41 pathway of light through the eye diagram
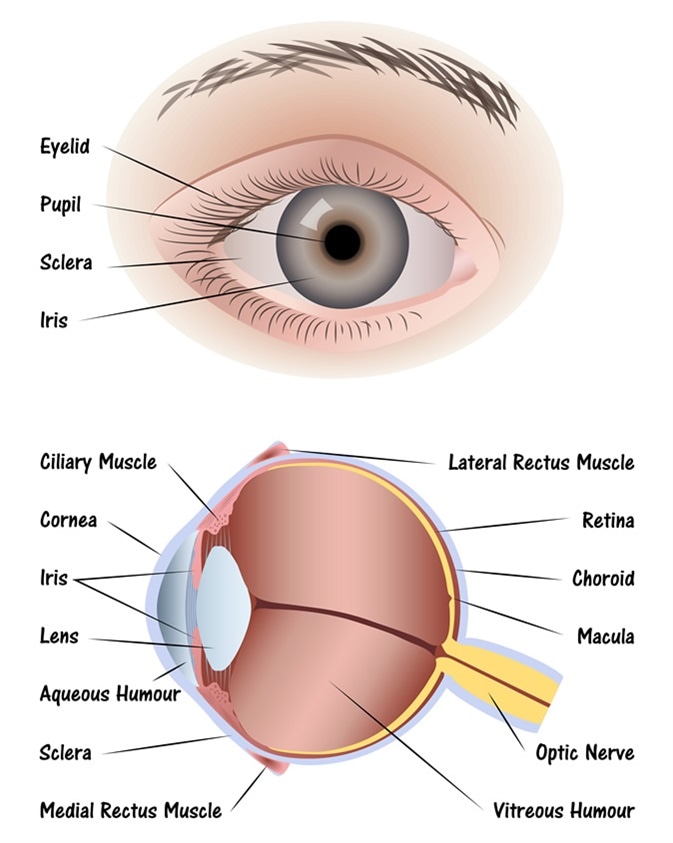
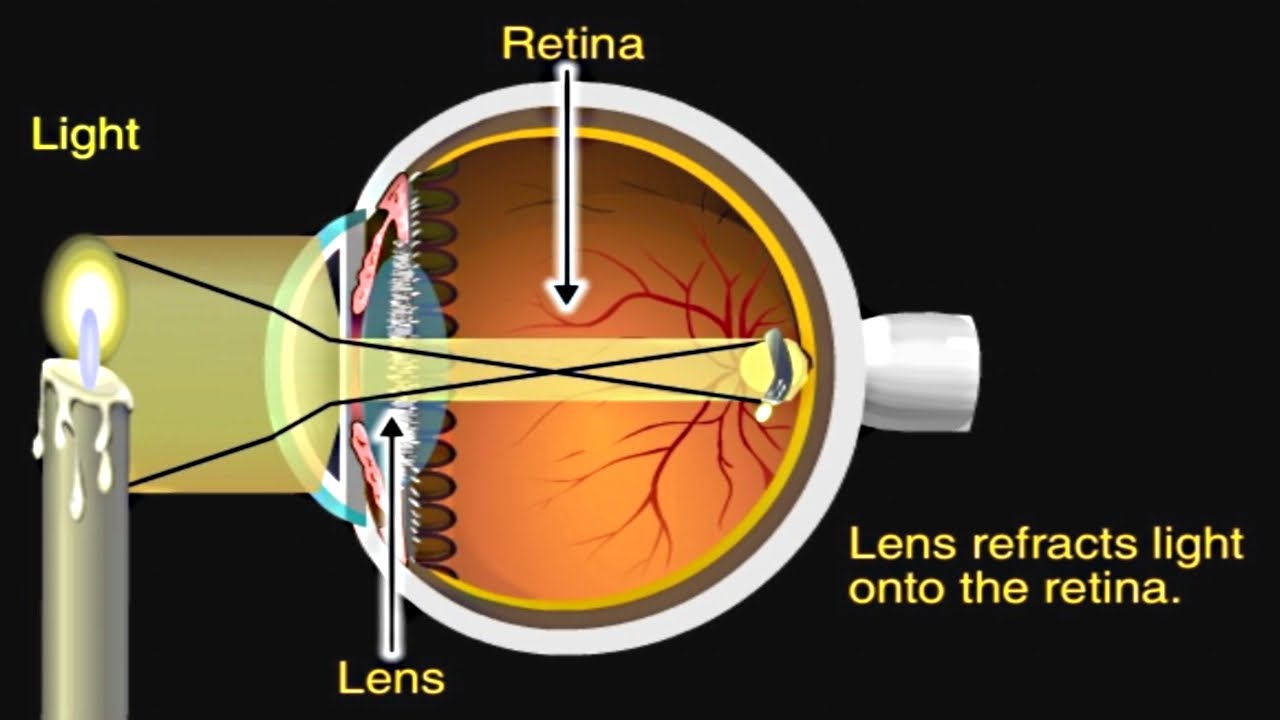
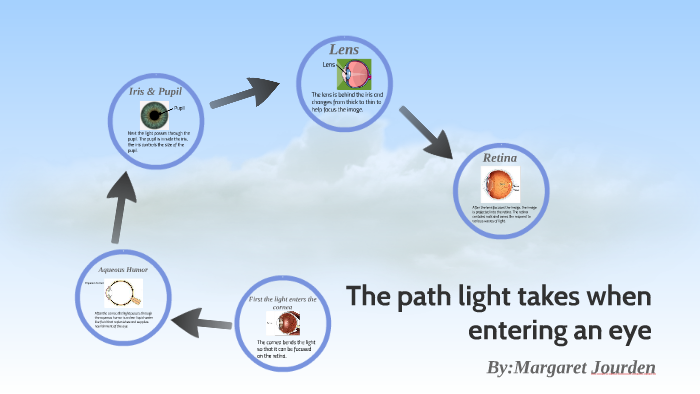
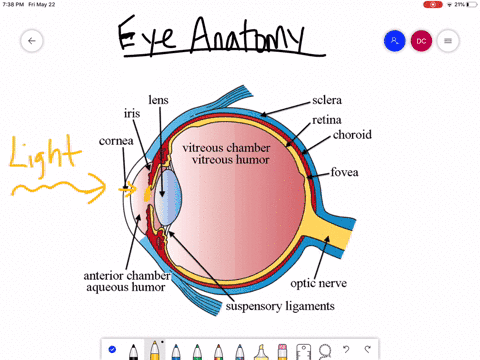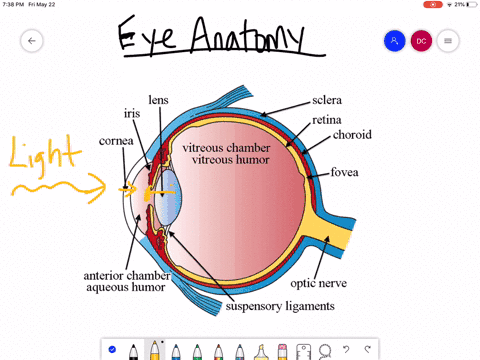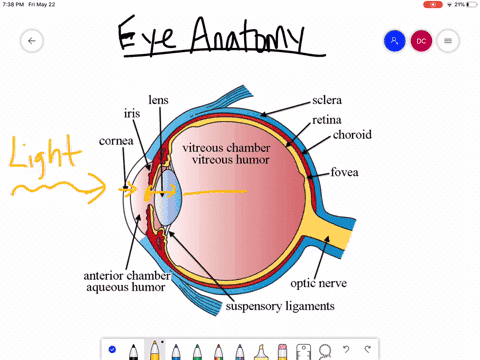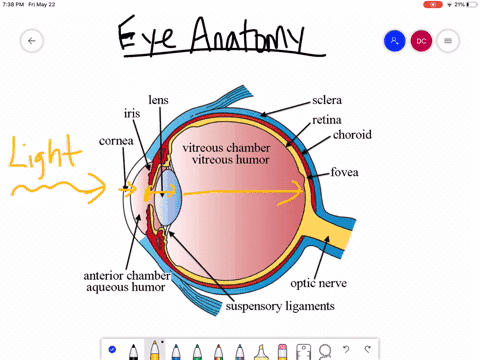
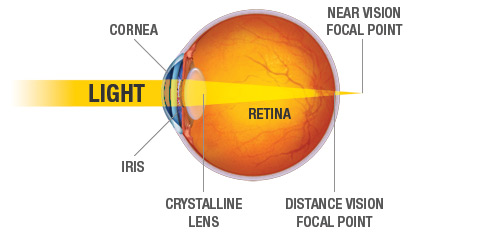
The eyes act as the initial point of contact through which photons pass to access the visual pathway. The visual pathway refers to the anatomical structures responsible for the conversion of light energy into electrical action potentials that can be interpreted by the brain. It begins at the retina and terminates at the primary visual cortex ... Light enters and travels through the cornea. 2. Goes throught the aqueous humor behind the cornea to the pupil. 3. Goes through the lens which is controlled in thickness by the muscles. 5. Goes through the vitreous humor and hits the retina. 6. The rods and cone cells of the retina are stimulated sending the information out through the optic nerve.
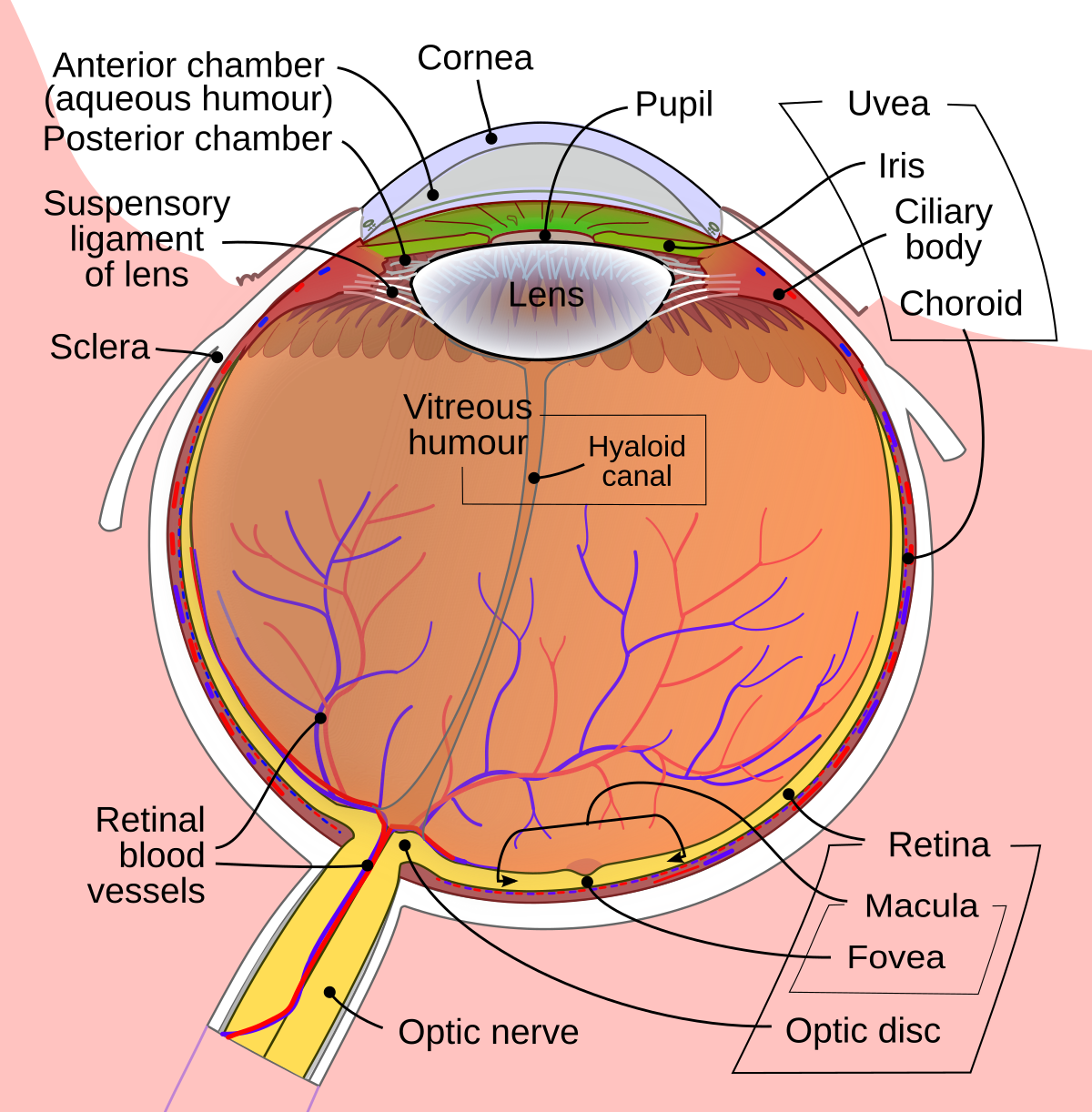
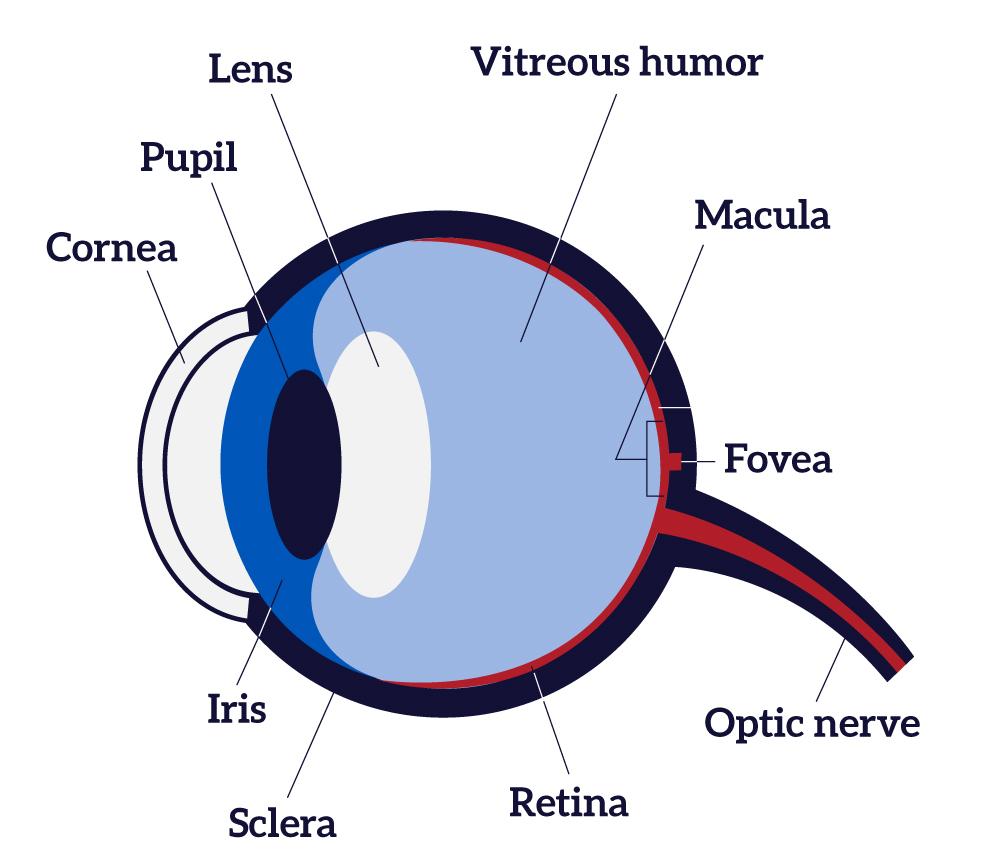
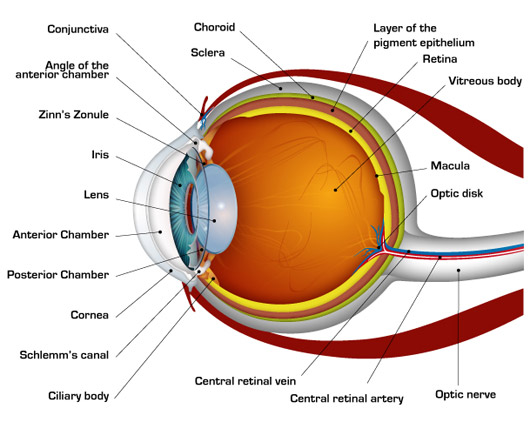
The visual pathway is the pathway over which a visual sensation is transmitted from the retina to the brain. This includes a cornea and lens that focuses images on the retina, and nerve fibers that carry the visual sensations from the retina through the optic nerve. Optic nerve fibers travel through the optic chiasma to the lateral geniculate ...

Pathway of light through the eye diagram
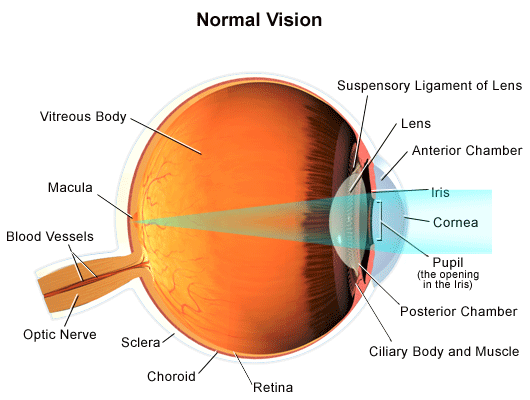
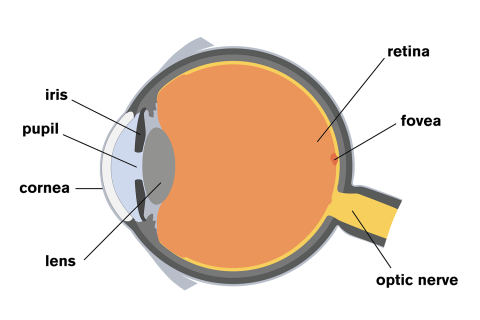
1. Light rays enter the eye through the cornea, the clear front "window" of the eye. The cornea's refractive power bends the light rays in such a way that they pass freely through the pupil the opening in the center of the iris through which light enters the eye. The iris works like a shutter in a camera. The eye is the major sensory organ involved in vision (Figure 1). Light waves are transmitted across the cornea and enter the eye through the pupil. The cornea is the transparent covering over the eye. It serves as a barrier between the inner eye and the outside world, and it is involved in focusing light waves that enter the eye. Vision is the special sense of sight that is based on the transduction of light stimuli received through the eyes. The eyes are located within either orbit in the skull. The bony orbits surround the eyeballs, protecting them and anchoring the soft tissues of the eye (Figure 1). The eyelids, with lashes at their leading edges, help to protect ...
Pathway of light through the eye diagram. light enters the posterior segment after the lens (posterior vitreous humor) 7 the refracted light travels through the retina, at the retina the photons pass by the ganglion, bipolar cells before striking a photo receptor (rods/cones) where it is absorbed and causes AP The Light Path through the Microscope. Rather than attempting to illustrate all ray paths using a single optical diagram, the distribution of light in a Köhler-illuminated microscope is here represented as four light paths of practical importance to the microscopist: The path taken by light emanating from the lamp filament, Jun 15, 2018 — Explanation: · 1. Cornea · 2. Aqueous Humor · 3. Pupil · 4. Lens · 5. Vitreous Humor · 6. Retina. Here's a diagram of the eye to follow along: https:/ ...1 answer · See below. Explanation: Light's path through the eye from the outside to the retina is as follows: 1. Cornea 2. Aqueous Humor 3. Pupil 4. ... The optic nerve (CN II) is the second cranial nerve, responsible for transmitting the special sensory information for vision.. It is developed from the optic vesicle, an outpocketing of the forebrain.The optic nerve can therefore be considered part of the central nervous system, and examination of the nerve enables an assessment of intracranial health.
What is normal vision? · Light enters the eye through the cornea. · From the cornea, the light passes through the pupil. · From there, it then hits the lens. · Next ... How the Eyes Work. All the different parts of your eyes work together to help you see. First, light passes through the cornea (the clear front layer of the eye). The cornea is shaped like a dome and bends light to help the eye focus. Some of this light enters the eye through an opening called the pupil (PYOO-pul). The path of light through the eye begins with the objects viewed and how they produce, reflect or alter light in various ways. When your eyes receive light, it begins a second journey through the eye's optical parts that adjust and focus light to the nerves that carry images to your brain. First, light must reflect off an object. The light travels through the clear cornea of the eye, and then the lens, which focuses the light onto the retina (the sensory tissue lining the back of the eye). In the retina, cells called rods detect light (they are photoreceptors) and cones detect colors.
Start studying Pathway of light through the Eye (steps 1-7). Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. What Is the Path of Light Through the Eye? According to The Merck Manual Home Health Handbook, light travels through the sclera, cornea, pupil and lens before stopping at the retina, respectively. Once at the retina, the information from the light is converted to electrical impulses for the brain to interpret. The Sensing Eye and the Perceiving Visual Cortex. As you can see in Figure 4.7 "Anatomy of the Human Eye", light enters the eye through the cornea, a clear covering that protects the eye and begins to focus the incoming light. The light then passes through the pupil, a small opening in the center of the eye.The pupil is surrounded by the iris, the colored part of the eye that controls the ... A ray diagram shows the path of light from an object to mirror to an eye. Incident rays - at least two - are drawn along with their corresponding reflected rays. Each ray intersects at the image location and then diverges to the eye of an observer. Every observer would observe the same image location and every light ray would follow the law of reflection.

Diagram Of An Eye Helps One Understand The Process Path In Which Light Image Travels Human Eye Diagram Diagram Of The Eye Eyeball Diagram
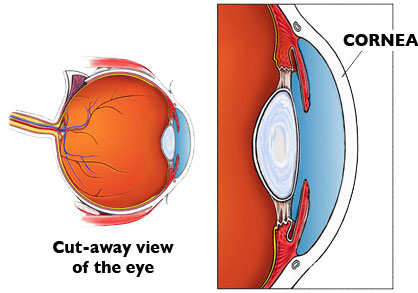
The cornea has the dual purpose of protecting the eye and refracting light as it enters the eye. After light passes through the cornea, a portion of it passes through an opening known as the pupil. Rather than being an actual part of the eye's anatomy, the pupil is merely an opening. The pupil is the black portion in the middle of the eyeball.
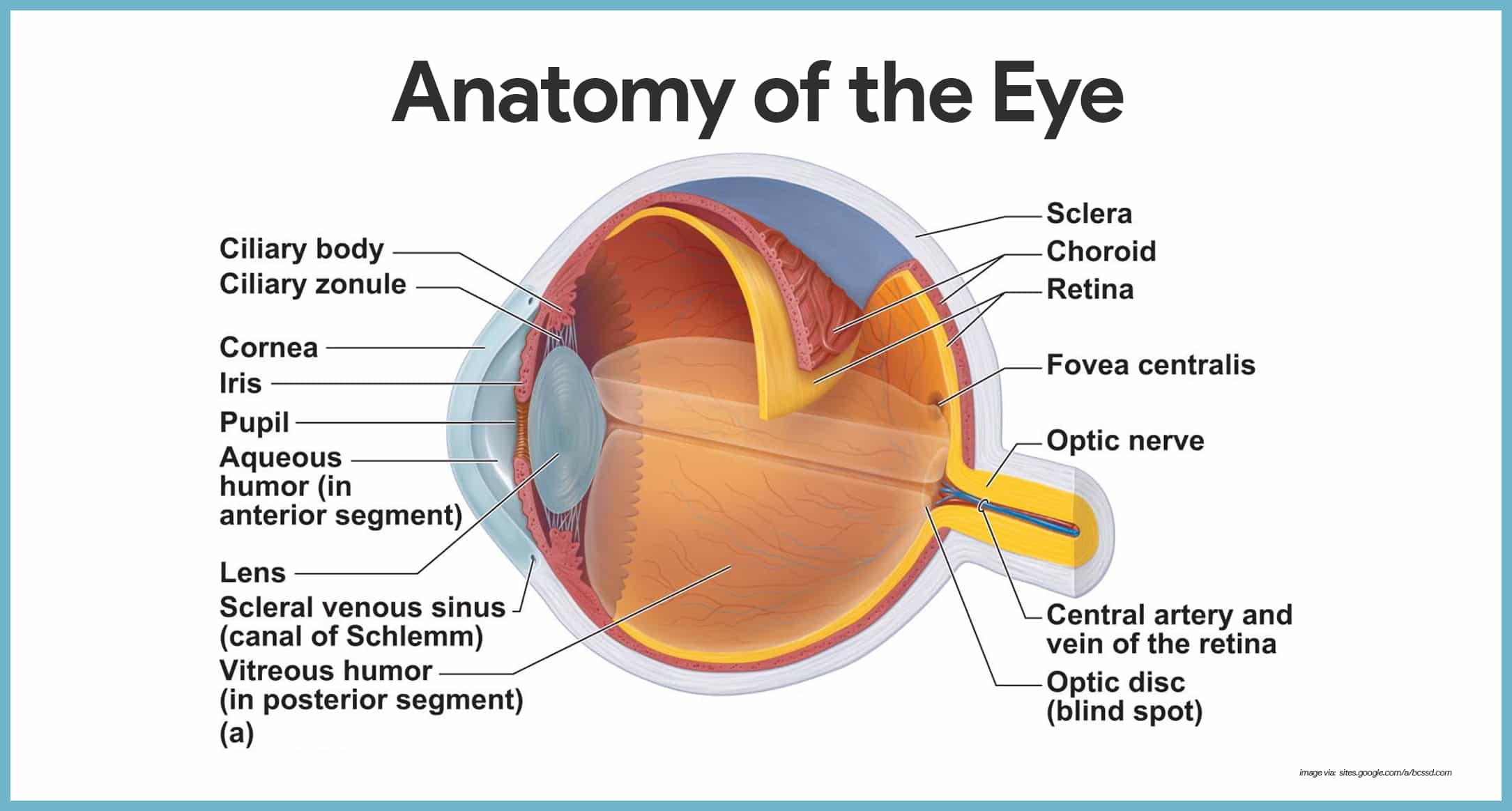
The visual pathway's primary task of converting light information into a picture of the outside world is moderated by neurons of the visual cortex. The optic nerve transmits the signals of the eye to the brain. In the eye, the visual pathway begins when light passes through the cornea, pupil, and lens, where it is inverted and projected onto ...
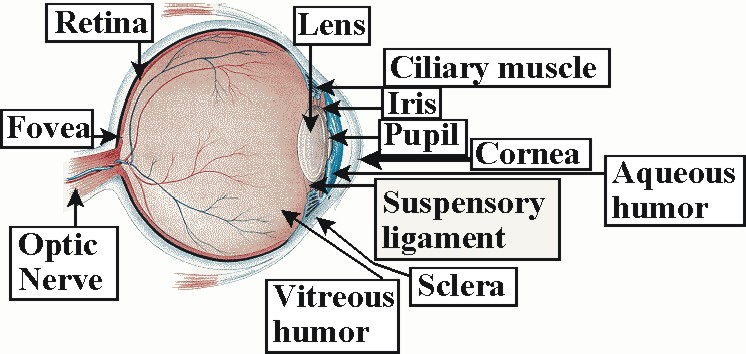
Light passes through the front of the eye (cornea) to the lens. The cornea and the lens help to focus the light rays onto the back of the eye (retina). The cells in the retina absorb and convert the light to electrochemical impulses which are transferred along the optic nerve and then to the brain.
The refraction of light through the human eye. Google Classroom Facebook Twitter. Email. Chemical and physical sciences practice passage questions. Practice: Understanding cardiac pressure-volume curves. Practice: Imaging tissue structures using muon tomography.
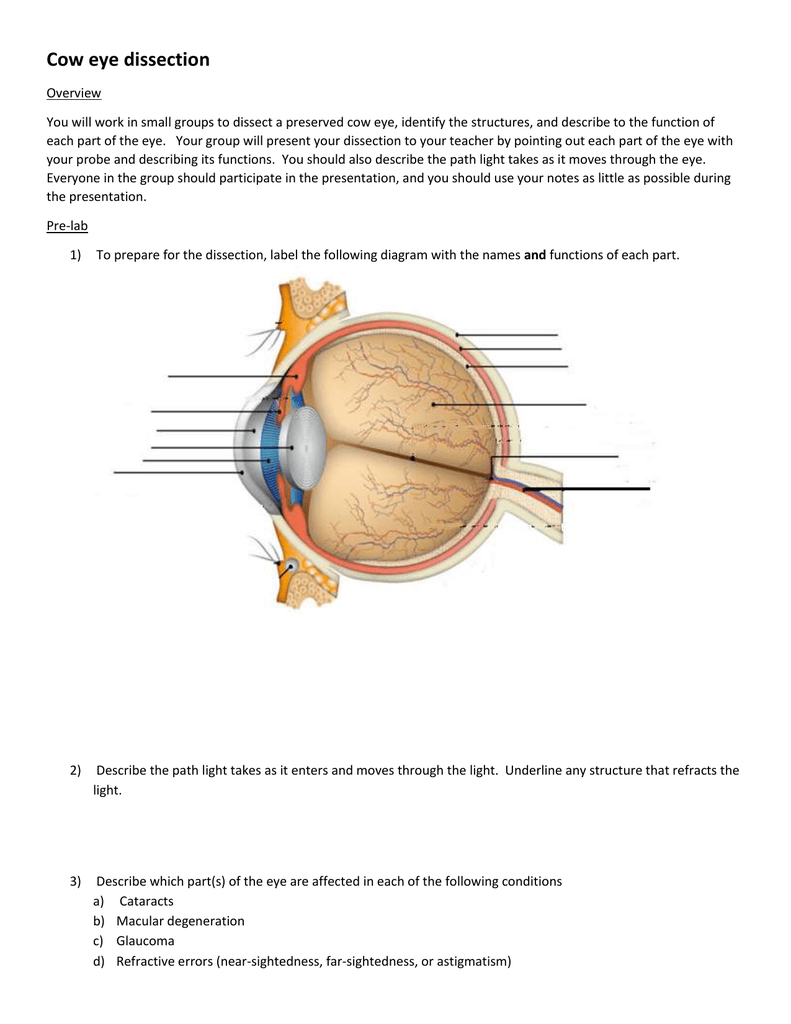
Question: Concept Map: The Pathway of Light through the Eye Complete the Concept Map to trace the pathway of light through the eye to the retina and explain how light is focused for distant or close vision. This problem has been solved! See the answer See the answer See the answer done loading.
Trace the pathway of light through the eye to the retina, and explain how light is focused for distant and close vision Light passes through the air into the eye through the cornea, aqueous humor, lens, and vitreous humor then passes through the entire neural layer of the retina to excite the photoreceptors
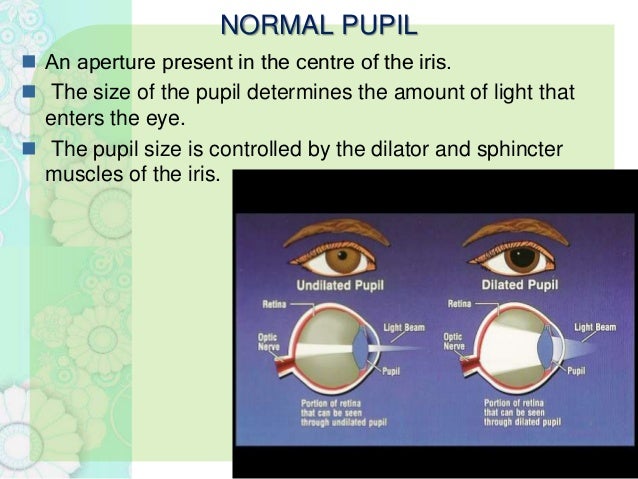
The iris allows more light into the eye (enlarging or dilating the pupil) when ... other nerve fibers (called the visual pathway) to the back of the brain, ...
Eyes That Capture Light The human eye is made up of various parts (continued) •Pupil: The dark circular opening at the center of the iris in the eye, where light enters the eye. •Iris: The colored part of the eye, a muscular diaphragm, that regulates light entering the eye by expanding and contracting the pupil.
Light reflex - The light reflex is mediated by the retinal photoreceptors and subserved by four neurones A. Afferent limb 1. First (sensory) connects each retina with both pretectal nuclei in the midbrain at the level of the superior colliculi. Ø Pupillary fibers travel along with the other fibres transmitting through the optic nerve.
Light passes through the front of the eye (cornea) to the lens. The cornea and the lens help to focus the light rays onto the back of the eye (retina). The cells in the retina absorb and convert the light to electrochemical impulses which are transferred along the optic nerve and then to the brain.
Different visual problems will occur depending on where the damage is. The black bars (labeled 1 through 5) indicate where damage may occur and the chart to the right of the pathway indicates the resulting "blind" area (gray shading) of the visual field. Damage at site #1: this would be like losing sight in the left eye.
through it. NOTE: The mirrors will fall out if you turn your periscope upside down. Object 0" 2" 3" 2" 3" 45° 45° 45° 45° Cut-out square of cardboard Observations, Data, and Conclusions Junior Home Scientist 1. Draw a diagram of the path a ray of light follows as it travels from an object, through the periscope, and into your eye. 2.
Pathway of light through the eye (Cornea image (Aqueous Humor image … ... Recieves the light and processes it. Here the image is most clear focused. ... Help to see ...
The Path of Light Through the Eye. By: Jake McDonald. Occipital lobe. Thalamus. The occipital lobe is located in the back of your brain and receives the impulses from the thalamus and turns it into sight. Optic nerve. Fovea. The thalamus is a small structure in your brain that relays your senses to the correct part of your brain.
Vision is the special sense of sight that is based on the transduction of light stimuli received through the eyes. The eyes are located within either orbit in the skull. The bony orbits surround the eyeballs, protecting them and anchoring the soft tissues of the eye (Figure 1). The eyelids, with lashes at their leading edges, help to protect ...
The eye is the major sensory organ involved in vision (Figure 1). Light waves are transmitted across the cornea and enter the eye through the pupil. The cornea is the transparent covering over the eye. It serves as a barrier between the inner eye and the outside world, and it is involved in focusing light waves that enter the eye.
1. Light rays enter the eye through the cornea, the clear front "window" of the eye. The cornea's refractive power bends the light rays in such a way that they pass freely through the pupil the opening in the center of the iris through which light enters the eye. The iris works like a shutter in a camera.

















0 Response to "41 pathway of light through the eye diagram"
Post a Comment