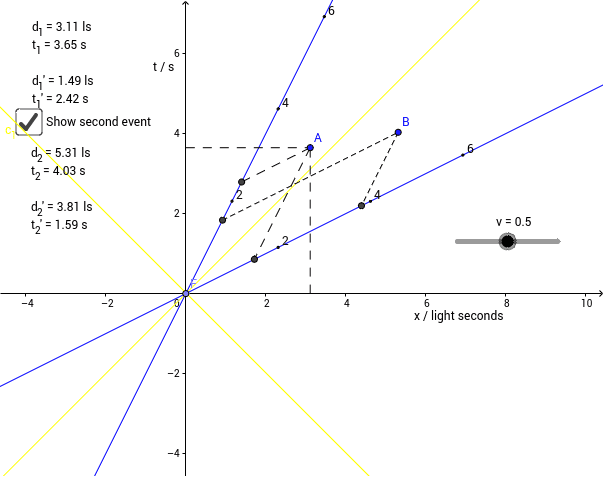
Science; Advanced Physics; Advanced Physics questions and answers (r03.4) The spacetime diagram below shows some Home frame axes and four events named (uncreatively) A, B, C, and D. Remeber that every answer to every question must be of the form "something=something", with the left-hand side being an appropriate name.

Space-time diagram
The trajectories of the Enterprise, the star, and the planet are shown on the space-time diagram. Assume that the planet is not moving relative to the star. The Enterprise will fly by at a constant velocity past the planet and beam up the students without stopping. The star goes supernova at space-time point S. The light from the supernova ... Lecture 13 Space Time Diagrams ASTR 340 Fall 2006 Dennis Papadopoulos Relativity Summary Relativity Postulates Laws of physics the same in all inertial frames Speed of light in vacuum constant Corollaries Space and time form a 4-dim continuum There are global space-time frames with respect to which non-accelerated objects move in straight lines at constant velocities (inertial frames ... { A point on the spacetime diagram is called an event. This is a point in space at a speci c moment in time. { The vertical value of this event is the time as measured by observer 1. { The horizontal value event is the position of the event as measured by observer 1. { Take a line from the event, parallel to the space axis of observer 2.
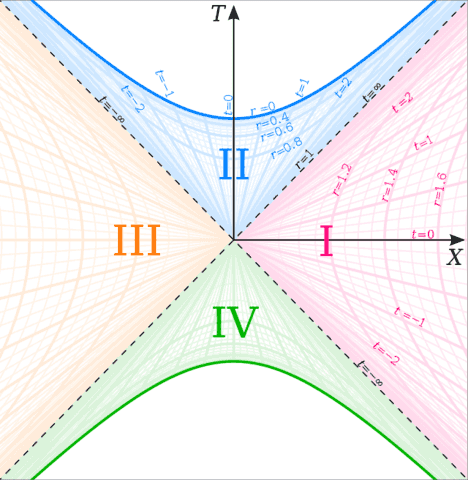
Space-time diagram. A spacetime diagram is a graphical illustration of the properties of space and time in the special theory of relativity.Spacetime diagrams allow a qualitative understanding of the corresponding phenomena like time dilation and length contraction without mathematical equations.. The history of an object's location throughout all time traces out a line, referred to as the object's world line, in ... A spacetime diagram (or Minkowski diagram) is a combination of two coordinate systems: one in which an observer is at rest relative to certain events, and another for an observer in relative motion to the first. In such a diagram, light rays always follow paths with a 45° slope. The time of an event is indicated by its intersection with the appropriate time axis. In a Flatland Minkowski Diagram, there are two axes for space (a plane), and one axis for time. Hence, a Flatland Minkowski Diagram is a 3-Space, with light cones as in the diagram below. Figure 1: Minkowski Diagrams. An event (a particular place at a particular time) is represented by a point on the Minkowski Diagram. Minkowski space (space-time) terms are used in mathematical physics and special relativity. It is a combination of three-dimensional Euclidean space and time into a four-dimensional multiplex, where space-time interval exists between any two events is not liable on the inertial frame of reference.
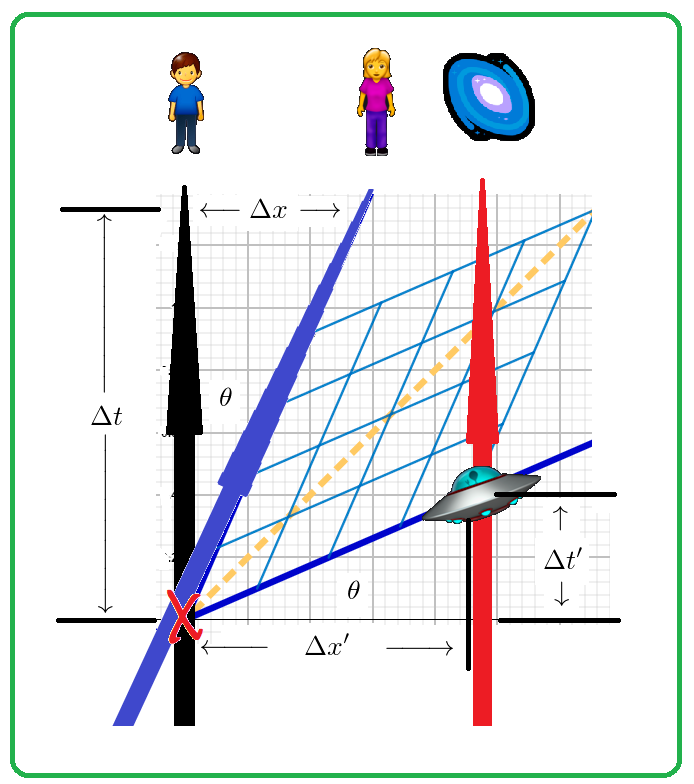
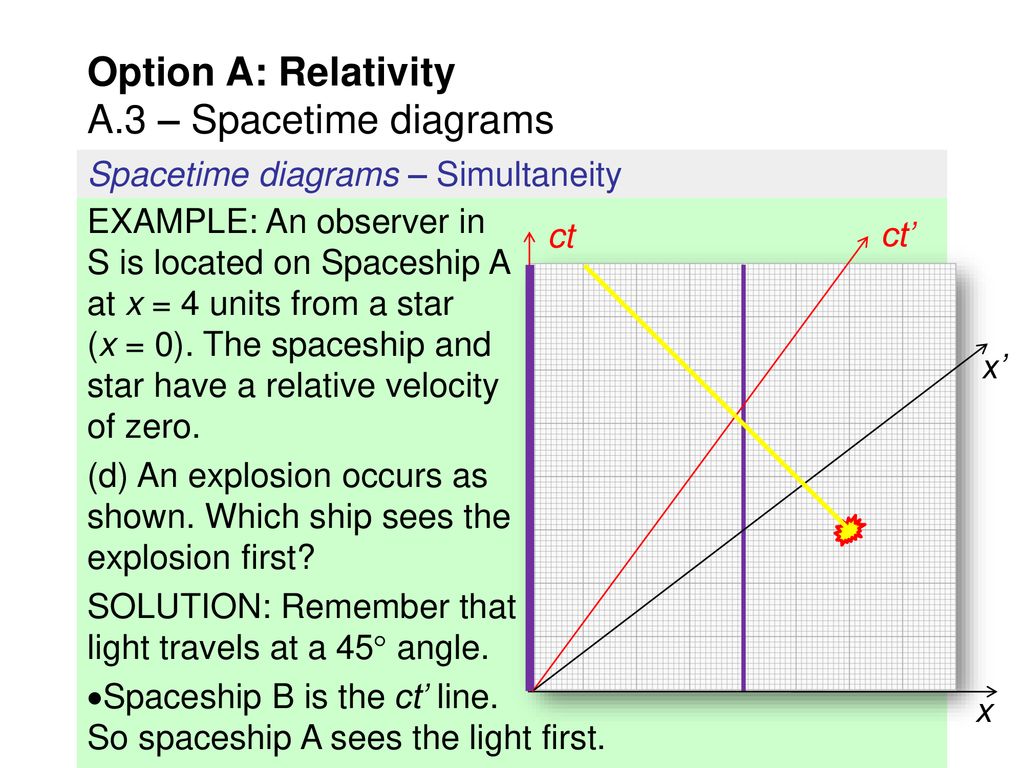
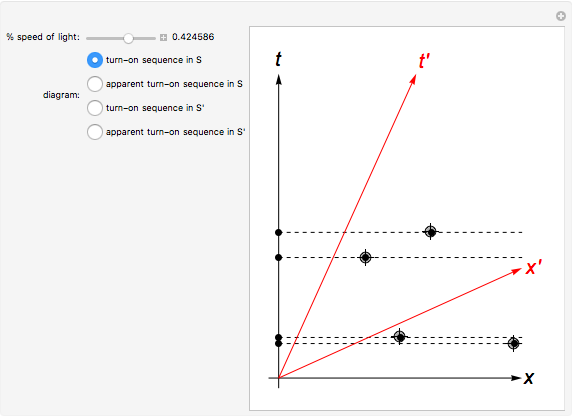
The diagram will show time dilation, the relativity of simultaneity and other effects of special relativity. The diagram will show the events as measured by the two observers as designed by Einstein: Each observer has a set of synchronized clocks and previously established distance points. Minkowski space time diagram Minkowski space time diagram. As already explained in our introduction, the special theory of relativity describes the relationship between physical observations made by different inertial or nonaccelarating observers, in the absence of gravity. Each such observer labels events in space-time by four inertial ... •A space-time diagram is a graph showing the position of objects (events) in a reference frame, as a function of time •Conventionally, space (#) is represented in the horizontal direction, and time (") runs upwards # We have scaled time by a factor of !, so it has the 1. In this diagram, which events (out of A, B, C and D) occur at the same time? Which events occur at the same place? 2. One division of the space axis corresponds to 1 meter. Construct a world line of the particle that is resting at 2 m from the reference event. time space A D B C O. time space
2.8 Spacetime Diagrams 3 We therefore have: and so the S0 coordinate system is oblique in the S spacetime diagram. Note. In the above representation, notice that the larger β is, the more narrow the "first quadrant" of the S0 system is and the longer the x0 and t0 units are (as viewed from S). Spacetime diagrams. One of the most illuminating ways of understanding the resolution of the so-called "twin paradox" is by analyzing carefully drawn, detailed spacetime diagrams for specific choices of trip distance and velocity. I have done so below for a trip of three lightyears undertaken at a speed of 3/5 c (giving a relativistic factor γ ... On a space-time diagram, it is the horizontal distance between two adjacent trajectories Time (t) (x) Traffic Flow Basics-Space Headway . Individual vehicle Traffic stream Speed [L/T] Time Headway [T] Flow [V/T] Space Headway [L] Density [V/L] Let's try to fill in the rest of the table. spacetime diagram, or simply a “spacetime diagram,” to illustrate and understand complex scenarios in special relativity. This diagram was originally developed by Hermann Minkowski in 1908 and is useful for objects that move at a substantial fraction of the speed of light. Background. We are interested in the dynamics of a system of objects: where objects are
A space-time diagram shows the history of objects moving through space (usually in just one dimension). A speci c point on a space-time diagram is called an \event." To make a space-time diagram, take many snapshots of the objects over time and set them on top of each other. Lines in the diagram are like \contrails" through time.
13 4. Time dilation from the Lorentz transformation Fig.10 Minkowski space-time diagram for the time dilation. The event C is located at (ct', x'=0) in the S' frame.(OC)S' = ct'. (OA)s = ct.The length OA in this figure corresponds to the length (OA)S', which is different from the length (OA)S measured in the S frame. (OA)S = k (OA)S' (the scaling factor k will be discussed
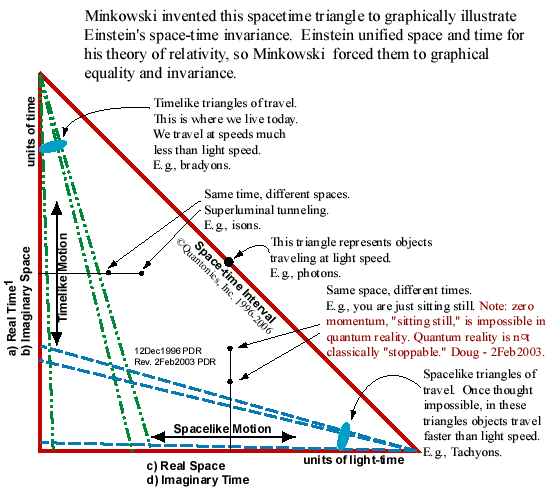
Minkowski Invented This Spacetime Triangle To Graphically Illustrate Einstein S Space Time Invariance Einstein Unified Space And Time For His Theory Of Relativity So Minkowski Forced Them To Graphical Equality And Invariance
the same as time goes on. When we say "as time goes on," we imply that we read the space-time diagram from bottom (t=0) to top. Imag-ine Planet A sends a spacecraft to Planet B at a speed of one half the speed of light (0.5c). The worldline of this spacecraft is represented by the blue line. It is sloped, because its po-sition changes with time.
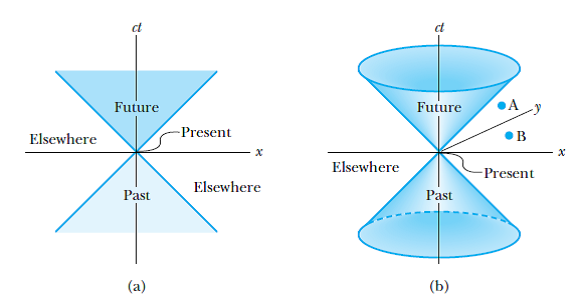
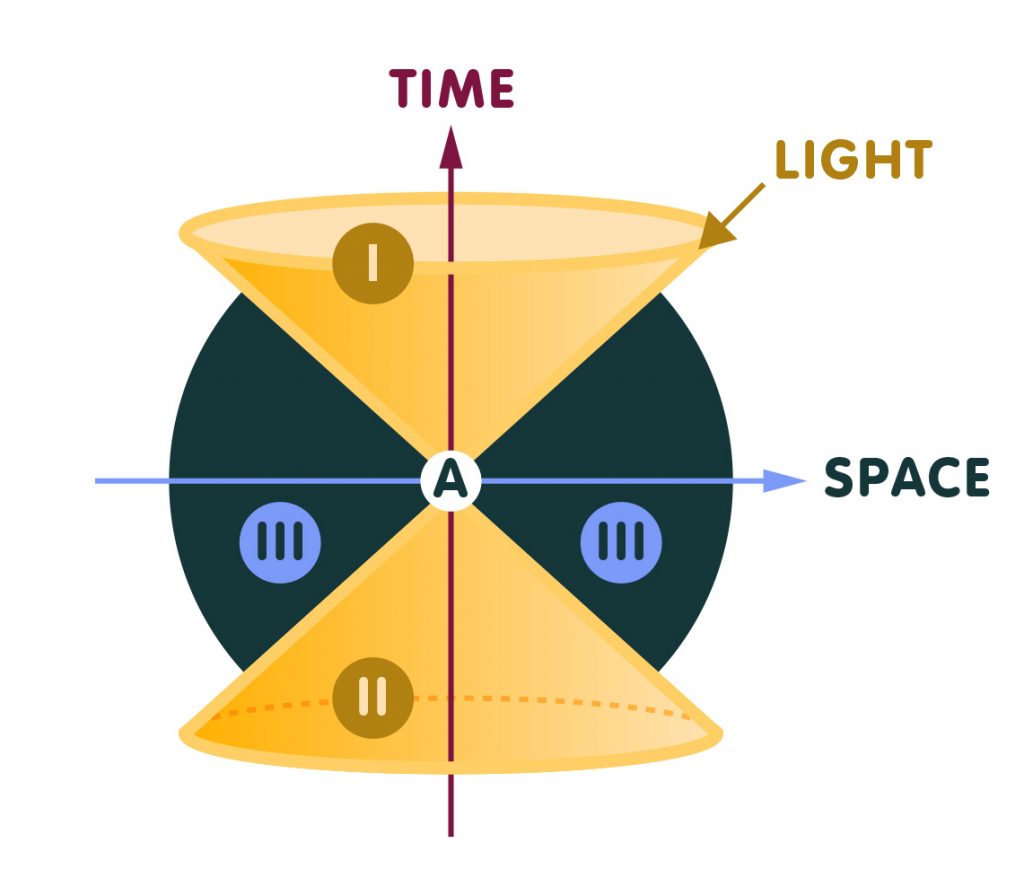
A space-time diagram is nothing more than a graph showing the position of objects as a function of time. The usual convention is that time runs up the diagram, so the bottom is the past, or early times, and the top is the future, or late times. A point on this graph describes both a position (the horizontal or x coordinate) and a time (the vertical or t coordinate). A "point" in space-time is called an event.
This point on our diagram, from my frame of reference, in the S frame of reference, this is the point time is, or space, or my distance, my distance from the origin in the positive-x direction is going to be, I just drop a, I just go parallel to my vertical axis, so I'm just going to do that, and I get 4.5 times 10 to the 8th meters, so 4.5 ...
The space time diagram, also known as Minkowski diagram, was developed in 1908 by Hermann Minkowski and provides an illustration of the properties of space and time in the special theory of relativity.It allows a qualitative understanding of the corresponding phenomena like time dilation and length contraction without mathematical equations.
The time-space diagram is a graph that describes the relationship between the location of vehicles in a traffic stream and the time as the vehicles progress along the highway. The following diagram is an example of a time-space diagram. Time-space diagrams are created by plotting the position of each vehicle, given as a distance from a ...
In a Flatland Minkowski Diagram, there are two axes for space (a plane), and one axis for time. Hence, a Flatland Minkowski Diagram is a 3-Space, with light cones as in the diagram below. Figure 1: Minkowski Diagrams. An event (a particular place at a particular time) is represented by a point on the Minkowski Diagram.
In this video we will draw some space time diagrams and look at events occurring inside and outside of light cones.
Minkowski Spacetime Diagrams Instructions. These are the instructions for my script-based spacetime diagram generator. Using a script-based system provides for a lot more options than could be easily accommodated with a graphical user interface (GUI). On the other hand, it requires reading instructions (sigh), which no one likes to do.
Space and Time included the first public presentation of spacetime diagrams (Fig. 1-4), and included a remarkable demonstration that the concept of the invariant interval (discussed below), along with the empirical observation that the speed of light is finite, allows derivation of the entirety of special relativity.
{ A point on the spacetime diagram is called an event. This is a point in space at a speci c moment in time. { The vertical value of this event is the time as measured by observer 1. { The horizontal value event is the position of the event as measured by observer 1. { Take a line from the event, parallel to the space axis of observer 2.
Lecture 13 Space Time Diagrams ASTR 340 Fall 2006 Dennis Papadopoulos Relativity Summary Relativity Postulates Laws of physics the same in all inertial frames Speed of light in vacuum constant Corollaries Space and time form a 4-dim continuum There are global space-time frames with respect to which non-accelerated objects move in straight lines at constant velocities (inertial frames ...
The trajectories of the Enterprise, the star, and the planet are shown on the space-time diagram. Assume that the planet is not moving relative to the star. The Enterprise will fly by at a constant velocity past the planet and beam up the students without stopping. The star goes supernova at space-time point S. The light from the supernova ...

Download A Spacetime Diagram Of The Laboratory Frame With The Spacetime Diagram Full Size Png Image Pngkit


















0 Response to "42 space-time diagram"
Post a Comment