40 on the hr diagram red supergiants like betelgeuse lie
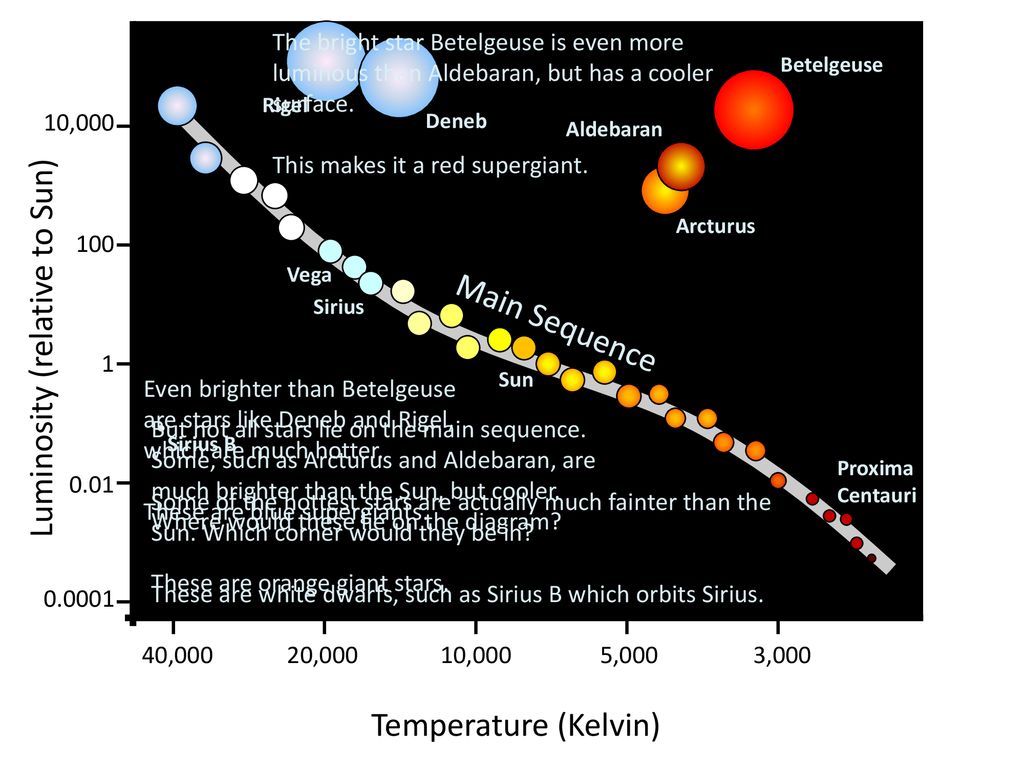
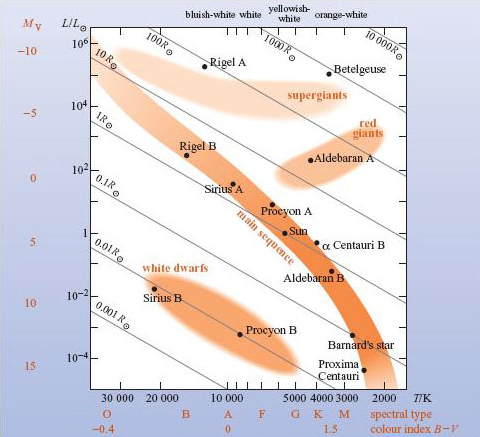
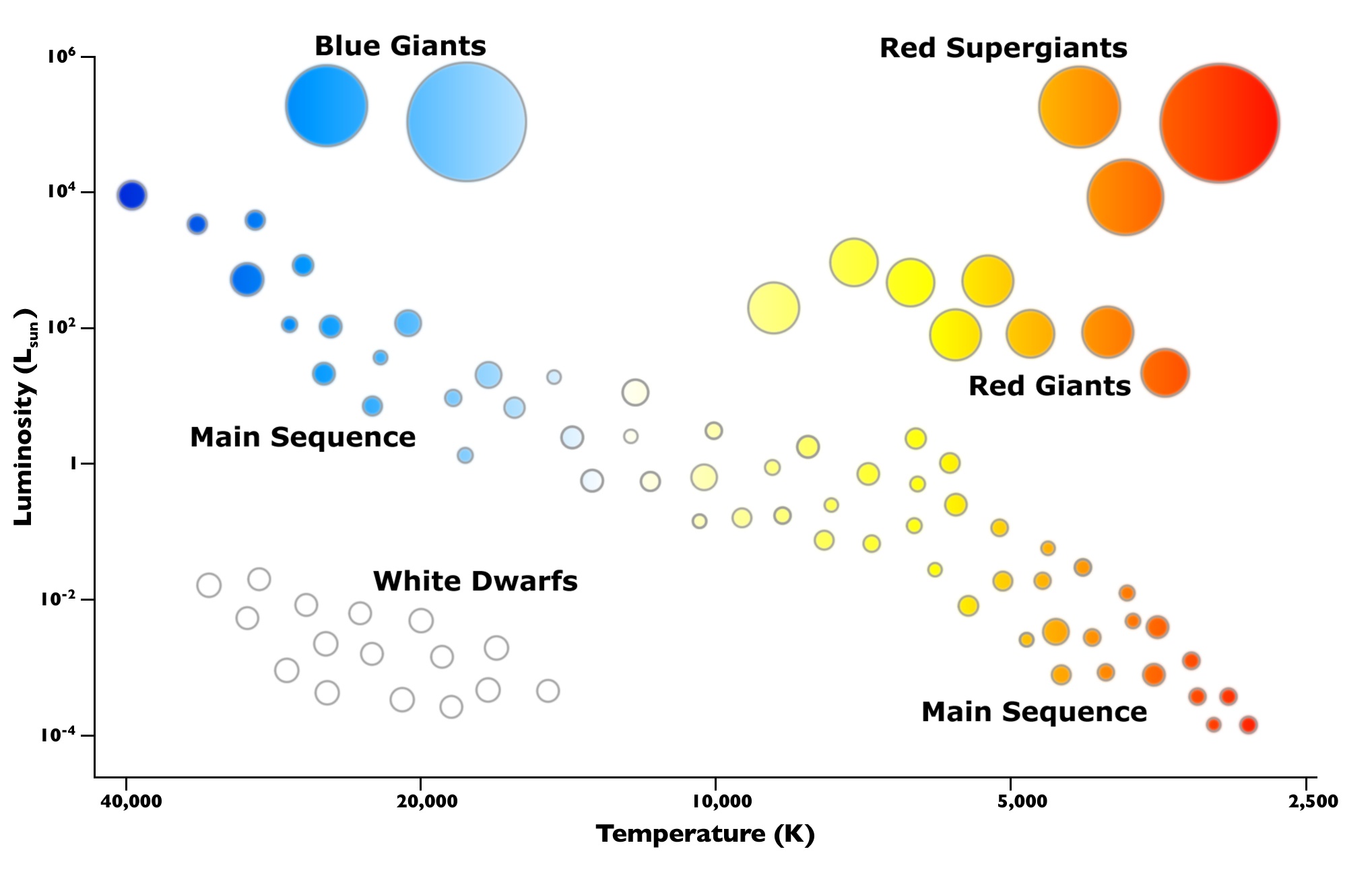
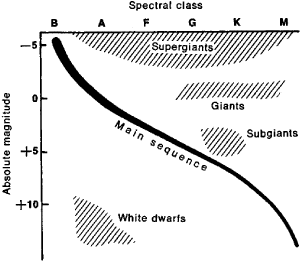
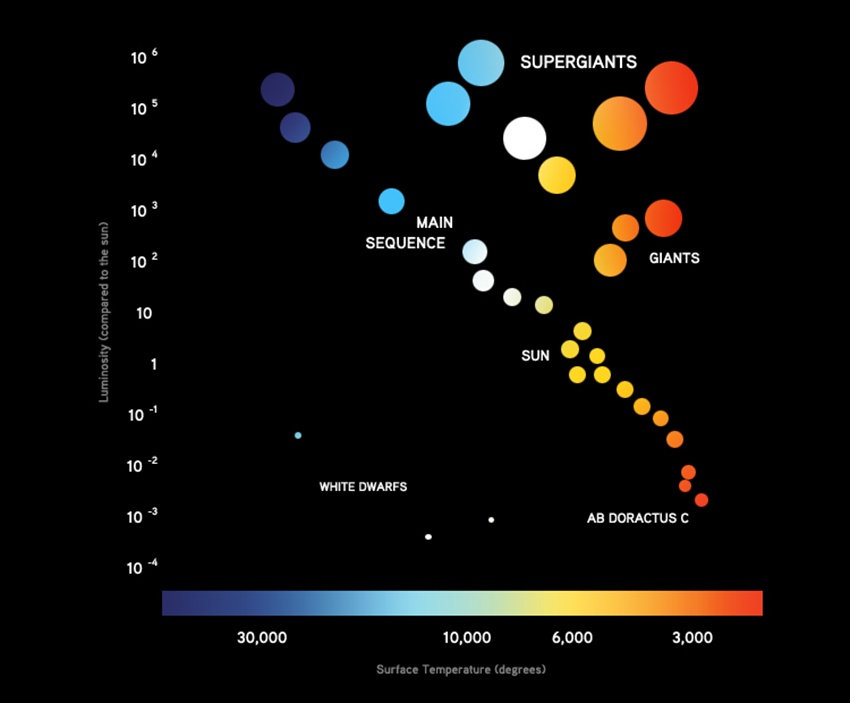
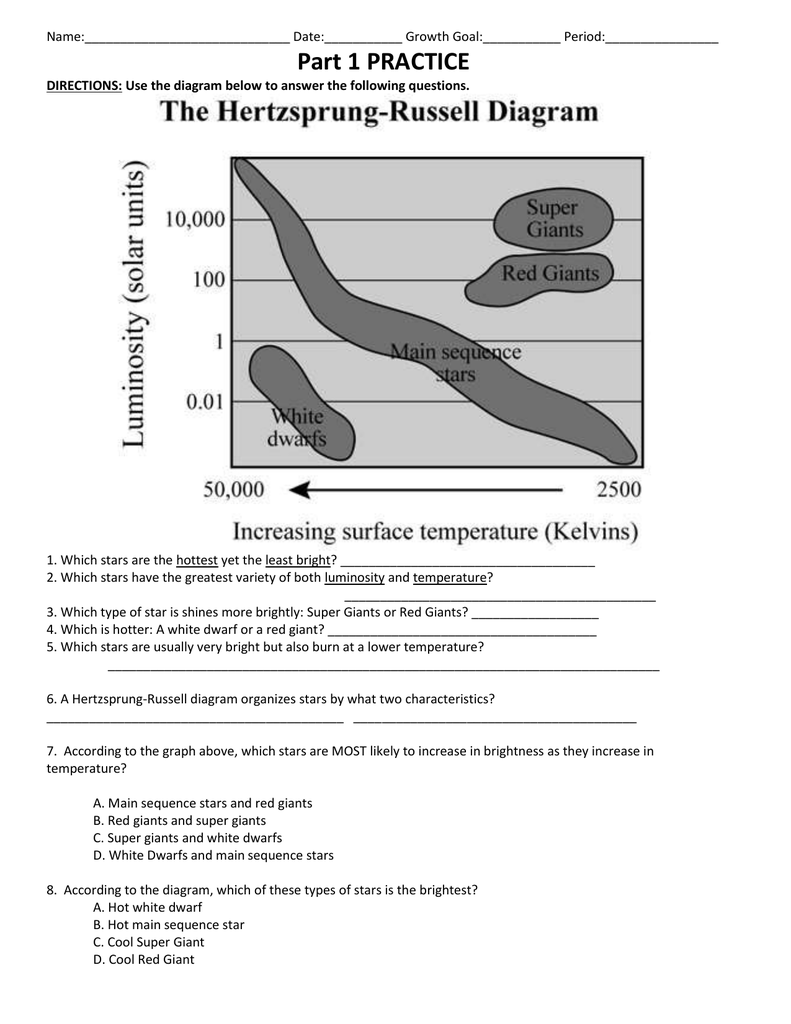
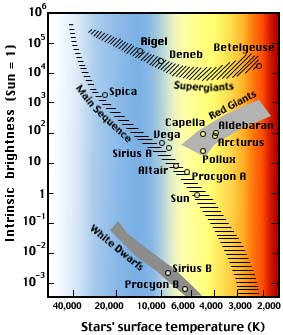
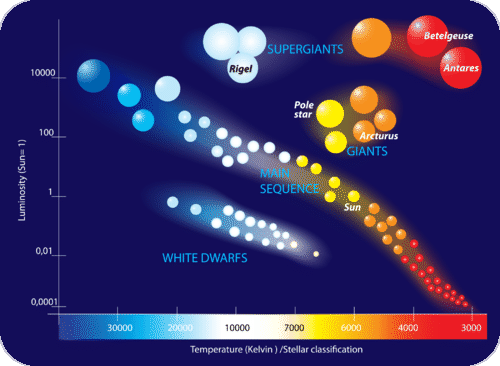
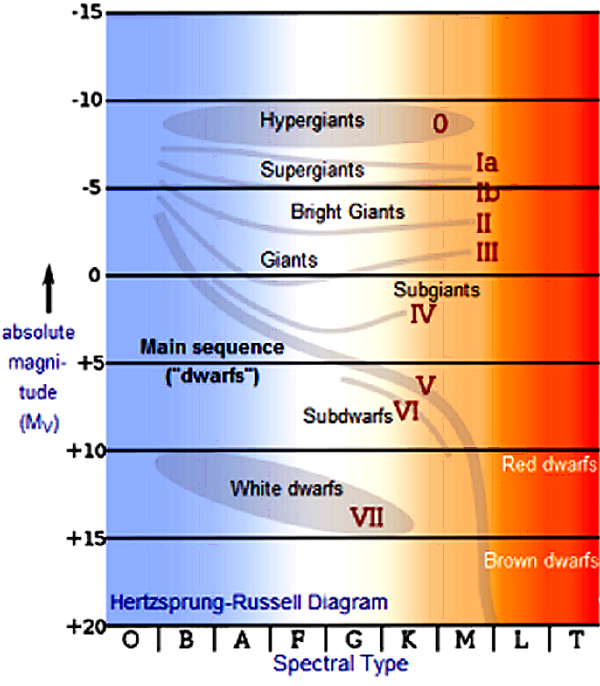
The White Dwarfs and Red Giants are different classes of stars that the H-R diagram helps us to identify. So the H-R diagram can tell us something about the size (radius) of the stars. The fact that the H-R diagrams for the nearby stars, the Pleiades star cluster, and the M3 star cluster are all different leads us to look for other differences ... burning dwarf stars like the Sun are found in a band running from top‐left to bottom‐right called the Main Sequence. Giant stars form their own clump on the upper‐right side of the diagram. Above them lie the much rarer bright giants and supergiants. At the lower‐left is the band of
On the H-R diagram, red supergiants like Betelgeuse lie. at the top right. Arrange the stellar spectra from hottest to coolest. obafgm. A star has a parallax of 0.01 arc seconds. Its distance is. 100 parsecs. ... On the H-R diagram, white dwarfs Sirius B and Procyon B lie. at the lower left.

On the hr diagram red supergiants like betelgeuse lie
Answer: Betelgeuse is usually the tenth-brightest star in the night sky and, after Rigel, the second-brightest in the constellation of Orion. It is a distinctly reddish semiregular variable star whose apparent magnitude, varying between +0.0 and +1.6, has the widest range displayed by any first-m... On the H-R diagram, red supergiants like Betelgeuse lie A. at the bottom left. B. at the bottom right. C. at the top right. D. at the top left. E. They can't be plotted, for they are not main sequence. Betelgeuse has a spectral type of M2lab signifying that it is a red class M star. the "lab" refers to it being an intermediate luminous supergiant. It has a luminosity of 140,000L. Referring to ...
On the hr diagram red supergiants like betelgeuse lie. On the H-R diagram, red supergiants like Betelgeuse lie at the top right. 33. As the Sun rotates, an individual sunspot can be tracked across its face. From eastern to western limb, this takes about two weeks. 34. A star's absolute magnitude is its apparent brightness as seen from 10 parsecs distance. 35. A star has a parallax of .05". This interactive applet might help you visualize some of the properties of the HR diagram. Star size. Of the 12 brightest stars in our sky, most are giants and supergiants. Our Sun is a main-sequence star dwarfed by a supergiant like Betelgeuse. Star mass ranges from 0.08xM sun to 100xM sun: A 2012 paper, proposed that this phenomenon was caused by Betelgeuse transitioning from a blue supergiant (BSG) to a red supergiant (RSG). There is evidence that in the late evolutionary stage of a star like Betelgeuse, such stars "may undergo rapid transitions from red to blue and vice versa on the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram, with ... Compared to a type A0 star, a type A9 star is bluer. more massive. hotter. more luminous. cooler. (Correct) 14. What can be said with certainty about a red star and a blue star? The red star is closer to Earth than the blue star. The red star has a greater radial velocity than the blue star. The red star is more massive than the blue star. The ...
On the H-R diagram, red supergiants like Betelgeuse lie A) at the bottom right. B) at the top left. C) at the bottom left. D) at the top right. E) They can't be plotted, for they are not main sequence. A star near the lower left of the H-R diagram is likely to be. hot, dim, and small. How long does it take an M-type star to reach the main sequence, compared to a star like our sun? ... On the H-R diagram, red supergiants like Betelgeuse lie. at the top right. As a star's evolution approaches the Type II supernova, we find. On the H-R diagram, red supergiants like Betelgeuse lie: A) At the bottom left. B) At the bottom right. C) At the top left. D) At the top right. E) They can't be plotted, for they are not main sequence. Answer: D. a. The bipolar jets ejected by a T Tauri variable. b. A planet surrounded by a glowing shell of gas. c. The disc of gas and dust surrounding a young star that will soon form a solar system. d. The ejected envelope, often bipolar, of a red giant surrounding a stellar core remnant. 71. On the H-R diagram, red super-giants like Betelgeuse lie a.
17) On the H-R diagram, red supergiants like Betelgeuse lie 17) A) at the bottom right. B) at the top left. C) at the bottom left. D) at the top right. E) They can't be plotted, for they are not main sequence. 29) On the H - R diagram, red supergiants like Betelgeuse lie 29) A) at the top right. B) at the bottom left. C) at the top left. D) at the bottom right. E) They can't be plotted, for they are not main sequence. 30) A star near the lower right of the H - R diagram is likely to be 30) A) blue, with high luminosity. Question 29: On the H-R diagram, red supergiants like Betelgeuse lie 1. at the top right. (!) 2. at the top left. 3. about the middle. 4. to the lower left edge. 5. on the bottom, coolest portion of the main sequence. Question 30: Of the elements in your body, the only one not formed in stars is 1. Carbon 2. Calcium 3. Iron 4. Aluminum 5 ... on horizontal tracks through the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram as they approach (and potentially leave behind) the realm of the red supergiants. Stars with birth masses < 15 M⊙ evolve along a red supergiant branch which takes the star on a steep path towards higher luminosity (and somewhat cooler temperature). These
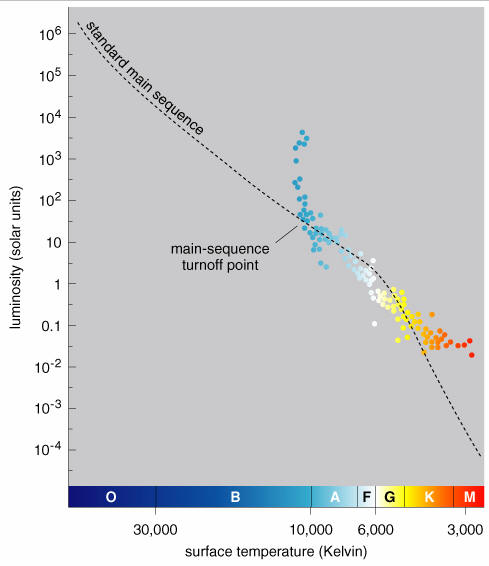
The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram the various stages of stellar evolution. By far the most prominent feature is the main sequence (grey), which runs from the upper left (hot, luminous stars) to the bottom right (cool, faint stars) of the diagram. The giant branch and supergiant stars lie above the main sequence, and white dwarfs are found below it.
On the H-R diagram, the bright blue stars that dominate the naked-eye sky lie: Definition. at the top left (Correct) ... On the H-R diagram, red supergiants like Betelgeuse lie: Definition. at the top right. (Correct) Term. The star's color index is a quick way of determining its: Definition. temperature. (Correct)
The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram, or H-R diagram, is a plot of stellar luminosity against surface temperature. Most stars lie on the main sequence, which extends diagonally across the H-R diagram from high temperature and high luminosity to low temperature and low luminosity.
H-R diagram red supergiants like Betelgeuse lie. at top right. apparent magnitude is brightest? greatest negative number ie: -23. Procyon lies 13 light years distant, parallax is.25'' ... On the H-R diagram, white dwarfs lie Sirius B and Procyon B lie: at the lower left.
On the H-R diagram, white dwarfs lie Sirius B and Procyon B lie. at the lower left. On the H-R diagram, red supergiants like Betelgeuse lie: At the top right. a star near the lower right of the H-R diagram is likely to be. red, with low luminosity. binary stars separated enough to be resolved in a telescope are called.
View HW08.docx from ENGL 1101 at Georgia Gwinnett College. HW #08 (Due: 04/01/2020) 1. On the H-R diagram, red supergiant's like Betelgeuse lie: Red supergiant's lie at the top right of the H-R
At the lower left corner of the H-R diagram are the smallest stars. Stars like Sirius B and Procyon B are just the opposite of the supergiants. They are extremely hot, dense, and dim. These are white dwarf stars that are about the size of the earth, and about as massive as the sun.
Red Giants On Hr Diagram 35 Images Faulkes Telescope Educational Guide On A Hertzsprung Diagram Where Would We Find Cfe Advanced Higher Fizzics
On the h r diagram red supergiants like betelgeuse lie. A star near the lower left of the h r diagram is likely to be. On the h r diagram red supergiants like betelgeuse lie at the top right arrange the stellar spectra from hottest to coolest. 100 times fainter than the human eye would be able to just barely detect.
Betelgeuse has a spectral type of M2lab signifying that it is a red class M star. the "lab" refers to it being an intermediate luminous supergiant. It has a luminosity of 140,000L. Referring to ...
On the H-R diagram, red supergiants like Betelgeuse lie A. at the bottom left. B. at the bottom right. C. at the top right. D. at the top left. E. They can't be plotted, for they are not main sequence.
Answer: Betelgeuse is usually the tenth-brightest star in the night sky and, after Rigel, the second-brightest in the constellation of Orion. It is a distinctly reddish semiregular variable star whose apparent magnitude, varying between +0.0 and +1.6, has the widest range displayed by any first-m...

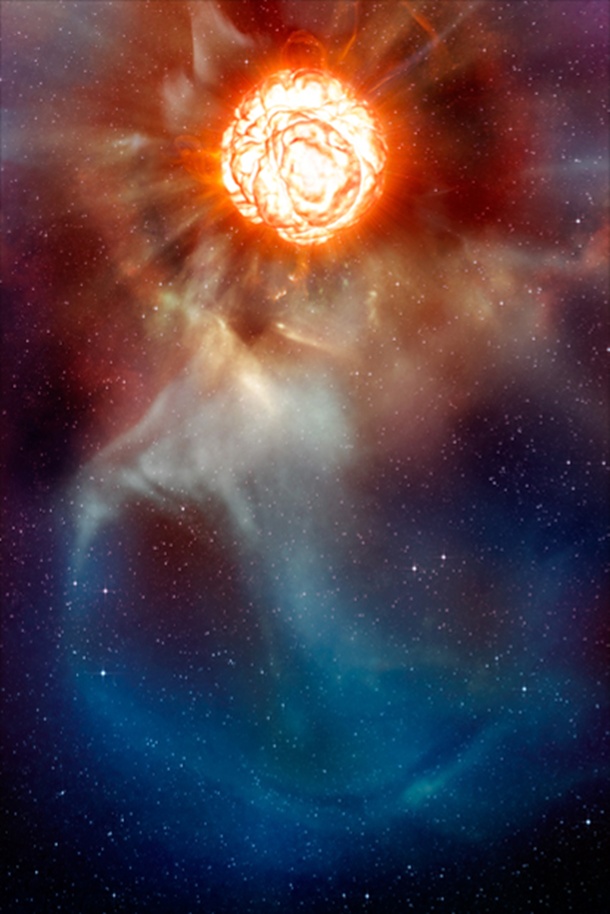
Space A Red Supergiant Star Betelgeuse Is Losing Its Brightness And Is Unusually Dim The Star Could Explode As A Supernova Shining Brighter Than The Full Moon Severe Weather Europe







:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/HR_diagram_from_eso0728c-58d19c503df78c3c4f23f536.jpg)















0 Response to "40 on the hr diagram red supergiants like betelgeuse lie"
Post a Comment