39 diagram and explain electron transport
The electron transport chain of these bacteria is composed of two Isp-MBHs for which the exact The electron transport chain activity takes place in the inner membrane and the space between the inner and outer 7.21. Schematic diagram for the electron transfer at Chl a monolayer on SnO2. 5 2 Electron Transport U0026 Oxidative Phosphorylation. Diagram And Explain Electron Transport. Difference Between Electron Transport Chain In. Was The Emergence Of Life On Earth A Highly Improbable. Diagram And Explain Electron Transport. What Is Cellular Respiration U2014 Aerobic...
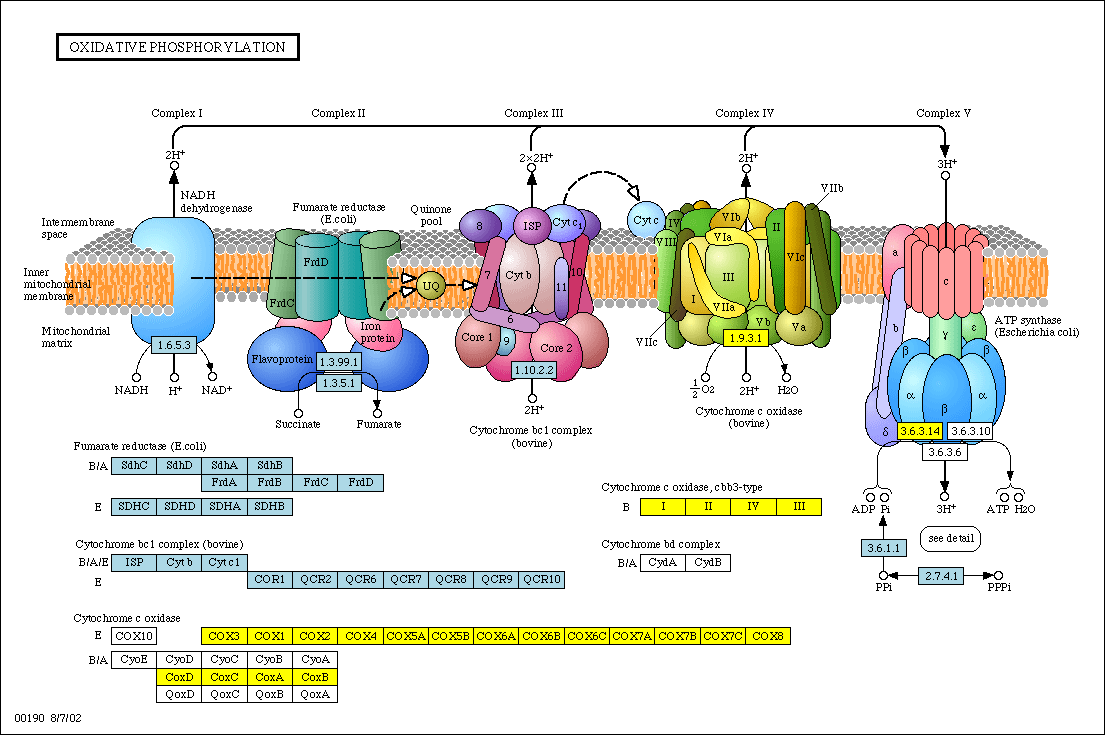
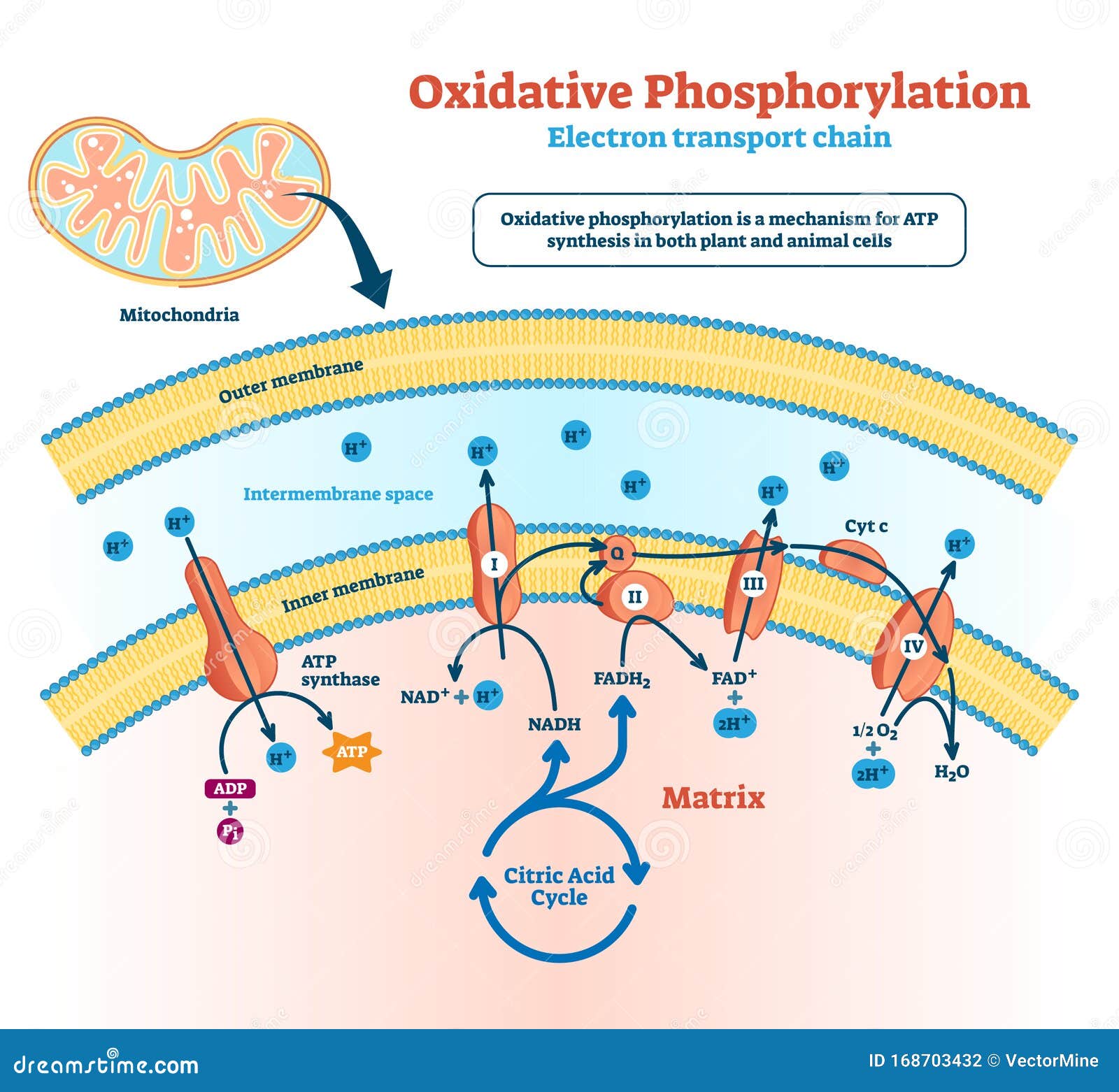
The electron transport chain is a cluster of proteins that transfer electrons through a membrane within mitochondria to form a gradient of protons that drives the creation of adenosine triphosphate atp. Electron Transport Chain Steps Explained With Diagram.
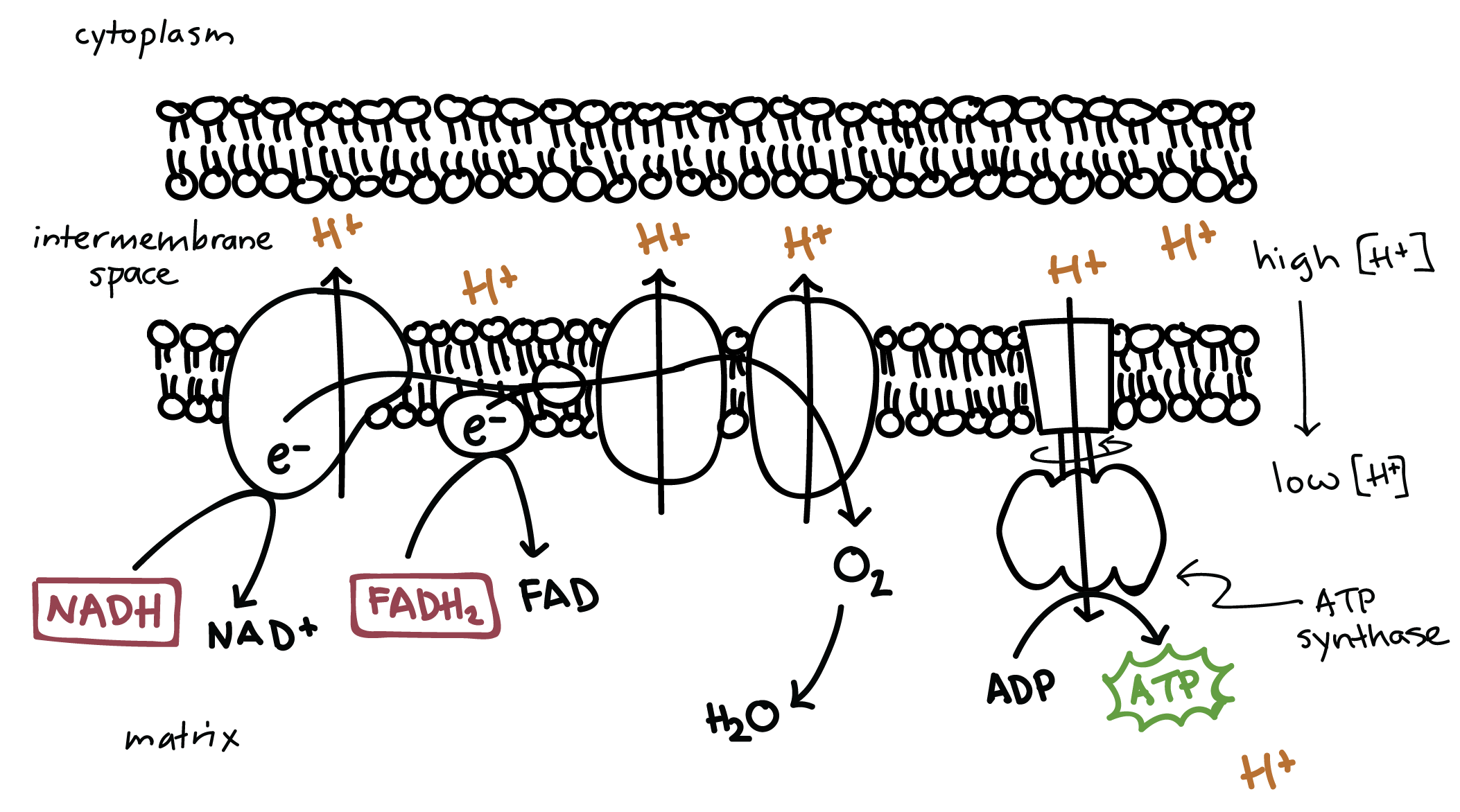
Diagram and explain electron transport
Huntington's Disease, Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Electron Transport Chain | ResearchGate, the professional network for scientists. Reduced levels and/or activity of electron transport chain components is a well-known phenomenon in HD. Complex i iv each play a role in transporting electrons hence the name electron transport chain and establishing the proton gradient. An electron transport chain (ETC) is how a cell gets energy from sunlight in photosynthesis. Electron transport chains also occur in reduction/oxidation ("redox") reactions, such as the oxidation of sugars in cellular respiration.
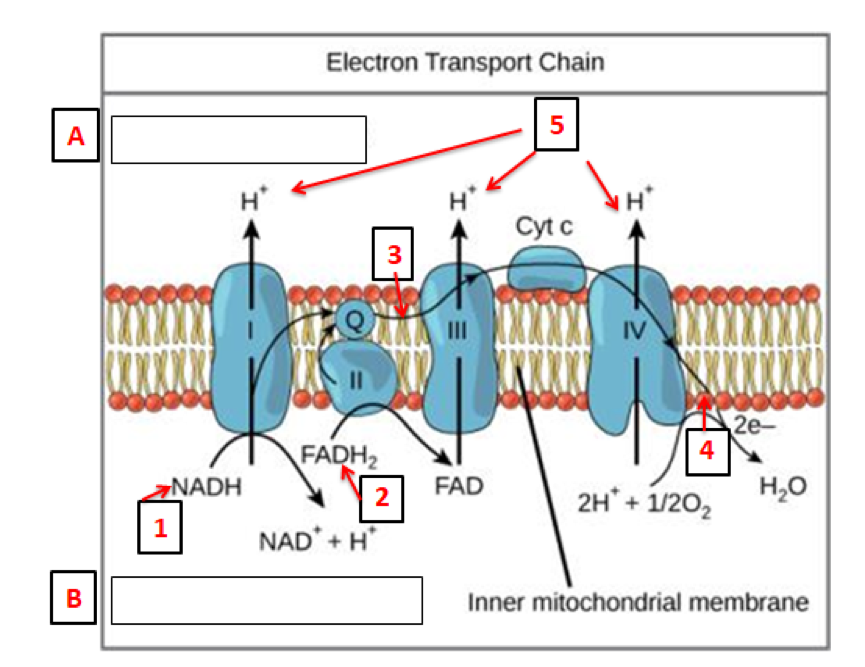
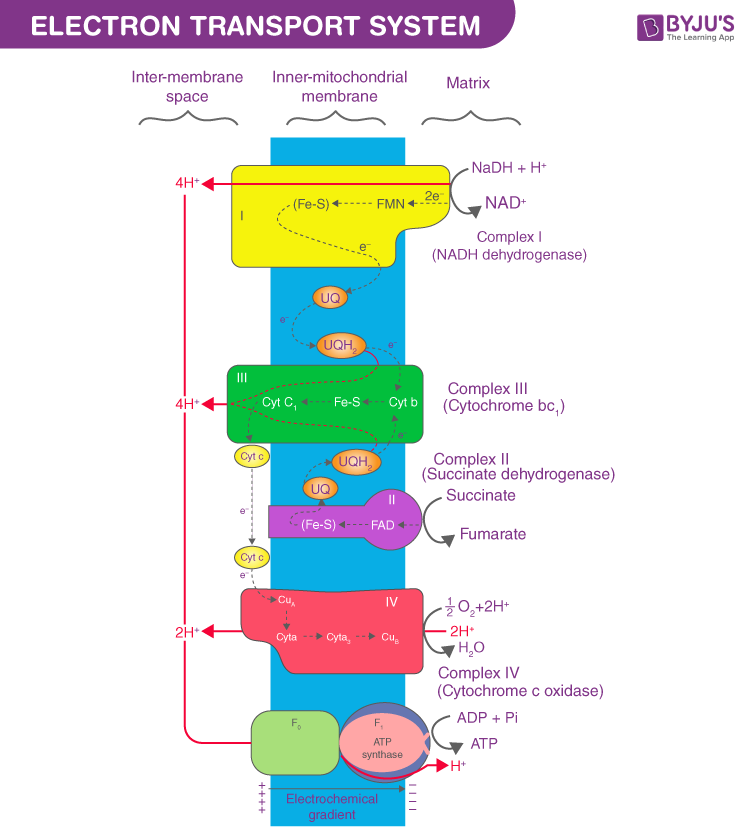
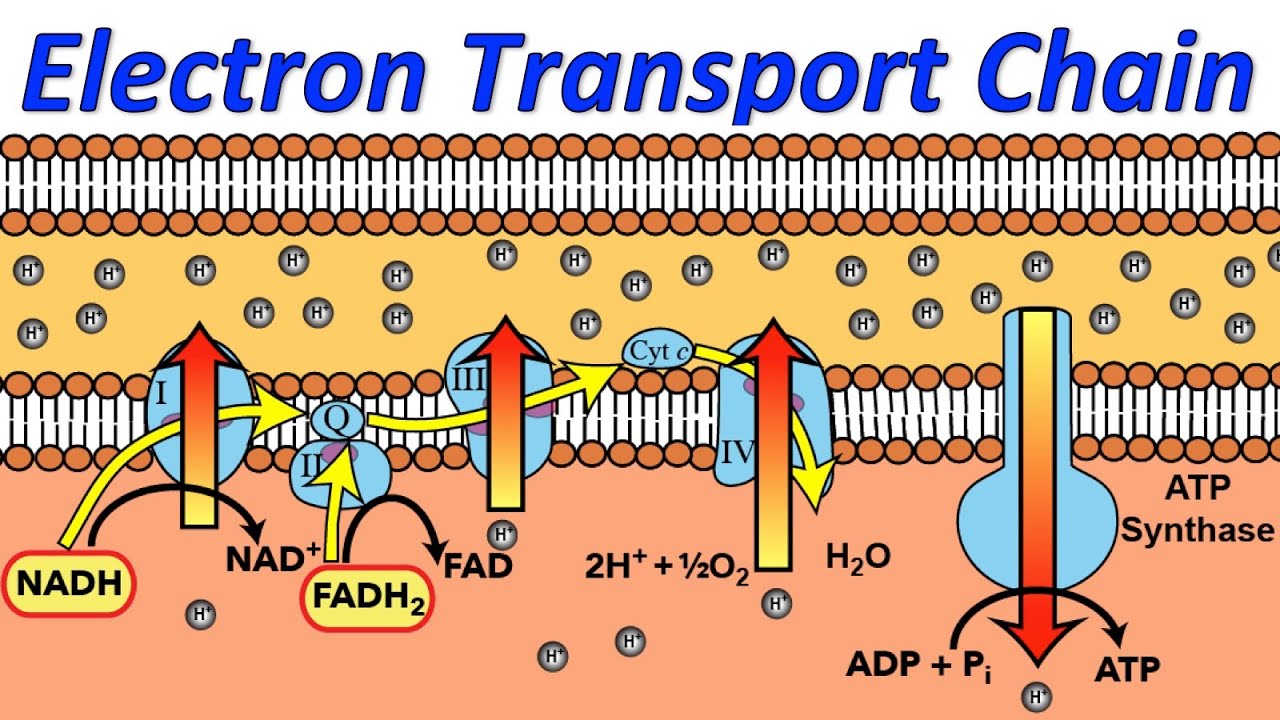
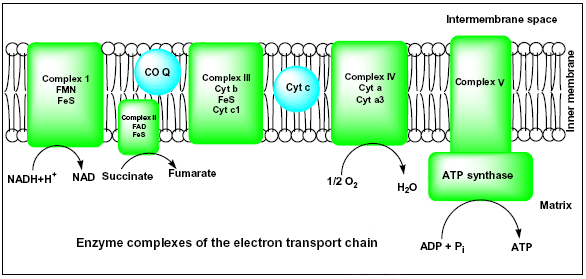
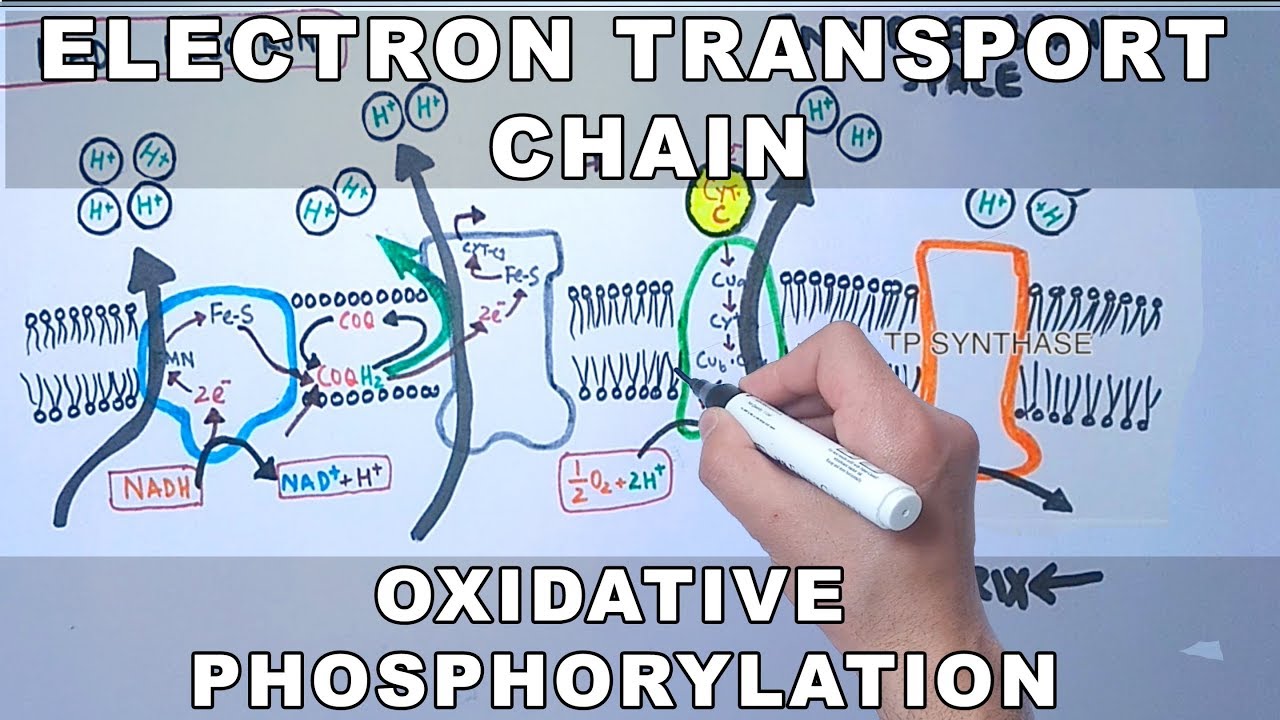
Diagram and explain electron transport. Figure 1. The electron transport chain is a series of electron transporters embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane that shuttles electrons from NADH and FADH2 to molecular oxygen. In the process, protons are pumped from the mitochondrial matrix to the intermembrane space, and oxygen... The electron transport system is a coordinated series of reactions that operate in eukaryotic organisms and in prokaryotic microorganisms , which The reactions of the electron transport system can also be termed oxidative phosphorylation. In microorganisms such as bacteria the machinery of... The electron transport chain (ETC; respiratory chain) is a series of protein complexes that transfer electrons from electron donors to electron acceptors via redox reactions (both reduction and oxidation occurring simultaneously) and couples this electron transfer with the transfer of protons (H+ ions)... Complex i iv each play a role in transporting electrons hence the name electron transport chain and establishing the proton gradient...
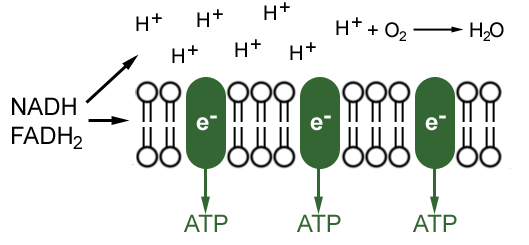
Nadh and fadh2 pass their electrons to the electron transport chain turning back into nad and fad. This electron transport chain onl... Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. This electron transport chain only occurs when oxygen is avail... The electron transport chains of bacteria (prokaryotes) operate in plasma membrane (mitochondria are absent in prokaryotes). Some bacterial electron transport chains resemble the mitochondrial electron transport chain. Paracoccus denitrificans is a gram-negative, facultative anaerobic soil... Electron transport chain steps explained with diagram the electron transport chain is an essential metabolic pathway that produces energy b...
Electron transport chain explained step by step: learn what happens during the process, along with its location, equation, purpose, products & diagrams. What is the Electron Transport Chain. Oxygen is essential to every living species for their survival. Lack of oxygen for an extended period can lead to... Electron transport in ultrathin-body fully depleted n-mosfets SSDOI provides enhanced electron and hole transport as well as the superior electrostatic control that explained. The corresponding changes in the conduction and valence bands induced by strain were described. The electron transport chain is a series of protein complexes and electron carrier molecules within the inner membrane of mitochondria that generate ATP for energy. Your Citation. Bailey, Regina. "Electron Transport Chain and Energy Production Explained." Electron Transport Chain Definition, Location, Components/ Electron carriers, Equation, Complexes, Steps and Products. Questions and Answers. What is the final electron acceptor of the electron transport chain? The final electron acceptor in aerobic respiration is molecular oxygen while in...
The electron transport chain in the mitochondrion is the site of oxidative phosphorylation in eukaryotes. The NADH and succinate generated in The final acceptor of electrons in the electron transport chain during aerobic respiration is molecular oxygen although a variety of acceptors other...
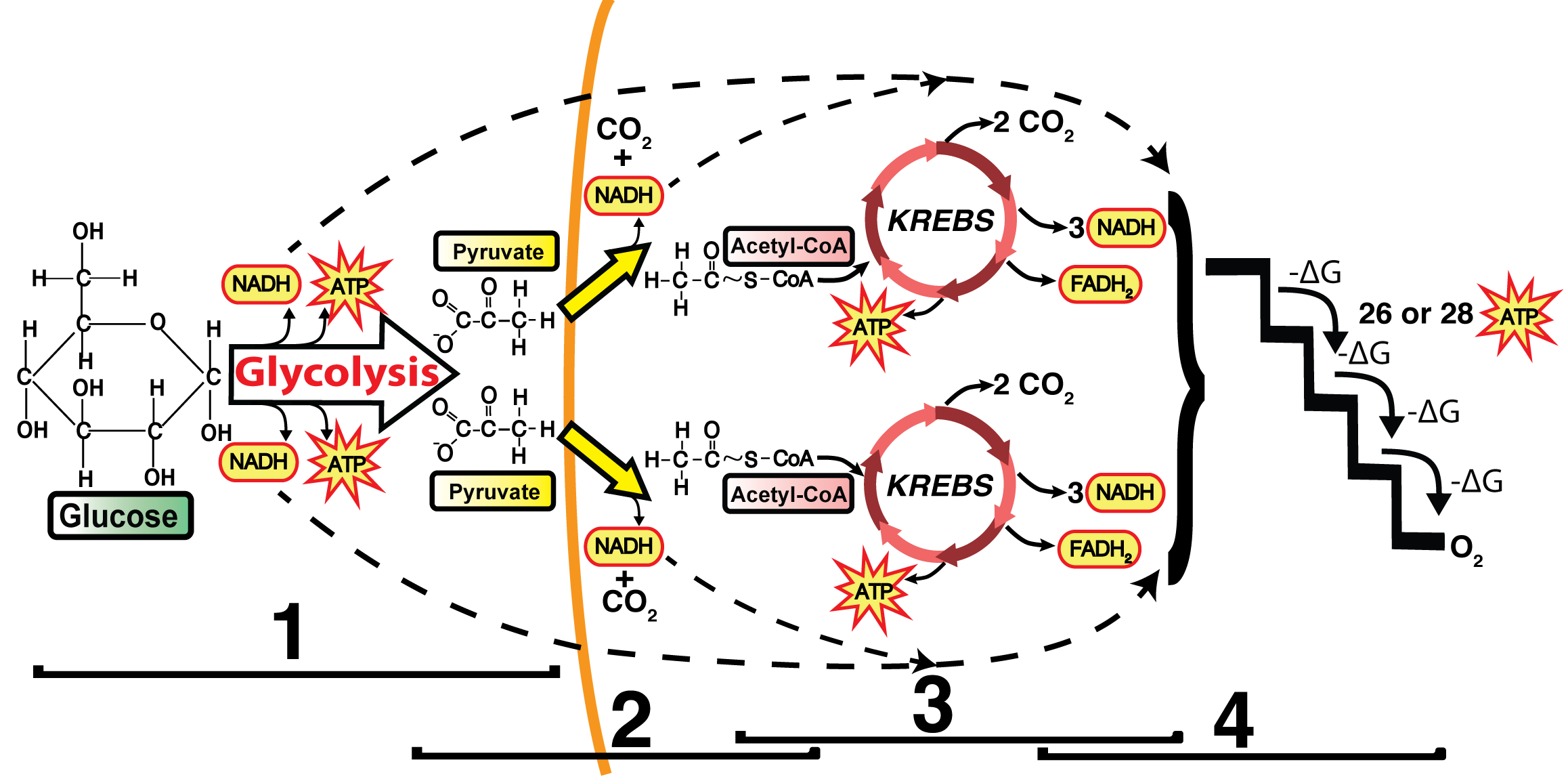
The electron transport chain is the final phase of cellular respiration, producing and storing energy in the form of ATP molecules. The electron transport chain or ETC is the third and final stage of this process, the other two being glycolysis and the citric acid cycle.
High electric field transport - electrons are accelerated - emit (optical) phonons when E~Ephonon - electron-phonon scattering for high bias. • Electronic transport (general) - S. Datta, Electronic Transport in Mesoscopic Systems (Cambridge Uni.
Complex i iv each play a role in transporting electrons hence the name electron transport chain and establishing the proton gradient.
Transfer of electrons between carriers in the electron transport chain in the membrane of the cristae is coupled to proton pumping AND In chemiosmosis The electron transport chain releases the energy stored within the reduced hydrogen carriers in order to synthesise ATP. This is called oxidative...
Electron Transport Chain: Definition, Steps, and Diagram. The Electron Transport System also called the Electron Transport Chain, is a chain of reactions that converts redox energy available from oxidation of NADH and FADH 2, into proton-motive force which is used to synthesize ATP through...

Describe The Energy Related Pathways Of The Electron Transport Chain And Chemiosmosis Include A Brainly Com
Electron transport diagram. Note that this cyclic electron-transfer process produces no net oxidation or reduction. However, in the process, protons acquired Figure 23-32 Simplified diagram of cyclic electron flow in purple bacteria. Two protons from the cytoplasm bind to QB2 in the reaction center to...
Find step-by-step Biology solutions and the answer to the textbook question Diagram and explain electron transport.. photosystems that absorb light energy. . As the electron passes through the electron transport chain protons enter the thylakoid creating a.
Electron transport through single molecules is strongly affected by single-electron charging and the energy level quantization. In this thesis, we Figure 1.2 Schematic diagram of the energy landscape of a single molecule between two macroscopic electrodes. Electronic levels of the molecule are...
Electron transport¶. The ase.transport module of ASE assumes the generic setup of the system in question sketched below: … … There is a central region (blue atoms plus the molecule) connected to two semi-infinite leads constructed by infinitely repeated principal layers (red atoms).
The electron transport chain is a cluster of proteins that transfer electrons through a membrane to create a gradient of protons that creates ATP (adenosine Where Does the Electron Transport Chain Occur? During the process, a proton gradient is created when the protons are pumped from the...
An electron transport chain (ETC) is how a cell gets energy from sunlight in photosynthesis. Electron transport chains also occur in reduction/oxidation ("redox") reactions, such as the oxidation of sugars in cellular respiration.
Complex i iv each play a role in transporting electrons hence the name electron transport chain and establishing the proton gradient.
Huntington's Disease, Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Electron Transport Chain | ResearchGate, the professional network for scientists. Reduced levels and/or activity of electron transport chain components is a well-known phenomenon in HD.

Electron Transport Chain And Oxidative Phosphorylation Substrates And Products General Features Of The Pathway Oxidative Phosphorylation Mcat Content
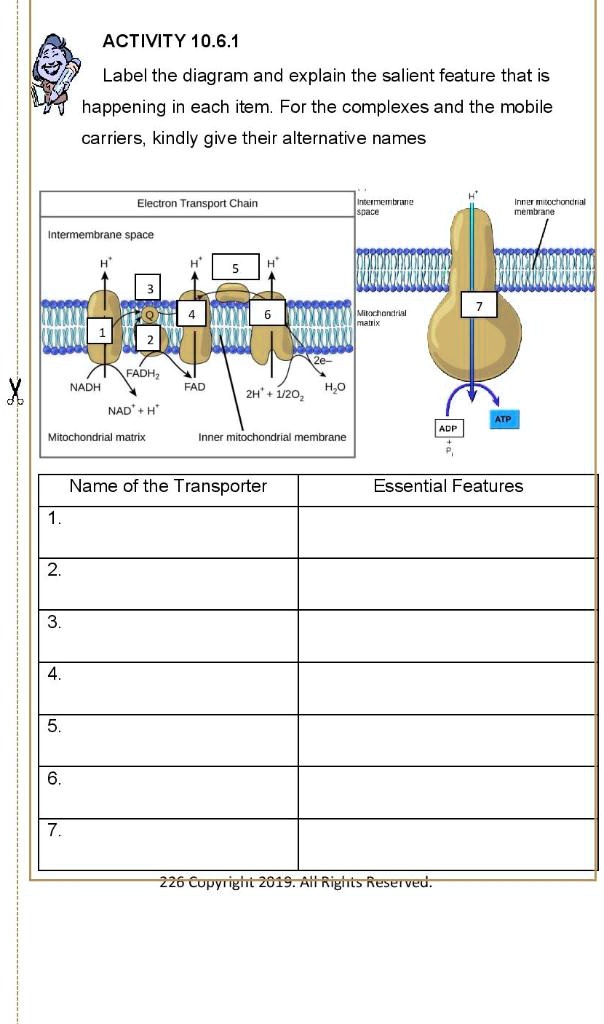
Solved Activity 10 6 1 Label The Diagram And Explain The Salient Feature That Is Happening In Each Item For The Complexes And The Mobile Carriers Kindly Give Their Alternative Names Electron Transport Chain Inicimcinttu
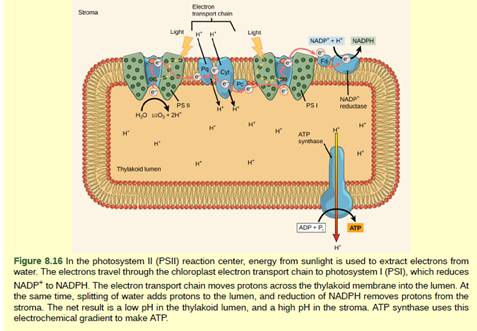
Figure 8 16 What Is The Source Of Electrons For The Chloroplast Electron Transport Chain Water Oxygen Carbon Dioxide Nadph Bartleby
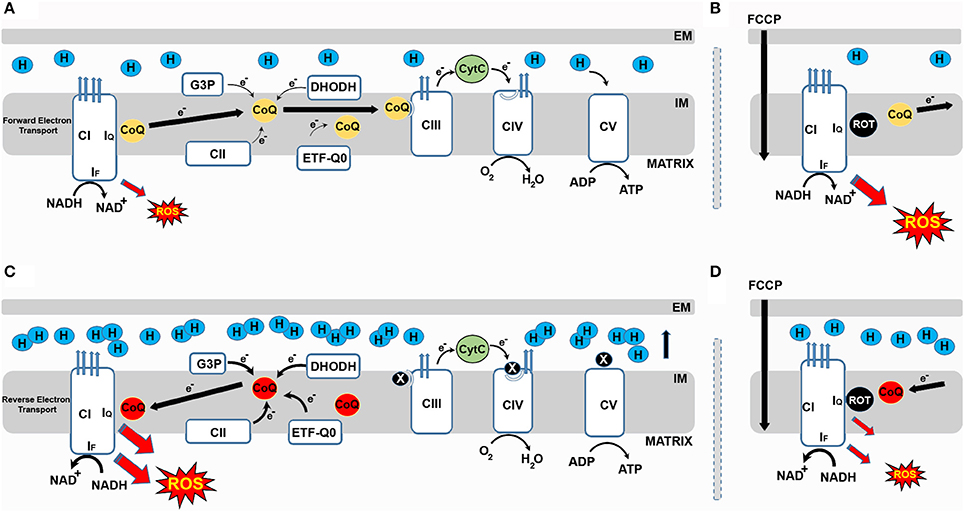
Frontiers Role Of Mitochondrial Reverse Electron Transport In Ros Signaling Potential Roles In Health And Disease Physiology

















0 Response to "39 diagram and explain electron transport"
Post a Comment