37 first class lever diagram
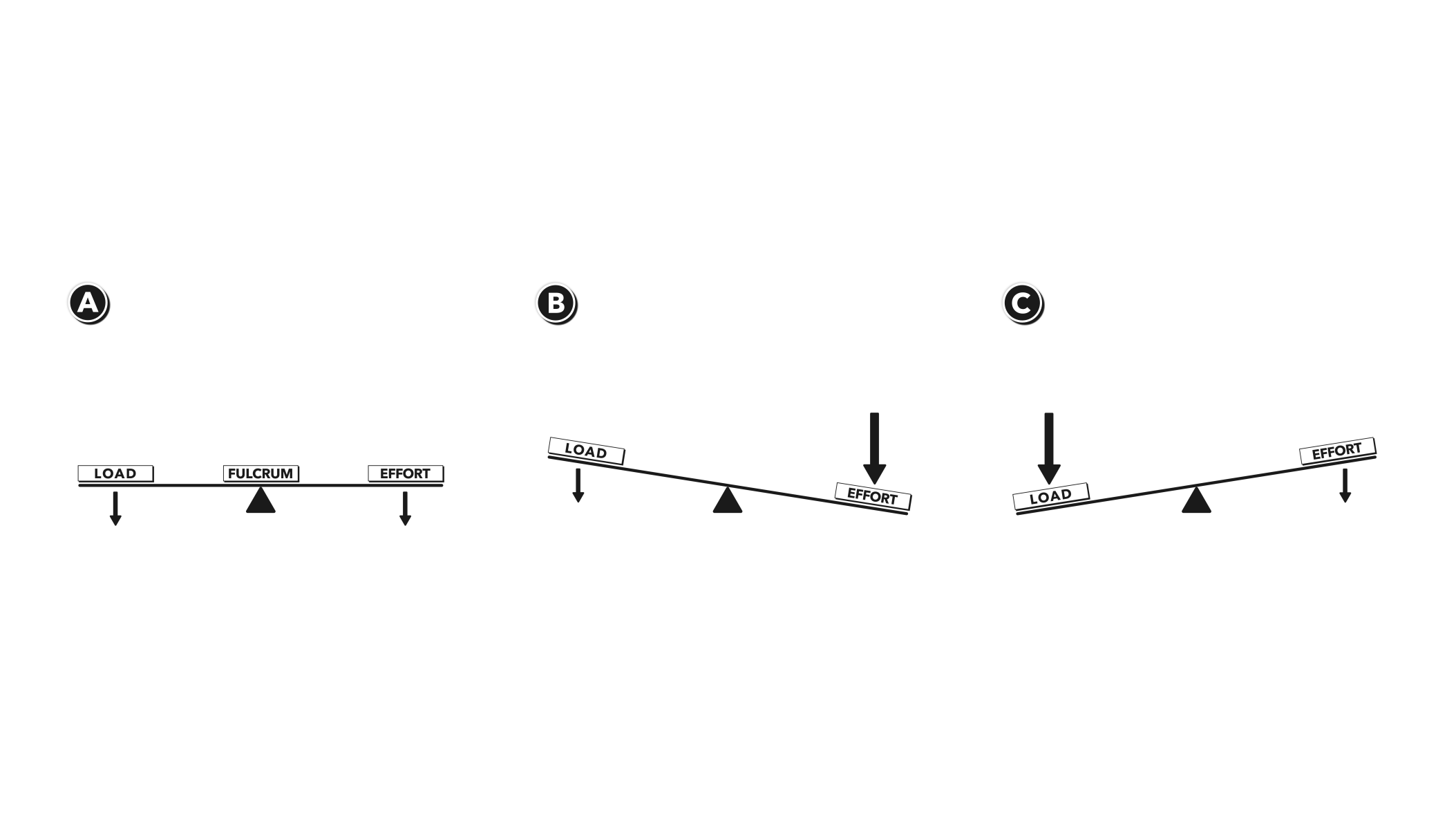
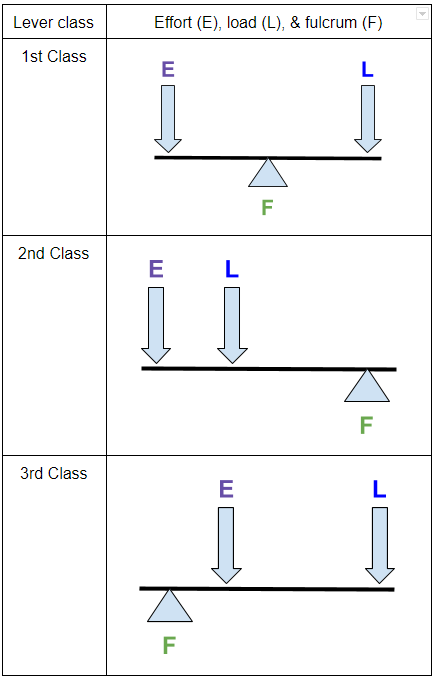
Match each type of lever with the correct diagram 2 See answers Advertisement Advertisement aristocles aristocles Class 1 lever. A Class 1 lever must have the fulcrum placed between the effort and load. So figure 1 is class 1 lever. Class 2 Lever. In class 2 lever effort arm length is bigger than load arm length. Lifting an object by hand requires applying a force directly on the object. Muscular strength must be facing upwards and intensity (measured in Newtons) should be greater than the weight of the object. This is possible only for lighter items. The lever is a simple machine that changes the magnitude and direction of the force applied to move an object.
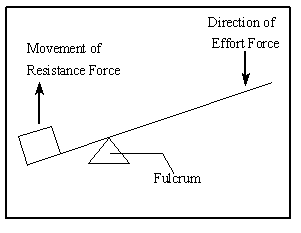
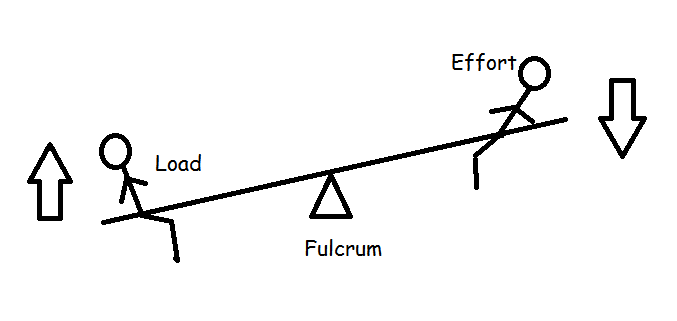
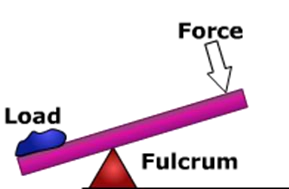
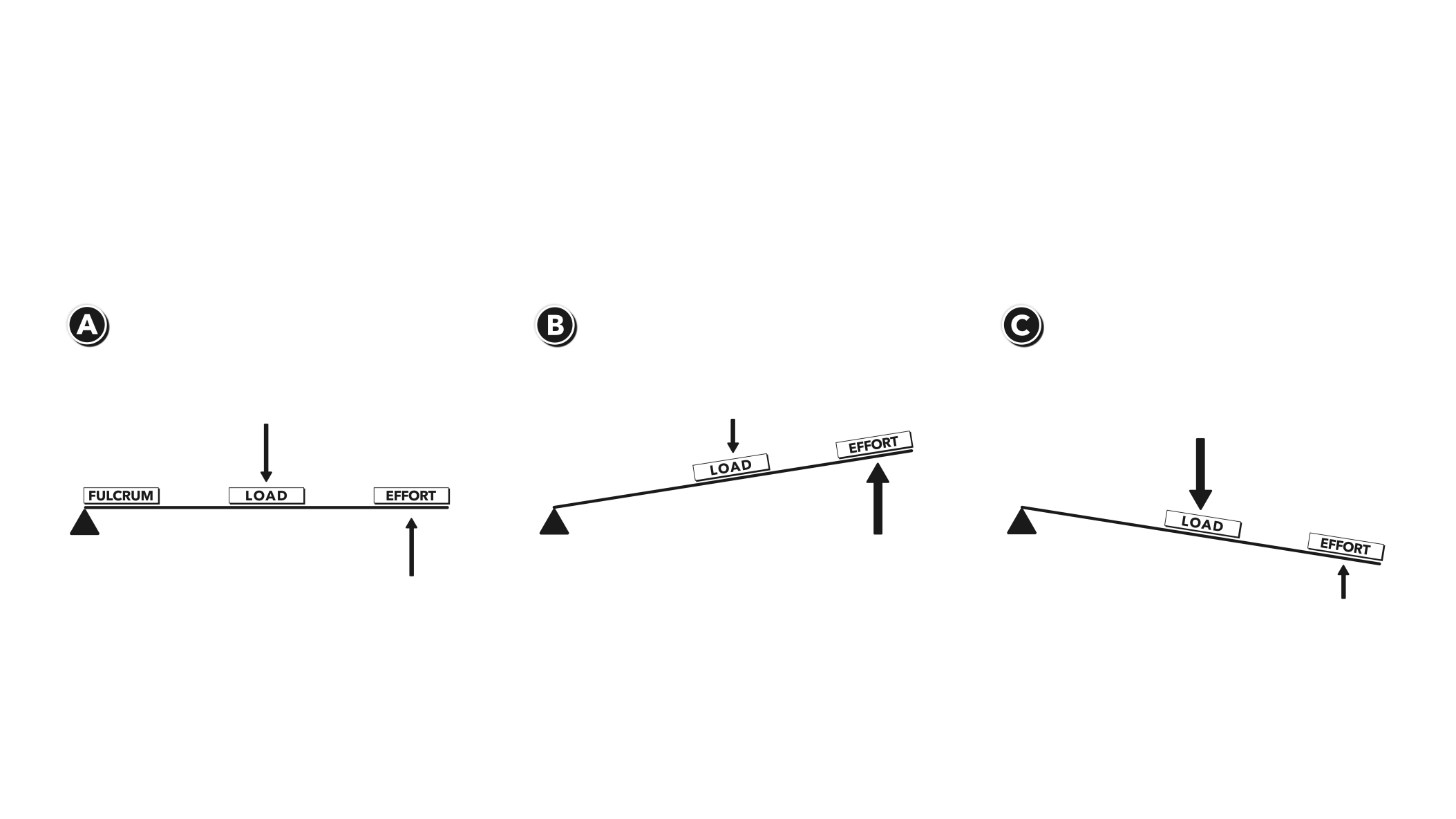
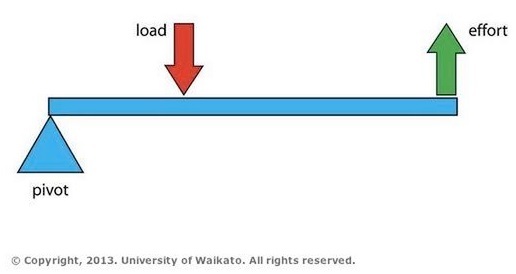
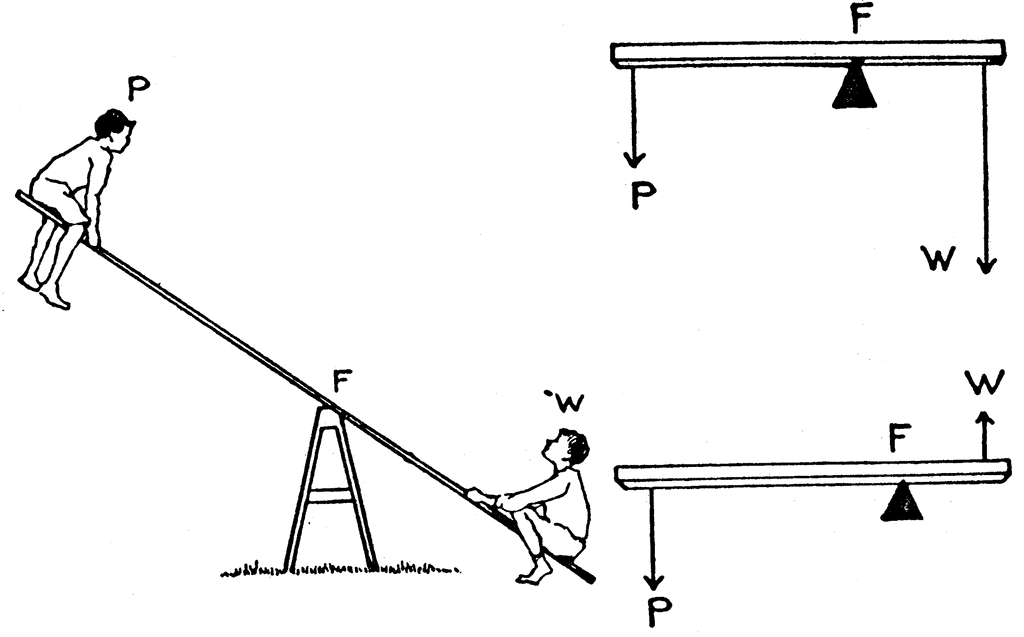
The Class of Lever is determined by the location of the load, fulcrum, and force. In a Class One Lever, the Fulcrum is located between the Load and the Force. The closer the Load is to the Fulcrum, the easier it is to lift (increased mechanical advantage). Examples include see-saws, crow bars, hammer claws, scissors, pliers, and boat oars.
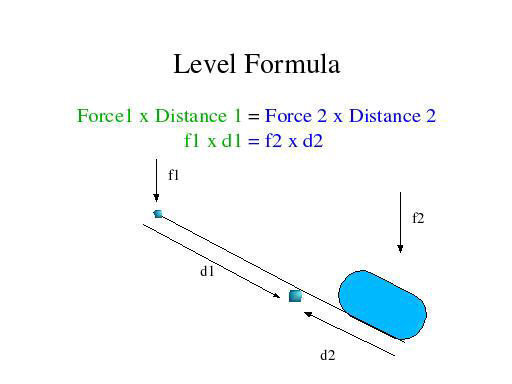
First class lever diagram
The three types of levers are as follows: (1) First Class lever or class I lever, (2) Second Class lever or class II lever, and. (3) Third Class lever or class III lever. These types are based on the relative position of the fulcrum, load, and effort in the lever body. The first class lever is one of three classes of levers and is one possible arrangement of muscles, bones, and joints found in the human body. While less common in the body than second and third class levers, the first class lever system is found in the neck at the atlanto-occipital joint and in the elbow joint. Using scissors represents the use of two first-class levers. A wheel and axle is also an example. Pulling a nail out of a wooden plank also represents a first-class lever. Second Class Lever. In this, the fulcrum is at one end and the force applied is on the other end. The weight is situated in the middle of these two.
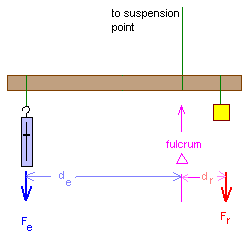
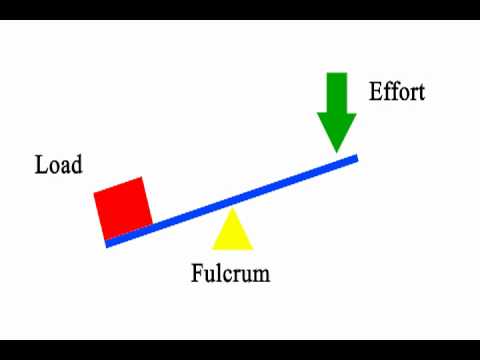
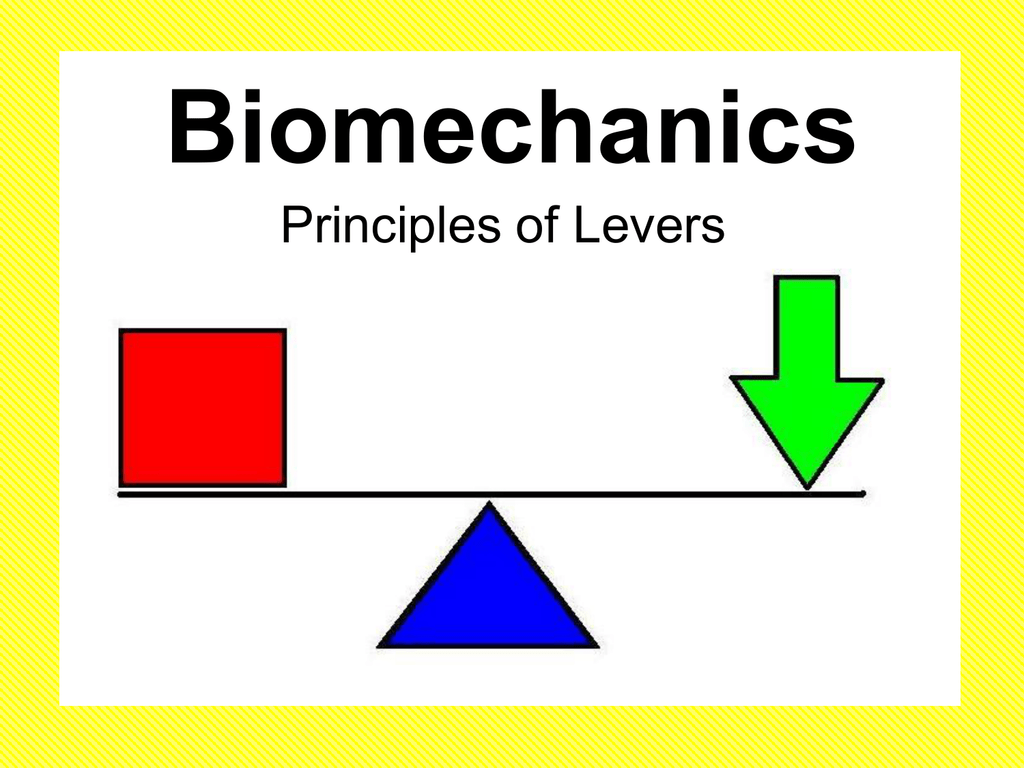
First class lever diagram. Levers can be classified into a) First class b) Second class c) Third class 4. First Class Lever a) Fulcrum is between the effort and the load b) Small effort is used to move a large load c) Effort is further from the fulcrum than load the load is d) Effort moves through a longer distance than the load. A lever mechanism where the input effort is higher than than the output load is often characterized as a third-class lever mechanism. Example - Third-Class (Order) Lever. A force (weight) of 1 pound is exerted at a distance of 2 ft from the fulcrum. The effort force at a distance of 1 ft from the fulcrum can be calculated as. F e = F l d l / d ... First class lever This type of lever is found in the neck when raising your head to head a football. The neck muscles provide the effort, the neck is the fulcrum, and the weight of the head is the ... Class 1 Levers: The fulcrum is between the effort and the load, which are applied at the opposite ends of the lever. 1st class lever examples are a seesaw and pliers. In the first-class levers, the load arm can be larger or smaller than the effort arm and their mechanical advantage can be greater than, less than or equal to one.
Using scissors represents the use of two first-class levers. A wheel and axle is also an example. Pulling a nail out of a wooden plank also represents a first-class lever. Second Class Lever. In this, the fulcrum is at one end and the force applied is on the other end. The weight is situated in the middle of these two. The first class lever is one of three classes of levers and is one possible arrangement of muscles, bones, and joints found in the human body. While less common in the body than second and third class levers, the first class lever system is found in the neck at the atlanto-occipital joint and in the elbow joint. The three types of levers are as follows: (1) First Class lever or class I lever, (2) Second Class lever or class II lever, and. (3) Third Class lever or class III lever. These types are based on the relative position of the fulcrum, load, and effort in the lever body.

Classify The Levers With Diagrams And Their Importance Also Explain Cbse Class 11 Physical Education Learn Cbse Forum










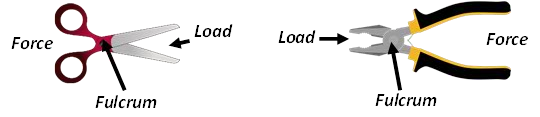





0 Response to "37 first class lever diagram"
Post a Comment